

Articles
What Is The Right Pipe Size For Plumbing
Modified: January 8, 2024
Looking for information about what size pipes to use for plumbing? Check out our helpful articles on pipe sizing and installation tips.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to plumbing projects, whether you’re renovating a bathroom or building a new home, understanding the appropriate pipe size is crucial. Choosing the correct pipe size ensures proper water flow and drainage throughout your plumbing system, preventing issues such as low water pressure or clogged pipes.
In this article, we will delve into the world of plumbing pipe sizes, exploring the factors to consider when determining pipe sizing and the different types of pipes commonly used in plumbing. We will also discuss how to determine the pipe size for water supply, drainage, and vent pipes. Lastly, we will highlight some common mistakes to avoid in the pipe sizing process.
Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional plumber, this guide will provide you with valuable insights into selecting the right pipe size for your plumbing needs.
Key Takeaways:
- Proper pipe sizing is crucial for efficient plumbing, considering factors like water demand, pressure, and material. Avoid common mistakes and consult professionals for accurate sizing to ensure a reliable plumbing system.
- Understanding the factors influencing pipe sizing and choosing the right pipe size is essential for optimal water flow, pressure, and drainage. Consulting plumbing codes, considering future expansion, and seeking professional help are key to a successful plumbing project.
Read more: How To Measure Plumbing Pipe Size
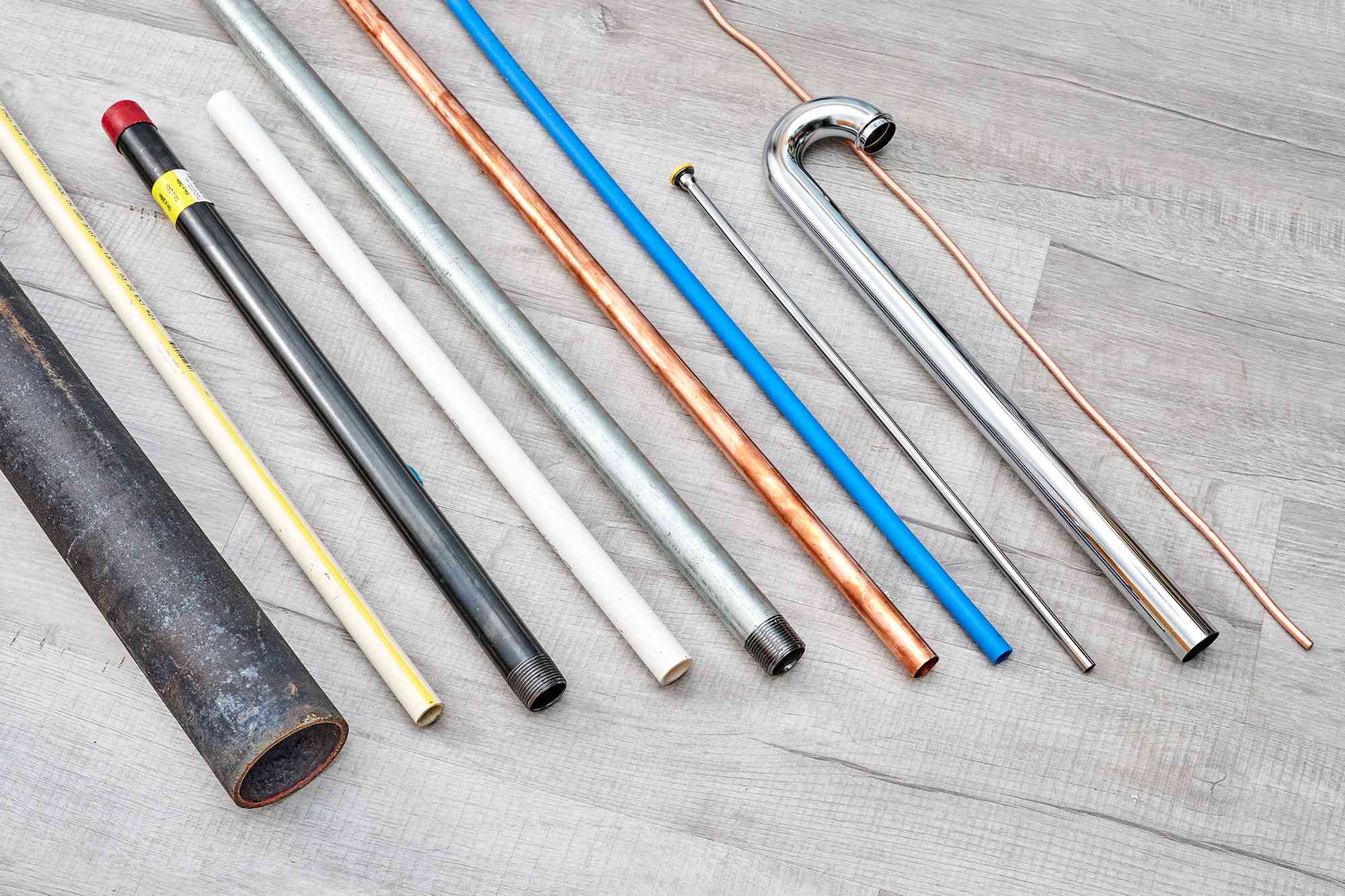
Understanding Plumbing Pipe Sizes
Plumbing pipe sizes refer to the diameter of a pipe, typically measured in inches. The size of a pipe plays a significant role in determining its water carrying capacity, pressure rating, and the overall efficiency of the plumbing system.
Plumbing pipes are available in various sizes, ranging from ½ inch to several inches in diameter. The most commonly used sizes in residential plumbing are ½ inch, ¾ inch, and 1 inch.
It’s important to note that the pipe size does not directly correlate with the volume of water it can carry. The volume of water is influenced by the pipe’s diameter, length, and material, as well as factors such as water pressure and flow rate.
Plumbing pipe sizes are classified into two categories: nominal pipe size (NPS) and inside diameter (ID). NPS refers to the approximate size of the pipe based on traditional sizing conventions, while ID represents the actual inside diameter of the pipe.
For example, a pipe labeled as 1 inch NPS may have an actual inside diameter slightly smaller than 1 inch. This difference accounts for the thickness of the pipe walls. Understanding these conventions is crucial when selecting the appropriate fittings and connectors for your plumbing system.
It’s worth noting that different countries may have different sizing conventions. In the United States, plumbing pipe sizes are typically measured in inches, while in other countries, such as the United Kingdom, metric sizing, such as millimeters, is more common.
Now that we have a basic understanding of plumbing pipe sizes, let’s explore the factors that need to be considered when determining pipe sizing for your specific plumbing project.
Factors to Consider for Pipe Sizing
When determining the appropriate pipe size for your plumbing project, it’s important to consider several factors that can impact the performance and efficiency of your plumbing system. These factors include:
- Water Demand: The amount of water required in your plumbing system plays a crucial role in determining the pipe size. Factors such as the number of fixtures, the flow rate of each fixture, and peak water demand should be considered. A higher water demand will require larger pipes to ensure adequate water supply.
- Water Pressure: The desired water pressure in your plumbing system is also an important consideration when sizing pipes. Higher water pressure may require larger pipe sizes to maintain proper flow and pressure throughout the system.
- Distance and Elevation: The distance between the water source and the fixtures, as well as any significant changes in elevation, can affect the pressure and flow of water. Longer distances and higher elevations may require larger pipe sizes to compensate for potential pressure losses.
- Material and Friction: The material of the pipe and the length of the pipe run can create friction, which can affect water flow. Different pipe materials have different friction coefficients, so it’s important to account for this when determining pipe size.
- Building Codes and Regulations: Local building codes and regulations may dictate minimum pipe sizes for certain plumbing applications. It’s essential to familiarize yourself with the codes and regulations in your area to ensure compliance.
By considering these factors, you can make informed decisions about the appropriate pipe size for your specific plumbing needs. It’s also advisable to consult with a professional plumber or use pipe sizing charts and calculators to ensure accurate and efficient pipe sizing.
Now that we understand the factors to consider, let’s explore the different types of pipes commonly used in plumbing systems.
Different Types of Pipes for Plumbing
Plumbing pipes come in various materials, each with its own unique characteristics and suitability for different plumbing applications. Here are some of the most common types of pipes used in plumbing:
- Copper Pipes: Copper pipes are a popular choice in plumbing due to their durability, resistance to corrosion, and ability to handle high temperatures and pressures. They are commonly used for water supply lines and can last for several decades with proper maintenance.
- PEX Pipes: PEX (cross-linked polyethylene) pipes have gained popularity in recent years due to their flexibility, easy installation, and resistance to freezing temperatures. PEX pipes are commonly used for both water supply and radiant heating systems.
- PVC Pipes: PVC (polyvinyl chloride) pipes are affordable, lightweight, and resistant to corrosion. They are commonly used for drain, waste, and vent (DWV) systems, as well as for irrigation and underground piping.
- CPVC Pipes: CPVC (chlorinated polyvinyl chloride) pipes are similar to PVC pipes but are specifically designed for hot water applications. CPVC pipes can handle higher temperatures and are commonly used for hot water supply lines.
- Galvanized Steel Pipes: Galvanized steel pipes are coated with zinc to protect against corrosion. While they were commonly used in the past, they have been largely replaced by other materials due to their tendency to rust and decrease water flow over time.
- PE Pipes: PE (polyethylene) pipes are durable, flexible, and resistant to chemical and UV damage. They are commonly used for underground water supply lines and irrigation systems.
Each type of pipe has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of material depends on factors such as the specific plumbing application, budget, and local building codes. It’s important to consult with a professional plumber or refer to local regulations to determine the appropriate pipe material for your plumbing project.
Next, let’s explore how to determine the pipe size for water supply systems.
Determining Pipe Size for Water Supply
Choosing the right pipe size for water supply systems is crucial to ensure optimal water flow and pressure throughout your plumbing system. Here are some guidelines to help you determine the appropriate pipe size:
- Calculate Water Demand: Determine the total water demand for your system by considering factors such as the number of fixtures, their flow rates, and peak water usage scenarios. This calculation will give you an estimate of the required water flow in gallons per minute (GPM).
- Consider Velocity and Friction Loss: The water flow velocity and friction loss play a significant role in pipe sizing. As a general rule, the water velocity should be kept below 5 feet per second to minimize pressure loss. Consider the length of the pipe run and the material’s friction coefficient to calculate the friction loss.
- Refer to Pipe Sizing Charts: Consult pipe sizing charts provided by plumbing codes or pipe manufacturers to match the required water flow and pressure with the appropriate pipe size. These charts consider factors such as pipe material, flow rate, and pressure to determine the suitable pipe diameter.
- Account for Future Expansion: It’s advisable to oversize the pipe slightly to accommodate any future expansions or changes in water demand. This will help ensure sufficient water supply and prevent potential issues with low water pressure.
- Consult with a Professional Plumber: If you’re unsure about the pipe sizing process or have complex plumbing requirements, it’s best to consult with a professional plumber. They have the expertise and experience to accurately size the pipes and ensure optimal performance of your water supply system.
Remember, pipe sizing for water supply is a critical aspect of your plumbing system’s design. Improper sizing can lead to problems such as low water pressure, increased energy consumption, and reduced system efficiency. Taking the time to determine the correct pipe size will ensure a reliable and well-functioning water supply system.
Now let’s move on to determining the pipe size for drainage systems.
When determining the size of pipes for plumbing, consider the water flow rate and the distance the water needs to travel. Larger diameter pipes are typically used for higher flow rates and longer distances, while smaller diameter pipes are suitable for lower flow rates and shorter distances.
Read more: What Is A Drain Pipe In Plumbing
Determining Pipe Size for Drainage
Proper pipe sizing is essential for efficient drainage systems, ensuring the smooth flow of wastewater and preventing issues such as clogs and backups. Here are some factors to consider when determining the pipe size for drainage:
- Fixture Drain Size: Determine the size of the fixture drains, such as sinks, toilets, and showers, that will be connected to the drainage system. This will give you an idea of the required pipe size to handle the expected wastewater flow.
- Drain Slope: The drain slope, also known as the pipe gradient, is the amount of downward slope the pipe needs to facilitate the flow of wastewater. The slope is typically specified in inches per foot and helps prevent the accumulation of debris and the formation of clogs. The required slope will impact the pipe size selection.
- Drainage Fixture Units (DFU): Drainage Fixture Units are a standardized measure used to calculate the total flow rate of wastewater from various fixtures. Different fixtures have different DFU values, and the sum of the DFUs helps determine the required pipe size. Refer to plumbing codes or guidelines for DFU values.
- Consider Venting: Vent pipes are essential for a properly functioning drainage system, as they allow air to enter the pipes and prevent vacuum pressure that can inhibit wastewater flow. Consider the size and placement of vent pipes when determining the pipe size for drainage, as these factors can impact the overall flow capacity.
- Refer to Plumbing Codes: Local plumbing codes and regulations provide guidelines for pipe sizing in drainage systems. These codes take into account factors such as fixture types, pipe slope, and venting requirements. Consult the codes applicable to your area to ensure compliance and optimal drainage performance.
- Seek Professional Guidance: If you’re uncertain about the pipe sizing process or have complex drainage requirements, it’s recommended to consult with a professional plumber. They can assess your specific needs, consider local regulations, and accurately size the pipes for optimal drainage performance.
By considering these factors and guidelines, you can determine the appropriate pipe size for your drainage system. Proper pipe sizing will ensure efficient wastewater flow, minimize clogs, and maintain the integrity of your plumbing system.
Now let’s move on to understanding vent pipe sizing in plumbing systems.
Understanding Vent Pipe Sizing
Vent pipes play a crucial role in plumbing systems by allowing air to enter the drainage system and preventing the buildup of negative pressure. Proper venting ensures a smooth flow of wastewater, prevents traps from being siphoned, and eliminates unpleasant odors. Here are important factors to understand when sizing vent pipes:
- Fixture Count: Consider the number and types of fixtures connected to the vent system. Each fixture requires a specific vent pipe size to maintain proper ventilation and prevent air blockages. Plumbing codes provide guidelines on the minimum vent pipe sizes based on fixture count.
- Drain Pipe Size: The size of the drain pipe connected to a fixture affects vent pipe sizing. A larger drain pipe typically requires a larger vent pipe to maintain the necessary air flow and pressure balance in the system.
- Distance and Height: The distance between the fixture and the vent stack and the height of the vent stack may influence the size of the vent pipe. Longer distances or taller vent stacks may require larger-diameter vent pipes to compensate for pressure loss and ensure adequate air supply.
- Plumbing Code Requirements: Local plumbing codes provide specific guidelines on vent pipe sizing, including minimum pipe diameter, maximum fixture unit loading, and required distances between vents and fixtures. It’s important to consult the plumbing codes in your area to ensure compliance and proper vent pipe sizing.
- Professional Assistance: Vent pipe sizing can be complex, especially for larger or more intricate plumbing systems. It’s recommended to consult with a professional plumber who has expertise in vent pipe sizing, as they can accurately assess your system’s requirements and ensure optimal venting performance.
By considering these factors and adhering to plumbing codes, you can determine the appropriate vent pipe size for your plumbing system. Proper vent pipe sizing ensures the efficient and safe operation of your drainage system while preventing issues such as trap seal loss and vent blockages.
Now let’s highlight some common mistakes to avoid in the pipe sizing process.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Pipe Sizing
Accurately sizing pipes for plumbing systems is crucial to ensure optimal performance and prevent potential issues. However, there are common mistakes that people often make in the pipe sizing process. By being aware of these mistakes, you can avoid them and ensure a successful plumbing project. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Not Considering Water Demand: Failing to account for the actual water demand of the plumbing system can lead to undersized pipes and insufficient water flow. It’s important to determine the required water flow rate and account for peak demand scenarios when sizing pipes.
- Not Considering Friction Loss: Friction loss occurs when water flows through pipes, and it can impact the overall water pressure in the system. Ignoring friction loss or not using accurate calculations can lead to inadequate water flow and pressure, resulting in inefficient plumbing performance.
- Underestimating Drainage Needs: Proper drainage pipe sizing is essential to prevent clogs and backups. Underestimating the required size of drain pipes can lead to poor drainage, frequent blockages, and costly repairs down the line.
- Ignoring Plumbing Codes: Local plumbing codes provide guidelines and specifications for pipe sizing in different applications. Not adhering to these codes can result in compliance issues and may even lead to unsafe or non-functional plumbing systems.
- Neglecting Future Expansion: Failing to consider future expansion or changes in water demand can lead to undersized pipes that cannot accommodate increased usage. It’s important to plan for potential growth and allow for flexibility in the pipe sizing process.
- Relying Solely on Online Calculators: While online pipe sizing calculators can be useful tools, they may not account for all the unique factors and considerations of your specific plumbing project. It’s always best to consult with a professional plumber who can analyze your plumbing needs and provide accurate pipe sizing recommendations.
- Failing to Seek Professional Help: Plumbing systems can be complex, and accurately sizing pipes requires expertise and experience. Failing to seek the assistance of a professional plumber can result in improper pipe sizing and potential issues in the plumbing system.
Avoiding these common mistakes and taking a diligent approach to pipe sizing will ensure a properly functioning plumbing system that meets your specific needs. By consulting with professionals, considering all relevant factors, and following local codes, you can prevent costly errors and enjoy a trouble-free plumbing experience.
Now let’s wrap up our discussion.
Conclusion
Choosing the correct pipe size is essential for any plumbing project to ensure optimal water flow, pressure, and drainage. By understanding the factors that influence pipe sizing, including water demand, water pressure, distance, and material, you can make informed decisions when selecting the appropriate pipe size for your specific plumbing needs.
Remember to consult plumbing codes and regulations in your area, as they provide guidelines for pipe sizing and ensure compliance with safety standards. Taking the time to measure and calculate water demand, consider friction loss, and plan for future expansion will result in a well-designed plumbing system that performs efficiently and reliably.
Avoid common mistakes such as underestimating water demand, neglecting drainage needs, and relying solely on online calculators. Instead, seek the guidance of professional plumbers who possess the expertise and experience to accurately size the pipes and ensure optimal performance of your plumbing system.
Whether you’re embarking on a DIY plumbing project or working with a professional plumber, understanding the importance of pipe sizing and avoiding common pitfalls will contribute to the success of your plumbing endeavors.
So, next time you undertake a plumbing project, take the time to carefully consider the pipe size. Your plumbing system will thank you with reliable water flow, proper drainage, and years of trouble-free operation.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is The Right Pipe Size For Plumbing
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Is The Right Pipe Size For Plumbing”