Home>diy>Architecture & Design>What Is CAD In Architecture


Architecture & Design
What Is CAD In Architecture
Modified: January 9, 2024
Discover how CAD (Computer-Aided Design) revolutionizes architecture and design, enhancing precision, efficiency, and creativity. Explore its benefits and applications in the industry.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
In the field of architecture, the perfect marriage of design and technology is essential to create stunning structures that stand the test of time. With advancements in computer technology, architects have been able to leverage powerful tools to optimize their design process and improve productivity. One such tool that has revolutionized the architecture industry is Computer-Aided Design (CAD).
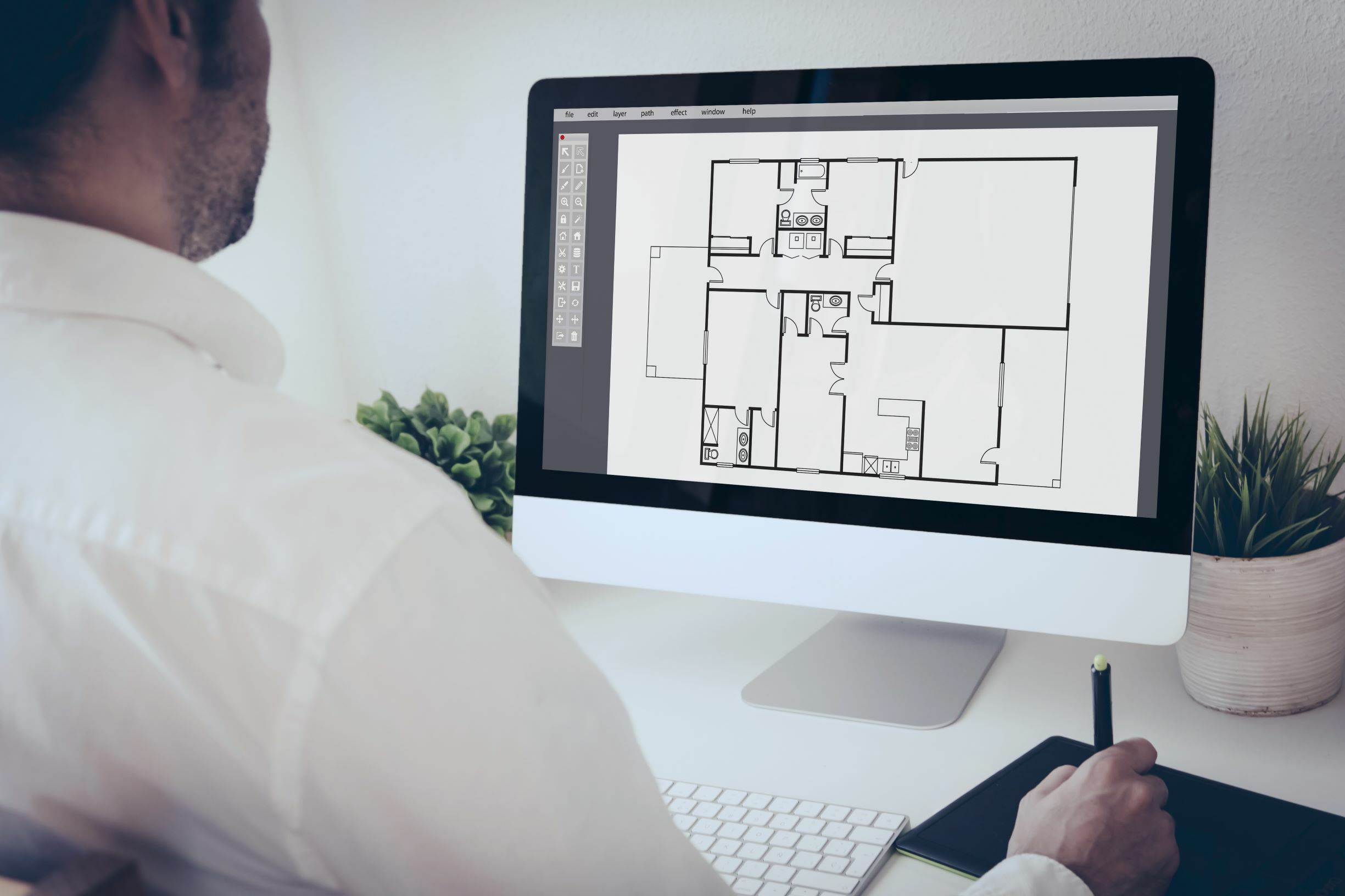
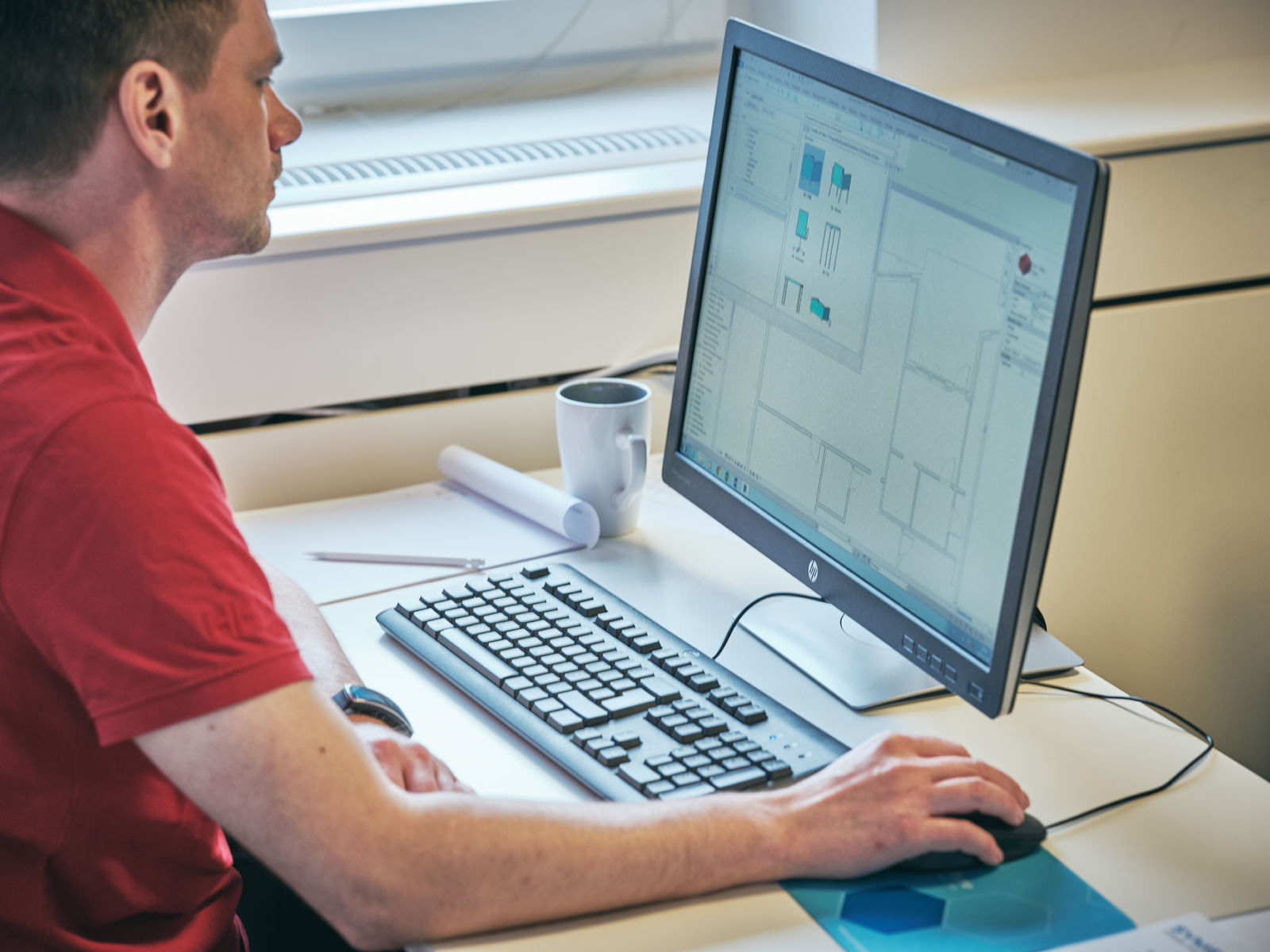
CAD, in simple terms, refers to the use of computer software to create, modify, and analyze architectural designs. It has become an integral part of the architectural workflow, allowing architects to visualize and communicate their ideas effectively. With CAD software, architects can now create detailed 2D and 3D models, generate accurate construction drawings, and simulate building performance.
With the rise of CAD software, architectural professionals have access to a wide range of tools and features that were previously unimaginable. From sketching initial concepts to producing construction-ready drawings, CAD plays a vital role in every stage of the architectural process.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the world of CAD in architecture, exploring its definition, the software programs commonly used, the benefits it offers to architects, the different applications within the field, as well as its challenges and limitations. We will also discuss the future trends in CAD for architecture.
So, buckle up as we explore the fascinating world of CAD and uncover how it is shaping the future of architecture.
Key Takeaways:
- CAD software empowers architects to create precise, detailed, and visually stunning designs, streamlining the design process and enhancing collaboration, ultimately leading to exceptional architectural projects.
- The future of CAD in architecture holds exciting trends such as VR/AR, generative design, AI, and sustainability analysis, offering architects opportunities to push the boundaries of creativity and innovation in building design.
Read more: What Is CAD?
Definition of CAD
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) refers to the use of computer software to create, modify, and analyze architectural designs. It is a digital tool that offers architects and designers the ability to create accurate and detailed models of buildings, spaces, and structures.
CAD software allows architects to work in a virtual environment where they can easily manipulate elements, test different design options, and explore various architectural concepts. Instead of relying solely on traditional drafting methods, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors, CAD streamlines the architectural design process by providing a digital platform for creating and editing designs.
The primary purpose of CAD in architecture is to enhance efficiency and accuracy. Architects can input precise dimensions, create realistic renderings, and generate automatic construction drawings with great precision. The software also offers tools for 3D modeling, simulation, and analysis, allowing architects to evaluate the structural integrity, energy performance, and environmental impact of their designs.
CAD software typically provides a range of features and functionalities to support the architectural design process. These may include tools for drawing and sketching, creating 3D models, generating floor plans, rendering photorealistic images, and producing construction documentation.
Over the years, CAD software has evolved to offer more advanced features and capabilities. Today, architects can incorporate Building Information Modeling (BIM) into their designs, which enables them to create intelligent 3D models that contain detailed information about the building’s components, materials, and specifications.
In summary, CAD in architecture is a digital design tool that empowers architects to create, modify, and analyze architectural designs with precision and efficiency. It replaces traditional drafting methods with a virtual platform where architects can visualize, manipulate, and evaluate their designs, ultimately resulting in better-designed buildings.
CAD Software in Architecture
In the field of architecture, there are numerous CAD software options available, each with its own unique set of features and capabilities. These software programs are designed specifically to cater to the needs of architects and provide them with a robust platform for creating, editing, and managing their architectural designs.
Some of the most popular CAD software programs used in architecture include:
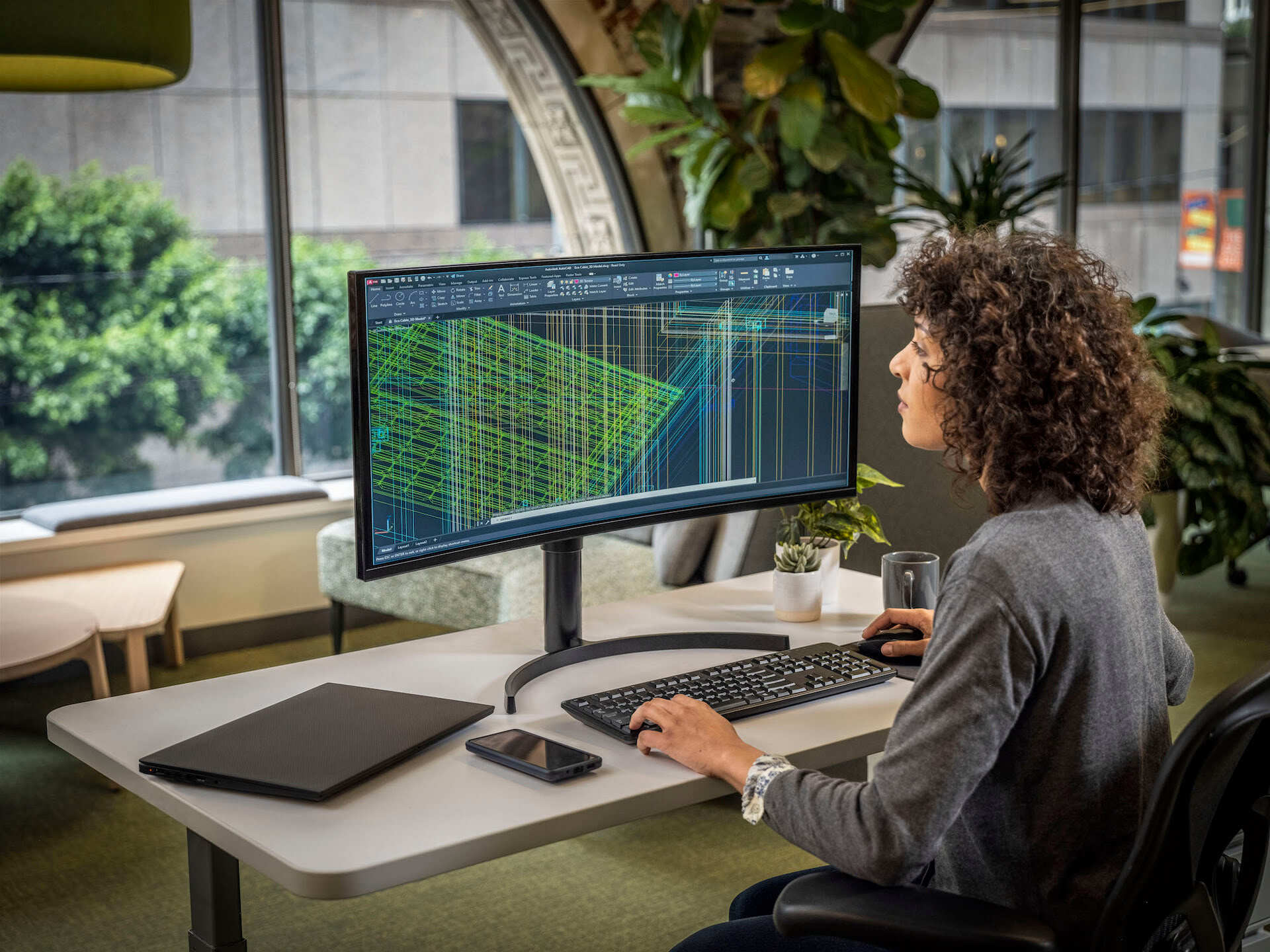
- AutoCAD: AutoCAD is one of the most widely used CAD software in the architecture industry. It offers a comprehensive set of tools for 2D drafting and 3D modeling, allowing architects to create precise and detailed designs. AutoCAD also supports parametric modeling, enabling architects to easily modify their designs and maintain design consistency.
- Revit: Revit, developed by Autodesk, is a powerful BIM software that has gained popularity among architects. It allows architects to create intelligent 3D models that contain not only geometry but also information about the building’s components and materials. Revit facilitates collaboration among design teams, streamlines the documentation process, and enables architects to analyze the performance of their designs.
- SketchUp: SketchUp is known for its user-friendly interface and intuitive 3D modeling tools. It is widely used by architects for concept modeling and visualization. SketchUp offers a vast library of ready-to-use 3D models, textures, and materials, making it easy for architects to quickly create stunning presentations and renderings.
- Rhino: Rhino, or Rhinoceros, is a versatile CAD software widely used in architecture, industrial design, and other creative fields. It offers advanced 3D modeling tools and supports various file formats, making it easy to exchange data with other design software. Rhino is known for its flexibility and is often used for complex projects that require intricate geometric forms.
These are just some of the CAD software programs available in the market. Each software has its own strengths and specialties, and architects often choose the one that best aligns with their workflow and design needs.
Furthermore, with the advancement of cloud computing, many CAD software now offer cloud-based solutions. This enables architects to access their designs from anywhere, collaborate with team members in real-time, and seamlessly integrate with other software and tools.
Overall, CAD software plays a crucial role in the architecture industry by providing architects with the necessary tools to create detailed designs, visualize concepts, analyze performance, and collaborate effectively.
Benefits of CAD in Architecture
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) has revolutionized the architecture industry by offering numerous benefits to architects and designers. Here are some of the key advantages of using CAD in architecture:
- Increased Efficiency: CAD software enables architects to work faster and more efficiently compared to traditional drafting methods. The software provides a range of tools and features that automate repetitive tasks, such as drawing and dimensioning, allowing architects to focus more on the creative aspects of their designs. Additionally, CAD software allows for easy modification and revision of designs, reducing the time and effort required to make changes.
- Precise and Accurate Designs: CAD software ensures a high level of accuracy and precision in architectural designs. Architects can input precise measurements, use snap and alignment tools to ensure proper alignment of elements, and easily make adjustments to the design. This results in accurate construction drawings, reducing the chances of errors and misinterpretations during the construction phase.
- Visualization and Rendering: CAD software provides powerful visualization tools that allow architects to create realistic 3D models and renderings of their designs. This enables clients and stakeholders to better understand the design concept and visualize the final outcome. Realistic renderings help in making informed decisions and can be used for presentations, marketing materials, and obtaining project approvals.
- Improved Collaboration: CAD software facilitates collaboration among architects, engineers, and other stakeholders involved in the design process. With CAD, multiple team members can work on the same project simultaneously, making it easier to share and exchange design files. This streamlines the collaboration process and ensures everyone is working on the most up-to-date version of the design.
- Enhanced Design Flexibility: CAD software offers architects the freedom to explore various design options and experiment with different ideas. With the ability to easily modify and iterate designs, architects can quickly test multiple design iterations, evaluate their feasibility, and make informed decisions on the best design solution.
- Integration with Building Information Modeling (BIM): Many CAD software programs are compatible with Building Information Modeling (BIM), which allows architects to create intelligent 3D models that contain information about building components, materials, and specifications. BIM integration enhances collaboration, coordination, and data management throughout the entire lifecycle of a building project.
- Efficient Documentation: CAD software simplifies the process of creating construction documentation. It automates the generation of accurate and detailed drawings, including floor plans, elevations, sections, and schedules. Architects can easily create and update documentation, reducing manual errors and ensuring consistency across all construction documents.
Overall, CAD software offers architects numerous benefits, including increased efficiency, precise designs, visualization capabilities, improved collaboration, design flexibility, BIM integration, and efficient documentation. By leveraging CAD technology, architects can streamline their design process, enhance communication with clients and stakeholders, and ultimately deliver exceptional architectural projects.
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) in architecture allows for precise and efficient creation of building designs. It’s essential for architects to have a strong understanding of CAD software to streamline the design process and communicate ideas effectively.
Applications of CAD in Architecture
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) has a wide range of applications in the field of architecture. Its versatility and capabilities make it an indispensable tool for architects throughout the design process. Here are some key applications of CAD in architecture:
- Concept Design: CAD software allows architects to sketch and develop their initial design concepts digitally. They can easily create 2D sketches and 3D models, enabling them to explore different design options, experiment with materials, and visualize the overall form and aesthetics of the building.
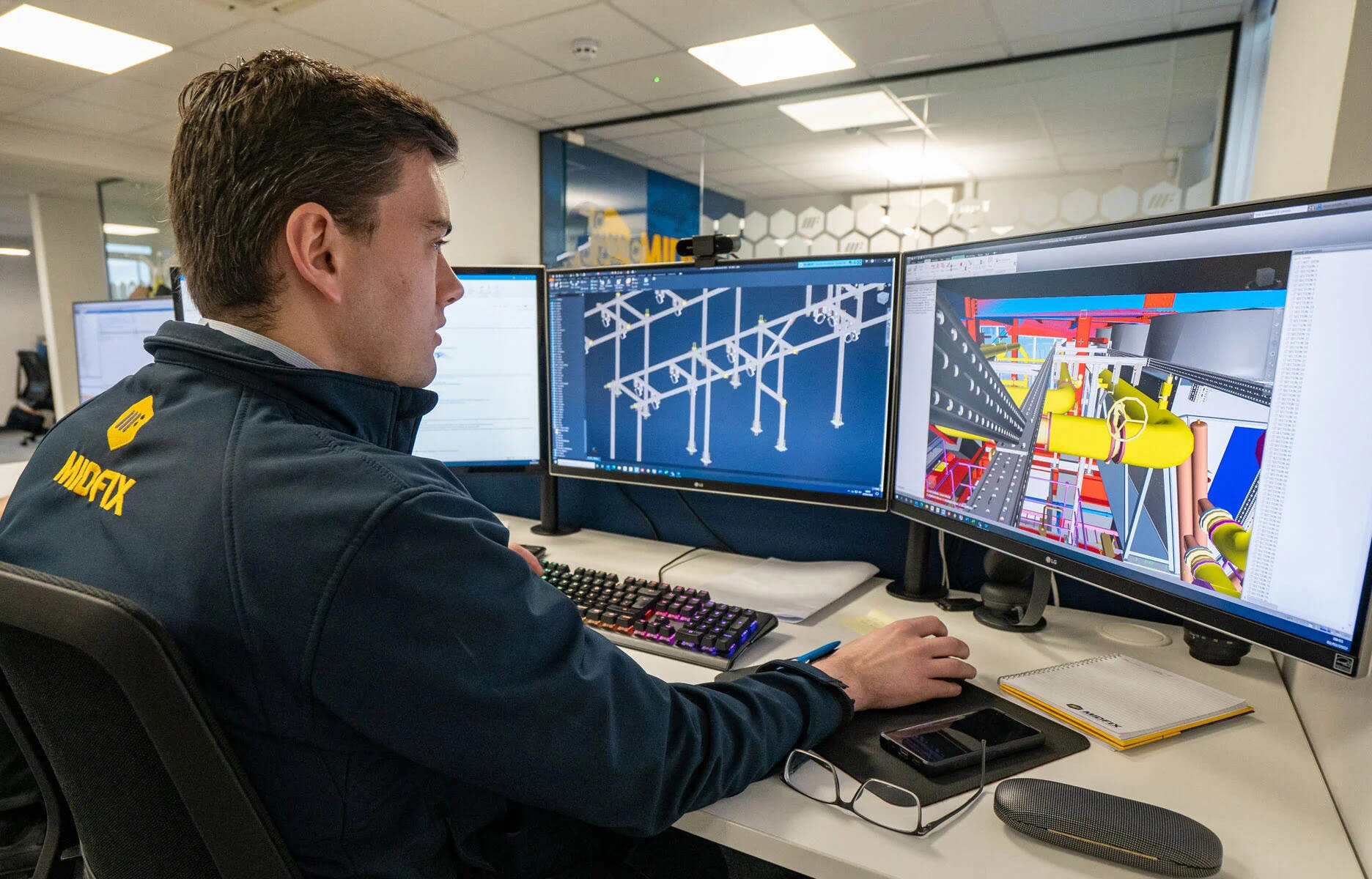
- 3D Modeling and Visualization: CAD software offers advanced 3D modeling capabilities, allowing architects to create detailed and realistic 3D models of their designs. These models can be further enhanced with textures, lighting, and realistic rendering to produce visually stunning representations of the proposed architecture. This helps clients, stakeholders, and even the architects themselves to visualize the final product before construction begins.
- Building Information Modeling (BIM): Many CAD software programs support BIM, which enables architects to create intelligent 3D models that contain detailed information about the building’s components, materials, and specifications. BIM integration ensures seamless collaboration and coordination among various disciplines involved in the project, such as structural engineers, MEP (mechanical, electrical, and plumbing) designers, and contractors.
- Construction Documentation: CAD software simplifies the creation of construction documentation. Architects can generate accurate and detailed floor plans, elevations, sections, and construction details using CAD tools. These drawings provide essential information for contractors, allowing them to understand and execute the design accurately during the construction phase.
- Structural Analysis: CAD software offers built-in tools for structural analysis and simulation. Architects can analyze the structural integrity of their designs, assess load-bearing capacities, and evaluate the behavior of the building under different conditions. This helps identify potential issues and optimize the design for maximum efficiency and safety.
- Sustainability Analysis: With the increasing emphasis on sustainable design, CAD software provides architects with tools to analyze the energy performance, daylighting, and thermal comfort of the building. This allows them to incorporate energy-efficient strategies, such as proper insulation, passive design techniques, and renewable energy systems, to minimize the building’s environmental impact.
- Interior Design: CAD software is not limited to the exterior design of buildings; it is also used in interior design. Architects can create detailed 3D models of interior spaces, test different material finishes, lighting designs, and furniture layouts. This helps in visualizing and refining the interior spaces and ensuring a cohesive design approach.
These are just a few examples of the applications of CAD in architecture. Depending on the specific project requirements, architects can utilize CAD software throughout the entire design process, from initial concept development to construction documentation, analysis, and visualization.
Overall, CAD plays a crucial role in streamlining the architectural design process, enhancing communication, promoting collaboration, and enabling architects to create innovative and sustainable buildings.
Read more: What Are CAD Software
Challenges and Limitations of CAD in Architecture
While Computer-Aided Design (CAD) brings numerous benefits to the field of architecture, it is not without its challenges and limitations. Here are some of the key challenges and limitations of CAD in architecture:
- Learning Curve: CAD software can be complex and require a significant amount of time and effort to learn. Architects and designers need to invest in training to become proficient in using the software effectively. Additionally, as technology continues to evolve, there is a need to stay updated with the latest features and functionalities of the CAD software.
- Software Compatibility: Collaboration among design teams can be hindered by software compatibility issues. Different CAD software programs may use different file formats, which may require file conversion or compatibility issues when sharing designs between architects, engineers, and other stakeholders. This can sometimes lead to data loss or formatting errors.
- Hardware Requirements: CAD software requires powerful computers with sufficient processing power and graphic capabilities. Architects need to invest in high-performance hardware and ensure regular maintenance and upgrades to ensure smooth and efficient operation of the software.
- Expense: CAD software, especially advanced versions with full features, can be expensive. This may pose a challenge for smaller architecture firms or individual architects who have limited resources. Additionally, there may be additional costs associated with software licenses, updates, and training.
- Limitations of Virtual Environment: While CAD software offers realistic 3D modeling and visualization capabilities, it cannot fully replace the experience of physically interacting with a space. Some intricate design details or spatial qualities may not be fully conveyed through a virtual environment, which can limit the understanding and appreciation of the design.
- Over-reliance on Software: The ease and convenience of CAD software may lead to over-reliance on the technology. Architects must remember that CAD software is a tool and not a substitute for design thinking and creativity. It is important to strike a balance between utilizing software capabilities and maintaining a design-focused approach.
- Integration with Construction Process: While CAD software facilitates the design and documentation phase, there are challenges in integrating the digital design with the construction process. Coordination between the design team and contractors is essential to ensure that the design intent is properly understood and implemented during the construction phase.
- Data Security: CAD files contain sensitive and proprietary design information. Architects must ensure proper security measures are in place to protect these files from unauthorized access, data breaches, or loss. Regular backup and secure file sharing practices must be followed to mitigate the risk of data loss.
Despite these challenges and limitations, CAD technology continues to bring significant advancements to the architectural field. Architects must remain aware of these limitations and critical factors to effectively utilize CAD software as a tool for creativity, collaboration, and design innovation.
Future Trends in CAD for Architecture
As technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace, the future of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) in architecture looks promising. Here are some key trends that are shaping the future of CAD for architecture:
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): VR and AR technologies have the potential to revolutionize the way architects design and experience spaces. With VR, architects can immerse themselves in a virtual environment and explore their designs in a more realistic and interactive manner. AR, on the other hand, enables architects to overlay digital models onto real-world spaces, aiding in visualizing and communicating design intentions.
- Generative Design: Generative design is an emerging trend that utilizes algorithms and computational methods to generate design solutions based on specific parameters and constraints. This approach allows architects to explore a wide range of design options and optimize for various factors, such as structural performance, energy efficiency, and aesthetics. It offers a more efficient and data-driven approach to design exploration.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI has the potential to transform the way architects design by automating certain aspects of the design process. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, extract insights, and generate design suggestions. This can help architects streamline their decision-making process and create more innovative and optimized designs.
- Cloud Collaboration: With the advancement of cloud computing, CAD software is becoming more cloud-based and collaborative. This allows architects and design teams to work on projects simultaneously, regardless of their geographic location. Cloud collaboration enables real-time sharing and editing of design files, fostering seamless communication and collaboration among team members.
- Parametric and Computational Design: Parametric design allows architects to define relationships between design parameters and create complex, adaptive, and customizable designs. Computational design, combined with parametric modeling, allows architects to utilize algorithmic processes to create innovative and intricate designs. This approach offers greater design flexibility and the ability to optimize designs for various parameters.
- Sustainability and Performance Analysis: The focus on sustainable design is expected to continue to grow in the future. CAD software will play a crucial role in analyzing the energy performance, daylighting, thermal comfort, and carbon footprint of buildings. Integration with simulation and analysis tools will enable architects to accurately assess the environmental impact of their designs and make informed decisions to optimize sustainability.
- Automation and Robotics: CAD software is likely to become more integrated with automation and robotics in the future. Robotic fabrication and construction techniques can be closely linked to CAD models, allowing for more precise and efficient construction processes. This integration can lead to an increased level of customization and complexity in architectural designs.
These are just a few examples of the future trends in CAD for architecture. As technology advances, there will be constant innovation and evolution in CAD software, enabling architects to push the boundaries of design and create buildings that are more sustainable, efficient, and aesthetically appealing.
Architects who stay updated on these trends and embrace the advancements in CAD technology will be well-equipped to navigate the future of architectural design and make a significant impact in the field.
Conclusion
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) has transformed the architectural industry, revolutionizing the way architects design, visualize, and communicate their ideas. From concept development to construction documentation, CAD software has become an indispensable tool for architects worldwide.
In this article, we explored the definition of CAD and its role in architecture. We discussed the various CAD software programs commonly used, such as AutoCAD, Revit, SketchUp, and Rhino, each offering its own set of features and capabilities. We also covered the benefits of CAD in architecture, including increased efficiency, precise designs, visualization capabilities, improved collaboration, design flexibility, integration with Building Information Modeling (BIM), and efficient documentation.
Additionally, we explored the different applications of CAD in architecture, such as concept design, 3D modeling and visualization, BIM integration, construction documentation, structural analysis, sustainability analysis, and interior design. We highlighted how CAD empowers architects to bring their designs to life, communicate effectively with clients and stakeholders, and optimize the performance and sustainability of their projects.
We also acknowledged the challenges and limitations of CAD in architecture, including the learning curve, software compatibility, hardware requirements, expense, limitations of the virtual environment, over-reliance on software, integration with the construction process, and data security. It is essential for architects to be aware of these challenges and address them appropriately to maximize the potential of CAD technology.
Looking ahead, we explored the future trends in CAD for architecture, including virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), generative design, artificial intelligence (AI), cloud collaboration, parametric and computational design, sustainability and performance analysis, and automation and robotics. These trends present exciting opportunities for architects to further enhance their design process, push the boundaries of creativity, and create sustainable and innovative buildings.
In conclusion, CAD has transformed the way architects design and has become an essential tool in the architecture industry. It streamlines the design process, improves productivity, enhances visualization and communication, and enables architects to create remarkable architectural designs. By staying updated on the latest trends and advancements in CAD technology, architects can continue to push the boundaries of innovation and create buildings that inspire and leave a lasting impact.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is CAD In Architecture
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Is CAD In Architecture”