Home>diy>Architecture & Design>What Is CAD?


Architecture & Design
What Is CAD?
Modified: January 9, 2024
Learn what CAD is and how it revolutionizes architecture design. Discover its powerful tools and techniques for creating precise and intricate designs.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced and digital world, technology has revolutionized various aspects of our lives, including how we design and create. One such technological innovation that has transformed the field of design and architecture is Computer-Aided Design, more commonly known as CAD. CAD has become an integral part of the design process, providing architects, engineers, and other professionals with a powerful tool that enhances creativity, efficiency, and precision.
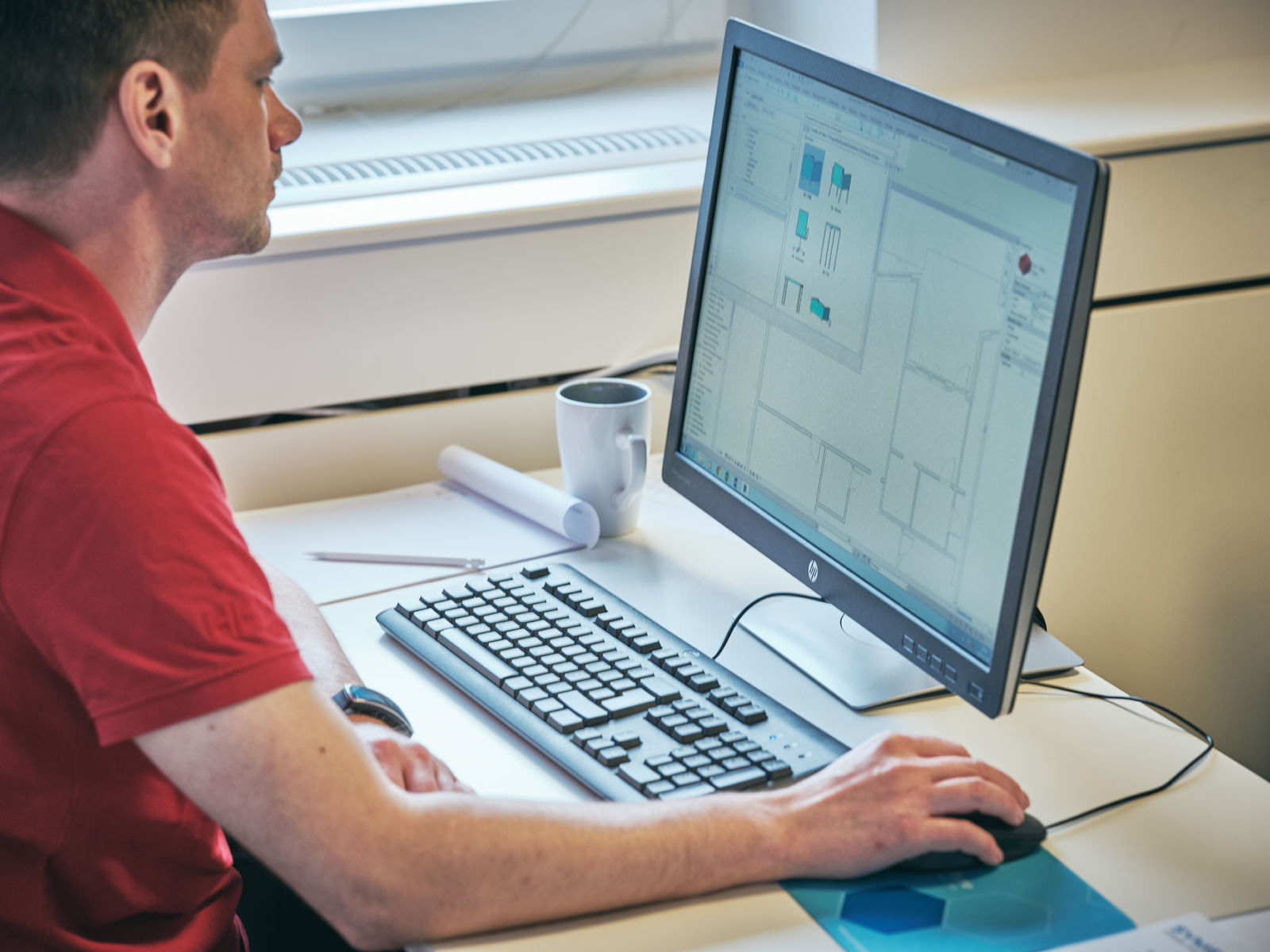
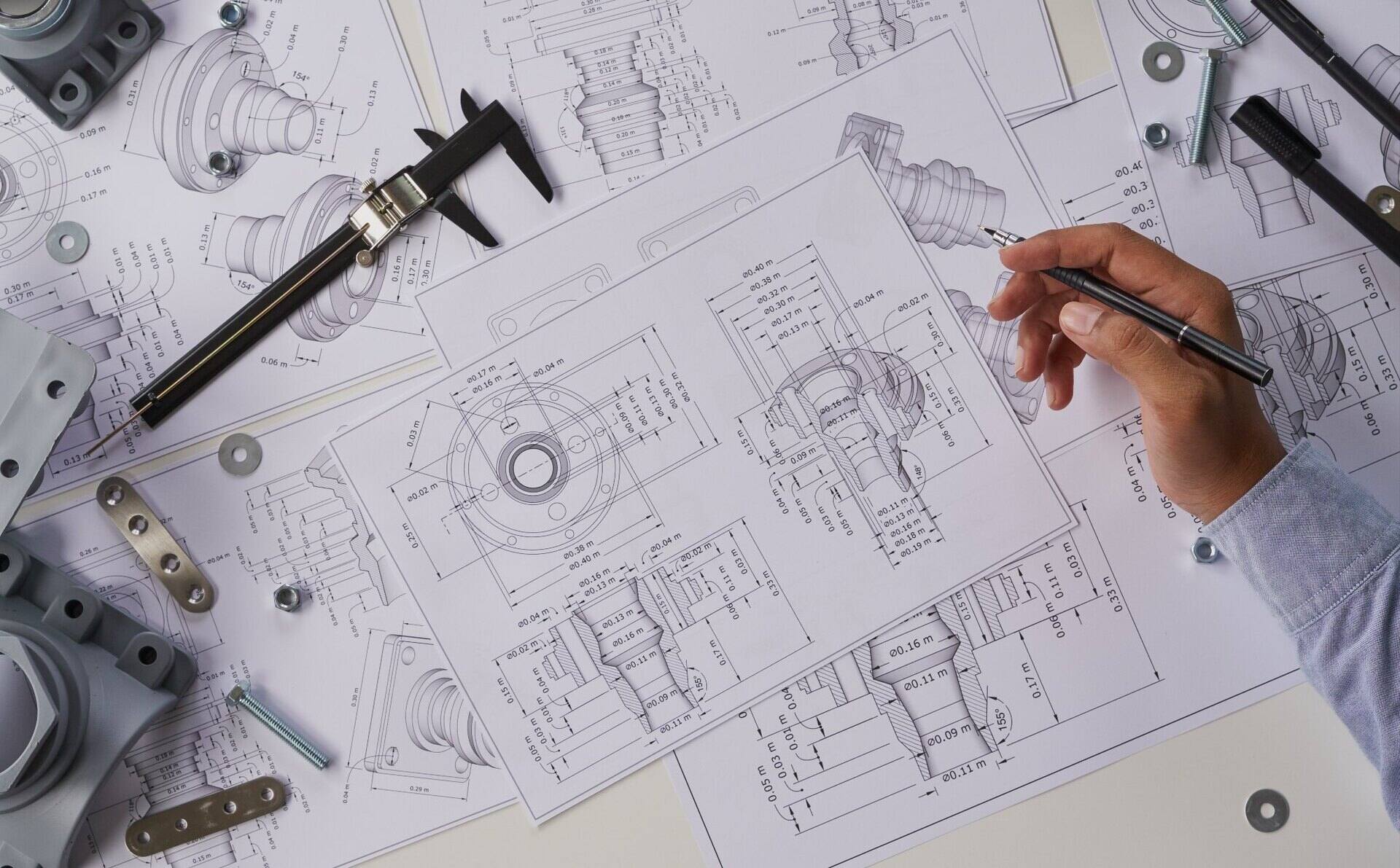
CAD, in its simplest form, can be defined as the use of computer software to create, modify, and optimize designs. It allows designers to create digital representations of physical objects and structures, empowering them to visualize, analyze, and refine their designs before they are brought to life. From intricate architectural plans to intricate mechanical parts, CAD has become a fundamental tool across various industries, offering a range of benefits and capabilities that were previously unimaginable.
The evolution of CAD dates back to the 1960s when early computer systems were being developed. During this time, computer technology was limited, and software programs were basic. However, as technology advanced, the capabilities of CAD software grew exponentially. Today, CAD software offers advanced features, such as 3D modeling, simulation, rendering, and animation, which have revolutionized the design process.
The uses of CAD are extensive and span across multiple industries. Architectural firms rely on CAD to create visually stunning and structurally sound building designs, enabling architects to explore various design options and make informed decisions. The manufacturing industry utilizes CAD to design and prototype products, streamlining the production process and reducing time and costs. CAD is also prevalent in the automotive and aerospace industries, where it is employed to create complex mechanical components and optimize aerodynamic designs.
The benefits of CAD are numerous and have made it an indispensable tool in the design world. Firstly, CAD provides greater accuracy and precision, minimizing errors and allowing designers to create highly detailed and intricate designs. It also enhances productivity by automating repetitive tasks and allowing users to easily make modifications. CAD software is equipped with advanced simulation and analysis tools that enable designers to test the performance and functionality of their designs virtually. This not only saves time and resources but also facilitates innovation and experimentation.
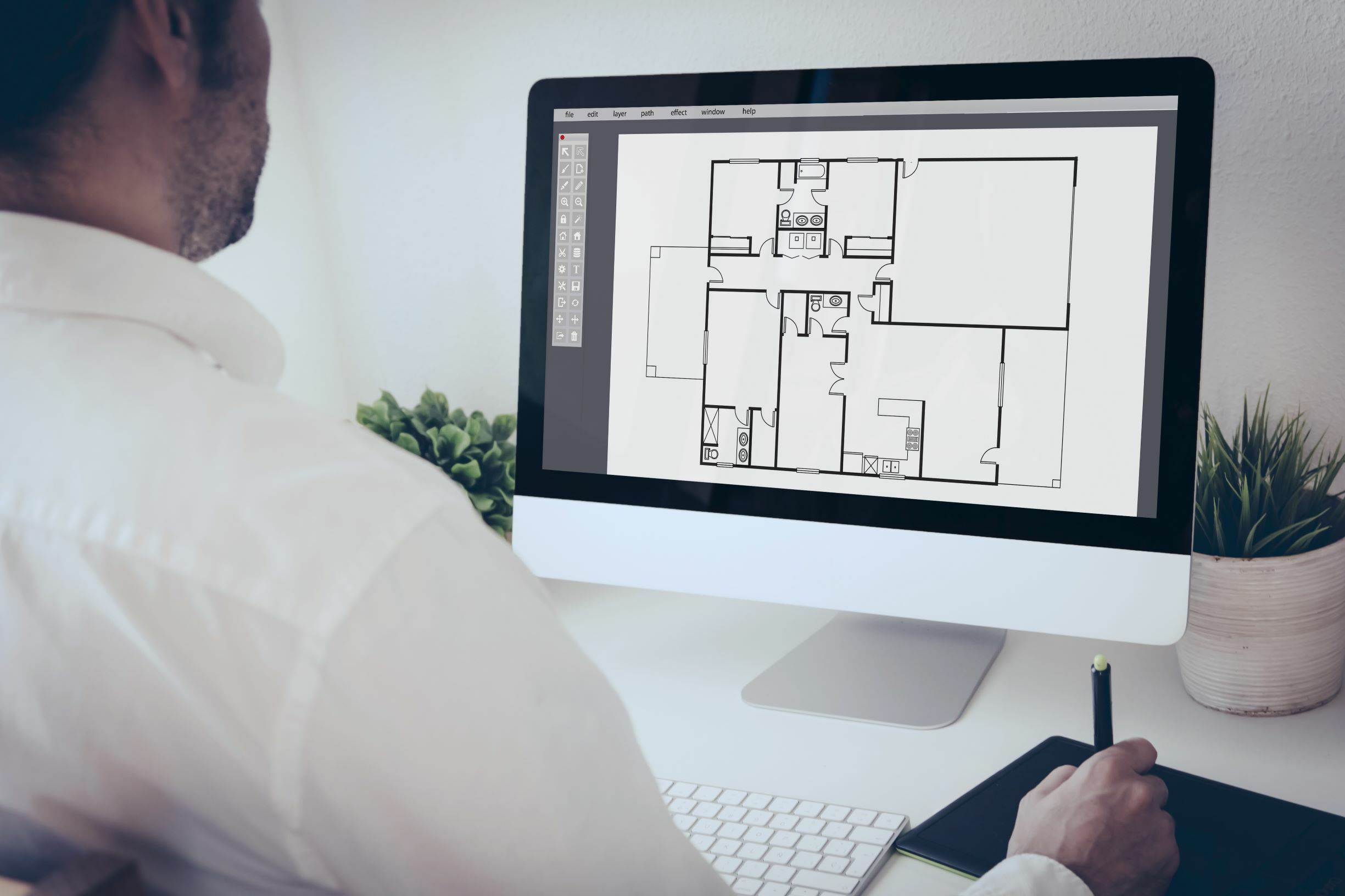
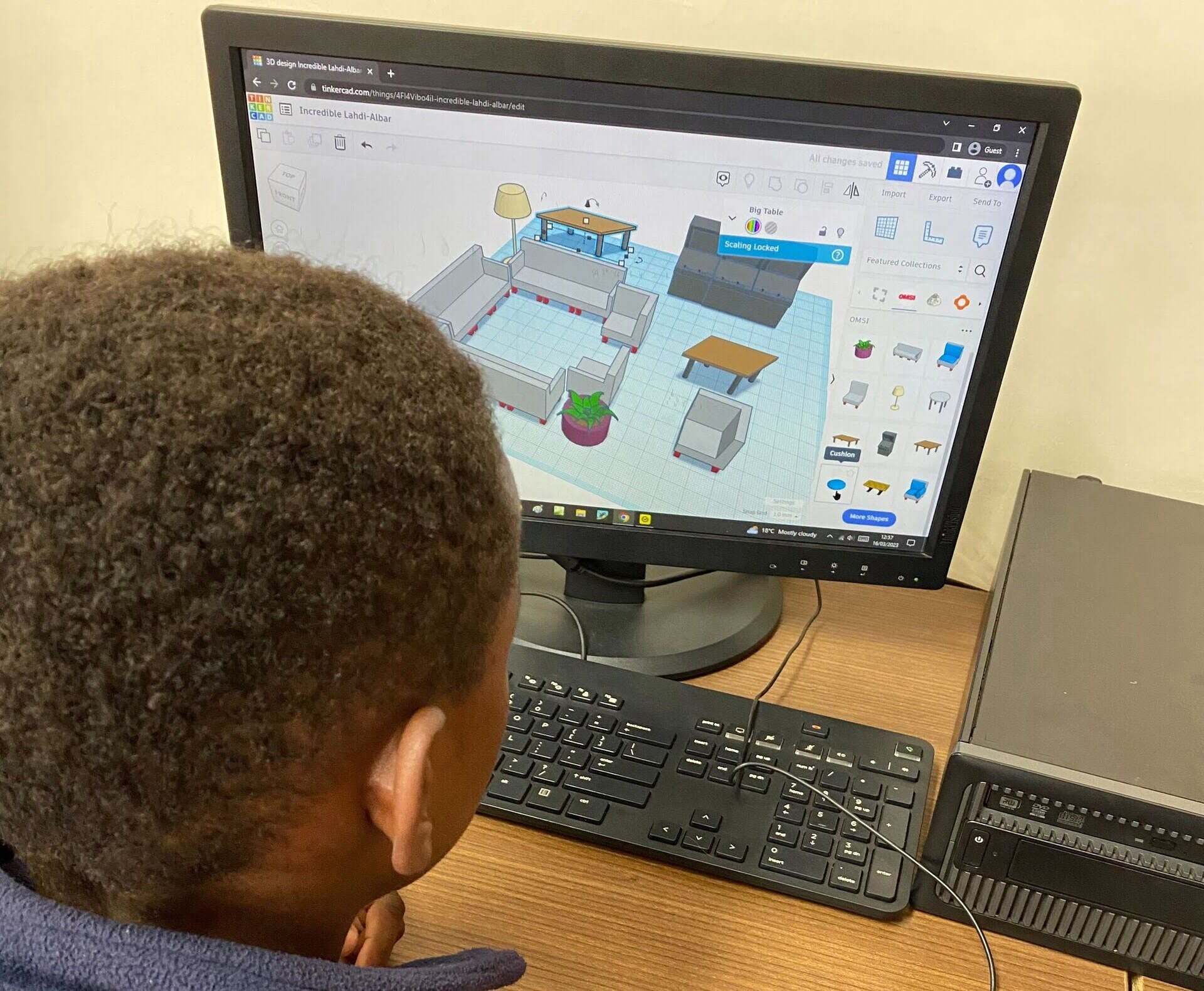
There are several types of CAD software available, each with its own set of features and applications. 2D CAD software is primarily used for creating 2-dimensional architectural and technical drawings. 3D CAD software, on the other hand, allows designers to create three-dimensional models, providing a more immersive and realistic representation of the design. There are also specialized CAD software programs for specific industries, such as electrical CAD for designing electrical systems and PCBs, and BIM (Building Information Modeling) software for comprehensive architectural design and construction management.
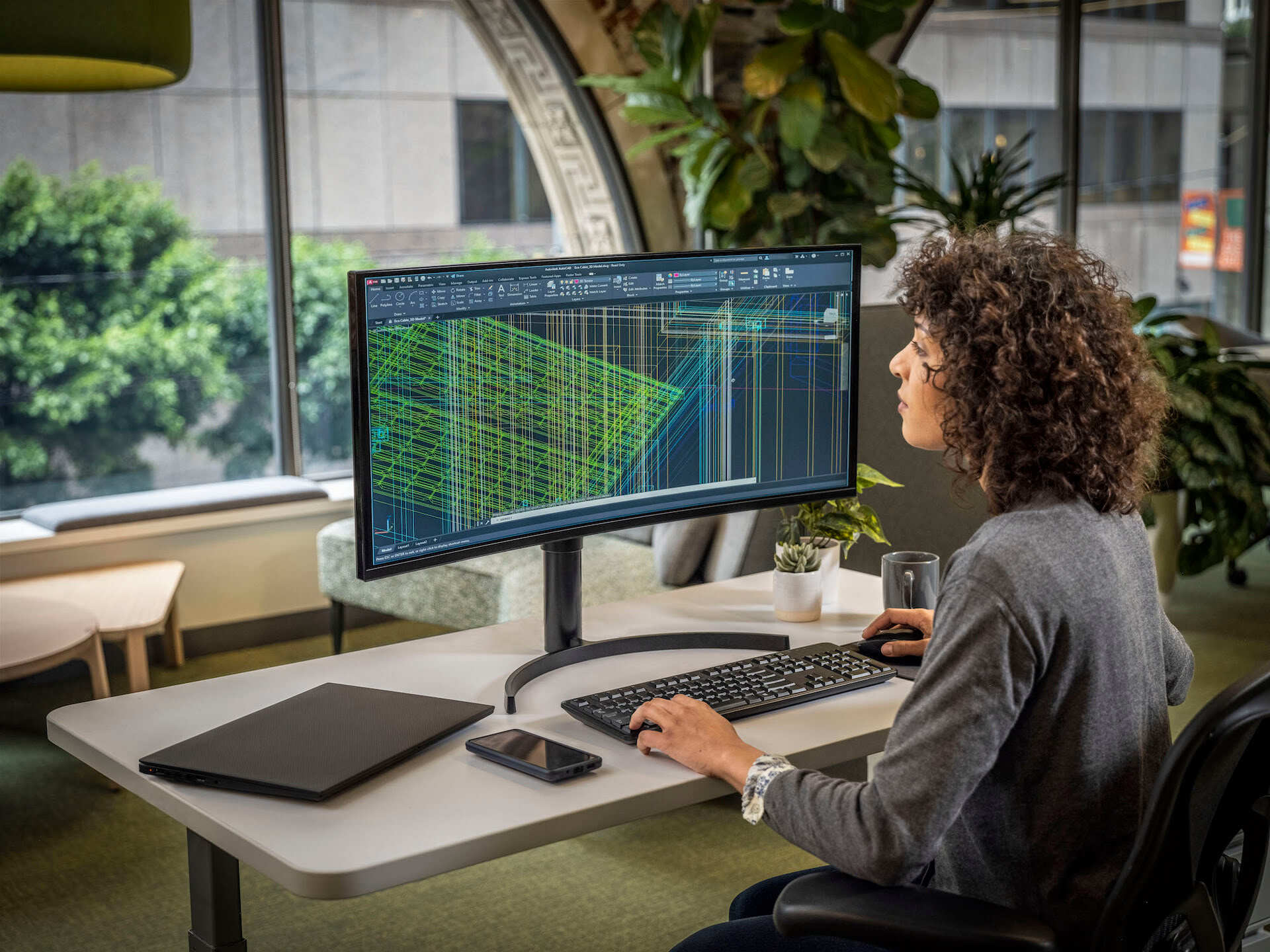
CAD works by utilizing geometric shapes, lines, and curves to create accurate representations of objects. Designers can manipulate these elements using various tools and functions to refine the design. CAD software also incorporates powerful rendering engines that can create realistic textures, lighting, and shadows, giving designers a visual understanding of how the final product will look. Additionally, CAD software supports parametric modeling, allowing users to define relationships and constraints between different elements of the design, ensuring consistency and ease of modification.
Key Takeaways:
- CAD has revolutionized design and engineering, offering efficiency, precision, and collaboration across industries. Its future integration with AI, VR/AR, and IoT promises even more innovative and sustainable solutions.
- From architecture to manufacturing, CAD empowers designers with advanced tools for visualization, simulation, and documentation. Its evolution continues to shape the future of design and drive technological advancements.
Read more: What Is CAD Workstation
Definition of CAD
Computer-Aided Design, commonly known as CAD, is a specialized software technology that enables designers and engineers to create, modify, and optimize designs with the help of computers. CAD software utilizes a combination of geometric shapes, lines, curves, and other graphical elements to represent objects in a digital format. It provides a powerful and efficient way to visualize, analyze, and refine designs before they are constructed in the physical world.
CAD offers a wide range of tools and functionalities that enable designers to create precise and complex designs with ease. Whether it’s architectural plans, mechanical parts, electrical systems, or industrial machinery, CAD software can handle a variety of design requirements. The software allows designers to manipulate and modify design elements effortlessly, enabling iterative design processes and facilitating collaboration between multiple stakeholders.
One of the key features of CAD software is its ability to create accurate and scaled models of objects. Whether it’s a simple 2-dimensional drawing or a detailed 3-dimensional model, CAD ensures that the design is represented with precision. The software provides tools for creating realistic textures, materials, and lighting effects, giving designers a better understanding of how the final product will look and function.
CAD software also offers advanced functionality, such as parametric modeling. This allows designers to define relationships and constraints between different elements of the design. For example, in architectural design, changing the dimensions of a room will automatically update the related elements, such as doors, windows, and furniture placements. This feature not only saves time but also ensures consistency and accuracy throughout the design process.
Another important aspect of CAD is its ability to perform simulations and analysis on designs. CAD software is equipped with powerful simulation tools that allow designers to test the performance, functionality, and structural integrity of their designs virtually. This helps to identify potential issues or flaws early in the design phase, saving time and resources that would have been required for physical prototypes and testing.
CAD has become an essential tool in various industries, including architecture, engineering, manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and many more. It has revolutionized the design process, enabling faster iteration, improved accuracy, and enhanced collaboration between designers, engineers, and other stakeholders. With the advent of 3D printing and other advanced manufacturing technologies, CAD plays a crucial role in transforming digital designs into physical objects.
In summary, CAD is a computer-based design software that allows designers and engineers to create, modify, and analyze designs in a digital environment. It offers a wide range of tools and functionalities that enhance efficiency, accuracy, and collaboration in the design process. CAD has become an indispensable tool in various industries, empowering designers to create innovative and complex designs with precision and confidence.
Evolution of CAD
The evolution of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) can be traced back to the 1960s when computer technology was in its early stages of development. During this time, computers were large, expensive, and limited in processing power. Despite these limitations, pioneering researchers saw the potential to use computers in the design process and began exploring the possibilities of CAD.
In the early stages, CAD software was mainly used for 2D drafting. Simple commands and functions were used to create basic drawings, such as architectural floor plans and engineering schematics. These early CAD systems relied on digitizing tablets and light pens for input and were primarily used in the aerospace and automotive industries, where precision and accuracy were paramount.
As computer technology advanced, so did CAD capabilities. The 1970s saw the development of 3D CAD systems, which allowed designers to create three-dimensional models of objects. This breakthrough revolutionized the design process, as it provided a more realistic and immersive representation of the design. 3D CAD systems utilized wireframe models, which consisted of lines and curves, to create the virtual objects.
In the 1980s, the introduction of solid modeling brought another significant advancement to CAD. Solid modeling allowed designers to represent objects as complete and tangible entities, rather than just wireframe models. This enabled more accurate visualization and analysis of designs, as well as the ability to perform complex operations such as interference checking and assembly simulations. Solid modeling laid the foundation for the integration of CAD with computer-aided engineering (CAE) and manufacturing (CAM) systems, creating a unified design environment known as CAD/CAM/CAE.
The 1990s and early 2000s marked a period of rapid development and adoption of CAD technology. CAD software became more user-friendly, with graphical user interfaces (GUIs) simplifying the design process. The introduction of parametric modeling allowed designers to define design features and establish relationships between elements, enabling efficient design modifications and updates. Additionally, advancements in rendering capabilities improved the visual representation of designs, making them more realistic and appealing.
With the advent of the Internet and cloud computing, CAD systems underwent another transformation. Online collaboration and cloud-based storage allowed designers and stakeholders to work together on projects in real-time, regardless of their physical location. This brought about greater efficiency, enhanced communication, and streamlined project management.
In recent years, CAD software has continued to evolve, incorporating cutting-edge technologies such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR). These technologies provide designers with immersive experiences, allowing them to explore and interact with their designs in a more intuitive and engaging way. The integration of AI and machine learning algorithms has also enhanced CAD’s capabilities, automating repetitive tasks and providing intelligent suggestions and optimizations.
The evolution of CAD has had a profound impact on various industries. It has transformed the way designers and engineers approach the design process, enabling faster iteration, improved accuracy, and enhanced collaboration. CAD has become an essential tool for professionals in architecture, engineering, manufacturing, and many other fields. As technology continues to advance, we can expect CAD to evolve further, allowing for even more sophisticated and innovative design solutions.
Uses of CAD
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) is a versatile tool that has numerous applications across a wide range of industries. From architecture to engineering to manufacturing, CAD has become an integral part of the design process, offering significant benefits and capabilities. Here are some of the key uses of CAD:
- Architecture: CAD revolutionized the architectural industry by providing architects with the ability to create detailed and precise building designs. Architects can use CAD software to create 2D and 3D models, develop floor plans, design structural elements, and visualize the overall look and feel of a building. CAD also enables architects to analyze the environmental impact and energy efficiency of their designs, improving sustainability and reducing costs.
- Engineering: CAD plays a crucial role in the engineering field. Engineers can use CAD software to create detailed drawings and models of mechanical, electrical, and civil engineering projects. CAD allows engineers to simulate and analyze the performance and functionality of their designs, identify potential issues, and make necessary modifications. It enhances efficiency, accuracy, and collaboration within engineering teams, leading to more efficient and reliable designs.
- Manufacturing: CAD has transformed the manufacturing industry by streamlining the product design and development process. Manufacturers can use CAD software to design and prototype products, create detailed manufacturing blueprints, and optimize production processes. CAD allows manufacturers to visualize the final product before it is manufactured, reducing costly errors and improving product quality. It also facilitates computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), where CAD models are used to control automated production machinery.
- Product Design: CAD is widely used in product design across various industries. Product designers can utilize CAD software to create detailed, realistic 3D models of their designs. CAD enables designers to explore different design variations, conduct virtual tests and simulations, and refine their designs based on feedback and user requirements. CAD also facilitates the transition from design to production, as manufacturers can use CAD models to develop molds, tooling, and prototypes.
- Interior Design: CAD has become a valuable tool for interior designers, allowing them to create precise and visually appealing designs for residential and commercial spaces. CAD software enables interior designers to develop floor plans, experiment with various furniture and decor options, and create realistic renderings of the final design. CAD also helps interior designers communicate their ideas to clients effectively, making the design process more collaborative and efficient.
- Automotive and Aerospace: CAD is extensively used in the automotive and aerospace industries for designing and manufacturing vehicles and aircraft. CAD software allows designers to create complex and intricate mechanical components, optimize aerodynamic designs, and simulate crash tests and structural analysis. CAD plays a crucial role in ensuring safety and precision in the design and manufacturing of automobiles, airplanes, and spacecraft.
- Electronics: CAD is widely employed in the electronics industry for designing printed circuit boards (PCBs) and electrical systems. Electrical engineers can use CAD software to develop schematics, lay out components on a PCB, and ensure proper connectivity and functionality. CAD allows for efficient and error-free design of electronic circuits, reducing time-to-market and improving the reliability of electronic devices.
These are just a few examples of the many uses of CAD across different industries. The flexibility and capabilities of CAD software make it an indispensable tool for professionals involved in design, engineering, manufacturing, and architecture. As technology continues to advance, CAD will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping the way we design and create the world around us.
Benefits of CAD
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) offers numerous benefits that have revolutionized the design process across various industries. From increased productivity to improved accuracy, CAD has become an indispensable tool for designers, engineers, and architects. Here are some of the key benefits of CAD:
- Increased Efficiency: CAD software automates many repetitive tasks and provides designers with a range of powerful tools and functions. This increases productivity by reducing the time and effort required to create and modify designs. CAD also enables designers to easily reuse and repurpose existing designs, saving time and enhancing efficiency in the design process.
- Improved Accuracy: CAD software allows for precise and accurate designs. Designers can create and modify designs with precision, ensuring that every detail is accounted for. CAD eliminates the manual errors associated with traditional drafting methods, resulting in more accurate and reliable designs.
- Visualization and Virtual Prototyping: CAD provides designers with the ability to visualize their designs in 2D and 3D, allowing for a better understanding of the final product. With CAD, designers can create realistic renderings, add textures and materials, and even simulate lighting and environmental effects. This virtual prototyping capability helps designers and stakeholders to make informed decisions and identify any design issues before production or construction.
- Streamlined Design Collaboration: CAD software facilitates collaboration between designers, engineers, and other stakeholders. Design files can be easily shared, reviewed, and modified by multiple team members simultaneously, regardless of their physical location. This streamlines communication, reduces errors, and improves coordination, leading to better overall project outcomes.
- Design Analysis and Optimization: CAD software comes equipped with analysis tools that allow designers to evaluate the performance and functionality of their designs. Virtual simulations and analyses can be performed to identify potential issues, test variations, and optimize designs. This helps to reduce the need for physical prototypes and costly iterations, saving time and resources.
- Cost and Time Savings: By eliminating the need for manual drafting and reducing errors, CAD software helps to save costs associated with rework and revisions. Virtual prototyping and simulations also help to identify design flaws early in the process, reducing the need for expensive modifications during production or construction. Additionally, CAD software allows for faster design iterations and modifications, reducing overall project timelines.
- Flexibility and Design Iteration: CAD offers designers the flexibility to easily modify and iterate their designs. Design elements can be easily changed, dimensions can be adjusted, and alternate design options can be explored. This flexibility allows designers to quickly respond to client feedback and changing project requirements, leading to improved design outcomes.
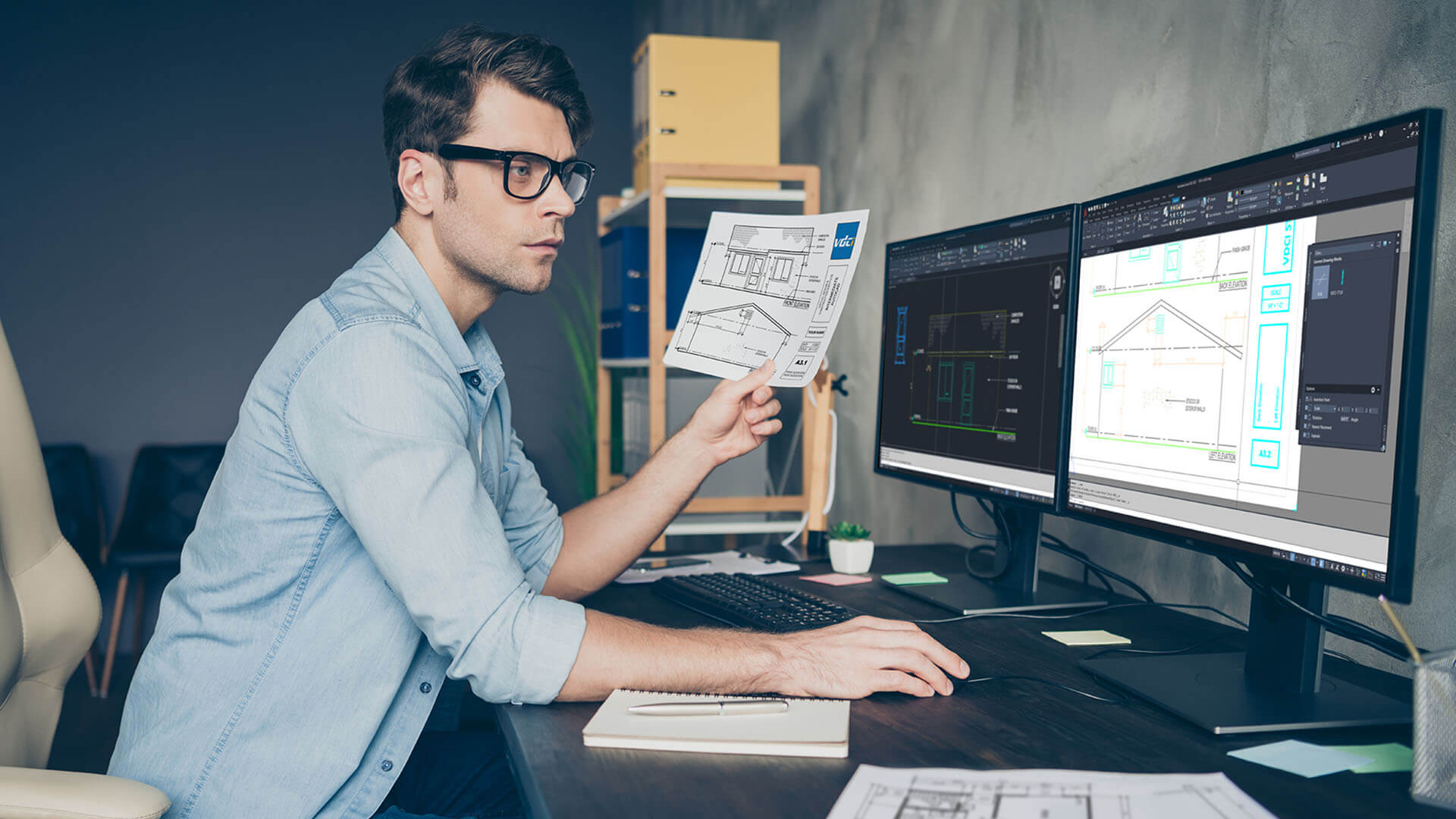
- Documentation and Technical Drawings: CAD software generates accurate and detailed technical drawings, including dimensions, annotations, and specifications. This helps to streamline documentation processes and enhances communication with manufacturers, contractors, and other stakeholders. CAD drawings also make it easier to comply with industry standards and regulations.
These benefits of CAD have made it an integral part of the design process across industries such as architecture, engineering, manufacturing, and more. CAD software empowers designers to create complex, precise, and innovative designs while improving efficiency, collaboration, and cost-effectiveness. As technology continues to advance, CAD will only become more powerful, further transforming the way we design and create the world around us.
When working with CAD software, it’s important to regularly save your work to prevent any potential loss of progress in case of a software crash or other unexpected issue.
Read more: What Are CAD Software
Types of CAD Software
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software comes in various types, each with its own set of features and applications. The type of CAD software chosen depends on the specific design requirements and the industry in which it will be used. Here are some of the common types of CAD software:
- 2D CAD: 2D CAD software is primarily used for creating two-dimensional drawings and technical illustrations. It is widely used in disciplines such as architecture, mechanical engineering, and electrical design. 2D CAD software allows designers to create accurate and detailed representations of objects using lines, arcs, circles, and other geometric shapes. These software programs provide a range of tools for drafting, annotation, dimensioning, and layer management.
- 3D CAD: 3D CAD software enables designers to create three-dimensional models of objects. It allows for a more realistic and immersive representation of the design, providing a better understanding of how the final product will look and function. 3D CAD software allows for the creation of complex shapes, surfaces, and volumes. It offers advanced features such as parametric modeling, assembly modeling, and photo-realistic rendering. 3D CAD software is widely used in industries such as product design, automotive design, and industrial engineering.
- Parametric CAD: Parametric CAD software allows designers to define relationships and constraints between various elements of the design. Parameters, such as dimensions and geometries, are linked together, enabling changes made to one part of the design to automatically update related parts. This feature provides flexibility and ease of modification, making parametric CAD software ideal for designs that require frequent revisions. Parametric CAD software is commonly used in product design and engineering.
- BIM Software: Building Information Modeling (BIM) software is a specialized type of CAD software used in architectural design and construction management. BIM software allows for the creation of comprehensive 3D models that represent not only the structural elements but also the functional and performance characteristics of a building. BIM software provides collaboration tools, clash detection, scheduling, and cost estimation capabilities. It facilitates efficient communication and coordination among architects, engineers, contractors, and other stakeholders involved in the building design and construction process.
- Electrical CAD: Electrical CAD software is designed specifically for creating electrical systems, circuits, and schematics. It provides a set of tools and symbols that allow designers to efficiently design and document electrical systems. Electrical CAD software helps in accurately representing the connections, wire numbering, and component placements in electrical designs. It also facilitates the generation of bills of materials (BOM) and wiring diagrams. Electrical CAD software is widely used in industries such as electronics, aerospace, and power generation.
- PLM Software: Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) software is a comprehensive software solution that encompasses various aspects of the product lifecycle, from design and manufacturing to maintenance and disposal. PLM software often includes CAD functionality as part of its suite of tools. It allows for seamless integration between design, engineering, manufacturing, and supply chain management processes. PLM software provides collaboration features, version control, document management, and workflow automation functionalities.
These are just a few examples of the types of CAD software available in the market. It’s important to choose the right type of CAD software that best suits the specific design requirements and industry needs. The selection of CAD software should consider factors such as the complexity of the design, collaboration requirements, compatibility with other software systems, and the technical expertise of the users.
How CAD Works
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software operates by utilizing a combination of powerful algorithms and interactive tools to create, modify, and optimize designs. Here is a general overview of how CAD works:
- Creating Geometric Shapes: CAD software allows designers to begin the design process by creating geometric shapes such as lines, arcs, circles, and polygons. These shapes serve as the building blocks for more complex designs.
- Manipulating and Modifying Elements: CAD software provides a range of interactive tools and commands that allow designers to manipulate and modify design elements. This includes tasks such as resizing, rotating, and translating objects, as well as creating copies, mirroring, and aligning elements.
- Defining Relationships and Constraints: CAD software supports the concept of parametric modeling, where designers can define relationships and constraints between different parts of the design. For example, a designer can establish that the length of a line is twice that of another line, or that two points must remain coincident. These relationships ensure consistency and allow for easy modifications by automatically updating related elements when changes are made.
- Creating 3D Models: CAD software enables designers to create three-dimensional models of objects. This is achieved by combining various geometric shapes and surfaces to represent the physical form of the design. The software provides tools for creating extrusions, revolutions, lofts, and sweeps, allowing for the generation of complex 3D shapes.
- Adding Detail and Features: CAD software offers a range of tools and functions to add detail and features to the design. This includes options for creating fillets, chamfers, holes, threads, and other design elements. These features help to enhance the functionality, aesthetics, and manufacturability of the design.
- Performing Analysis and Simulation: CAD software often includes analysis and simulation capabilities that allow designers to evaluate the performance and functionality of their designs. This can involve simulating stress and strain, thermal analysis, fluid flow, and other physical properties. By conducting these analyses virtually, designers can identify design flaws, optimize the design, and reduce the need for physical prototypes and testing.
- Generating Technical Drawings and Documentation: CAD software allows designers to generate accurate and detailed technical drawings. These drawings include dimensions, annotations, and specifications necessary for manufacturing or construction. CAD software provides tools for creating multiple views, section cuts, and exploded views, as well as automated generation of bills of materials (BOM) and other documentation.
- Rendering and Visualization: CAD software incorporates rendering engines that can create realistic visual representations of the design. This includes applying textures, materials, and lighting effects to create visually appealing renderings. The software enables designers to view the design from different angles, adjust camera perspectives, and create high-resolution images or animations.
- Collaboration and File Management: CAD software supports collaboration and file management functionalities. Design files can be shared and accessed by multiple users, allowing for real-time collaboration and version control. CAD software often includes features for reviewing, commenting, and annotating designs, facilitating an efficient exchange of feedback and ideas between team members.
These steps provide a general overview of how CAD software works. Each CAD software may have different interfaces, features, and workflows, but the core principles remain the same. CAD software empowers designers to create, modify, analyze, and visualize their designs in a digital environment, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and collaboration throughout the design process.
CAD in Various Industries
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) has found extensive applications in numerous industries, transforming the way design and development are carried out. Here are some of the industries that greatly benefit from the use of CAD software:
- Architecture: The architectural industry heavily relies on CAD for the creation of detailed building designs. CAD software allows architects to develop precise floor plans, elevations, and sections. It enables the visualization of architectural structures in 3D, incorporating textures, materials, and lighting effects. CAD helps architects explore design options, communicate with clients, and streamline the construction documentation process.
- Engineering: CAD plays a vital role in various engineering disciplines, including civil engineering, mechanical engineering, and electrical engineering. Engineers use CAD software to create detailed design models, annotate technical drawings, and simulate the performance of structures and systems. CAD assists in optimizing engineering designs, analyzing stresses, flows, and thermal properties, and ensures adherence to engineering standards and specifications.
- Manufacturing: CAD software has revolutionized the manufacturing industry by improving the design and production of products. Manufacturers employ CAD to create 3D models of components and assemblies, generate manufacturing blueprints, and simulate machining or production processes. CAD ensures accurate prototyping, optimizes material usage, and facilitates efficient manufacturing methods such as computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) and 3D printing.
- Automotive and Aerospace: The automotive and aerospace industries rely on CAD for design and development purposes. CAD software is used to create complex vehicle and aircraft components, optimize aerodynamics, and validate structural integrity through simulations. CAD aids in the integration of systems, such as engines or avionics, and assists in prototyping and testing before production. CAD enables rapid innovation and drives advancements in these highly competitive industries.
- Product Design: CAD software is a valuable asset for product designers across a wide range of industries. It allows designers to create detailed 3D models of products, simulate their functionality, and refine their designs iteratively. CAD facilitates collaboration between designers, engineers, and manufacturers, ensuring that design intent is communicated accurately, resulting in successful product development and launch.
- Fashion Design: CAD has made significant inroads into the fashion industry. Fashion designers use CAD software to create digital representations of garments, develop textile patterns, and experiment with color combinations. CAD enables designers to visualize how garments will look on different body types and streamslines the process of creating tech packs for manufacturing. CAD has also opened up opportunities for virtual fashion shows and online retail experiences.
- Interior Design: CAD software is widely used in the interior design industry to create detailed layouts, 3D models, and renderings of interior spaces. Designers can explore different furniture arrangements, experiment with materials and lighting, and present their designs to clients in a realistic and immersive manner. CAD software helps interior designers visualize and showcase their design concepts effectively.
- Electronics: The electronics industry leverages CAD software to design electronic circuits and PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards). CAD allows electronics engineers to develop schematics, place components on PCB layouts, and ensure proper connectivity and functionality. CAD assists in designing compact and densely populated PCBs, reducing the time and cost associated with manual layout and prototyping.
These examples illustrate the broad spectrum of industries that benefit from the use of CAD software. CAD has become an essential tool in the design and development process across diverse sectors, enabling faster and more efficient design iterations, ensuring accuracy, and facilitating collaboration between teams. As technology continues to evolve, CAD will continue to shape and enhance industries by enabling greater innovation and productivity.
Future of CAD
The future of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) holds exciting possibilities as technology continues to advance and new trends emerge. Here are some key areas that indicate the future direction of CAD:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: AI has the potential to transform the CAD landscape. Machine learning algorithms can be integrated into CAD software to automate repetitive design tasks and provide intelligent suggestions and optimizations. AI can assist designers in generating design variations and exploring innovative solutions. Additionally, AI-powered simulations can enhance accuracy and efficiency in analyzing and optimizing designs.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) Capabilities: VR and AR technologies have started to make their mark in CAD. VR allows designers to immerse themselves in a virtual environment, providing a more intuitive and immersive design experience. AR overlays digital designs onto the real world, enabling designers to visualize and interact with their designs in real-time. The integration of VR and AR into CAD software will enable more accurate prototyping, faster decision-making, and enhanced collaboration.
- Cloud-based Collaboration: CAD software is increasingly moving towards cloud-based platforms, allowing for real-time collaboration and remote access to design files. Cloud-based CAD enables seamless collaboration between geographically dispersed teams, streamlines version control, and simplifies design review processes. This trend will continue to evolve, making CAD more accessible and enhancing global design collaboration.
- Generative Design: Generative design is an emerging concept that uses algorithms to explore and generate multiple design iterations based on specified requirements and constraints. This approach allows for innovative design solutions that humans may not have conceived. By defining the problem statement and design parameters, generative design algorithms can automatically generate optimized designs, unlocking new possibilities for designers and engineers.
- Integration with Internet of Things (IoT): As IoT continues to expand, CAD will play a crucial role in the design and development of IoT-enabled products and systems. Integration with IoT will allow CAD software to consider and optimize the physical and digital aspects of a design, ensuring seamless connectivity, functionality, and interaction with the IoT ecosystem.
- Advancements in 3D Printing: The growing adoption of 3D printing technology will further influence the future of CAD. CAD software will continue to evolve to support the intricacies and complexities of 3D printing. This includes incorporating design features specific to additive manufacturing, such as lattice structures and support material optimization. CAD will enable designers to unleash the full potential of 3D printing and push the boundaries of design innovation.
- Sustainability and Green Design: As environmental sustainability becomes a global priority, CAD will play a crucial role in promoting green design practices. CAD software will incorporate tools and functionalities to analyze and optimize the energy efficiency, material usage, and carbon footprint of designs. This shift towards sustainable design will not only benefit the environment but also contribute to cost savings and improved building performance.
The future of CAD is undoubtedly exciting, with technologies such as AI, VR/AR, cloud-based collaboration, generative design, IoT integration, advancements in 3D printing, and a focus on sustainability shaping the landscape. These advancements will empower designers, engineers, and architects to create more innovative, optimized, and sustainable designs. As CAD continues to evolve, it will revolutionize the design process and drive advancements in various fields, making way for a more connected, efficient, and sustainable future.
Read more: What Is A CAD Designer
Conclusion
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) has undoubtedly revolutionized the way we design, create, and build. From its early beginnings to its current advanced capabilities, CAD has transformed numerous industries and empowered designers, engineers, and architects to push the boundaries of innovation and creativity. From architecture to manufacturing to product design, CAD has become an indispensable tool that offers a wide range of benefits and functionalities.
CAD software has facilitated an increase in efficiency and productivity by automating repetitive tasks, streamlining collaboration, and enabling faster design iterations. With CAD, designers can create accurate and precise designs, visualize them in 2D and 3D, and perform simulations and analysis to optimize functionality and performance. CAD has become an essential part of industries such as architecture, engineering, manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and more.
The future of CAD looks promising, with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, virtual reality, augmented reality, generative design, cloud-based collaboration, integration with the Internet of Things, and advancements in 3D printing. These technologies will further enhance the capabilities of CAD, enabling designers to create more innovative, optimized, and sustainable designs. With the integration of AI, CAD software will become smarter, automating tasks, providing intelligent suggestions, and revolutionizing the design process.
Furthermore, virtual reality and augmented reality will enable designers to immerse themselves in their designs, enhancing visualization and collaboration. Cloud-based collaboration will make it easier for teams to work together across geographical boundaries, while generative design will unlock new possibilities by automatically generating optimized solutions. Integration with the Internet of Things will ensure seamless connectivity and functionality, and advancements in 3D printing will push the boundaries of what is possible in design and manufacturing.
In conclusion, CAD has transformed the way we design and create, and its impact will continue to grow in the future. By embracing the power of CAD and staying at the forefront of technological advancements, designers, engineers, and architects can unlock their full potential and drive innovation in their respective fields. CAD has become an integral part of the design process, and its continued evolution will shape the way we shape our world.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is CAD?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Is CAD?”