Home>diy>Architecture & Design>What Are CAD Software


Architecture & Design
What Are CAD Software
Modified: January 9, 2024
Discover the power of CAD software for architecture design. Unleash your creativity and enhance your design process with intuitive tools and seamless collaboration.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of CAD software, where creativity meets precision and design meets innovation. In today’s digital age, Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software has revolutionized the way architects, engineers, and designers create, visualize, and communicate their ideas.
CAD software is a powerful tool that allows users to create, modify, and optimize designs with utmost accuracy and efficiency. From designing complex 3D models to creating detailed architectural plans, CAD software has become an indispensable part of various industries, ranging from architecture and engineering to manufacturing and product development.
In this article, we will delve into the world of CAD software, exploring its definition, applications, advantages, limitations, and popular software options available in the market. So, let’s dive in and discover the wonders that CAD software has to offer!
Key Takeaways:
- CAD software revolutionizes design, offering precision, efficiency, and collaboration across industries. It empowers professionals to create, modify, and visualize complex designs with unprecedented accuracy and innovation.
- The future of CAD software is driven by trends such as cloud-based solutions, VR/AR integration, generative design, and AI assistance. These advancements promise to enhance design capabilities, efficiency, and collaboration, shaping the future of innovation.
Read more: What Is NX CAD Software
Definition of CAD Software
CAD software, also known as Computer-Aided Design software, is a specialized tool used by professionals to create, modify, and visualize 2D and 3D designs. It provides a digital platform where users can draft, edit, and manipulate various elements of a design, such as geometric shapes, lines, dimensions, and textures.
With CAD software, designers can create accurate and detailed representations of their ideas, allowing for precise measurements, analysis, and simulations. These software packages offer a wide range of tools and functionalities, including drawing tools, modeling capabilities, rendering options, and collaboration features.
Modern CAD software goes beyond just creating static designs. It enables users to perform complex tasks such as analyzing stress and strain on a component, simulating real-world conditions, and even generating automated manufacturing instructions. CAD software acts as a virtual workspace where designers can explore different design iterations, make adjustments on the fly, and visualize their concepts in a realistic manner.
One of the key features of CAD software is its parametric modeling capability, which allows users to create designs with defined parameters. This means that changes made to one aspect of the design automatically update all related elements, ensuring design consistency and reducing errors.
Overall, CAD software offers a versatile and efficient solution for design professionals, providing the necessary tools and functionalities to bring their ideas to life in a digital environment.
Next, we will explore the various applications of CAD software and how it is transforming industries across the board.
Applications of CAD Software
CAD software finds application in a wide range of industries and disciplines, revolutionizing the way professionals approach design and innovation. Here are some key domains where CAD software plays a crucial role:
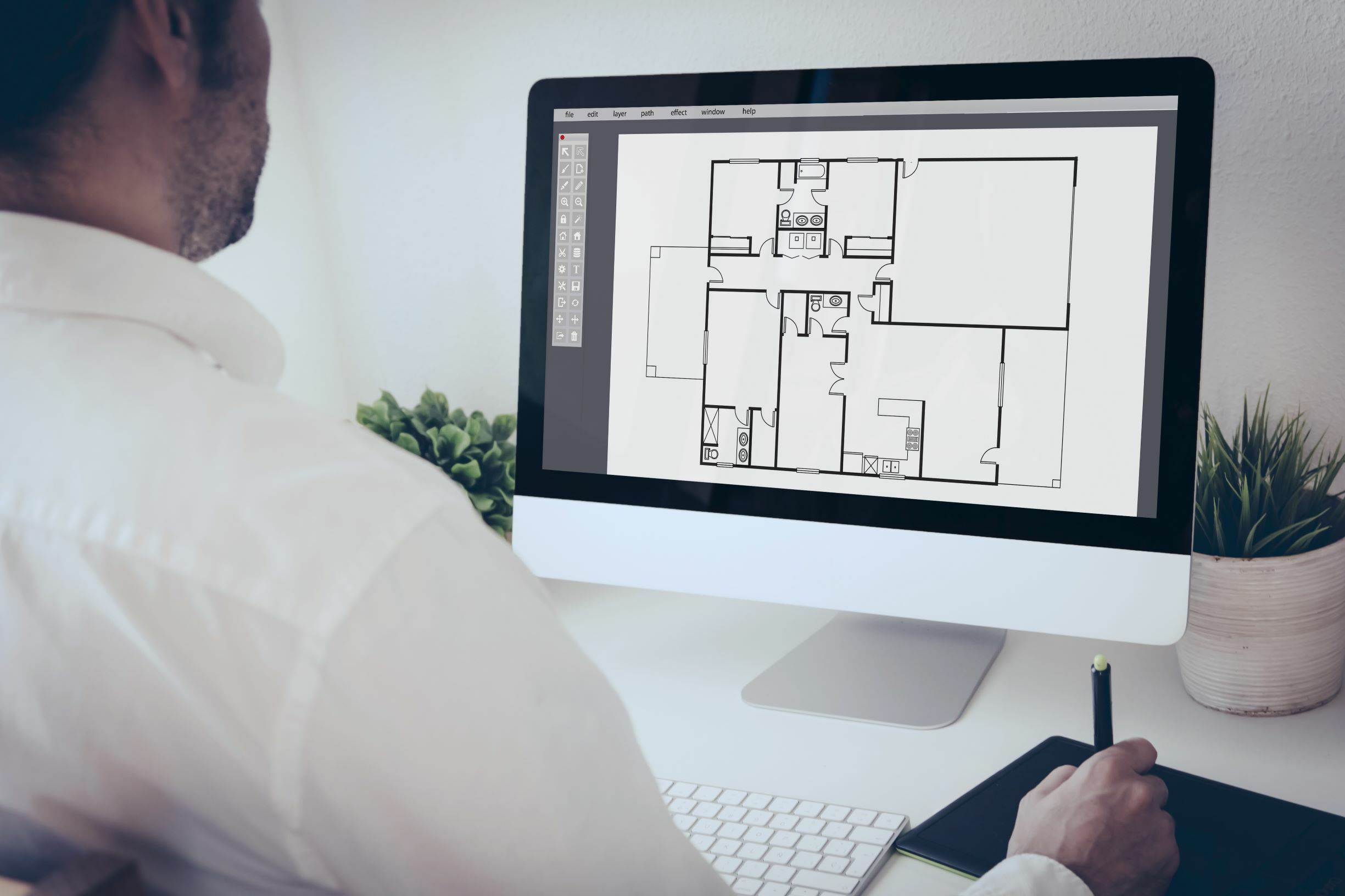
- Architecture and Construction: CAD software is extensively used by architects, engineers, and construction professionals to create detailed architectural drawings, floor plans, and structural designs. It allows for precise measurement and analysis of building components, facilitating efficient design collaboration and ensuring accurate construction.
- Product Design and Manufacturing: CAD software is a cornerstone of product design and manufacturing processes. It enables designers to create 3D models of products, test prototypes, and optimize designs before manufacturing. Manufacturers can use CAD software to generate accurate production drawings, perform simulations, and streamline the manufacturing process.
- Mechanical and Electrical Engineering: CAD software plays a vital role in mechanical and electrical engineering, allowing professionals to design and analyze complex machinery, equipment, and electrical systems. It enables visualization, simulation, and optimization of mechanical and electrical components, ensuring efficient and reliable designs.
- Automotive and Aerospace Engineering: CAD software is extensively used in the automotive and aerospace industries for designing vehicles, aircraft, and their respective components. It enables engineers to create detailed 3D models, analyze aerodynamics, and simulate real-world performance, leading to safer and more efficient designs.
- Industrial and Manufacturing Processes: CAD software finds application in industrial design, aiding in the creation of prototypes and production optimization. It enables designers to visualize and simulate manufacturing processes, plan assembly lines, and analyze production costs, resulting in streamlined operations and improved productivity.
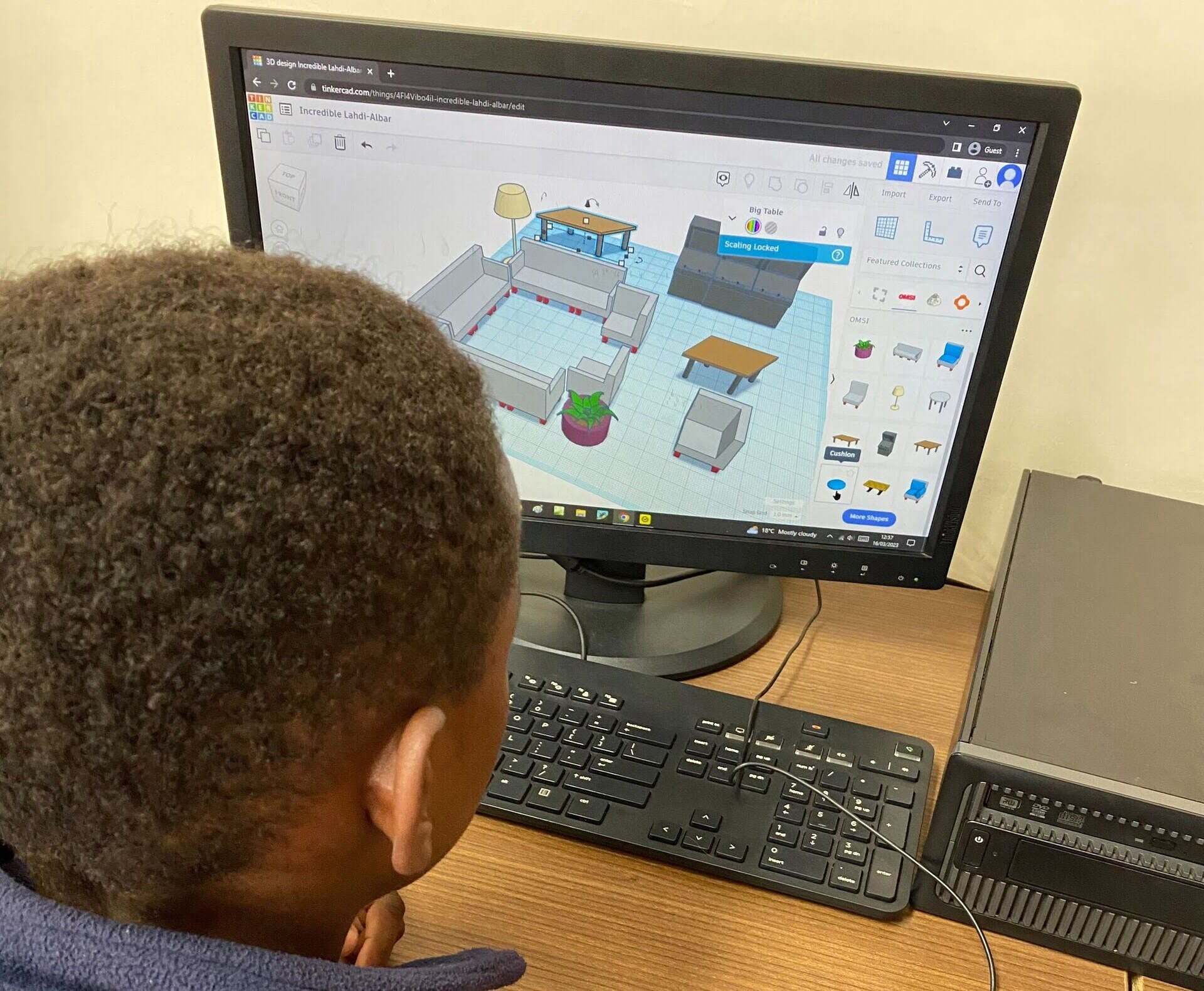
- Interior Design: CAD software is becoming increasingly popular in the field of interior design. It allows designers to create virtual representations of spaces, experiment with different furniture layouts, visualize lighting effects, and even render realistic images to help clients visualize the final result.
- Education and Research: CAD software is widely used in educational institutions and research facilities to teach and explore concepts in engineering, architecture, and design. It provides students and researchers with hands-on experience in creating and analyzing complex designs, fostering innovation and experimentation.
The applications of CAD software are vast and continuously expanding, as more industries recognize its value in enhancing design efficiency, collaboration, and innovation.
Now that we have explored the applications of CAD software, let’s move on to discussing its advantages and how it benefits professionals in their day-to-day work.
Advantages of CAD Software
CAD software offers numerous advantages to professionals in various fields. Here are some key benefits that make CAD software an essential tool in the design process:
- Increased Efficiency: CAD software significantly improves design efficiency by providing a digital workspace where designers can create, edit, and iterate designs quickly and accurately. It eliminates the need for manual drafting, reducing the time and effort required to produce detailed drawings.
- Enhanced Precision: CAD software allows for precise measurements, geometric calculations, and accurate positioning of design elements. Designers can avoid human errors commonly associated with manual drafting, resulting in highly accurate and consistent designs.
- Design Iteration and Exploration: CAD software enables designers to explore multiple design options and iterations easily. With the ability to make quick changes and experiment with different parameters, designers can optimize their designs and find the best solutions for their projects.
- Visualization and Realistic Renderings: CAD software offers advanced visualization capabilities, allowing designers to create realistic 3D models, renderings, and simulations. This helps stakeholders and clients better understand the design concepts, visualize the final product, and make informed decisions.
- Collaboration and Communication: CAD software facilitates seamless collaboration among design teams, as multiple users can work on the same project simultaneously. It enables real-time communication, easy sharing of design files, and efficient coordination between architects, engineers, and other stakeholders.
- Parametric Design and Automation: CAD software’s parametric modeling feature allows designers to create designs with defined parameters, making it easy to make adjustments and modifications as needed. Additionally, CAD software can automate repetitive tasks, such as generating drawings and bills of materials, saving time and reducing errors.
- Integration with Manufacturing and Analysis Tools: CAD software integrates seamlessly with other tools and technologies, such as computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) and finite element analysis (FEA) software. This integration allows for smooth transitions from design to manufacturing and analysis, ensuring design optimization and verifying structural integrity.
- Cost and Time Savings: CAD software can lead to significant cost and time savings throughout the design and manufacturing process. With accurate designs, reduced errors, and streamlined workflows, companies can save money on material waste, rework, and project delays.
These advantages highlight the value of CAD software in improving design productivity, accuracy, collaboration, and cost-efficiency. As technology advances, CAD software continues to evolve, offering even more innovative features to enhance the design process.
However, it is important to be aware of the limitations and challenges associated with CAD software, which we will discuss in the next section.
Limitations of CAD Software
While CAD software offers a multitude of benefits, it also has its limitations. Understanding these limitations can help designers and engineers make informed decisions and mitigate potential challenges. Here are some common limitations of CAD software:
- Learning Curve: CAD software can be complex and require a learning curve, especially for beginners. Mastering the various tools, features, and workflows may take time and effort, which can affect productivity in the initial stages.
- Cost of Software and Hardware: High-quality CAD software can be costly, especially for professional-grade applications. Additionally, CAD software may require powerful hardware specifications to run smoothly, which can add to the overall investment.
- File Compatibility: CAD software uses proprietary file formats, which may not be compatible with other CAD software or may require conversion. This can lead to challenges when collaborating with stakeholders who use different software or versions.
- Over-reliance on Computer Systems: CAD software heavily relies on computer systems for processing power, memory, and graphics capabilities. System crashes, hardware malfunctions, or software incompatibilities can disrupt the workflow and potentially lead to data loss.
- Focus on Visualization over Constructability: CAD software excels in creating stunning visual representations of designs, but it may not fully address constructability issues. Design elements that are visually appealing in the digital environment may be difficult or costly to produce in the physical realm.
- Loss of Hand-drawing Skills: With the prevalence of CAD software, traditional hand-drawing skills may diminish. While CAD software offers convenience and accuracy, it is important to maintain a balance between digital and manual design skills.
- Design Limitations: CAD software has limitations in representing certain complex design elements accurately. For example, intricate organic shapes or surfaces may require specialized software or manual techniques to achieve the desired level of detail.
- Software Updates and Compatibility: CAD software is constantly evolving, with new updates and version releases. This can create compatibility issues when working with colleagues or clients who are using different software versions or have not upgraded.
Despite these limitations, CAD software remains an indispensable tool in the design and engineering fields. Understanding these limitations allows professionals to make informed decisions, leverage the advantages of the software, and overcome challenges effectively.
Now that we have explored the advantages and limitations of CAD software, let’s move on to discussing some popular CAD software options available in the market.
When choosing CAD software, consider factors such as compatibility with your operating system, ease of use, available features, and customer support.
Read more: What Is The Best Free CAD Software
Popular CAD Software in the Market
There are several CAD software options available in the market, each offering unique features and functionalities. Here are some of the most popular CAD software packages widely used by professionals:
- AutoCAD: AutoCAD, developed by Autodesk, is one of the most widely used CAD software in various industries. It offers a comprehensive set of tools for 2D drafting, 3D modeling, and visualization. AutoCAD provides parametric capabilities, integration with other Autodesk software, and extensive customization options.
- SolidWorks: SolidWorks is a powerful 3D CAD software used primarily in mechanical and product design. It offers a user-friendly interface, robust modeling capabilities, and advanced simulation tools. SolidWorks is known for its parametric design capabilities, sheet metal design features, and integration with manufacturing processes.
- CATIA: CATIA, developed by Dassault Systèmes, is widely used in the aerospace and automotive industries. It offers comprehensive design and analysis capabilities, allowing for complex surface modeling, assembly design, and simulation. CATIA is known for its advanced tools for designing aerospace structures, automotive components, and electrical systems.
- SketchUp: SketchUp, developed by Trimble, is a popular CAD software for architectural and interior design. It offers intuitive 3D modeling tools, a vast library of pre-built components, and easy-to-use rendering features. SketchUp is known for its user-friendly interface, quick design iterations, and compatibility with various file formats.
- Fusion 360: Fusion 360, also developed by Autodesk, is a cloud-based CAD software that provides a complete solution for 3D modeling, simulation, and manufacturing. It offers parametric modeling, generative design tools, and seamless collaboration features. Fusion 360 is popular among startups, small businesses, and makers due to its accessibility and affordability.
- Revit: Revit, also developed by Autodesk, is a BIM (Building Information Modeling) software widely used in the architecture, engineering, and construction industries. It offers tools for creating detailed 3D models, generating construction documentation, and performing energy analysis. Revit enables collaboration and coordination among project stakeholders through its shared model environment.
- Pro/E (Creo): Pro/Engineer, now known as Creo, is a parametric 3D CAD software used in various industries. It offers extensive capabilities for product design, simulation, and manufacturing. Creo is known for its robust feature-based modeling, advanced assembly management, and integration with other PTC products.
- MicroStation: MicroStation, developed by Bentley Systems, is widely used in the architecture, engineering, and construction industries. It offers a comprehensive set of 2D and 3D design tools, along with advanced visualization and analysis capabilities. MicroStation is known for its interoperability, allowing for seamless integration with other software and file formats.
These are just a few examples of the popular CAD software options available in the market. The choice of CAD software depends on factors such as specific industry needs, project requirements, team collaboration, and personal preferences. It is essential to carefully evaluate the features, capabilities, and compatibility of each software before making a decision.
Now that we have explored some popular CAD software options, let’s move on to understanding how CAD software works and its key features.
How CAD Software Works
CAD software operates on the principles of computer-aided design, leveraging advanced algorithms and graphical user interfaces to facilitate the creation, modification, and visualization of designs. Here’s a simplified overview of how CAD software works:
1. Creating the Design: The design process begins with the creation of a new design file or opening an existing one. Designers can start by sketching out their ideas using drawing tools such as lines, circles, and arcs. They can then manipulate these basic shapes to create more complex geometric forms.
2. Defining Parameters and Constraints: CAD software allows designers to define parameters and constraints for their designs. This means specifying dimensions, angles, relationships, and other design rules. These parameters ensure that the design remains consistent and can be easily modified in the future.
3. Building the 3D Model: CAD software provides a range of tools for creating 3D models based on the 2D sketches. Designers can extrude, revolve, sweep, or loft the 2D shapes to generate 3D objects. They can then manipulate these objects by rotating, scaling, or mirroring them to achieve the desired design.
4. Applying Materials and Textures: CAD software allows designers to apply materials, colors, and textures to their designs to enhance their visual representations. This helps in creating realistic renderings and improving the visualization of the final product.
5. Analyzing and Simulating: CAD software often includes analysis and simulation tools that enable designers to test the structural integrity, performance, and behavior of their designs. These tools can simulate factors such as stress, strain, fluid dynamics, and heat transfer, providing valuable insights before the physical manufacturing stage.
6. Documenting and Annotating: CAD software facilitates the creation of precise and detailed technical drawings. Designers can generate 2D drawings from the 3D models, including dimensions, annotations, and other necessary information for manufacturing or construction purposes.
7. Collaboration and Sharing: CAD software enables designers to collaborate with team members, clients, and stakeholders. They can share their designs, invite others to review and provide feedback, and incorporate changes seamlessly into the design. Collaboration tools streamline communication and ensure everyone is on the same page.
8. Exporting and 3D Printing: CAD software allows designers to export their designs in various file formats for different purposes. These designs can be sent to manufacturing facilities for production, shared with clients for approval, or used for 3D printing to create physical prototypes.
CAD software combines the capabilities of drafting, modeling, rendering, analysis, and collaboration into a single platform, empowering professionals to create complex designs efficiently and accurately. Now that we understand how CAD software functions, let’s explore some key features that make it an indispensable tool in the design process.
Key Features of CAD Software
CAD software offers a wide range of features that contribute to its effectiveness and versatility in the design process. Here are some key features commonly found in CAD software:
- Drawing Tools: CAD software provides a variety of drawing tools, such as lines, arcs, circles, and polygons, to create precise 2D sketches as the foundation for the design.
- Parametric Modeling: CAD software allows designers to create designs with defined parameters, which can be easily adjusted and modified. This provides flexibility and efficiency in making design changes.
- 3D Modeling: CAD software enables the creation of complex 3D models by extruding, revolving, sweeping, or lofting 2D shapes. This facilitates the visualization and exploration of designs in three dimensions.
- Rendering and Visualization: CAD software offers rendering capabilities to generate realistic images of the designs, including material textures, lighting effects, and shadows. This allows for better visualization and presentation of the final product.
- Assembly Design: CAD software allows designers to create and manipulate assemblies, which are collections of multiple parts. It provides tools for positioning, aligning, and constraining components within the assembly.
- Simulation and Analysis: CAD software often includes simulation tools for analyzing the behavior and performance of designs. This can include stress analysis, motion simulation, fluid dynamics, and thermal analysis.
- Documentation: CAD software enables the generation of detailed technical drawings, including dimensions, annotations, and symbols. These drawings are essential for manufacturing, construction, and communication purposes.
- Collaboration Tools: CAD software offers collaboration features that allow multiple users to work on a design simultaneously. It enables real-time communication, version control, and the ability to share and receive feedback on designs.
- Integration with Manufacturing: CAD software integrates with other tools and technologies used in the manufacturing process. This includes computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software for generating toolpaths and instructions for machining or additive manufacturing processes.
- Customization: CAD software often allows for customization, enabling users to create custom menus, scripts, and shortcuts to streamline their workflows and adapt the software to their specific needs.
These key features of CAD software empower designers to efficiently create, modify, and visualize designs with accuracy and precision. Each software package may offer additional features and functionalities tailored to specific industries or design disciplines.
As technology continues to evolve, CAD software is continuously enhanced with new features and updates to cater to the evolving needs of designers and engineers. Let’s now take a look at the future trends in CAD software.
Future Trends in CAD Software
The field of CAD software is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the changing needs of design professionals. Here are some key future trends that are shaping the future of CAD software:
- Cloud-based CAD: Cloud-based CAD software is gaining popularity, offering the flexibility of accessing designs from anywhere and facilitating seamless collaboration among team members. Cloud-based CAD eliminates the need for high-end hardware, provides automatic software updates, and enables real-time data synchronization.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR): VR and AR technologies are being integrated into CAD software, allowing designers to visualize and interact with their designs in immersive environments. This enhances design evaluation, presentation, and collaboration, providing a more intuitive and realistic experience.
- Generative Design: Generative design, enabled by artificial intelligence and machine learning, is a growing trend in CAD software. It allows designers to input design constraints and parameters, and the software can generate optimized design options based on algorithms, providing innovative and efficient solutions.
- Simulation-Driven Design: CAD software is expanding its simulation capabilities, enabling designers to perform more complex simulations early in the design process. The integration of simulation tools within CAD software allows for seamless feedback and optimization, resulting in improved performance and reduced prototyping costs.
- Parametric Optimization: CAD software is moving towards parametric optimization, where designs can be automatically optimized based on predefined goals and constraints. The software can explore design iterations and suggest improvements, allowing for faster and more efficient design optimization.
- Integration with Internet of Things (IoT) and Data Analytics: CAD software is increasingly integrating with IoT and data analytics, enabling designers to incorporate sensor data and analyze real-time performance of designs. This integration facilitates the design of smart and connected products, enhancing functionality, efficiency, and user experience.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Assistance: AI is being incorporated into CAD software to assist designers in various tasks. From automated drawing generation to predictive modeling, AI can help streamline workflows, improve design quality, and reduce repetitive tasks, allowing designers to focus on more creative aspects.
- Real-time Collaboration and Version Control: CAD software is improving collaboration capabilities, allowing multiple designers to work on the same project simultaneously. Real-time collaboration and version control features ensure seamless communication, efficient design iterations, and better coordination among team members.
- Improved Design Communication: CAD software is evolving to enhance design communication beyond traditional drawings. It allows for the integration of 3D models, animations, and interactive presentations, enabling clearer visualization and better understanding of design concepts for clients, stakeholders, and non-technical team members.
- Simulation-Driven Manufacturing and Additive Manufacturing: CAD software is increasingly integrated with manufacturing and additive manufacturing processes. It enables designers to optimize designs for specific manufacturing techniques, simulate the manufacturing process, and generate instructions for 3D printing and other advanced manufacturing methods.
These future trends in CAD software indicate the direction in which the industry is headed, bringing advancements that enhance design capabilities, efficiency, collaboration, and integration with emerging technologies. Design professionals can look forward to more powerful and intuitive CAD software that enables them to push the boundaries of creativity and innovation.
Now that we have explored the future trends, let’s wrap up our discussion on CAD software.
Read more: What Kind Of Software Is A CAD Program
Conclusion
CAD software has revolutionized the way professionals approach design, providing a digital platform that enhances efficiency, accuracy, and collaboration. From architects and engineers to product designers and manufacturers, CAD software has become an indispensable tool in various industries.
In this article, we explored the definition of CAD software and its applications in architecture, engineering, industrial design, and more. We discussed the advantages of CAD software, including increased efficiency, enhanced precision, design exploration, and collaboration capabilities. We also highlighted the limitations of CAD software, such as the learning curve, compatibility issues, and the over-reliance on computer systems.
Furthermore, we explored some of the most popular CAD software options available in the market, such as AutoCAD, SolidWorks, CATIA, and SketchUp, each catering to specific industries and design needs. We discussed the key features that make CAD software essential, including drawing tools, parametric modeling, 3D visualization, analysis capabilities, and collaboration tools.
Looking towards the future, we identified trends that will shape the evolution of CAD software, including cloud-based solutions, virtual and augmented reality integration, generative design, simulation-driven optimization, and the integration of IoT, data analytics, and AI. These trends promise to enhance the design process, streamline workflows, and unlock new possibilities in the world of design and innovation.
In conclusion, CAD software has transformed the way we design, enabling us to create, modify, and visualize complex and precise designs with unprecedented efficiency. It empowers professionals to push the boundaries of creativity, collaborate seamlessly, and embrace the latest technologies in their design processes. As the field continues to advance, CAD software will undoubtedly play a vital role in shaping the future of design in a wide range of industries.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Are CAD Software
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “What Are CAD Software”