Home>diy>Planning & Engineering>What Is Considered Light Industrial Zoning


Planning & Engineering
What Is Considered Light Industrial Zoning
Modified: October 20, 2024
Learn more about light industrial zoning and how it relates to planning and engineering. Gain insight into what is considered under this zoning classification.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
In the field of urban planning and land use, zoning plays a crucial role in determining how different areas of a city or town can be used. It helps create a balance between residential, commercial, and industrial activities. One important category of zoning is light industrial zoning, which is specifically designed to accommodate manufacturing, storage, and related activities.
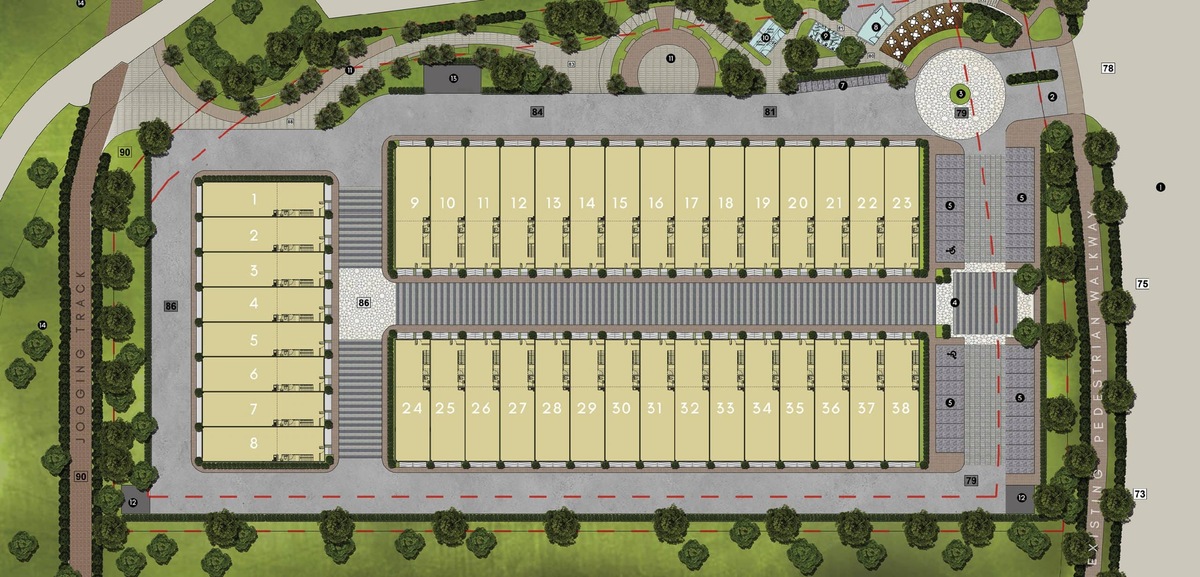
Light industrial zoning refers to the allocation of land for light manufacturing and small-scale industrial activities. It sets the guidelines and regulations for what types of businesses can operate in designated areas. This type of zoning is often found in areas near transportation hubs, such as airports, ports, or major highways, to enable efficient movement of goods and materials.
Light industrial zoning serves as a bridge between purely commercial and heavy industrial zoning. It allows for a diverse range of businesses that require more space and flexibility than might be available in commercial zones but don’t generate the noise, pollution, or heavy traffic associated with heavy industry. This zoning category aims to strike a balance between economic development and the well-being of nearby residential communities.
In this article, we will explore the various aspects of light industrial zoning, including its definition, characteristics, allowed uses, restrictions, benefits, as well as some examples of its implementation. Understanding these aspects will shed light on the importance and impact of light industrial zoning in our communities.
Key Takeaways:
- Light industrial zoning provides designated areas for manufacturing, research, and warehousing, balancing economic growth with community well-being. It fosters job creation, industrial diversity, and innovation while addressing environmental concerns and promoting urban planning.
- Challenges in light industrial zoning include land availability, neighborhood compatibility, infrastructure needs, and evolving industries. Overcoming these challenges requires comprehensive planning, community engagement, and effective regulations to ensure positive economic and social impacts.
Read more: What Is Considered Landscaping?
Definition of Light Industrial Zoning
Light industrial zoning, also known as industrial park zoning, is a specific category of land use zoning that designates certain areas for light manufacturing, warehousing, research and development, and other related industrial activities. It sets the parameters and regulations for how these areas can be developed and utilized.
Light industrial zoning typically outlines the specific types of businesses and industries that are allowed to operate within the designated areas. It may include a range of industries such as small-scale manufacturing, assembly, packaging, distribution, and storage. The purpose of this zoning category is to provide designated spaces for industrial activities that do not pose significant hazards or create excessive noise, pollution, or traffic.
Light industrial zones are often strategically located near transportation networks, such as highways, railways, or airports, to facilitate the movement of goods and materials. They are designed to accommodate businesses that require larger floor areas, higher ceiling heights, and more flexible layouts than what may be available in commercial or residential zones.
Under light industrial zoning regulations, there may be specific requirements regarding building setbacks, height limitations, parking provisions, and landscaping. These regulations help maintain a balance between industrial activities and the surrounding areas, ensuring compatibility with neighboring uses, such as residential or commercial properties.
It is important to note that the specific definitions and regulations for light industrial zoning can vary between different jurisdictions and municipalities. Local zoning codes and ordinances outline the specific criteria and requirements for this type of zoning, ensuring that it aligns with the overall goals and objectives of the community.
Characteristics and Purpose of Light Industrial Zones
Light industrial zones are characterized by several key features that distinguish them from other types of zoning categories. Understanding these characteristics is essential for comprehending the purpose and function of light industrial zoning.
1. Land Use: Light industrial zones are primarily designated for light manufacturing and related activities. They provide a suitable environment for businesses that require more space, larger buildings, and specialized infrastructure.
2. Infrastructure: Light industrial zones are equipped with the necessary infrastructure to support industrial activities. This may include roads with sufficient capacity for truck traffic, utility services such as electricity, water, and sewer, and sometimes specialized facilities like loading docks or rail connections.
3. Accessibility: Light industrial zones are often located near major transportation routes, making it easier for businesses to transport goods and materials to and from their facilities. Proximity to highways, railways, and airports enhances accessibility and reduces logistical challenges.
4. Zoning Regulations: Light industrial zones have specific regulations and restrictions in place to ensure proper land use and mitigate potential negative impacts on surrounding areas. This includes limitations on noise levels, air emissions, hours of operation, and setbacks from residential or sensitive zones.
5. Flexibility: Light industrial zones offer more flexibility for businesses’ operational needs. The larger lot sizes and building footprints allow for diversified uses, including manufacturing, storage, distribution, research and development, and office spaces.
The purpose of light industrial zones is to provide a suitable environment for businesses engaged in light manufacturing and related activities. These zones serve several important purposes:
1. Economic Development: Light industrial zones promote economic growth by attracting businesses that contribute to job creation and the local economy. These zones provide opportunities for the establishment of small-to-medium-sized enterprises, fostering entrepreneurship and innovation.
2. Industrial Diversity: Light industrial zones accommodate a diverse range of industries, from food processing to electronics assembly. This allows for a balanced mix of businesses, helping to avoid concentration in a single sector and promoting a more resilient and sustainable industrial ecosystem.
3. Environmental Considerations: By separating light industrial activities from residential and commercial areas, light industrial zones help minimize environmental impacts. The zoning regulations aim to prevent pollution, excessive noise, and other potential nuisances that could affect nearby communities.
4. Urban Planning: Light industrial zoning plays a crucial role in urban planning, ensuring that land is used efficiently and effectively. It helps create a well-structured city or town by designating appropriate areas for different types of activities, including industrial development.
Overall, light industrial zones provide the necessary framework and environment for businesses that fall within the scope of light industrial activities. They balance economic development with environmental considerations, promoting a harmonious coexistence between industries and neighboring communities.
Allowed Uses in Light Industrial Zones
Light industrial zones accommodate a wide range of businesses and activities that fall within the light industrial category. These zones are designed to provide suitable spaces for manufacturing, storage, and related operations. Some of the common allowed uses in light industrial zones include:
- Manufacturing: Light industrial zones allow for various types of manufacturing activities, such as assembly, fabrication, production, and packaging. These may include industries like textiles, electronics, furniture, machinery, food processing, and many others.
- Warehousing and Distribution: Light industrial zones are often utilized for warehousing and distribution centers. These facilities serve as storage hubs for products, inventory, and materials. Businesses involved in logistics or supply chain management often find light industrial zones ideal for their operations.
- Research and Development: Many light industrial zones allocate space for research and development (R&D) activities. These can include laboratories and facilities for scientific experimentation, testing, and innovation. Light industrial zones can foster collaboration and advancements in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and technology.
- Office Spaces: Light industrial zones may include provisions for office spaces, particularly for businesses that require a combination of industrial and administrative functions. These spaces can be used for management, administrative work, sales, and customer service.
- Storage Facilities: Light industrial zones often allow for the establishment of storage facilities, including self-storage units and warehouses. These are essential for businesses that require additional space to store their products, equipment, or raw materials.
- Service Industries: Some light industrial zones may permit certain service industries related to the light industrial activities. Examples may include repair and maintenance shops, equipment rental services, packaging and labeling services, or transportation companies.
The specific allowed uses in light industrial zones may vary based on local zoning regulations and the specific needs of each community. It is essential to consult local zoning ordinances or seek advice from urban planning authorities to ascertain the precise list of permitted uses in a particular light industrial zone.
It is worth noting that even within light industrial zones, there may be further sub-classifications based on the specific activities permitted. These sub-classifications can help ensure compatibility between businesses, prevent excessive impacts on neighboring properties, and maintain the overall character of the zone.
By providing suitable spaces for various industrial activities, light industrial zones support economic growth, job creation, and innovative developments. They offer a platform for businesses to thrive, contributing to the overall prosperity of the community.
Restrictions and Limitations in Light Industrial Zones
While light industrial zones offer flexibility and opportunities for businesses, they also come with specific restrictions and limitations to ensure compatibility with the surrounding community and mitigate potential negative impacts. These restrictions are put in place to maintain a balance between industrial activities and the well-being of nearby residents and businesses. Some common restrictions and limitations in light industrial zones include:
- Noxious or Hazardous Materials: Light industrial zones typically have restrictions on the storage or use of noxious or hazardous materials. This is to prevent potential risks to the environment, public health, and safety. Businesses may need to comply with specific regulations and obtain appropriate permits for handling such materials.
- Noise and Odor Levels: Zoning regulations often outline acceptable noise and odor levels that businesses must adhere to. Limits are set to minimize disturbances to nearby residential areas. Businesses using equipment or machinery that generate significant noise may have operating restrictions to ensure they operate within acceptable limits.
- Outdoor Storage and Display: Light industrial zones may have restrictions on outdoor storage or display of materials, products, or equipment. This helps maintain a visually appealing environment and prevent potential hazards or nuisances to neighboring properties.
- Hours of Operation: A light industrial zone may have specific hours of operation restrictions in place, particularly in relation to noise and traffic impacts. This ensures that businesses operate within reasonable hours to minimize disturbances to nearby residents.
- Signage: Regulations governing signage may apply to light industrial zones. This includes restrictions on the size, placement, and design of signs to maintain a visually cohesive environment and prevent visual clutter.
- Parking and Traffic: Light industrial zones typically have requirements for parking spaces to accommodate employees, customers, and delivery vehicles. Traffic management measures may also be in place to prevent congestion and ensure the safe movement of vehicles in and out of the zone.
- Setbacks and Buffer Zones: Zoning regulations often establish minimum setbacks and buffer zones between light industrial properties and residential or sensitive areas. These setbacks help minimize the potential impact of industrial activities on neighboring properties and maintain a harmonious coexistence.
It is crucial for businesses to be aware of these restrictions and limitations before establishing or operating in a light industrial zone. Adhering to these regulations not only ensures compliance with local laws but also helps foster positive relationships with the surrounding community.
Local zoning authorities and planning departments can provide specific details on the restrictions and limitations applicable to a particular light industrial zone. Consulting with these authorities early in the planning process is essential to ensure that businesses can meet the necessary requirements and operate responsibly within the designated zone.
By implementing these restrictions and limitations, light industrial zones aim to create a balance between industrial activities and the quality of life in surrounding areas. This helps create a sustainable and harmonious urban environment where different land uses can coexist effectively.
Light industrial zoning typically allows for activities such as small-scale manufacturing, warehousing, and distribution. It may also permit some commercial and office uses. Be sure to check local zoning regulations for specific allowed uses and restrictions.
Benefits of Light Industrial Zoning
Light industrial zoning provides several benefits for both communities and businesses. By designating specific areas for light manufacturing, warehousing, and related activities, light industrial zoning supports economic growth, promotes job creation, and maintains a balanced urban environment. Here are some key benefits of light industrial zoning:
- Economic Development: Light industrial zones attract businesses, leading to job creation and economic opportunities. These zones cater to industries that require larger floor areas, specialized infrastructure, and proximity to transportation networks. By providing suitable spaces for industrial activities, light industrial zoning contributes to local economic growth.
- Job Opportunities: Light industrial zones create employment opportunities for individuals with different skills and qualifications. These zones often support a variety of industries, from manufacturing to research and development, which require a diverse workforce. Job opportunities in light industrial zones can enhance the overall socio-economic well-being of the community.
- Industrial Diversity: Light industrial zoning encourages a diverse mix of industries within a community. By accommodating various sectors such as manufacturing, logistics, and research and development, these zones foster a robust and resilient industrial ecosystem. This diversity can help reduce dependency on a single industry and enhance the stability of the local economy.
- Infrastructure Development: Light industrial zones often require supportive infrastructure such as transportation networks, utilities, and other amenities. The development and maintenance of these infrastructures not only benefit the light industrial businesses but also improve overall connectivity and accessibility within the community.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: By designating specific areas for light industrial activities, zoning regulations help minimize the potential negative environmental impacts. These regulations ensure that businesses comply with noise, air quality, waste management, and other environmental standards, protecting the surrounding community and natural resources.
- Improved Urban Planning: Light industrial zoning plays a crucial role in urban planning by allocating appropriate spaces for different land uses. It helps create a well-structured city or town by strategically locating industrial activities near transportation hubs and separating them from residential or commercial areas. This zoning category ensures efficient land use and promotes a harmonious coexistence of diverse land uses within a community.
- Stimulated Innovation and Research: Light industrial zones often promote research and development activities alongside manufacturing. This fosters innovation, collaboration, and technological advancements within industries. By encouraging R&D, light industrial zoning can lead to the creation of new products, processes, and technologies that drive economic growth and enhance competitiveness.
Overall, light industrial zoning provides numerous benefits for the community, businesses, and the overall economy. It supports economic development, job opportunities, and infrastructure improvements, while also ensuring environmental protection and fostering innovation. The careful planning and implementation of light industrial zones contribute to creating sustainable and vibrant communities.
Comparison with Other Zoning Categories
Light industrial zoning plays a unique role in the overall zoning framework, particularly when compared to other categories such as residential, commercial, and heavy industrial zoning. Understanding the differences between these zoning categories is key to better appreciating the purpose and function of light industrial zoning.
Residential Zoning: Residential zoning is primarily intended for housing and associated activities. It aims to create neighborhoods where people can live comfortably and peacefully. Residential zones typically have restrictions on the type and scale of non-residential activities allowed, ensuring a predominantly residential character. In contrast, light industrial zoning focuses on accommodating non-residential activities related to manufacturing, storage, and research and development.
Commercial Zoning: Commercial zoning is designated for businesses involved in retail, office spaces, services, and entertainment. It caters to activities that directly serve consumers, such as shopping centers, restaurants, offices, and hotels. While light industrial zoning may include limited provisions for office spaces or certain service industries, its primary focus is on accommodating light manufacturing, warehousing, and related industrial activities. Commercial zones are usually more densely developed than light industrial zones and are often located in areas with high foot traffic and easy accessibility.
Heavy Industrial Zoning: Heavy industrial zoning, also known as industrial zoning, is designed for large-scale industrial activities that involve heavy machinery, hazardous materials, and significant environmental impacts. These zones are generally located away from residential areas due to the intensity of the operations. Heavy industrial zones are characterized by industries such as heavy manufacturing, chemical production, mining, and power generation. In contrast, light industrial zoning is more lenient in terms of environmental impacts and is often located near transportation hubs for efficient movement of goods.
Compared to these other zoning categories, light industrial zoning provides a middle ground between purely residential or commercial activities and heavy industrial operations. It allows for a range of light manufacturing, storage, and research and development activities that require larger spaces and specialized infrastructure, but with less impact on the surrounding environment and adjacent land uses.
Light industrial zoning offers a more diverse industrial environment compared to heavy industrial zones by accommodating various industries, catering to smaller-scale businesses, and encouraging innovation. However, it is important to note that light industrial zoning still implements regulations and restrictions to address potential nuisances to neighboring areas, such as noise, odor, or traffic congestion.
The proper balance between these various zoning categories is crucial in urban planning. It ensures that different land uses are appropriately situated within a community, promoting a well-functioning and harmonious environment that meets the needs of residents, businesses, and the overall economy. Light industrial zoning, in particular, provides a necessary space for businesses to operate and grow, contributing to economic development while maintaining compatibility with the surrounding community.
Challenges and Issues in Light Industrial Zoning
While light industrial zoning offers numerous benefits, there are also several challenges and issues that can arise in its implementation. These challenges stem from various factors such as land availability, neighborhood compatibility, infrastructure requirements, and evolving industry needs. Understanding and addressing these challenges are essential for effective light industrial zoning and successful urban planning. Here are some common challenges and issues:
- Land Availability: Finding suitable land for light industrial zones can be a challenge in urban areas with limited available space. Competition for land among various uses, such as residential and commercial, can restrict the allocation of land for light industrial purposes. Creative land-use strategies, such as repurposing brownfields or redevelopment in strategic locations, may help overcome this challenge.
- Neighborhood Compatibility: Balancing the needs of light industrial activities with the concerns of neighboring residential or commercial areas can be a challenge. Noise, traffic, pollution, and visual impacts are often cited as potential issues. Proper zoning regulations, buffer zones, setbacks, and design considerations can help mitigate these concerns and foster compatibility between light industrial activities and neighboring land uses.
- Infrastructure Requirements: Light industrial zones typically require specialized infrastructure, such as transportation networks, utility services, and access to resources. Ensuring sufficient infrastructure capacity and upgrading existing infrastructure to meet the needs of light industrial activities can be costly and complex. Collaboration between government authorities, utility providers, and private developers is crucial to address these infrastructure challenges in a coordinated manner.
- Changing Industry Landscape: The nature of light industrial activities is dynamic, and industries evolve over time. New technologies, automation, and changing market demands can impact the requirements of light industrial businesses. Zoning regulations need to be regularly updated to accommodate these changes, allowing for flexibility and adaptability within light industrial zones.
- Environmental Concerns: While light industrial activities are generally less environmentally intensive than heavy industrial operations, mitigating potential pollution or environmental impacts can still be a challenge. Proper regulations, monitoring systems, and enforcement mechanisms are necessary to ensure compliance with environmental standards and protect the health and well-being of the surrounding community.
- Community Engagement and Stakeholder Collaboration: Involving the community and stakeholders in the planning and decision-making process is essential to address concerns, build support, and enhance transparency. Engaging affected residents, businesses, local organizations, and community groups can help identify potential issues early on and work towards finding mutually beneficial solutions.
Confronting these challenges requires a comprehensive approach that takes into account the unique characteristics of each community. Developing clear and well-defined zoning regulations, conducting thorough impact assessments, promoting stakeholder collaboration, and implementing effective enforcement mechanisms are crucial steps in addressing the challenges and issues associated with light industrial zoning.
By proactively identifying and addressing these challenges, communities can harness the potential benefits of light industrial zoning while mitigating any negative impacts. This helps ensure that light industrial zones contribute positively to economic development, job creation, and the overall quality of life in the community.
Examples of Light Industrial Zoning Regulations
Light industrial zoning regulations can vary between jurisdictions and municipalities, as they are tailored to the specific needs and goals of each community. However, there are some common elements and examples of regulations that are often found in light industrial zoning. Here are a few examples:
- Permitted Uses: Light industrial zoning regulations outline the specific types of businesses and activities that are permitted within the designated zones. This may include manufacturing, storage, research and development, office spaces, and certain service industries.
- Building Size and Design Guidelines: Zoning regulations may include requirements for building sizes, heights, setbacks, and architectural design to ensure compatibility with the surrounding area. These guidelines help maintain a visually cohesive environment and prevent building structures that are out of character with the overall community aesthetic.
- Noise and Odor Control: Light industrial zones often have regulations in place to control noise levels and mitigate potential odors. These regulations ensure that industrial operations do not significantly disturb neighboring residential or commercial zones. Limits may be set for noise emissions during certain hours of the day or specific decibel thresholds.
- Parking and Traffic Management: Light industrial zoning regulations may include provisions for parking requirements to accommodate the needs of employees, customers, and delivery vehicles. They may also require implementing traffic management measures to avoid congestion and ensure safe traffic flow within the zone.
- Environmental Standards: Regulations pertaining to environmental standards are critical in light industrial zoning. These standards may include limits on air and water pollution, waste management requirements, and measures to protect local ecosystems. Compliance with these standards ensures sustainable and responsible industrial practices.
- Hours of Operation: Light industrial zones often have restrictions on operating hours to minimize nuisances such as noise during late night or early morning hours. These regulations help maintain a harmonious coexistence between industrial activities and nearby residential or commercial areas.
- Buffer Zones and Setbacks: Light industrial zoning often establishes buffer zones and setbacks from residential or sensitive areas. These regulations require a certain minimum distance between industrial properties and neighboring properties. Buffer zones help mitigate potential impacts on adjacent land uses and protect the quality of life of nearby residents.
It is important to note that these examples are not exhaustive, and the specific regulations may vary by jurisdiction. Local zoning ordinances, land use plans, and zoning maps provide detailed information on the specific regulations and requirements for light industrial zoning in a particular area.
Communities can also consider incorporating additional incentives or requirements in their light industrial zoning regulations to align with specific community goals. For example, they may offer tax incentives or grants to businesses that meet certain sustainability or job creation criteria. These additional measures can further support economic development and ensure that light industrial zoning aligns with the overall vision of the community.
By carefully considering and implementing well-crafted light industrial zoning regulations, communities can create an environment that fosters economic growth, supports responsible industrial practices, and preserves the overall well-being of the community.
Read more: What Is Considered A Wildflower
Conclusion
Light industrial zoning plays a vital role in urban planning, providing designated areas for light manufacturing, warehousing, and related industrial activities. It strikes a balance between economic development and the well-being of surrounding communities. By understanding the definition, characteristics, and purpose of light industrial zoning, we can appreciate its importance in creating vibrant and sustainable cities.
Allowed uses in light industrial zones range from manufacturing and research and development to warehousing and distribution. These zones support economic growth, job creation, and industrial diversity. However, they also come with restrictions and limitations to ensure compatibility with neighboring areas, including noise control, hours of operation, and setbacks.
Light industrial zoning offers numerous benefits, such as stimulating economic development, providing job opportunities, and promoting innovation. It also helps address environmental concerns, improves urban planning, and fosters a diverse industrial ecosystem. Nevertheless, there are challenges to overcome, including land availability, neighborhood compatibility, infrastructure requirements, and evolving industry needs.
The success of light industrial zoning hinges on comprehensive planning, community engagement, and effective regulations and enforcement. Examples of light industrial zoning regulations include defining permitted uses, setting building design guidelines, controlling noise and odors, managing parking and traffic, enforcing environmental standards, and establishing buffer zones and setbacks.
Ultimately, light industrial zoning contributes to the overall well-being and prosperity of communities. By providing a designated space for light industrial activities, it enables economic growth, job creation, and innovation while minimizing potential negative impacts on neighboring areas. The careful planning and implementation of light industrial zoning create a harmonious urban environment where businesses can thrive, residents can enjoy a high quality of life, and the community as a whole can prosper.
Eager to understand more about zoning types? If this discussion on light industrial zoning piqued your interest, you'll definitely want to check out our insight on commercial zoning. There, we delve into what defines commercial areas, the activities typically permitted, and how these spaces impact urban development. It's a perfect follow-up to broaden your understanding of urban planning and its effects on our daily surroundings.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is Considered Light Industrial Zoning
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.











0 thoughts on “What Is Considered Light Industrial Zoning”