Home>diy>Architecture & Design>Egyptian Design For Building A House: Why Do Africans Use It?


Architecture & Design
Egyptian Design For Building A House: Why Do Africans Use It?
Modified: January 24, 2024
Discover the artistry of Egyptian architecture-design in building houses. Learn why Africans embrace this unique style, blending history and cultural influences. Explore its significance today!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
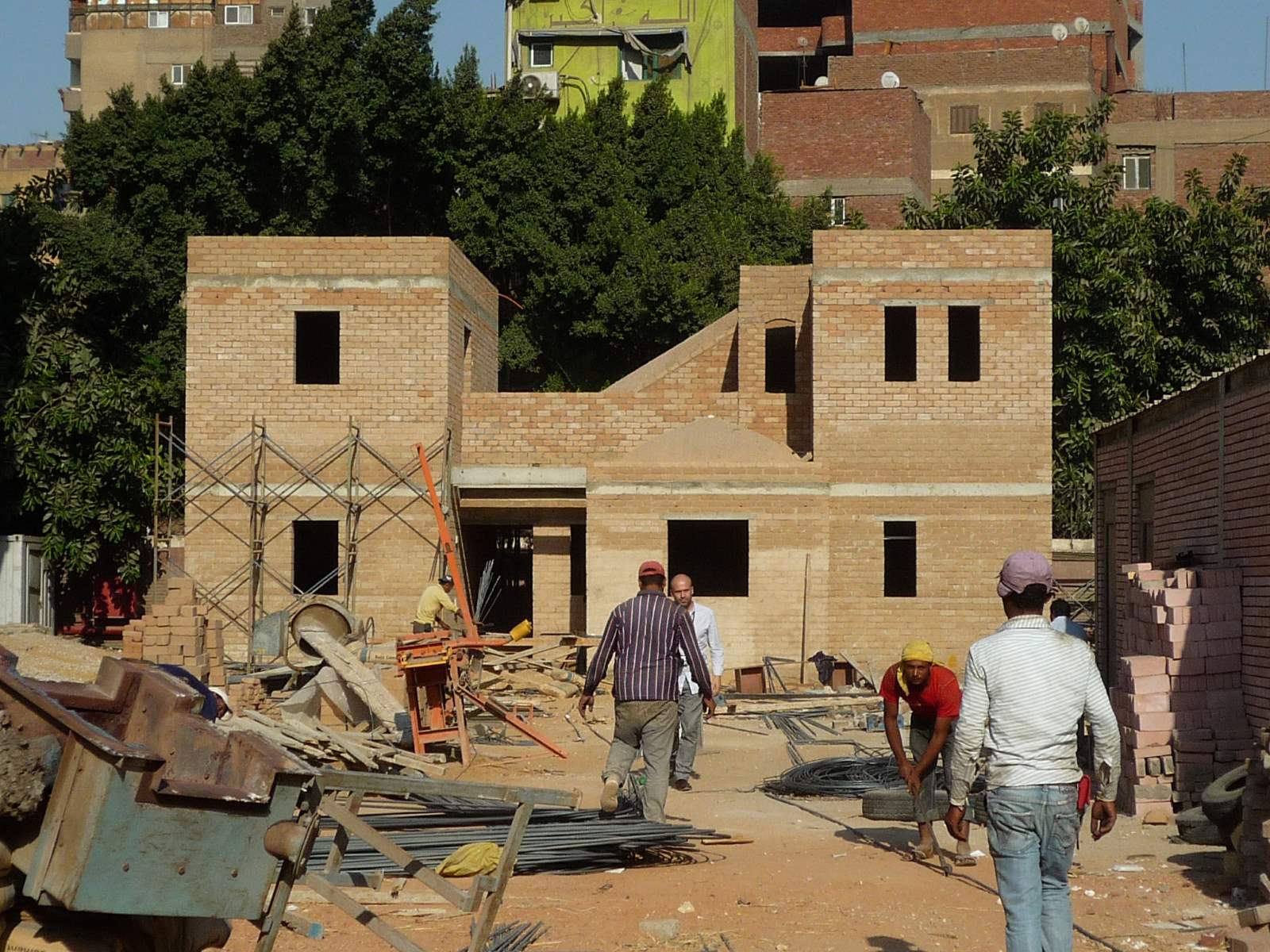
The use of Egyptian design in African architecture has a rich history dating back centuries. This unique architectural style, characterized by its intricate detailing, geometric patterns, and symmetrical layouts, has not only withstood the test of time but has also become deeply embedded in the cultural fabric of many African communities.
Egyptian design, also known as Egyptian architecture, is a result of the ancient civilization that flourished along the Nile River. The architectural techniques and aesthetic principles developed by the Egyptians have influenced and inspired architectural styles across Africa. The use of Egyptian design in building houses has become a prominent choice for many Africans, not only for its historical significance but also for its practical advantages and cultural significance.
Throughout this article, we will explore the historical background of Egyptian design in Africa, delve into its characteristics, discuss the practical advantages and cultural significance it holds, examine the sustainability and environmental considerations, explore the challenges and limitations of implementing this style, and showcase some examples of African houses built with Egyptian design.
By understanding the essence of Egyptian design and its relevance in the African context, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the craftsmanship and cultural significance of this architectural style.
Key Takeaways:
- Egyptian design in African architecture reflects a rich historical exchange, offering practical benefits and cultural significance. It connects communities to their heritage while providing sustainable and energy-efficient living spaces.
- Despite challenges, Egyptian design inspires African architecture, blending ancient aesthetics with modern functionality. From Nubian houses to Lamu’s fusion, it showcases cultural pride and enduring relevance.
Read more: How To Build A Carport Attached To House
Historical Background of Egyptian Design in Africa
The influence of Egyptian design in Africa can be traced back to the ancient Egyptian civilization that thrived along the Nile River over 4,000 years ago. During this time, Egyptian architects developed unique construction techniques and design principles that left an indelible mark on the architectural landscape of the continent.
Egyptian design found its way into Africa through trade routes and cultural exchanges across the Sahara and the Red Sea. As a result, various African kingdoms and empires, such as the Nubians, Kushites, and Axumites, adopted elements of Egyptian architecture and incorporated them into their own building practices.
One of the most notable examples of Egyptian influence can be seen in the Kushite kingdom of Meroë, located in present-day Sudan. The Kushites, who conquered and ruled over Egypt for a period, adopted Egyptian architectural styles, such as the use of towering pyramids, grand temples, and elaborate tombs. These structures not only served as religious and burial sites but also as symbols of wealth, power, and social status.
Outside of Sudan, Egyptian design can also be found in the ancient city of Timbuktu in Mali. Timbuktu, once a major center of trade and learning, showcases mud-brick houses and mosques that feature geometric patterns, arched doorways, and decorative motifs reminiscent of Egyptian architectural style.
Furthermore, the Swahili Coast of East Africa, with its rich trading history, also bears the influence of Egyptian design. The architecture in cities such as Lamu and Mombasa showcases intricate carved wooden doors, domed rooftops, and narrow alleys, mirroring the style of ancient Egyptian architecture.
Overall, the historical background of Egyptian design in Africa reflects the interconnectivity and cultural exchange that occurred throughout the continent. The adoption and adaptation of Egyptian architectural features by various African civilizations demonstrate the enduring impact and appeal of this unique architectural style.
Characteristics of Egyptian Design
Egyptian design is characterized by distinctive features that set it apart from other architectural styles. These features not only reflect the rich cultural heritage of ancient Egypt but also serve practical and aesthetic purposes in African architecture. Here are some key characteristics of Egyptian design:
1. Monumental Scale: Egyptian architecture is known for its grandeur and monumental scale. Structures such as pyramids, temples, and tombs were built on a massive scale, symbolizing the power and authority of the ruling pharaohs. This impressive scale is often replicated in African houses built with Egyptian design, creating a sense of prominence and importance in the community.
2. Symmetry and Geometry: Egyptian design exhibits a strong emphasis on symmetry and geometric patterns. Buildings are often laid out in a symmetrical manner, with precise alignments and perfectly balanced elements. Geometric motifs, such as chevrons, lotus flowers, and intricate mosaics, are intricately integrated into the architecture, creating visually stunning patterns.
3. Use of Columns and Capitals: Egyptian architecture prominently features columns, which provide structural support and add aesthetic appeal. The columns are often adorned with elaborate capitals, with designs inspired by nature, such as the lotus and papyrus plants. These columns and capitals add a sense of elegance and sophistication to Egyptian-style buildings in Africa.
4. Ornate Detailing: Egyptian design is renowned for its intricate and ornate detailing. Carvings, hieroglyphics, and reliefs are commonly found on the walls of temples and tombs. African houses built using Egyptian design also incorporate these decorative elements, with intricate carvings on doors, windows, and facades, adding a touch of elegance and cultural significance.
5. Earthy Materials: Egyptian architecture often utilizes earthy and natural materials, such as limestone, mud bricks, and wood. These materials not only reflect the local availability but also contribute to the sustainability and environmental friendliness of Egyptian-style houses in Africa.
6. Integration of Natural Elements: Egyptian design seamlessly integrates natural elements into the architecture. Water features, courtyards, and gardens are commonly incorporated, creating a harmonious connection with the surrounding environment. This integration of nature brings a sense of tranquility and serenity to Egyptian-style houses, enhancing the overall quality of living.
7. Durability and Longevity: Egyptian architecture, known for its durability, has stood the test of time. This longevity is a testament to the structural integrity and craftsmanship employed in Egyptian design. African houses built with Egyptian design often share this same emphasis on durability, ensuring that the structures can withstand the elements and serve generations to come.
These characteristics of Egyptian design contribute to its timeless appeal and make it a popular choice for African communities looking to build houses that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also reflect their cultural heritage and values.
Practical Advantages of Egyptian Design for Building a House
Egyptian design offers several practical advantages for building houses in African communities. These advantages stem from the architectural techniques and design principles developed over centuries by the ancient Egyptians. Here are some practical advantages of Egyptian design:
1. Thermal Comfort: African climates can be hot and arid, and Egyptian design incorporates techniques to enhance thermal comfort. The use of thick walls, shading devices, and strategic positioning of windows and ventilation openings helps to regulate indoor temperatures naturally, reducing the need for excessive air conditioning. This makes Egyptian-style houses more energy-efficient and comfortable to live in.
2. Structural Stability: Egyptian architecture is renowned for its structural stability. The design includes load-bearing walls, buttresses, tall columns, and expansive foundations, ensuring the stability and longevity of the structures. African houses built with Egyptian design inherit this structural stability, providing peace of mind to homeowners and a solid foundation for their dwellings.
3. Natural Ventilation: Ventilation is crucial in tropical climates, and Egyptian design incorporates features that promote natural airflow. The layout of rooms, positioning of windows, and the inclusion of internal courtyards encourage cross-ventilation, allowing fresh air to circulate throughout the house. This natural ventilation helps to improve indoor air quality and reduce the reliance on mechanical ventilation systems.
4. Natural Lighting: Egyptian design prioritizes natural lighting, utilizing large windows, skylights, and open spaces to allow ample natural light to enter the house. This not only reduces the dependence on artificial lighting during the day but also creates a bright and inviting atmosphere inside the house. Natural light has been proven to promote overall well-being and energy efficiency.
5. Cultural Continuity: For many African communities, Egyptian design holds cultural significance, representing a connection to their ancestral past. Constructing houses in the Egyptian style allows these communities to preserve their cultural heritage and pass it on to future generations. It fosters a sense of pride and identity, strengthening community ties and cultural continuity.
6. Local Resource Usage: Egyptian design commonly incorporates locally available materials such as mud bricks, stone, and timber. By utilizing these materials, African communities can reduce transportation costs while supporting local economies. Additionally, the use of natural and sustainable materials aligns with the principles of eco-friendly construction and reduces the carbon footprint of the houses.
7. Versatility and Adaptability: Egyptian design can be adapted to various house sizes and layouts, making it a versatile choice for African communities. Whether it is a small dwelling or a larger family home, Egyptian design allows for flexibility in accommodating the needs and preferences of homeowners. It can be combined with modern construction techniques to create contemporary African houses that retain the essence of Egyptian architecture.
These practical advantages make Egyptian design a compelling choice for building houses in African communities. It combines functional considerations with cultural significance, creating spaces that are both practical and rooted in tradition.
Cultural Significance of Egyptian Design in African Communities
Egyptian design holds significant cultural importance in many African communities. It represents a connection to the rich and ancient history of the African continent, as well as the cultural exchange between different civilizations. Here are some key aspects of the cultural significance of Egyptian design in African communities:
1. Symbolism and Identity: Egyptian design carries deep symbolism that resonates with African communities. It represents a sense of pride in African civilization, highlighting the achievements, knowledge, and architectural prowess of ancient Egypt. By incorporating Egyptian design in their houses, African communities express their identity and cultural heritage, fostering a sense of belonging and unity.
2. Spiritual and Religious Significance: Ancient Egyptian architecture was closely intertwined with religious beliefs and rituals. Temples and tombs were constructed to honor deities and celebrate the afterlife. African communities that embrace Egyptian design often incorporate spiritual elements into their houses. This could include dedicating a space for ancestral shrines, creating sacred areas for rituals, or using architectural elements symbolizing protection and spiritual connection.
3. Cultural Exchange and Fusion: Egyptian design represents the historical cultural exchange that occurred throughout Africa. The adoption of Egyptian architectural elements by various African civilizations showcases the fusion and blending of different cultural influences. By embracing Egyptian design, African communities demonstrate their openness to cultural exchange and celebrate the diversity and interconnectedness of African cultures.
4. Preserving Traditional Craftsmanship: Egyptian design requires intricate craftsmanship, including carving, masonry, and decorative arts. By incorporating Egyptian design in house construction, African communities support and preserve traditional craftsmanship skills that have been passed down through generations. This enriches local artistry and contributes to the cultural economy of the community.
5. Educational and Historical Significance: Egyptian design serves as a source of education and historical significance for African communities. By constructing houses with Egyptian design, residents and visitors gain a deeper understanding of ancient Egyptian civilization, its architectural achievements, and its impact on African architecture. This fosters a sense of cultural awareness and appreciation for the historical roots of African societies.
6. Sense of Continuity: Embracing Egyptian design in house construction allows African communities to maintain a sense of continuity with their ancestral past. It connects present generations with the architectural traditions and practices that have shaped their societies over centuries. This sense of continuity reinforces cultural identity and provides a sense of rootedness and belonging in a rapidly changing world.
Overall, the cultural significance of Egyptian design in African communities is profound. It is a celebration of African heritage, an expression of cultural identity, and a link to the history and traditions that have shaped the African continent. By incorporating Egyptian design in their houses, African communities honor their past while creating spaces that embody a vibrant and dynamic present.
When incorporating Egyptian design into a house, consider using elements such as hieroglyphic motifs, columns, and intricate carvings to add a touch of ancient African culture to your home.
Read more: What Type Of Brick Is Used To Build A House
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Egyptian design offers several sustainability and environmental benefits for building houses in African communities. The architectural techniques and design principles of ancient Egypt promote eco-friendly practices and harmonious integration with the natural environment. Here are some key sustainability and environmental considerations of Egyptian design:
1. Use of Local and Natural Materials: Egyptian design often incorporates locally available and natural materials, such as mud bricks, stone, and timber. By utilizing materials sourced from the local environment, African communities can reduce the carbon footprint associated with transportation. Additionally, natural materials are renewable, biodegradable, and have a lower impact on the environment compared to synthetic alternatives.
2. Energy Efficiency: Egyptian design promotes energy efficiency through passive design strategies. The thick walls and strategic positioning of windows and ventilation openings help to optimize natural lighting and airflow, reducing the need for artificial lighting and mechanical cooling systems. By maximizing natural light and ventilation, Egyptian-style houses in Africa lower energy consumption and contribute to a more sustainable living environment.
3. Water Management: In arid regions where water scarcity is a concern, Egyptian design incorporates water management techniques. The inclusion of courtyard spaces and water features, such as ponds or fountains, allows for water collection and evaporation, helping to cool the surrounding environment. Additionally, the design may include systems for rainwater harvesting and graywater recycling, reducing reliance on scarce water resources.
4. Thermal Mass and Insulation: Egyptian architecture uses thick walls and thermal mass to regulate indoor temperatures naturally. Mud bricks and stone, known for their excellent thermal properties, absorb and store heat during the day and release it slowly at night, maintaining a more stable temperature inside the house. This reduces the need for artificial cooling or heating systems, minimizing energy consumption and reliance on fossil fuels.
5. Integration with Surrounding Landscape: Egyptian design harmoniously integrates with the surrounding landscape, taking into consideration factors such as topography, wind patterns, and solar orientation. By adapting the design to fit into the natural contours of the land, Egyptian-style houses in Africa minimize disruption to the ecosystem and preserve the beauty and integrity of the surrounding environment.
6. Longevity and Durability: Egyptian architecture is known for its durability and longevity, standing as a testament to the sustainability of the design. African houses built with Egyptian design benefit from this long-lasting construction, reducing the need for frequent maintenance, repairs, and material replacements. By constructing durable structures, African communities can minimize waste generation and promote a more sustainable built environment.
7. Connection with Nature: Egyptian design embraces the connection between architecture and nature. The inclusion of courtyards, gardens, and open spaces creates a seamless transition between the indoor and outdoor environments, fostering a sense of harmony and balance. This connection with nature not only enhances the quality of life for residents but also promotes a sustainable and environmentally conscious lifestyle.
With its emphasis on local materials, energy efficiency, and integration with the natural environment, Egyptian design offers a sustainable approach to building houses in African communities. By adopting these principles, African communities can create homes that are not only culturally significant but also contribute to a more sustainable future.
Challenges and Limitations of Egyptian Design Implementation
While Egyptian design offers numerous benefits, there are also challenges and limitations to consider when implementing this architectural style in African communities. These challenges can arise from various factors, including practical constraints, cultural considerations, and modern building regulations. Here are some key challenges and limitations of Egyptian design implementation:
1. Availability of Skilled Labor: Egyptian design requires specialized craftsmanship and techniques that may not be readily available in all African communities. The intricate carvings, decorative elements, and masonry work demand skilled artisans with knowledge and experience in the specific architectural style. The scarcity of such skilled labor can pose a challenge in successfully implementing Egyptian design.
2. Cost and Affordability: Constructing houses with Egyptian design can be more expensive compared to conventional building methods. The use of natural and traditional materials, as well as intricate detailing, can drive up the overall cost of the construction project. This can be a limitation for communities with limited financial resources, making it difficult to pursue Egyptian design for their houses.
3. Modern Building Codes and Regulations: Egyptian design may not always align with modern building codes and regulations in African countries. Building regulations are often updated to prioritize safety, accessibility, and environmental sustainability. Thus, incorporating certain elements of Egyptian design, such as the use of traditional techniques or specific materials, may face regulatory restrictions, making it challenging to fully embrace the architectural style.
4. Adaptation to Modern Lifestyles: Egyptian design, rooted in ancient civilizations, may not always cater to the needs and preferences of modern lifestyles. The layout and functionality of Egyptian-style houses might not align with contemporary living patterns, such as the need for open-concept spaces, multiple bathrooms, or larger kitchens. Balancing the traditional aesthetic with modern living requirements can be a limitation when implementing Egyptian design.
5. Modern Infrastructure and Utilities: Egyptian design often emphasizes natural ventilation and lighting, which may not fully accommodate modern infrastructure, such as air conditioning systems, electrical wiring, or complex plumbing. Incorporating these essential utilities while ensuring they do not compromise the integrity of the architectural style can be a challenge for implementing Egyptian design.
6. Cultural Appropriation and Sensitivity: Egyptian design is deeply rooted in the cultural heritage and traditions of ancient Egypt. It is essential to approach the implementation of Egyptian design in African communities with cultural sensitivity and respect, ensuring that it does not create an impression of cultural appropriation or disrespect towards the ancient civilization. Care must be taken to honor the cultural significance of Egyptian design while adapting it appropriately to the local context.
7. Maintenance and Preservation: The preservation and maintenance of Egyptian-style houses can be demanding due to the intricate detailing and use of specific materials. Regular upkeep, such as repairs to carvings, protection against weathering, and preservation of historical authenticity, requires dedicated effort and resources. This can be a limitation in communities with limited capacity or expertise for the ongoing maintenance of Egyptian-style houses.
Despite these challenges and limitations, the cultural and practical advantages of Egyptian design continue to inspire African communities. By understanding and addressing these limitations, communities can find ways to adapt Egyptian design to fit their needs and embrace its rich architectural heritage.
Case Studies: Examples of African Houses Built with Egyptian Design
Across Africa, there are inspiring examples of houses built with Egyptian design, showcasing the fusion of ancient aesthetics and modern functionality. Here are a few notable case studies:
1. The Nubian Houses in Sudan: In the Nubian region of Sudan, there are numerous houses built with Egyptian design influence. These houses feature vibrant colored exteriors, intricate carvings, and geometric patterns reminiscent of ancient Egyptian architecture. The use of mud bricks and locally sourced materials maintains the authenticity and sustainability of the design. The Nubian houses showcase the adaptation of Egyptian design to fit the local climate and cultural context.
2. The Mamluk House in Cairo, Egypt: Within Egypt itself, the Mamluk House stands as a testament to the enduring influence of Egyptian design. Dating back to the 14th century, this house showcases the intricate wooden carvings, vaulted ceilings, and geometric patterns that are characteristic of Egyptian architecture. It serves as an architectural heritage site, offering visitors a glimpse into the rich cultural history of the region and the architectural techniques employed during that era.
3. The Lamu Houses in Kenya: Lamu, a UNESCO World Heritage site in Kenya, boasts a unique blend of Swahili and Egyptian design influences. The houses in Lamu feature intricately carved wooden doors, coral stone walls, and open-air courtyards that create a cooling effect. This fusion of architectural styles represents centuries of cultural exchange between the Swahili Coast and Egypt, resulting in houses that are not only aesthetically stunning but also environmentally responsive.
4. The Kom Ombo House in Aswan, Egypt: Located on the banks of the Nile River in Aswan, the Kom Ombo House showcases the fusion of Egyptian design principles with contemporary architecture. The house incorporates elements such as arched windows, geometric patterns, and unique ornamentation, paying homage to ancient Egyptian heritage. The design also prioritizes energy efficiency, with passive cooling techniques and the use of locally sourced materials.
5. The Aksumite Houses in Ethiopia: Aksum, an ancient city in Ethiopia, features houses that have drawn inspiration from Egyptian architecture. These houses exhibit similar characteristics, such as the use of stone and intricate carvings. The Aksumite houses are a testament to the architectural connections between ancient Egypt and the Aksumite Empire, showcasing the lasting influence of Egyptian design in East Africa.
These case studies highlight the diverse ways in which Egyptian design has found expression in African architecture. They showcase the adaptability and versatility of the design, as well as the cultural significance it holds for different communities across the continent.
By drawing inspiration from ancient Egypt and melding it with contemporary needs and local contexts, these houses exemplify the enduring influence and relevance of Egyptian design in African communities.
Conclusion
Egyptian design has a captivating allure that has transcended time and geographic boundaries, finding a special place in African architecture. From the historical background to the practical advantages, cultural significance, sustainability considerations, challenges, and case studies, it is evident that Egyptian design offers a wealth of benefits and inspiration for building houses in African communities.
The historical roots of Egyptian design in Africa showcase the enduring influence of an ancient civilization and the cultural exchange that shaped the continent’s architectural landscape. The characteristics of Egyptian design, such as symmetry, geometry, and ornate detailing, contribute to the aesthetic appeal and sense of grandeur embodied in African houses embracing this style.
Practical advantages, such as thermal comfort, structural stability, natural ventilation, and sustainability considerations, make Egyptian design a viable and attractive choice for African communities. By utilizing local materials, embracing passive design principles, and integrating with the natural environment, Egyptian-style houses can provide energy-efficient and culturally significant spaces that connect inhabitants to their cultural heritage.
The cultural significance of Egyptian design resonates deeply within African communities. It symbolizes pride in African civilization, spiritual and religious connections, and a sense of cultural continuity. By incorporating Egyptian design in their houses, African communities preserve traditional craftsmanship and educate future generations about their historical roots and architectural achievements.
Despite the practical and cultural benefits of Egyptian design, it is important to acknowledge the challenges and limitations. These can include the availability of skilled labor, cost considerations, modern building regulations, adaptation to modern lifestyles, and the need for cultural sensitivity and maintenance efforts. By addressing these challenges, African communities can successfully implement Egyptian design while ensuring it remains respectful and relevant to their unique contexts.
The numerous case studies of African houses built with Egyptian design demonstrate the versatility and adaptability of this architectural style. From the Nubian houses in Sudan to the Mamluk house in Cairo, the Lamu houses in Kenya, the Kom Ombo house in Egypt, and the Aksumite houses in Ethiopia, these examples showcase the fusion of ancient aesthetics and modern functionality.
In conclusion, Egyptian design holds a special place in African architecture, reflecting a connection to the continent’s rich heritage and cultural exchange. The blend of historical significance, practical advantages, sustainability considerations, and cultural pride make Egyptian-style houses a captivating choice for African communities. By embracing this unique architectural style, Africans are able to construct homes that are not only functional and sustainable but also serve as symbols of cultural identity and a testament to the enduring legacy of ancient Egypt.
Frequently Asked Questions about Egyptian Design For Building A House: Why Do Africans Use It?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “Egyptian Design For Building A House: Why Do Africans Use It?”