Home>diy>Building & Construction>What Is CAD In Construction


Building & Construction
What Is CAD In Construction
Modified: January 6, 2024
Discover the importance of CAD in building construction and how it revolutionizes architectural design and project management. Learn how CAD streamlines processes and enhances efficiency in construction projects.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
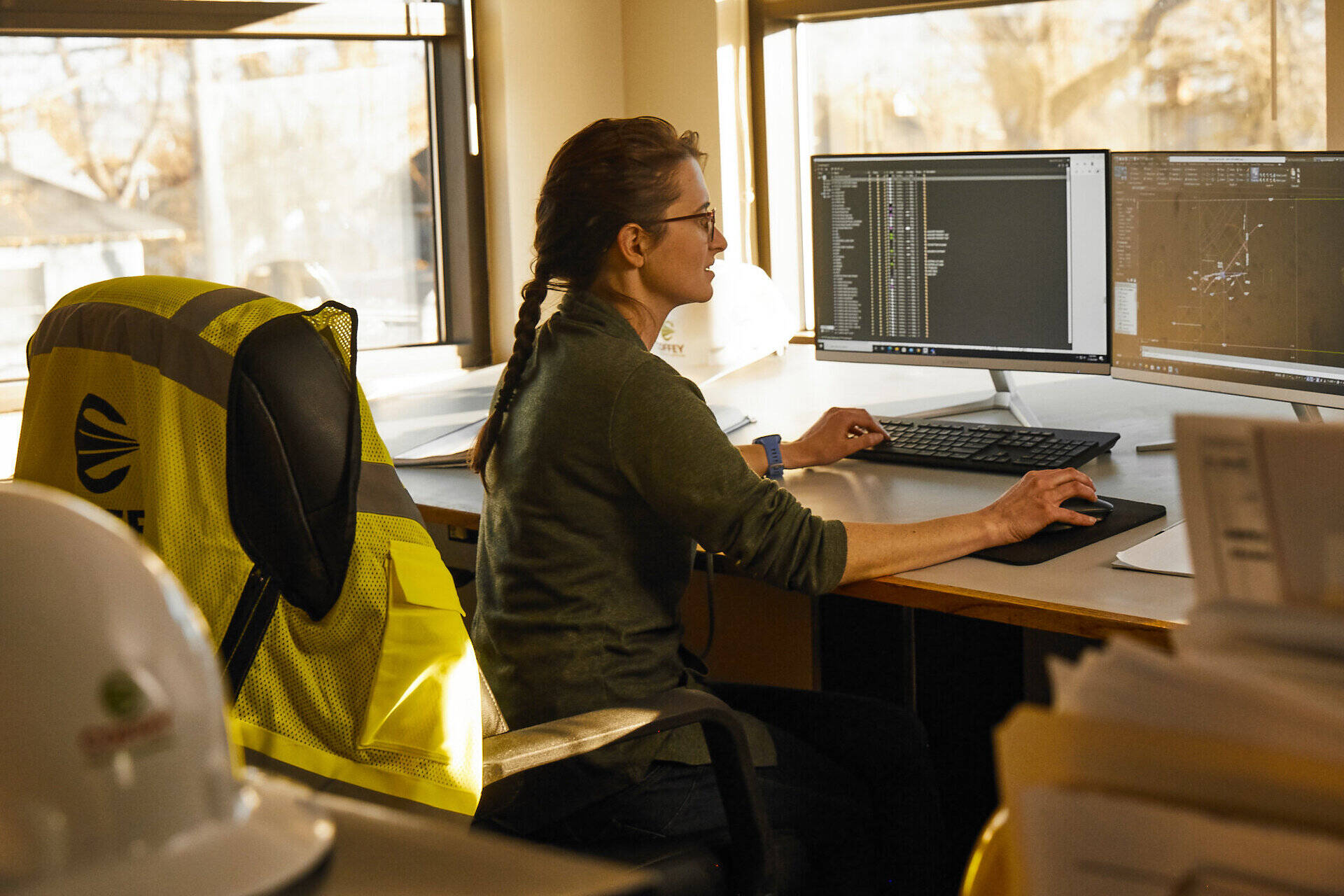
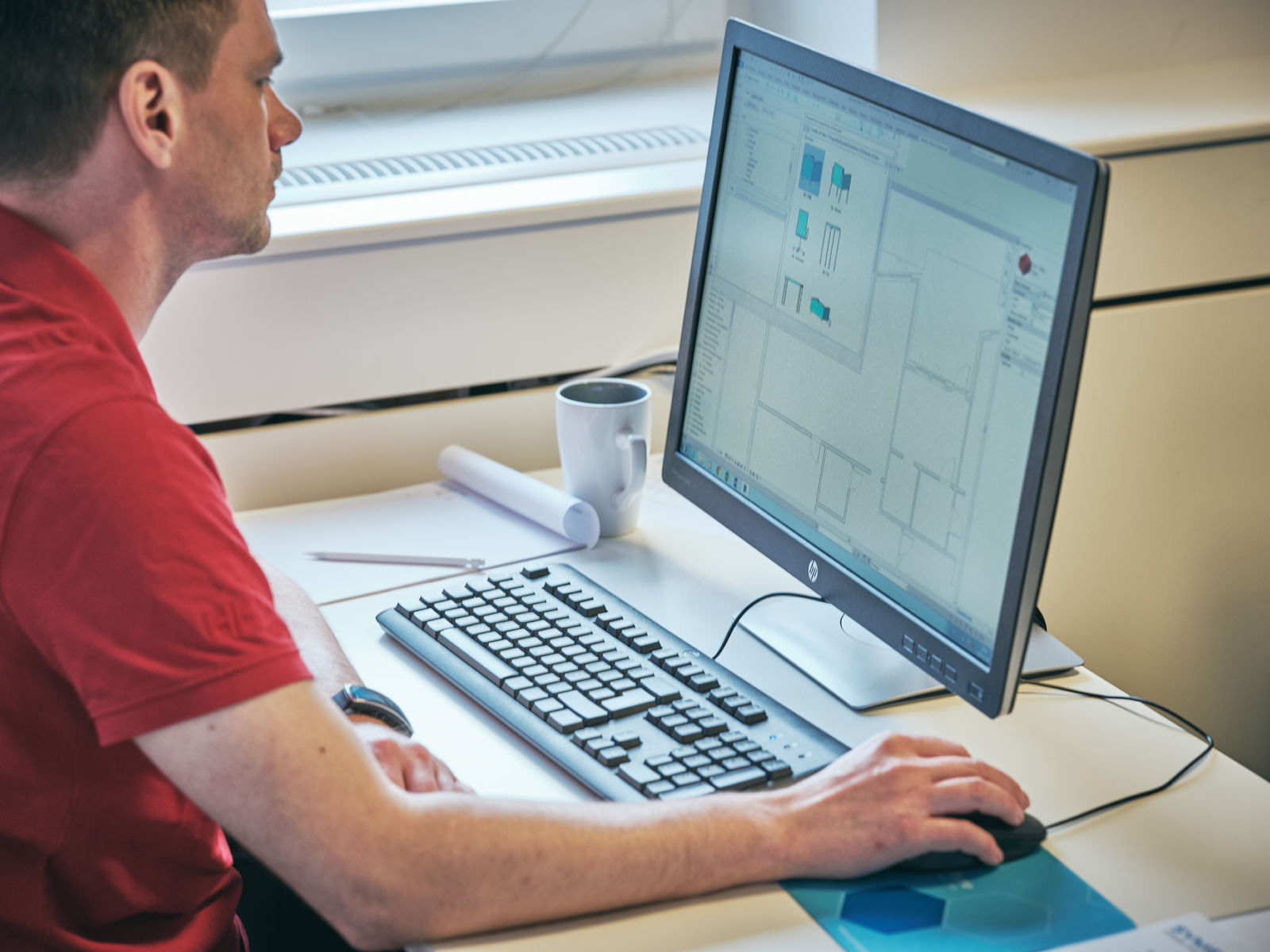
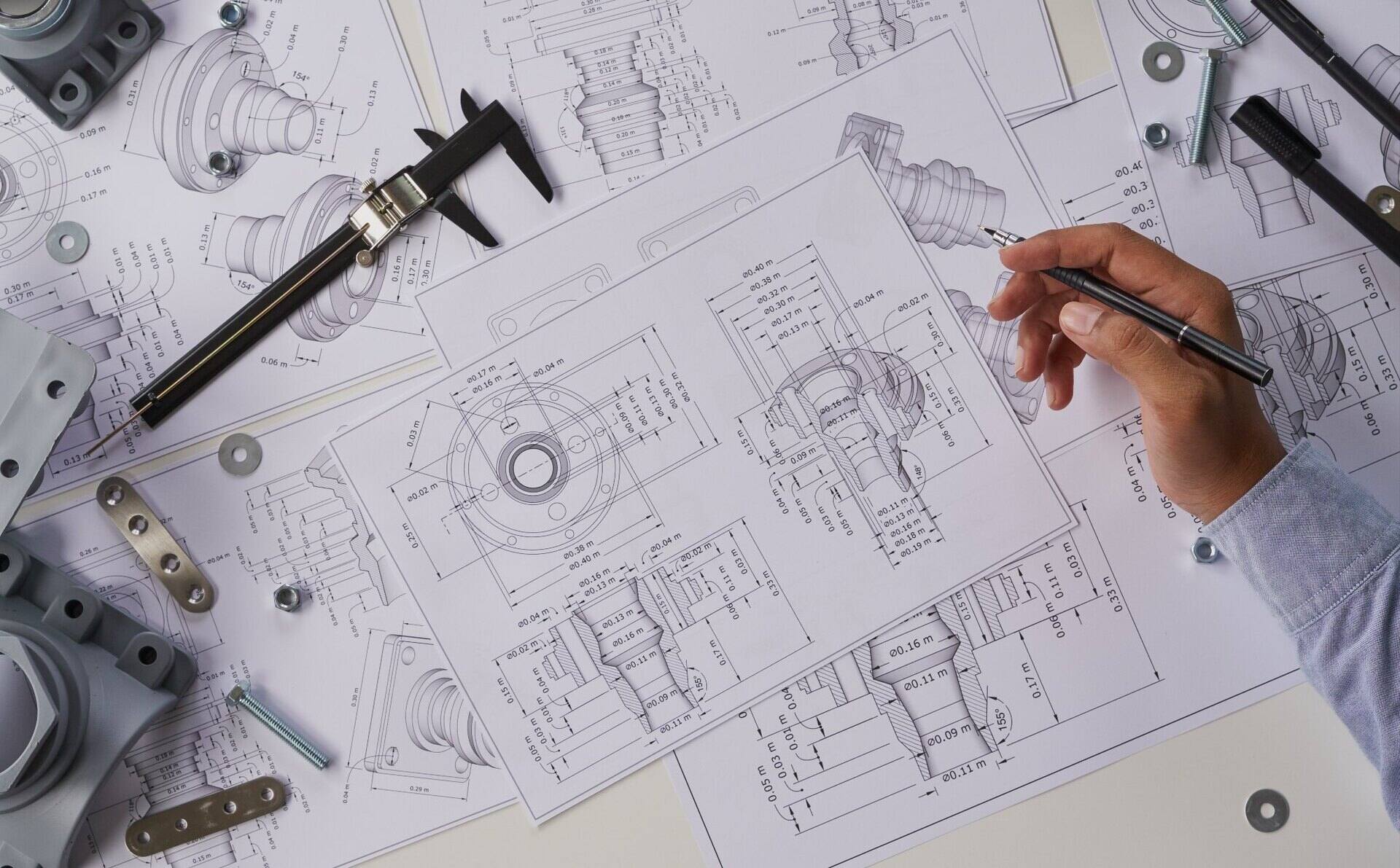
In the ever-evolving world of construction, technology has become an indispensable tool for streamlining processes and optimizing efficiency. One such technological advancement is Computer-Aided Design (CAD), which has revolutionized the construction industry. CAD is a powerful software that enables architects, engineers, and construction professionals to create detailed and accurate digital models of buildings and structures.
In this article, we will delve into the world of CAD in construction, exploring its definition, history, importance, applications, benefits, challenges, and future trends. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the role CAD plays in shaping the modern construction landscape.
Key Takeaways:
- CAD in construction revolutionizes design, visualization, and collaboration, leading to increased accuracy, efficiency, and cost savings. Its future trends, including BIM integration and AI, promise even smarter and sustainable infrastructure.
- While CAD offers numerous benefits, its implementation in construction comes with challenges such as cost, training, and compatibility. Overcoming these challenges is crucial for successful utilization and integration of CAD in construction projects.
Read more: What Is CAD?
Definition of CAD in Construction
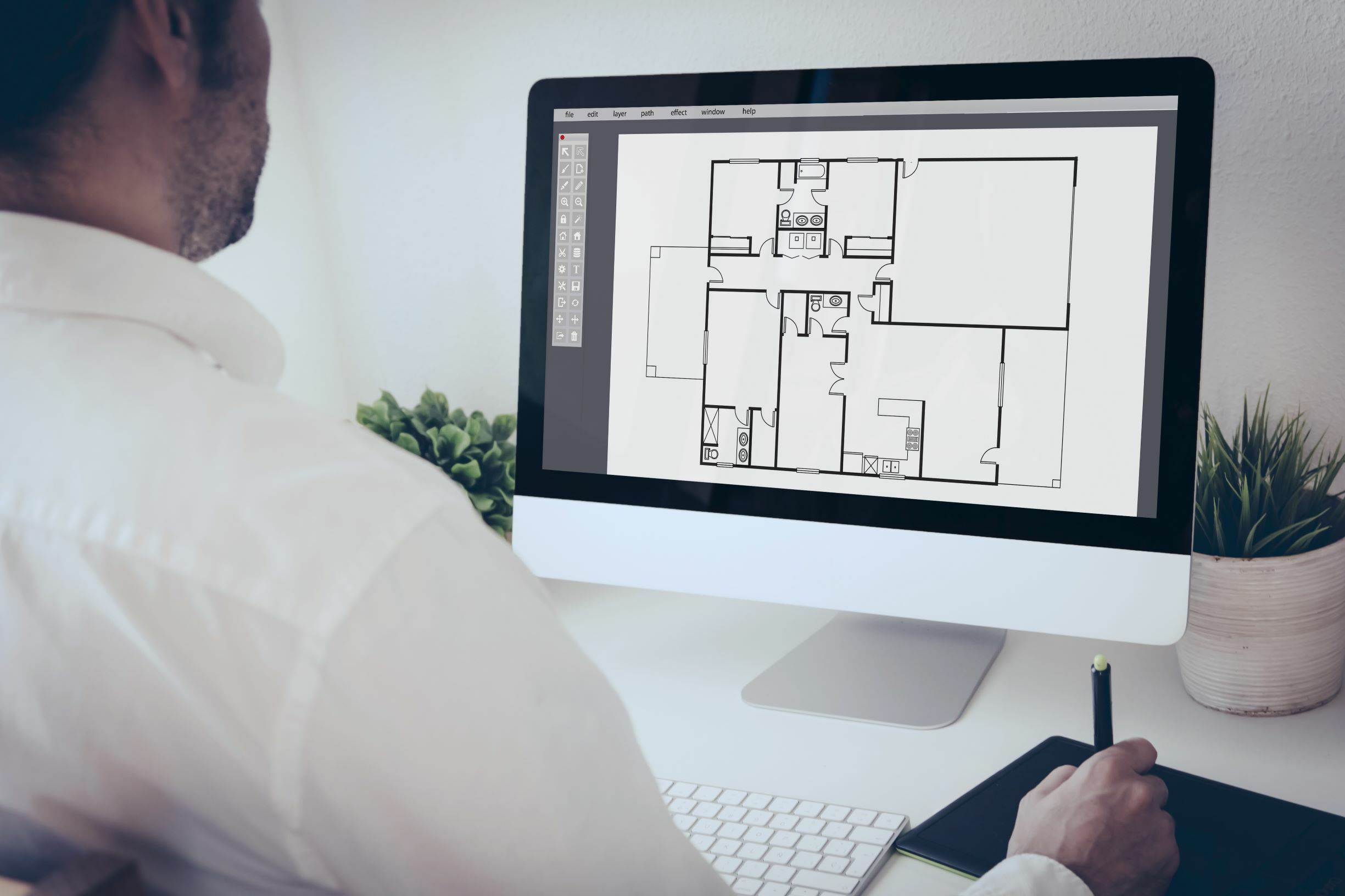
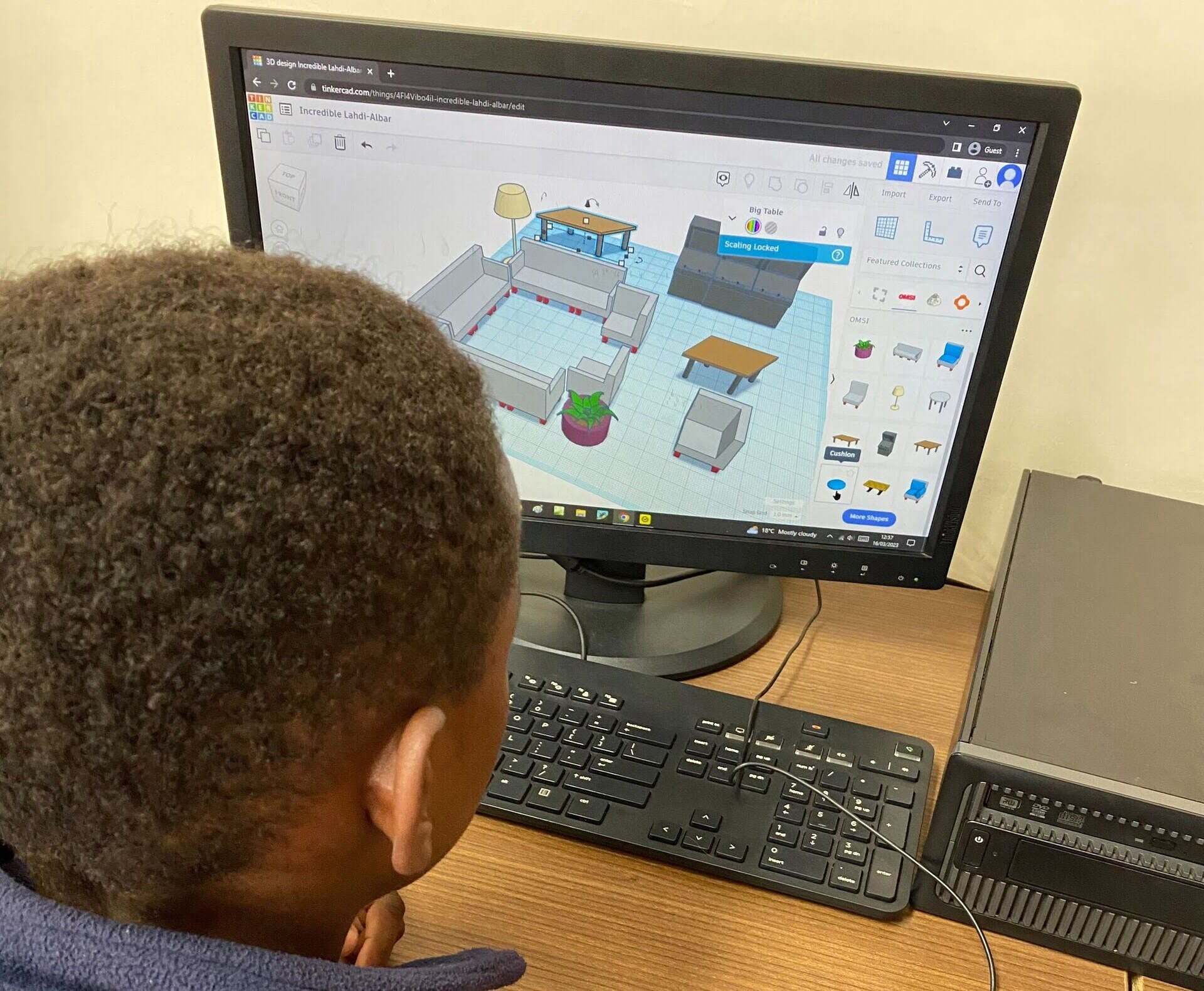
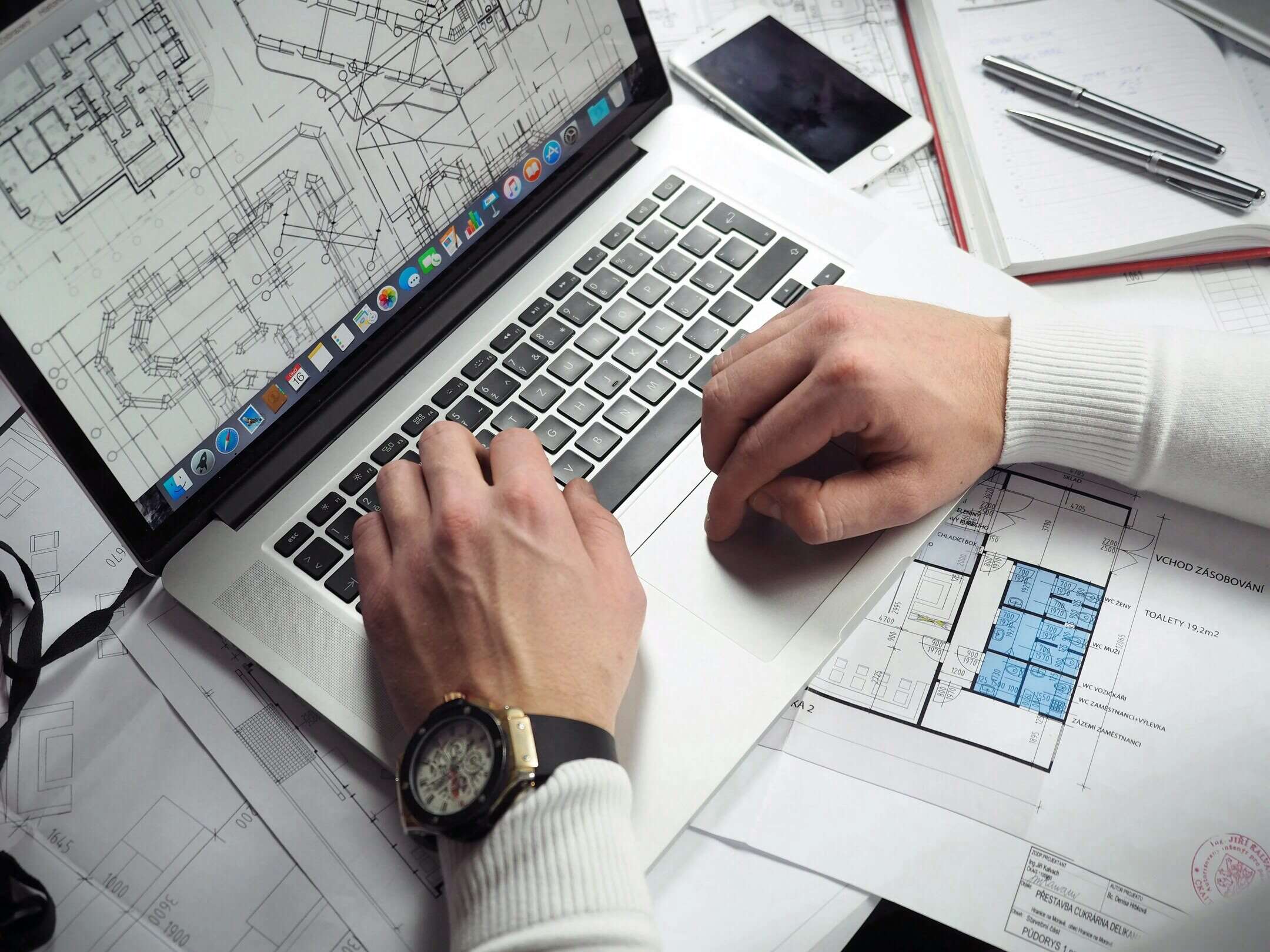
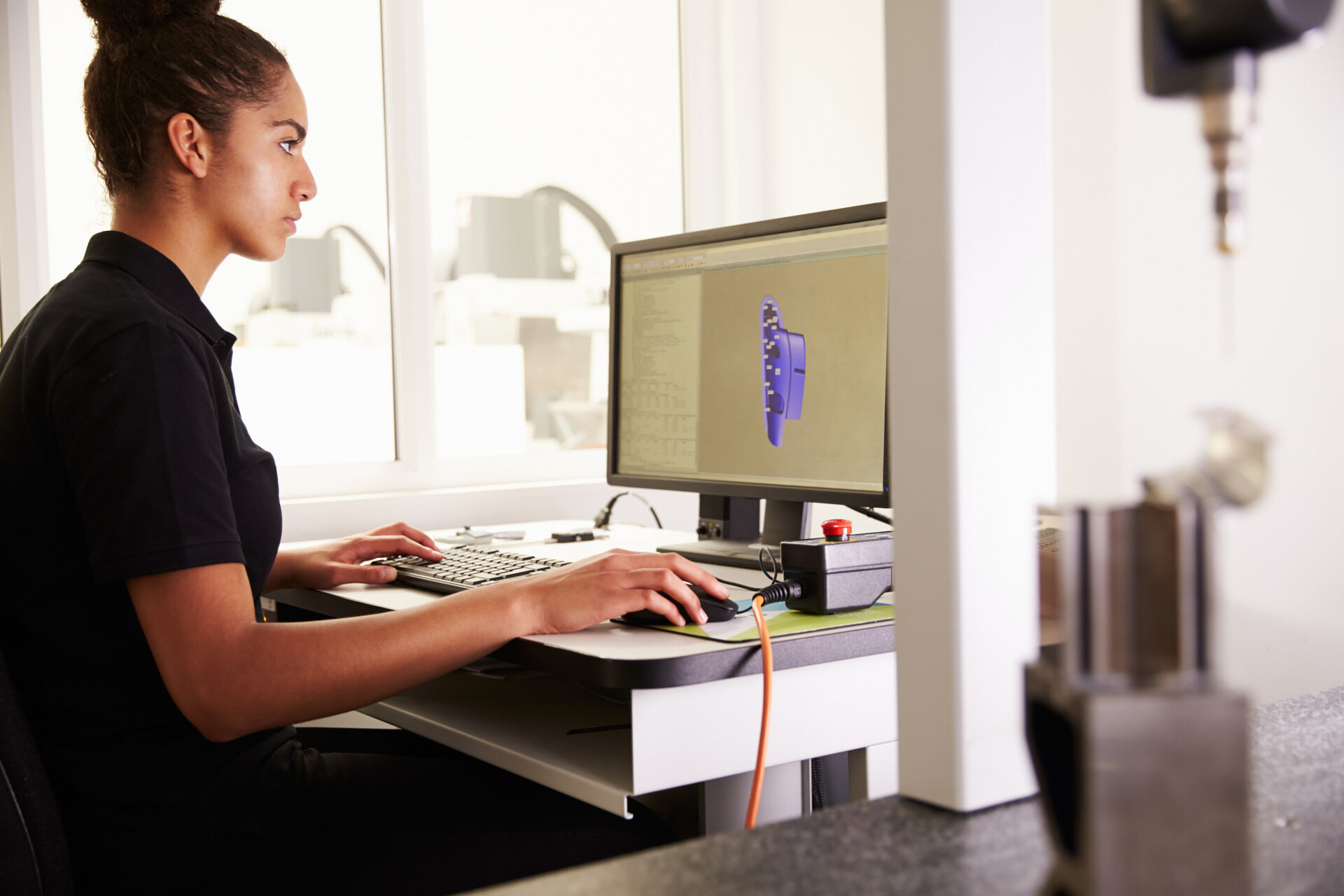
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) is a technology that uses specialized software to create two-dimensional (2D) and three-dimensional (3D) digital models of buildings, infrastructure, and other structures. It provides architects, engineers, and construction professionals with the tools and capabilities to visualize, design, analyze, and document projects with high levels of accuracy and precision.
CAD in construction goes beyond simple digital drafting; it enables designers to create virtual representations of plans, elevations, sections, and even complex structural systems. The software allows for the inclusion of detailed information such as dimensions, materials, textures, and finishes, making it an invaluable asset in the construction industry.
With CAD, professionals can easily manipulate and modify designs, allowing for quick iterations and revisions before construction begins. This virtual environment reduces errors and allows for better communication and collaboration among stakeholders involved in the construction process.
CAD software typically includes a range of tools and features, including drawing and editing tools, parametric modeling, rendering capabilities, and even simulation and analysis functions. These tools assist in creating realistic representations of structures and help streamline the design and construction process.
Overall, CAD in construction provides a digital platform where architects, engineers, and construction professionals can visually conceptualize and communicate their ideas and designs, ultimately resulting in improved project outcomes.
Brief History of CAD in Construction
The roots of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) in the construction industry can be traced back to the 1960s when computers began to be utilized for engineering and architectural purposes. The advent of CAD marked a significant shift from manual drafting methods to digital design processes.
In the early days, CAD systems were rudimentary and limited in functionality. They primarily focused on creating 2D drawings and lacked the advanced tools and capabilities we have today. However, even these simple systems offered advantages such as improved accuracy, faster drafting, and the ability to store and retrieve drawings digitally.
Throughout the 1970s and 1980s, significant advancements were made in CAD technology. The introduction of 3D modeling capabilities expanded the scope of CAD in construction, allowing for more realistic representations of buildings and structures. Architects and engineers could now visualize and analyze designs from different perspectives, leading to better decision-making and problem-solving.
By the 1990s, CAD usage became more widespread in the construction industry. The introduction of more user-friendly interfaces and increased processing power of computers made CAD systems more accessible to professionals. The software offered a wide range of tools and features, including parametric modeling, rendering, and structural analysis, enabling architects and engineers to create complex and intricate designs with precision.
As technology continued to advance, so did the capabilities of CAD. The integration of Building Information Modeling (BIM) further transformed CAD in construction. BIM built upon the foundation of CAD by incorporating not only geometry but also comprehensive data and information about a building. This holistic approach allowed for better collaboration, improved project coordination, and enhanced facilities management.
Today, CAD is an indispensable tool in the construction industry. It has become more intuitive, versatile, and powerful, enabling professionals to create intricate designs, simulate real-world conditions, and optimize the construction process as a whole. Some CAD systems even have cloud-based collaboration features that facilitate real-time collaboration and communication among team members.
Looking ahead, the future of CAD in construction is filled with exciting possibilities. Advancements in artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and augmented reality are poised to revolutionize the way architects, engineers, and construction professionals interact with CAD systems, making the design and construction process even more efficient and immersive.
Importance of CAD in Construction
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) has become an integral part of the construction industry, offering numerous benefits and advantages. Its importance in modern construction cannot be overstated. Here, we will explore some of the key reasons why CAD is so crucial in the field:
1. Accuracy and Precision: CAD allows for precise and accurate modeling of buildings and structures. Designers can create detailed drawings with precise measurements, ensuring that components fit together seamlessly. This accuracy helps reduce errors, avoid costly rework, and ensure that the final product matches the initial design intent.
2. Visualization and Communication: CAD enables architects, engineers, and construction professionals to visualize and communicate design concepts effectively. With 3D modeling and realistic renderings, stakeholders can get a comprehensive understanding of the project, including spatial relationships, materials, and finishes. This aids in better decision-making and ensures that all parties are on the same page throughout the construction process.
3. Design Exploration and Iteration: CAD allows for easy exploration of design options and quick iterations. Digital modeling tools enable professionals to test different configurations, evaluate their impact, and refine the design. This iterative process helps optimize the design for aesthetics, functionality, and constructability, leading to better overall project outcomes.
4. Improved Efficiency: CAD significantly improves efficiency in the construction industry. Designers can leverage the software’s features to automate repetitive tasks, generate accurate quantity takeoffs, and create detailed construction documentation. This streamlines the design and documentation process, saving time and effort that can be allocated to other critical aspects of the project.
5. Precise Project Coordination: CAD facilitates precise project coordination among various stakeholders. By creating a digital model, different disciplines such as architecture, structural engineering, mechanical engineering, and plumbing can work together to identify and resolve conflicts before construction begins. This coordination minimizes conflicts, improves efficiency, and reduces the risk of unforeseen issues during construction.
6. Cost and Time Savings: By allowing for accurate design and planning, CAD helps minimize errors and change requests during construction. This reduces costly rework and delays, resulting in significant cost and time savings. Additionally, CAD can enable the optimization of materials, leading to efficient use and reduced waste, further contributing to cost savings.
Overall, the importance of CAD in construction lies in its ability to enhance accuracy, improve communication and collaboration, optimize designs, streamline processes, and ultimately deliver better quality projects in a more efficient and cost-effective manner.
Applications of CAD in Construction
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) has a wide range of applications in the construction industry. It is utilized throughout the entire project lifecycle, from conceptualization and design to construction and facility management. Here are some key areas where CAD is extensively used:
1. Architectural Design: CAD is widely employed in architectural design to create detailed floor plans, elevations, and sections. It allows architects to visualize and communicate their design ideas effectively. With CAD, architects can explore different design options, experiment with materials and finishes, and create realistic 3D models to showcase their vision to clients and stakeholders.
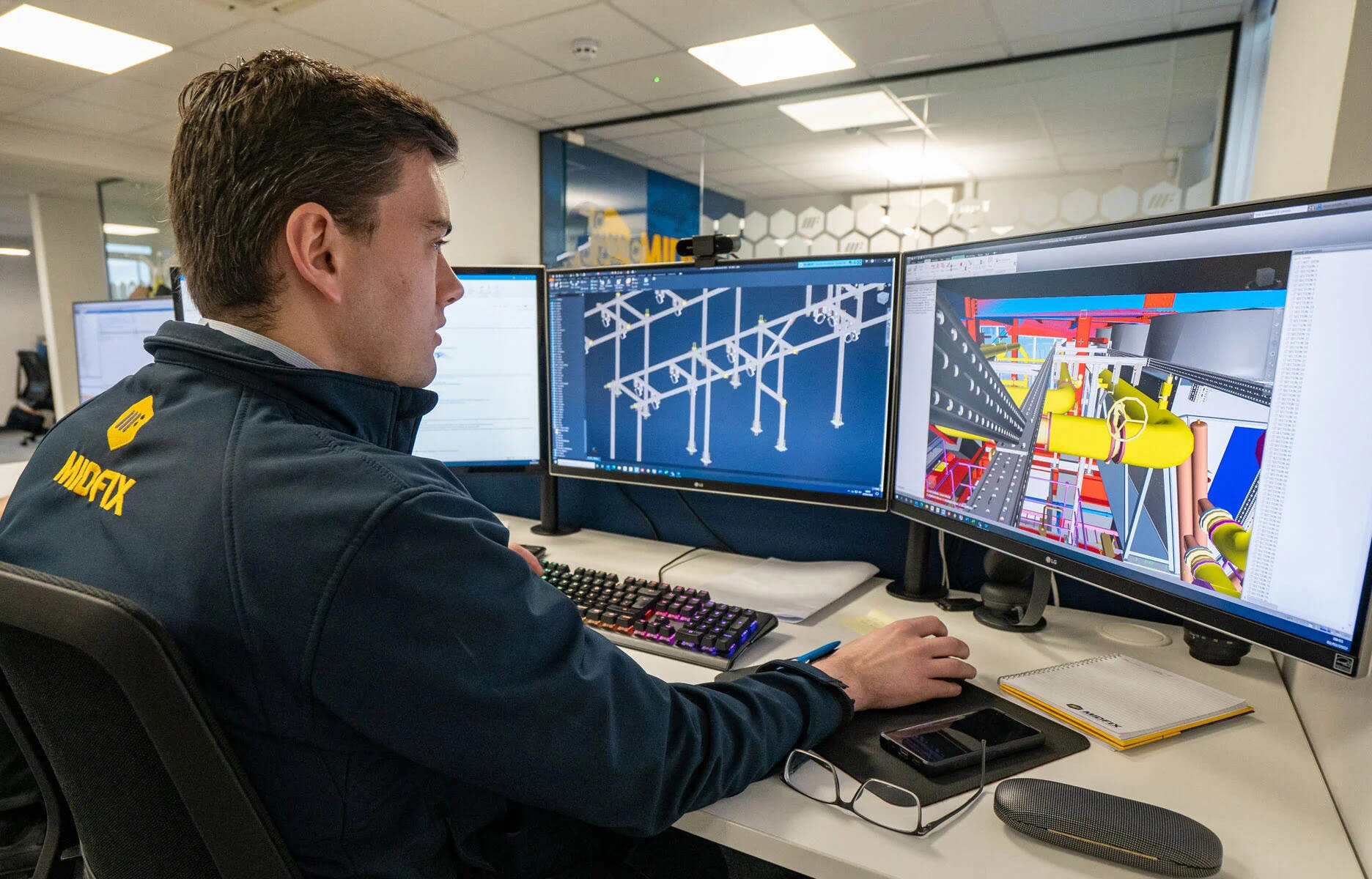
2. Structural Engineering: CAD plays a crucial role in structural engineering, allowing engineers to design and analyze complex structural systems. With CAD, engineers can create accurate structural models, perform calculations, and simulate real-world conditions to ensure structural integrity. This helps identify potential issues and optimize the design for strength, stability, and safety.
3. MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing) Systems: CAD is extensively used in the design and coordination of MEP systems. It enables professionals to create detailed 3D models of mechanical, electrical, and plumbing components, ensuring proper placement, sizing, and coordination. This coordination helps avoid clashes and conflicts between systems, ensuring seamless integration during construction.
4. Construction Documentation: CAD is essential for generating accurate construction documentation, including detailed drawings, specifications, and schedules. These documents provide contractors and subcontractors with the necessary information to carry out construction activities. CAD enables the creation of clear and comprehensive construction documentation, reducing ambiguity and errors during the construction phase.
5. Clash Detection and Coordination: Using CAD, clash detection and coordination tools help identify conflicts between different building systems before construction begins. By overlaying models of various trades, such as architectural, structural, and MEP, potential clashes can be detected and resolved early on. This ensures a smooth construction process and avoids costly rework due to clashes.
6. Facility Management: CAD is increasingly being used in facility management to create accurate as-built models of buildings and infrastructure. These models serve as a digital representation of the physical assets and contain valuable information, such as maintenance schedules, equipment locations, and utility systems. With CAD, facility managers can efficiently manage and maintain buildings, improving operational efficiency and reducing lifecycle costs.
In addition to these specific applications, CAD is also employed in areas such as construction visualization and presentation, site planning, landscape design, and interior design. Its versatility and wide range of tools make it a valuable asset across multiple disciplines in the construction industry.
When using CAD in construction, make sure to regularly save your work and create backups to prevent loss of important design and project data.
Read more: What Are CAD Software
Benefits of Using CAD in Construction
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) has become a fundamental tool in the construction industry, offering numerous benefits and advantages to professionals involved in the design and construction process. Here are some key benefits of using CAD in construction:
1. Increased Efficiency: CAD software streamlines the design process, allowing professionals to create and modify designs quickly and accurately. It eliminates the need for manual drafting, saving time and reducing the chances of errors. With the ability to copy and reuse elements, CAD enables designers to efficiently create design templates, reducing repetitive tasks and enhancing productivity.
2. Improved Accuracy and Precision: CAD ensures a higher level of accuracy and precision in design documentation. Measurements, dimensions, and details can be precisely defined and controlled within the software, reducing the risk of human error. This accuracy leads to better quality construction and minimizes costly rework due to design discrepancies.
3. Enhanced Visualization and Communication: CAD enables professionals to create realistic 3D visualizations of buildings and structures, allowing clients and stakeholders to better understand and visualize the final outcome. These visualizations facilitate effective communication and collaboration, ensuring that everyone involved in the project shares a common understanding of the design intent and goals.
4. Design Flexibility and Iteration: CAD provides designers with the flexibility to explore and iterate design ideas quickly and easily. Digital models can be easily modified, enabling designers to test different design alternatives and assess their impact. This iterative process results in optimized designs that meet both functional and aesthetic requirements.
5. Collaboration and Coordination: CAD facilitates seamless collaboration and coordination among different disciplines involved in the construction process. By sharing digital models, professionals can identify and resolve clashes or conflicts between architectural, structural, and MEP systems before construction begins. This coordination minimizes costly errors and delays, ensuring smooth project execution.
6. Cost and Time Savings: By reducing errors and improving efficiency, CAD helps save both time and money during the construction process. Accurate design documentation generated by CAD minimizes the chances of costly rework and change orders. Additionally, CAD enables accurate material takeoffs, optimizing material usage and reducing waste, resulting in further cost savings.
7. Simulations and Analysis: CAD software often includes tools for simulations and analysis, allowing professionals to assess factors such as structural integrity, energy efficiency, and environmental impact. These simulations help identify potential design flaws and make informed decisions to improve performance and sustainability.
8. Documentation and Record-Keeping: CAD facilitates the creation of detailed and organized design documentation, including drawings, specifications, and schedules. Digital records are easily accessible and can be updated throughout the project lifecycle, ensuring that accurate and up-to-date information is readily available to all stakeholders.
Overall, the benefits of using CAD in construction are vast and far-reaching. It empowers professionals to work more efficiently, achieve higher levels of accuracy, enhance collaboration, save time and money, and ultimately deliver better quality projects.
Challenges in Implementing CAD in Construction
While Computer-Aided Design (CAD) has numerous benefits, there are also a few challenges that can arise during its implementation in the construction industry. These challenges need to be addressed to ensure successful integration and utilization of CAD in construction projects. Here are some key challenges:
1. Cost and Investment: Implementing CAD software requires a significant investment in terms of licenses, hardware, and training. The cost of setting up the necessary infrastructure and providing training to staff can be a challenge for smaller firms or projects with limited budgets. It’s important to carefully assess the return on investment and the overall project requirements before committing to CAD implementation.
2. Learning Curve: CAD software can be complex and may have a steep learning curve, especially for users who are not familiar with computer-aided design tools. It requires time and effort to train staff to effectively use the software and navigate its features. Adequate training and ongoing support are essential to overcome this challenge and ensure that the software is utilized to its full potential.
3. Compatibility and Integration: CAD software must be compatible and seamlessly integrate with other project management tools and software systems used throughout the project lifecycle. Incompatibilities can lead to data loss, inconsistencies, and project delays. It’s crucial to ensure that CAD software can integrate with existing systems or to choose one that is compatible with other tools used within the organization.
4. Data Management and Security: CAD files can be large and require efficient data management and storage solutions. Version control, backup procedures, and access control must be implemented to safeguard the integrity and security of CAD files. Failure to manage data effectively can result in confusion, data loss, or unauthorized access to sensitive project information.
5. Training and Skill Development: CAD software and tools continue to evolve, requiring ongoing training and skill development for users to stay updated with the latest features and capabilities. Continuous training programs and professional development initiatives are necessary to ensure that staff can effectively utilize CAD software and adapt to advancements in the field.
6. Resistance to Change: Introducing CAD to a construction organization may face resistance from employees who are accustomed to traditional manual drafting methods. Resistance to change can hinder the successful implementation of CAD. It is important to provide clear communication, training, and support to address any concerns or resistance and ensure the smooth transition to using CAD in the organization.
7. Scalability and Standardization: CAD implementation should consider the scalability of the software and the organization’s future requirements. As project sizes and complexities grow, ensuring that the CAD system is capable of handling the increased demands becomes crucial. Standardization of CAD practices and procedures across the organization is also essential to maintain consistency and efficiency.
Addressing these challenges requires careful planning, adequate resources, and a commitment to continuous improvement. By doing so, construction companies can maximize the benefits of CAD while minimizing any potential setbacks during its implementation.
Future Trends of CAD in Construction
As technology continues to rapidly advance, the future of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) in the construction industry holds exciting possibilities. Here are some emerging trends that are likely to shape the future of CAD in construction:
1. Building Information Modeling (BIM) Integration: The integration of CAD and Building Information Modeling (BIM) is set to become even more prevalent. BIM incorporates not only the geometric representations of buildings but also comprehensive data and information about the project. This integrated approach allows for better collaboration, coordination, and decision-making throughout the construction lifecycle.
2. Cloud-Based Collaboration: Collaborative CAD platforms hosted on the cloud are gaining popularity. Cloud-based CAD allows multiple stakeholders to access and work on a project simultaneously, regardless of their geographical location. Real-time collaboration and communication enhance efficiency, accuracy, and project coordination, fostering seamless collaboration among architects, engineers, contractors, and clients.
3. Mobile CAD: Mobile devices are increasingly becoming powerful tools for CAD applications. Mobile CAD software allows professionals to access, view, and modify drawings on their smartphones or tablets. This flexibility enables on-site inspections, real-time updates, and immediate decision-making, enhancing productivity and reducing delays in the construction process.
4. Virtual and Augmented Reality: Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) technologies have the potential to transform the way CAD is used in construction. VR can create immersive experiences, enabling stakeholders to virtually walk through and experience buildings before they are constructed. AR overlays digital information onto the physical environment, assisting with on-site operations and maintenance tasks.
5. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning algorithms are being integrated into CAD software to automate repetitive tasks and improve design outcomes. AI can generate design options based on predefined criteria, enabling designers to explore a wider range of possibilities. Machine learning algorithms can analyze data to predict and optimize building performance, energy efficiency, and structural integrity.
6. Generative Design: Generative design is an emerging concept where CAD algorithms can propose and optimize design solutions based on specified constraints and goals. Using advanced optimization techniques, generative design algorithms can explore countless design possibilities and determine the most efficient and innovative solutions, revolutionizing the architectural and structural design process.
7. Sustainability and Green Design: CAD tools will continue to evolve to support sustainable design practices. Energy analysis and simulation tools will become more robust, allowing designers to evaluate the energy performance of buildings and identify opportunities for energy savings. CAD software will also provide greater integration of sustainable materials, systems, and strategies into the design process.
These trends indicate that CAD in construction will continue to evolve, offering increased collaboration, automation, customization, and optimization. These advancements will enhance the design process, improve project coordination, and ultimately lead to the construction of smarter, more sustainable, and efficient buildings and infrastructure.
Conclusion
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) has transformed the construction industry, revolutionizing the way architects, engineers, and construction professionals design, visualize, and communicate their ideas. The benefits of CAD in construction are vast, ranging from increased accuracy and precision to improved efficiency, communication, and collaboration.
With CAD, professionals can create detailed digital models, simulate real-world conditions, and optimize designs for functionality, aesthetics, and constructability. This enhances decision-making, minimizes errors, reduces costs, and saves valuable time throughout the construction process.
CAD finds applications in various areas of construction, including architectural design, structural engineering, MEP coordination, and construction documentation. It enables seamless collaboration among different disciplines, ensuring effective project coordination and minimizing clashes and conflicts.
Despite the many advantages, implementing CAD in construction does come with challenges. These challenges include initial investment costs, training requirements, data management, and resistance to change. However, with careful planning, proper training, and adequate resources, these challenges can be overcome, leading to successful implementation and utilization of CAD in construction projects.
Looking ahead, the future of CAD in construction is bright. Trends such as BIM integration, cloud-based collaboration, mobile CAD, virtual and augmented reality, artificial intelligence, and sustainable design will shape the future of CAD in the construction industry. These emerging technologies and advancements will foster innovation, streamline processes, and lead to the creation of smarter, more sustainable, and efficient buildings and infrastructure.
In conclusion, CAD has become an indispensable tool for the modern construction industry. Its ability to enhance accuracy, improve communication and collaboration, optimize designs, and streamline processes makes it a vital asset for architectural, engineering, and construction professionals. As technology continues to advance, CAD will continue to evolve and play a crucial role in shaping the future of construction.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is CAD In Construction
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Is CAD In Construction”