Home>diy>Planning & Engineering>What Does A Zoning Officer Do


Planning & Engineering
What Does A Zoning Officer Do
Modified: October 20, 2024
Discover the role of a zoning officer in the field of planning and engineering. Learn about their responsibilities and how they contribute to land use and development regulations.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
A zoning officer plays a critical role in the planning and development of cities and towns. They are responsible for enforcing zoning codes and regulations to ensure that land use is in compliance with local ordinances. Their work contributes to the overall organization, safety, and aesthetics of a community.
In this article, we will explore the various responsibilities of a zoning officer, the importance of zoning codes, the permitting and inspection processes, managing zoning violations, collaboration with developers and city officials, community engagement, and the training and education required for this role.
So, let’s dive in and gain a deeper understanding of what a zoning officer does and how their work impacts the development and growth of our communities.
Key Takeaways:
- Zoning officers are essential for maintaining order and responsible development within communities. Their duties include enforcing zoning codes, collaborating with stakeholders, and engaging with the public to ensure sustainable growth.
- Through training and education, zoning officers acquire the expertise to interpret and enforce zoning regulations effectively. Their role contributes to the overall well-being and development of communities.
Read more: What Does A Zoning Engineer Do
Responsibilities of a Zoning Officer
A zoning officer is responsible for overseeing and enforcing zoning regulations to ensure that land use within a municipality conforms to the prescribed guidelines. Here are some of the key responsibilities that a zoning officer typically holds:
- Interpreting Zoning Codes: One of the primary tasks of a zoning officer is to interpret the zoning codes and regulations established by the local government. This involves comprehending the intricate details of zoning ordinances and being able to provide guidance to citizens, developers, and city officials on the permissible land uses and development standards.
- Reviewing Development Plans: Zoning officers review building and development plans to ensure they comply with the applicable zoning laws. This includes examining site plans, architectural drawings, and other relevant documents to assess whether the proposed project aligns with the zoning requirements.
- Issuing Permits: Zoning officers are responsible for issuing permits for various types of development projects, such as building permits, zoning variances, conditional use permits, and special exceptions. They review permit applications, verify compliance with zoning regulations, and approve or deny permits accordingly.
- Conducting Inspections: Zoning officers conduct regular inspections of properties to verify that they are being used in accordance with the approved permits and zoning regulations. Inspections may cover areas such as setbacks, parking spaces, signage, landscaping, and other relevant aspects of land use.
- Handling Zoning Violations: When zoning violations occur, it is the duty of the zoning officer to investigate complaints and take appropriate actions. This may involve issuing violation notices, coordinating with property owners to rectify the violations, and if necessary, taking legal action to enforce compliance.
- Maintaining Zoning Records: Keeping accurate records is crucial for a zoning officer. They are responsible for maintaining detailed records of zoning permits, violations, inspection reports, and other relevant documentation. These records play an essential role in ensuring transparency and facilitating future zoning decisions.
- Providing Public Assistance: Zoning officers act as a resource for the public, offering guidance and assistance regarding zoning matters. They answer inquiries, provide information on zoning regulations, assist citizens with applications, and address any concerns or complaints related to land use.
These are just some of the key responsibilities that a zoning officer handles. Their role is vital in maintaining order and facilitating responsible development within a community.
Zoning Codes and Regulations
Zoning codes and regulations are the legal frameworks that govern land use and development within a municipality. They provide guidelines and restrictions on how land can be utilized, ensuring that different areas of a community are designated for specific purposes. Here are some essential aspects of zoning codes and regulations:
- Zoning Districts: Zoning codes establish different districts within a municipality, such as residential, commercial, industrial, and mixed-use. Each district has specific regulations regarding the types of buildings, activities, and land uses permitted.
- Land Use Regulations: Zoning regulations dictate how land can be used within each zoning district. They specify the allowable uses, such as single-family homes, multi-family buildings, retail stores, offices, manufacturing facilities, and more.
- Development Standards: Zoning codes also outline development standards that must be met within each district. These may include requirements for setback distances, building height limits, parking spaces, landscaping, signage, infrastructure, and other aspects that contribute to the overall appearance and functionality of a community.
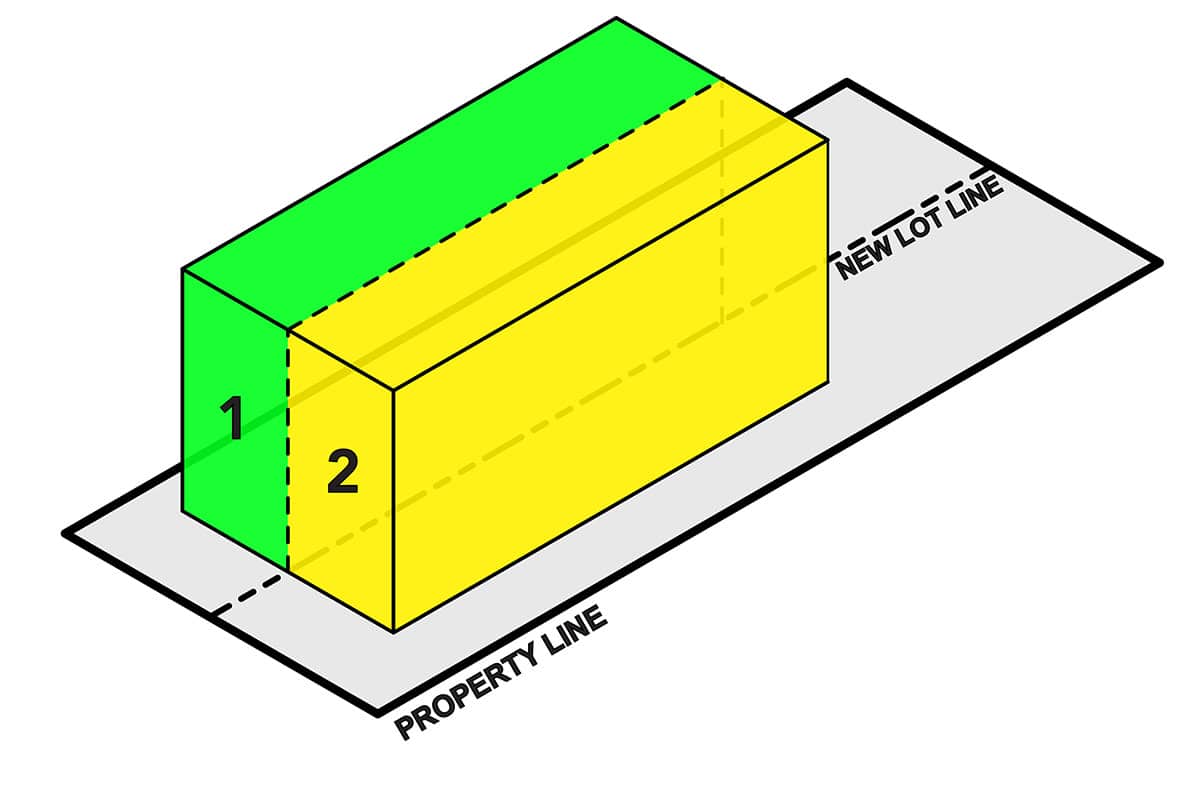
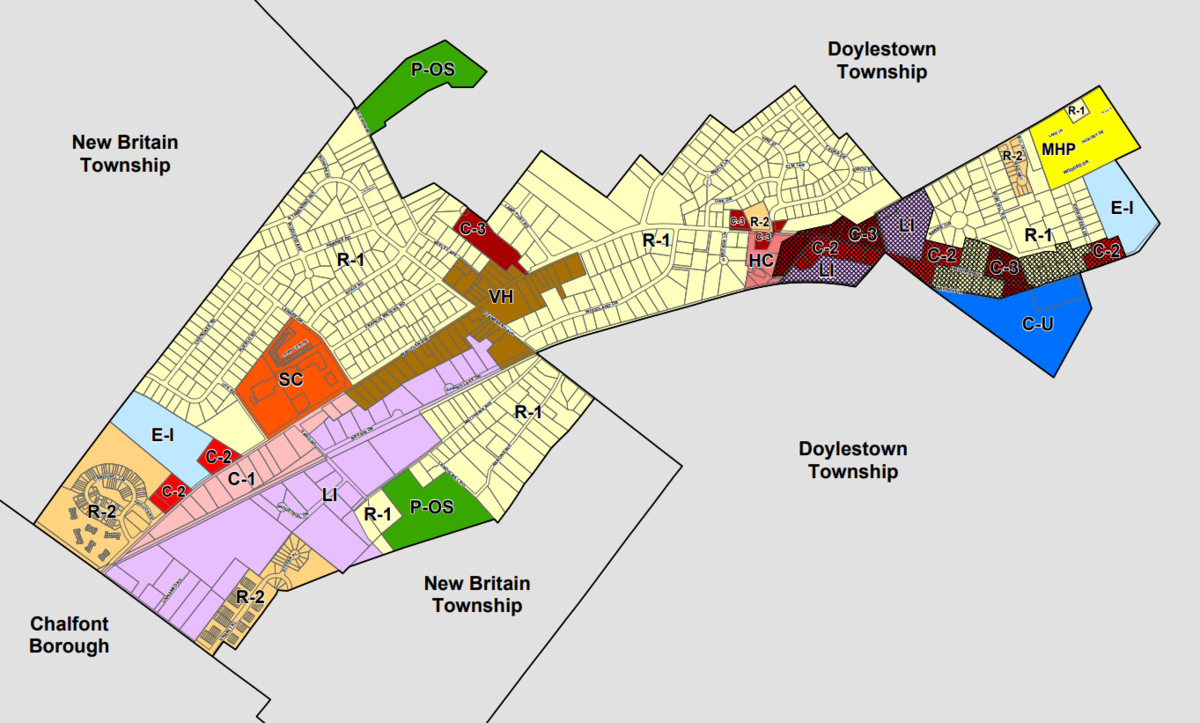
- Zoning Map: A zoning map is a visual representation of the various zoning districts within a municipality. It shows the boundaries of each district, allowing property owners, developers, and residents to understand the zoning regulations that apply to specific areas.
- Zoning Amendments: Zoning codes are not static and can be amended over time to accommodate changing needs and priorities. Zoning officers may play a role in proposing or reviewing zoning amendments, which require public hearings and approvals from local governing bodies.
- Overlay Districts: Some communities may have overlay districts, which are additional zoning regulations that apply to specific areas or features within a municipality. These may include historic preservation districts, environmentally sensitive areas, or special planning districts with unique requirements.
- Zoning Board of Appeals: Zoning codes often establish a zoning board of appeals, which is responsible for hearing and deciding on requests for variances, special exceptions, or other relief from the strict application of zoning regulations. The zoning officer may collaborate with the zoning board to provide insights and guidance on these matters.
Zoning codes and regulations serve as a crucial tool for maintaining the character, functionality, and compatibility of different areas within a municipality. They ensure that land use is aligned with community goals, promoting orderly growth and preserving the quality of life for residents.
Permitting and Inspection Processes
The permitting and inspection processes are key components of a zoning officer’s role in ensuring compliance with zoning regulations. These processes are designed to review and monitor development projects and ensure that they meet the necessary standards and requirements. Let’s take a closer look at the permitting and inspection processes:
- Permit Applications: Property owners or developers seeking to undertake a construction or development project must submit permit applications to the zoning office. These applications typically include detailed plans, drawings, and supporting documentation that demonstrate compliance with zoning codes and regulations.
- Plan Review: Zoning officers conduct a thorough review of the permit applications to assess compliance with zoning requirements. They examine factors such as setbacks, building height, parking, landscaping, and any special considerations specific to the project. The objective is to ensure that the proposed development aligns with the zoning regulations of the municipality.
- Permit Issuance: If the permit application meets all the zoning code requirements, the zoning officer will issue the permit. This permit grants the property owner or developer permission to proceed with the proposed project in accordance with the approved plans and specifications.
- Inspections: Once construction or development begins, zoning officers conduct periodic inspections throughout the process. These inspections help ensure that the work being carried out aligns with the approved plans and that zoning regulations are being followed. Inspections may cover various aspects such as structural integrity, setbacks, utility connections, and overall compliance with zoning codes.
- Correction Notices: If any violations or shortcomings are identified during inspections, the zoning officer issues correction notices to the property owner or developer. These notices outline the specific issues that need to be addressed to bring the project into compliance with the approved plans and applicable zoning regulations. The property owner or developer is given a designated time frame to rectify the violations.
- Final Inspections: Once the project is complete, a final inspection is conducted to verify that all corrections have been made and the development complies with the approved plans and zoning regulations. If the final inspection is successful, a certificate of occupancy or completion is issued, signifying that the property can be occupied or utilized according to its intended purpose.
The permitting and inspection processes are crucial for ensuring that developments adhere to zoning regulations and contribute to the orderly growth and development of the community. Zoning officers play a vital role in overseeing these processes and upholding the integrity of zoning codes and standards.
Managing Zoning Violations
Managing zoning violations is an important aspect of a zoning officer’s responsibilities. Zoning violations occur when property owners or developers fail to comply with the established zoning codes and regulations. It is the zoning officer’s duty to investigate complaints, enforce compliance, and take appropriate actions to rectify the violations. Let’s delve into the process of managing zoning violations:
- Complaint Investigation: Zoning officers receive complaints from community members, neighboring property owners, or other officials regarding alleged zoning violations. They will investigate these complaints to determine if a violation has occurred.
- Evidence Gathering: During the investigation, the zoning officer collects evidence to support or refute the claims of a zoning violation. This may involve site visits, interviews with involved parties, review of documents, and any other necessary actions to gather relevant information.
- Violation Notice: If a zoning violation is confirmed, the zoning officer issues a violation notice to the property owner or responsible party. The notice outlines the specific violation(s) and includes a timeframe for compliance.
- Communication and Education: In some cases, property owners may be unaware of the zoning regulations or may have unintentionally violated them. The zoning officer may engage in communication and education efforts to help the property owner understand the requirements and assist in finding ways to rectify the violation.
- Enforcement Actions: If the property owner fails to comply with the violation notice within the given timeframe, the zoning officer may take enforcement actions. This can include fines, citations, or legal proceedings to bring the property into compliance.
- Collaboration with Legal Authorities: In certain complex cases, the zoning officer may collaborate with legal authorities, such as city attorneys or local courts, to enforce compliance with zoning regulations. This may involve seeking court injunctions or pursuing legal remedies to resolve the violation.
- Follow-Up Inspections: After issuing a violation notice, the zoning officer conducts follow-up inspections to ensure that the property owner has taken the necessary steps to rectify the violation. If compliance is achieved, the case is closed. If not, further enforcement actions may be pursued.
Effectively managing zoning violations is crucial for maintaining the integrity of zoning regulations and preserving the character and functionality of the community. Zoning officers play a significant role in enforcing compliance and ensuring a fair and orderly development process.
A zoning officer is responsible for enforcing local zoning regulations, reviewing building permit applications, and ensuring compliance with land use laws. They also conduct site inspections and address zoning violations.
Read more: What Does The Knob Under An Office Chair Do
Collaboration with Developers and City Officials
A zoning officer plays a crucial role in collaborating with developers and city officials to facilitate responsible and compliant development within a municipality. This collaboration involves working closely with various stakeholders to ensure that zoning regulations are followed and that development projects align with the community’s goals and vision. Let’s explore the significance of collaboration in the context of zoning officers:
- Development Proposal Review: Zoning officers work closely with developers during the review of development proposals. They provide expertise in interpreting zoning codes and regulations and offer guidance to developers on how to modify their plans to align with the zoning requirements. This collaboration ensures that proposed developments address community needs while adhering to zoning standards.
- Development Agreement Negotiation: In some cases, zoning officers may participate in negotiating development agreements with developers. These agreements may specify conditions or requirements that developers must meet, such as the inclusion of affordable housing units or the provision of public amenities. Collaborative discussions ensure that the interests of both the community and the developer are considered and balanced.
- Public Outreach and Input: Zoning officers often organize public meetings or workshops to gather input from community members regarding development proposals or changes to zoning regulations. They collaborate with developers and city officials to create opportunities for public engagement and to ensure that the concerns and suggestions of the community are taken into account during the decision-making process.
- Technical Support: Zoning officers provide technical support to developers throughout the project planning and design stages. They assist in understanding zoning codes, explaining requirements, and addressing any concerns or challenges that may arise. This collaborative approach helps developers navigate the zoning process more efficiently and effectively.
- Collaboration on Variances and Exceptions: When developers seek variances or exceptions to zoning regulations, zoning officers collaborate with them and present their case to the zoning board of appeals or other reviewing bodies. Zoning officers provide expertise, present relevant information, and help in crafting arguments that justify granting the requested variances or exceptions.
- Policy Development: Zoning officers collaborate with city officials and other stakeholders in the development or revision of zoning policies. They provide insights and expertise on the practical implications of proposed changes and work collectively to ensure that these policies align with the broader goals of the community.
- Continued Communication: Zoning officers maintain open lines of communication with developers and city officials throughout the development process. This ongoing collaboration allows for the resolution of any issues or concerns that may arise and facilitates a smooth and compliant construction process.
Collaboration between zoning officers, developers, and city officials is essential for achieving well-planned and sustainable development. By working together, they can strike a balance between economic growth, community interests, and the adherence to zoning regulations, ultimately contributing to the overall betterment of the municipality.
Community Engagement and Public Outreach
Community engagement and public outreach are essential components of a zoning officer’s responsibilities. Engaging with the community helps zoning officers gather valuable input, educate residents about zoning regulations, and foster a sense of collaboration and transparency. Here are some important aspects of community engagement and public outreach:
- Public Meetings: Zoning officers organize public meetings and workshops to provide the community with an opportunity to learn about and provide feedback on proposed development projects or changes to zoning regulations. These meetings serve as a platform for residents to voice their concerns, ask questions, and offer suggestions.
- Community Surveys: Zoning officers may conduct surveys to gather residents’ opinions and preferences on various zoning-related matters. These surveys can provide valuable insights into community priorities and help shape zoning policies and regulations accordingly.
- Information Dissemination: Zoning officers are responsible for effectively communicating zoning regulations and processes to the public. This may include creating informative brochures, websites, or social media platforms that provide easily understandable information about zoning codes, permit applications, and the development review process.
- Neighborhood Associations: Zoning officers actively engage with neighborhood associations and community groups to build relationships and foster collaboration. They attend meetings, address concerns, and provide updates on zoning issues that may impact the specific neighborhood or community.
- Site Visits and Inspections: Zoning officers may conduct site visits and inspections in response to community concerns or to proactively monitor compliance with zoning regulations. This visibility allows residents to witness the enforcement process and ensures that the community sees the zoning officer as an accessible resource.
- Educational Workshops: Zoning officers may organize educational workshops or training sessions for community members, property owners, and neighborhood organizations. These workshops aim to enhance public understanding of zoning regulations, development processes, and the benefits of responsible land use planning.
- Collaboration with Civic Organizations: Zoning officers collaborate with civic associations, environmental groups, or other organizations to gather insights and perspectives on zoning matters. This collaboration allows for a diverse range of perspectives to be considered in the decision-making process.
- Transparency and Feedback: Zoning officers strive to maintain transparency in their work by providing updates on zoning-related projects and decisions. They are open to receiving feedback from the community and actively seek input on future zoning initiatives.
Community engagement and public outreach initiatives conducted by zoning officers create a platform for dialogue and collaboration between local government and community members. By involving the public in the decision-making process, zoning officers can ensure that zoning regulations reflect the needs and aspirations of the community.
Zoning Officer Training and Education
To effectively carry out their responsibilities, zoning officers undergo specialized training and education that equips them with the knowledge and skills required to interpret and enforce zoning regulations. Here are some key aspects of zoning officer training and education:
- Zoning Codes and Regulations: Zoning officers receive training on the specific zoning codes and regulations of their municipality. They study the intricacies of the zoning ordinances and familiarize themselves with the various zoning districts, land use regulations, and development standards applicable in the community.
- Land Use Planning: Zoning officers often receive education in urban and regional planning, where they learn about the principles and practices of land use planning. This includes topics such as comprehensive planning, zoning principles, sustainable development, and community design.
- Legal and Regulatory Knowledge: Zoning officers acquire a working knowledge of relevant laws and legal principles pertaining to zoning and land use. This includes understanding constitutional limitations, case law, and administrative procedures relevant to zoning enforcement and decision-making.
- Permitting and Building Inspection: Zoning officers receive training on permitting processes, including reviewing permit applications for compliance with zoning regulations. They also learn about building inspection techniques to ensure that construction projects adhere to approved plans and zoning requirements.
- Communication and Conflict Resolution: Zoning officers undergo training in effective communication, negotiation, and conflict resolution. These skills enable them to interact with the public, developers, and city officials in a professional, empathetic, and collaborative manner.
- Continuing Education: Zoning officers participate in ongoing professional development to stay updated on changes in zoning laws, regulations, and industry trends. Continuing education courses, workshops, and conferences provide opportunities for zoning officers to expand their knowledge and refine their skills.
- Collaboration and Leadership: Zoning officers are trained in collaboration techniques and leadership skills as they often work closely with developers, city officials, and community members. This training equips them with the ability to facilitate meetings, engage stakeholders, and navigate complex decision-making processes.
- Ethics and Professional Conduct: Zoning officers are trained on professional ethics and the importance of maintaining impartiality and fairness in their role. They learn about conflicts of interest, confidentiality, and the ethical responsibilities associated with their position.
Zoning officer training and education ensure that individuals in this role have the necessary expertise to interpret zoning regulations, make informed decisions, handle zoning violations, and engage with stakeholders effectively. By staying up to date with evolving laws and best practices, zoning officers can fulfill their vital role in promoting responsible land use and contributing to the overall development and well-being of their communities.
Conclusion
Zoning officers play a vital role in shaping the development and growth of our communities. Their responsibilities include enforcing zoning codes, reviewing development plans, issuing permits, conducting inspections, managing zoning violations, collaborating with developers and city officials, engaging with the community, and staying informed through ongoing training and education.
Zoning codes and regulations serve as the foundation for zoning officers’ work, establishing guidelines for land use and development within a municipality. Through their diligent enforcement, zoning officers ensure that projects align with these regulations, contributing to organized and sustainable growth.
The permitting and inspection processes are central to a zoning officer’s responsibilities, ensuring that development projects meet zoning requirements. Zoning officers work closely with developers and city officials, collaborating to facilitate responsible development that benefits both the community and those involved in the projects.
Zoning officers also play a crucial role in managing zoning violations, investigating complaints, and taking appropriate actions to enforce compliance. By engaging with the community through public meetings, education workshops, and collaboration with civic organizations, zoning officers foster transparency and ensure that community voices are heard and considered in decision-making processes.
Efficient and effective training and education programs equip zoning officers with the necessary knowledge and skills to carry out their duties. By staying updated on zoning laws and regulations, honing their communication and negotiation abilities, and adopting ethical practices, zoning officers are well-prepared to fulfill their responsibilities and serve their communities.
In conclusion, the work of zoning officers is instrumental in shaping our surroundings and maintaining the integrity and functionality of our communities. Their commitment to enforcing zoning regulations, collaborating with stakeholders, and engaging with the public ensures responsible growth, vibrant neighborhoods, and a high quality of life for residents.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Does A Zoning Officer Do
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.









0 thoughts on “What Does A Zoning Officer Do”