Home>diy>Planning & Engineering>What Does C-2 Zoning Mean

Planning & Engineering
What Does C-2 Zoning Mean
Modified: January 9, 2024
Learn about C-2 zoning and its meaning in planning and engineering. Understand the regulations and limitations associated with this zoning designation.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to urban planning and development, zoning is a crucial component that helps ensure the proper allocation and use of land within a municipality. Zoning regulations define the specific activities and purposes allowed for different areas, known as zones, within a city or town. One such zoning designation is C-2 zoning, which has its own set of rules and restrictions.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of C-2 zoning and explore what it means for land use and development. We will examine the permitted uses, building regulations, setbacks and density requirements, as well as the parking and access requirements associated with C-2 zones. Additionally, we will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of C-2 zoning, and provide real-life case studies to illustrate its implementation.
Whether you are a potential commercial property owner, a developer, or simply interested in understanding the dynamics of zoning, this article will serve as a comprehensive guide to help you navigate the world of C-2 zoning.
Key Takeaways:
- C-2 zoning fosters vibrant commercial areas, offering a diverse range of businesses while balancing the needs of residents and visitors. It can revitalize urban spaces and enhance economic opportunities.
- While C-2 zoning brings commercial vibrancy, it also poses challenges such as traffic congestion and parking issues. Careful consideration and community collaboration are crucial for successful implementation.
Read more: What Does B2 Zoning Mean
Definition of C-2 Zoning
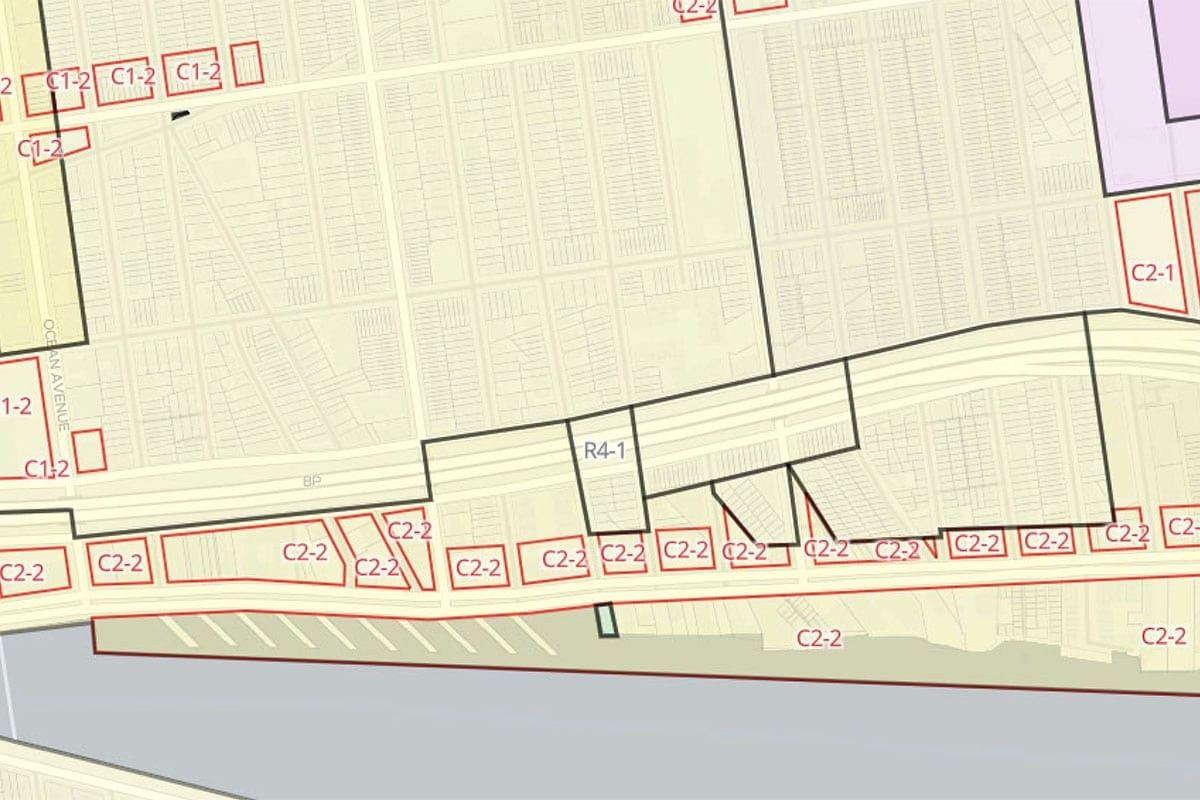
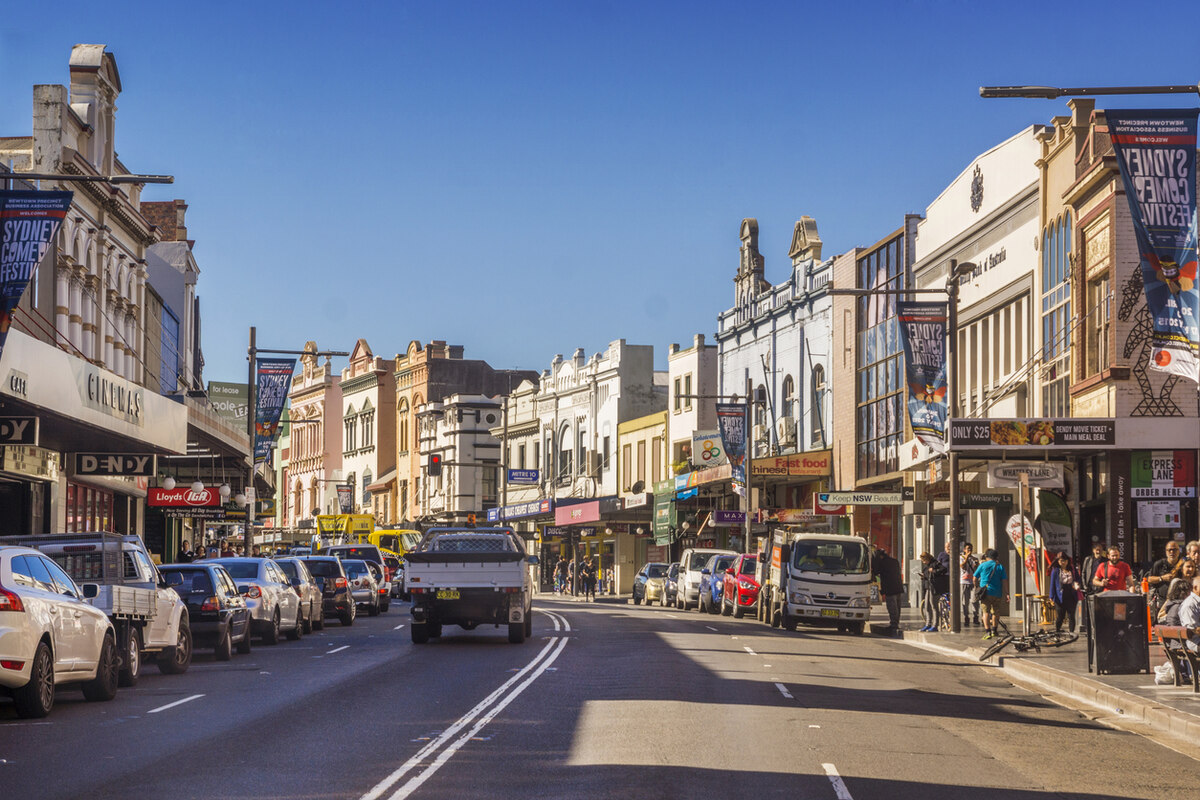
In the realm of zoning classifications, C-2 zoning refers to specific areas within a city that have been designated for mixed-use commercial purposes. The “C” in C-2 stands for commercial, indicating that these areas are primarily intended for commercial activities such as retail, offices, and services.
C-2 zoning typically allows for a wide range of commercial uses, including but not limited to, restaurants, convenience stores, beauty salons, medical offices, and small-scale manufacturing. This zoning designation is often found in commercial corridors or areas that have a high volume of pedestrian and vehicular traffic.
It is important to note that C-2 zoning does not exclusively mean commercial activities. Depending on local regulations, certain types of residential uses may also be permitted within C-2 zones, such as apartments or live-work units. However, the primary focus of C-2 zoning remains on accommodating various commercial ventures.
The purpose of C-2 zoning is to facilitate vibrant commercial areas that are easily accessible and cater to the needs of both local residents and visitors. By establishing clear guidelines for land use within C-2 zones, city planners aim to create a balanced urban environment where businesses can thrive while complementing the surrounding community.
Allowed Land Uses in C-2 Zones
C-2 zoning allows for a diverse array of commercial land uses to thrive within designated areas. These land uses are carefully regulated to ensure compatibility with the surrounding neighborhood and maintain the overall character of the area. Here are some of the common land uses permitted in C-2 zones:
- Retail Stores: C-2 zones often house a variety of retail establishments, ranging from clothing boutiques and electronics stores to grocery stores and pharmacies.
- Restaurants and Cafes: From small cafes to fine dining establishments, C-2 zones provide space for different types of food and beverage establishments.
- Professional Offices: C-2 zoning allows for the operation of professional services such as law firms, accounting offices, real estate agencies, and architectural firms.
- Personal Services: Salons, spas, fitness centers, and other personal service providers can find a home in C-2 zones.
- Entertainment Venues: Movie theaters, bowling alleys, performance spaces, and other entertainment venues can be established within C-2 zones.
- Hotels and Lodging: C-2 zoning may permit hotels, motels, and other short-term lodging accommodations, ensuring convenient access for visitors.
- Medical Facilities: C-2 zones may allow for medical and dental clinics, hospitals, and other healthcare service providers.
- Automotive Services: C-2 zoning can accommodate auto repair shops, car dealerships, and other automotive-related businesses.
This list is by no means exhaustive, as the specific land uses permitted in C-2 zones can vary depending on local regulations and zoning ordinances. It is important for developers and business owners to consult the specific zoning laws of the municipality to ensure compliance.
While C-2 zones primarily focus on commercial activities, some jurisdictions also allow for a level of residential use within these areas. This can include apartments, condominiums, or live-work units. However, the residential component is typically secondary to the commercial aspect in C-2 zoning.
Overall, C-2 zoning offers a wide range of possibilities for businesses and developers, providing a platform for diverse commercial activities and creating vibrant, mixed-use neighborhoods.
Building Regulations in C-2 Zones
Building regulations play a crucial role in maintaining the structural integrity and aesthetic harmony of C-2 zones. These regulations outline the specific requirements and standards that must be followed when constructing, renovating, or expanding buildings within C-2 zoning areas.
Here are some key building regulations typically enforced in C-2 zones:
- Height Restrictions: C-2 zoning often specifies maximum building heights to ensure that new structures do not overshadow neighboring buildings or disrupt the overall streetscape. These height restrictions vary depending on the specific zoning ordinance and the height limitations set by local authorities.
- Architectural Design Guidelines: To maintain a cohesive visual appearance, C-2 zones may have architectural design guidelines that dictate the style, materials, and overall aesthetic of buildings within the area. These guidelines aim to create a unified and attractive streetscape that enhances the character of the neighborhood.
- Façade Requirements: C-2 zoning may also have requirements for building façades, such as the use of certain materials, window placements, or signage regulations. These guidelines are intended to promote architectural diversity and prevent the proliferation of monotonous or visually unappealing structures.
- Setback Regulations: Setbacks refer to the minimum distance between a building and the property line or adjacent buildings. C-2 zoning typically includes setback requirements to ensure adequate breathing room and create a sense of openness between structures. These setbacks may vary depending on the specific context and the desired relationship between buildings and public space.
- Building Safety Standards: Building regulations in C-2 zones also encompass requirements to ensure the safety of occupants and visitors. This includes compliance with fire safety codes, accessibility standards, and other relevant building codes and regulations.
It is important for developers and property owners to carefully review the building regulations specific to their jurisdiction and adhere to these guidelines when planning and constructing new buildings or making modifications to existing structures.
By enforcing building regulations, C-2 zones aim to create a visually appealing and harmonious environment that promotes high-quality construction, enhances the pedestrian experience, and contributes to the overall aesthetic and functionality of the commercial area.
Setbacks and Density Requirements in C-2 Zones
In order to maintain a balanced and comfortable urban environment, C-2 zoning typically includes regulations regarding setbacks and density requirements. These guidelines aim to regulate the spatial relationships between buildings, ensure adequate access to sunlight and fresh air, and prevent overcrowding within the designated area.
Setbacks:
Setbacks refer to the minimum distance required between a building and the property line, street, or adjacent buildings. Setbacks are put in place to provide open space around buildings, create visual breaks between structures, and allow for pedestrian circulation. The specific setback requirements may vary depending on the local zoning regulations and the unique characteristics of each C-2 zone. For example, a city may require a minimum front setback to maintain the continuity of the streetscape or a rear setback to provide privacy for neighboring properties.
Density Requirements:
Density requirements dictate the maximum number of units or square feet allowed per lot area in C-2 zoning. This helps regulate population density and prevent overcrowding in commercial areas. Density requirements may be expressed in various ways, such as floor-area ratio (FAR) or dwelling units per acre. For instance, a C-2 zone may have a maximum FAR of 3, meaning that the total floor area of all buildings on a lot cannot exceed three times the area of the lot itself.
The density requirements in C-2 zones are influenced by various factors, including the local population, infrastructure capacity, and the desired balance between commercial and residential activities. City planners and zoning authorities carefully consider these factors to establish density requirements that align with the goals and vision of the community.
It is important for developers and property owners to consult the specific setback and density regulations of their municipality to ensure compliance when planning new developments or modifications to existing properties in C-2 zones.
By implementing setbacks and density requirements, C-2 zoning aims to create a harmonious urban fabric that balances the need for commercial activity with the preservation of open space and the overall livability of the area.
C-2 zoning typically allows for a wide range of commercial uses, including retail, office, and service establishments. It’s important to check the specific zoning regulations for any restrictions or special requirements in a particular area.
Read more: What Does R2 Zoning Mean
Parking and Access Requirements in C-2 Zones
Parking and access requirements are essential components of C-2 zoning regulations. These requirements aim to ensure that commercial developments within C-2 zones have adequate parking facilities and safe, convenient access for both vehicles and pedestrians.
Parking Requirements:
C-2 zoning typically includes guidelines for the number of parking spaces required for different types of commercial activities. The specific parking requirements can vary depending on factors such as the size of the development, the type of business, and the local zoning ordinances. For example, a small retail store may have fewer parking spaces required compared to a larger shopping center. Parking requirements may take into account factors such as the expected number of employees, customer capacity, and vehicle trip generation. These requirements are put in place to minimize parking congestion, ensure sufficient parking availability, and promote a positive experience for visitors to the area.
Access Requirements:
C-2 zoning also addresses access requirements to ensure safe and efficient movement within the commercial area. These requirements may include regulations related to driveway locations, pedestrian walkways, and vehicular circulation. For instance, C-2 zoning may specify the width and location of entry and exit points for parking lots, the provision of accessible pedestrian pathways, and the designation of loading zones for deliveries. These access requirements help maintain traffic flow, pedestrian safety, and accessibility for all users of the C-2 zone.
In some cases, C-2 zoning may encourage alternative transportation options such as bicycle parking or provisions for public transit access. This promotes sustainability and reduces the dependence on private vehicles within the commercial area.
By incorporating parking and access requirements, C-2 zoning aims to balance the need for convenient access to commercial establishments with the goal of maintaining the overall functionality, safety, and efficiency of the area.
Developers and property owners should consult the specific parking and access regulations outlined in their local zoning ordinances to ensure compliance and plan for sufficient parking and access when establishing or renovating commercial establishments in C-2 zones.
Advantages and Disadvantages of C-2 Zoning
C-2 zoning, like any other zoning classification, comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these pros and cons is crucial for developers, property owners, and community members alike. Let’s explore the advantages and disadvantages of C-2 zoning:
Advantages:
- Commercial Vibrancy: C-2 zoning promotes the development of vibrant commercial areas by allowing a diverse range of commercial uses. This fosters economic growth, job opportunities, and a lively atmosphere.
- Convenience: C-2 zones often provide convenience to residents by bringing necessary goods and services closer to home. This can reduce travel distances and make daily errands more convenient.
- Mixed-Use Development: C-2 zoning encourages mixed-use developments, integrating commercial establishments with other land uses such as residential or office spaces. This creates a sense of community, fosters walkability, and enhances the overall livability of the area.
- Increased Property Values: Proximity to well-planned C-2 zones can positively impact property values by attracting consumers, stimulating local economies, and providing desirable amenities.
- Urban Revitalization: C-2 zoning can play a vital role in urban revitalization efforts, transforming underutilized or distressed areas into thriving business districts that attract investment and generate employment opportunities.
Disadvantages:
- Traffic Congestion: C-2 zoning can potentially lead to increased traffic congestion, especially in areas with limited transportation infrastructure. This can cause delays, inconvenience, and frustration for both motorists and pedestrians.
- Noise and Disturbances: The presence of commercial activities within C-2 zones may result in increased noise levels and disturbances for nearby residential areas, impacting the quality of life for residents.
- Loss of Community Character: C-2 zoning can transform the character of a neighborhood by introducing new buildings, architectural styles, and commercial activities. This can be seen as either positive or negative, depending on individual perspectives and the desire to maintain the existing community identity.
- Parking Challenges: Meeting parking requirements within C-2 zones can be a challenge, particularly in densely populated areas. Insufficient parking can lead to congestion, limited parking availability for visitors, and potential conflict between businesses and residents over parking spaces.
- Pressure on Infrastructure: With increased commercial activities, C-2 zoning may put additional strain on existing infrastructure, including water, sewer, and utility systems. This may require upgrades to accommodate the increased demand.
It’s important to note that the advantages and disadvantages of C-2 zoning are context-dependent and can vary based on the specific characteristics of each area. Municipalities and community stakeholders should carefully consider these factors to strike a balance and ensure the benefits outweigh the potential drawbacks.
Case Studies: Examples of C-2 Zoning Implementation
Examining real-life examples of C-2 zoning implementation can provide valuable insights into how this zoning classification can shape and transform urban areas. Here are two case studies highlighting successful instances of C-2 zoning:
Case Study 1: Downtown Commercial District
In the city of XYZ, a downtown area was designated as a C-2 zoning district. The local government recognized the historic and cultural significance of the area and aimed to revitalize it into a vibrant commercial hub. The C-2 zoning regulations allowed for a mix of retail, dining, and entertainment establishments, along with a limited number of residential units to foster a live-work-play environment.
The implementation of C-2 zoning transformed the previously underutilized downtown area into a bustling district that attracted local residents and visitors alike. The introduction of new businesses, coupled with the preservation of architectural heritage, enhanced the overall appeal of the area. The zoning regulations ensured that new developments aligned with the desired aesthetic and maintained the relationship between buildings and public spaces, creating a cohesive and inviting streetscape.
Case Study 2: Commercial Corridor Revitalization
In the suburb of ABC, a commercial corridor had experienced a decline due to changing consumer preferences and increased competition from shopping malls on the outskirts of the city. Recognizing the potential for revitalization, the local authorities implemented C-2 zoning to encourage commercial growth and redevelopment along the corridor.
The C-2 zoning allowed for a mix of retail, office, and service-oriented businesses, as well as limited residential components above ground-level establishments. The zoning regulations also focused on improving pedestrian access and streetscape enhancements to create a more walkable and aesthetically pleasing environment.
Through the implementation of C-2 zoning, the commercial corridor in ABC saw a significant transformation. Vacant storefronts were filled with new businesses, contributing to a vibrant and economically thriving area. The increased pedestrian activity, coupled with the mix of commercial and residential uses, added life and vitality to the once-neglected corridor. Local businesses experienced increased foot traffic, residents enjoyed easy access to amenities, and the community as a whole benefited from the revitalized commercial corridor.
These case studies demonstrate the positive impact of C-2 zoning when appropriately implemented. By carefully considering the specific characteristics and goals of an area, C-2 zoning can play a pivotal role in revitalizing urban spaces, creating economic opportunities, and fostering a vibrant community atmosphere.
Conclusion
C-2 zoning, with its focus on mixed-use commercial activities, plays a vital role in shaping the urban landscape and fostering vibrant communities. By defining the allowed land uses, building regulations, setbacks and density requirements, and parking and access requirements, C-2 zoning ensures the proper allocation and utilization of land within commercial areas.
Through case studies and examples, we have seen the positive outcomes of C-2 zoning implementation. From downtown commercial districts to revitalized commercial corridors, C-2 zoning has transformed underutilized areas into thriving economic hubs. The advantages of C-2 zoning include increased commercial vibrancy, convenience for residents, mixed-use development, increased property values, and urban revitalization.
However, there are also potential challenges and disadvantages associated with C-2 zoning, such as traffic congestion, noise disturbances, the loss of community character, parking challenges, and pressure on infrastructure. It is important for municipalities and stakeholders to carefully consider these factors and prioritize the goals and visions of the community when implementing C-2 zoning regulations.
In conclusion, C-2 zoning provides a framework for creating vibrant, mixed-use commercial areas that enhance the quality of life for residents and contribute to the economic vitality of a city. By striking a balance between commercial activities, residential components, and well-planned infrastructure, C-2 zoning can create thriving neighborhoods where people can live, work, and play in harmony.
As urban areas continue to evolve, C-2 zoning will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of our cities. It is crucial for city planners, developers, and community members to work together to ensure that C-2 zoning is implemented thoughtfully and responsibly, in order to create livable, sustainable, and prosperous urban environments for all.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Does C-2 Zoning Mean
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.










0 thoughts on “What Does C-2 Zoning Mean”