Home>diy>Architecture & Design>What Is The Purpose Of A Floor Plan


Architecture & Design
What Is The Purpose Of A Floor Plan
Modified: March 6, 2024
Discover the importance of floor plans in architecture and design. Learn how these detailed visual representations provide a comprehensive understanding of space and functionality, enhancing the planning process.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
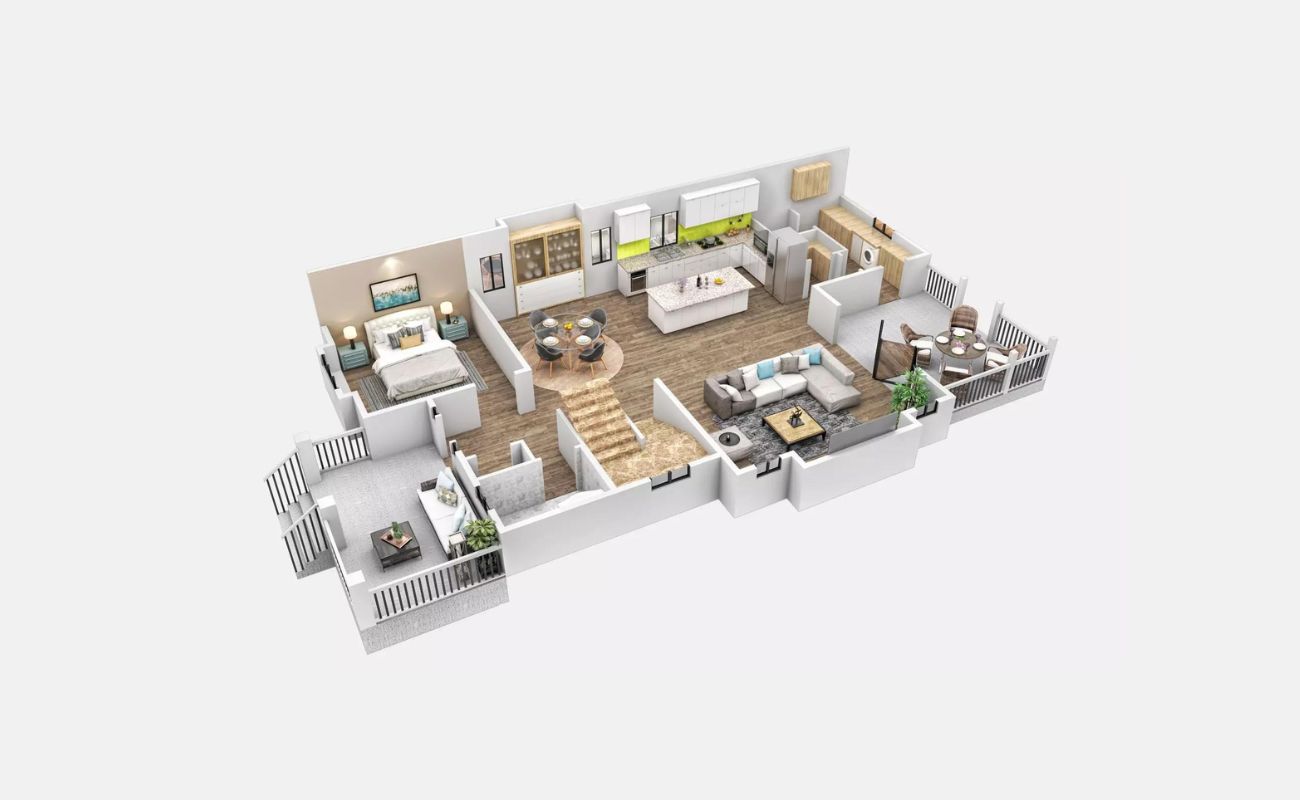
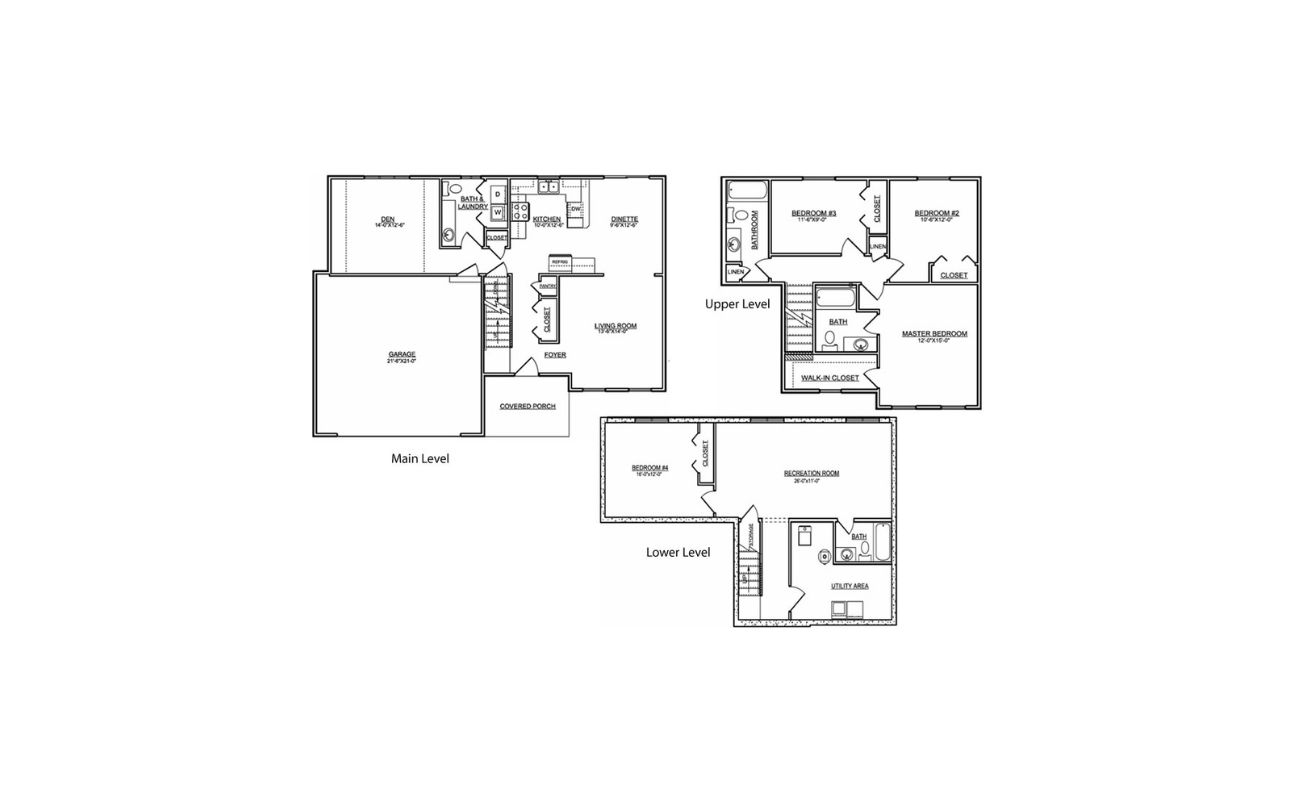
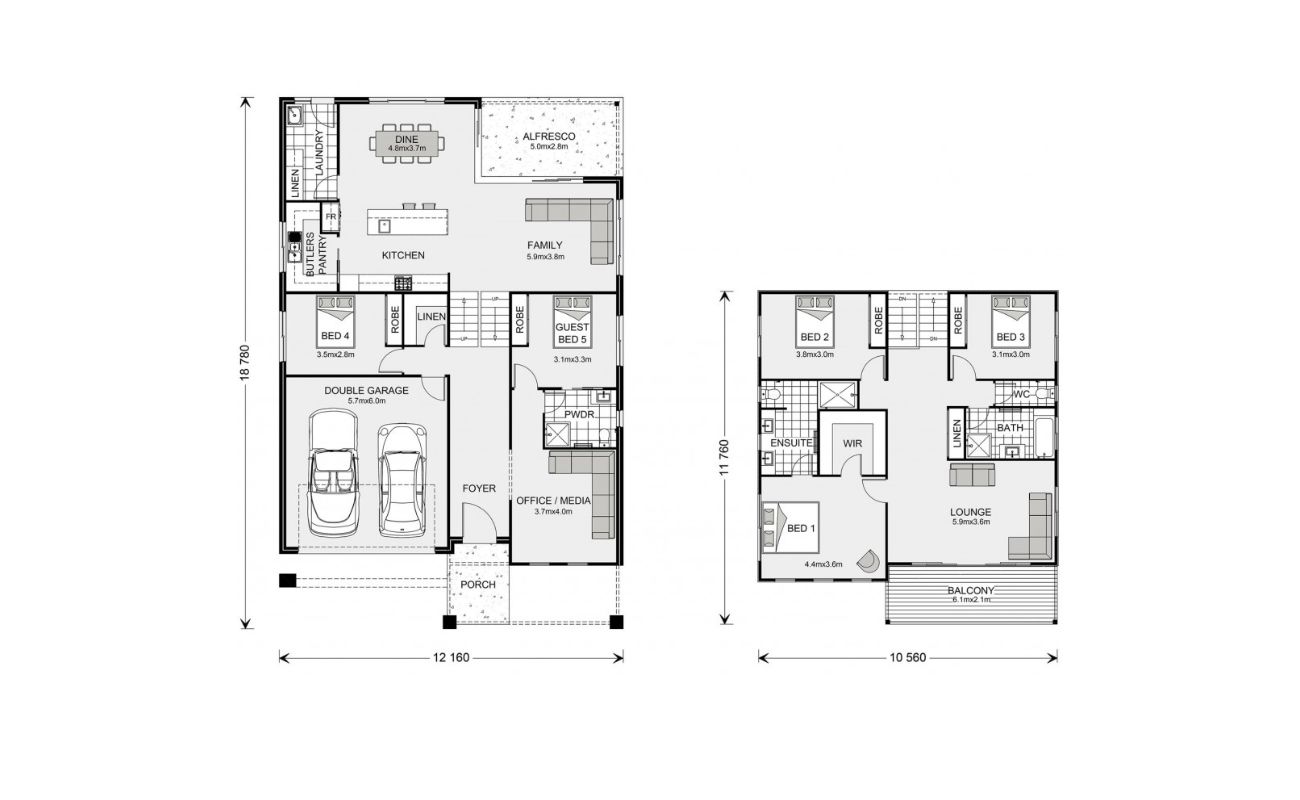
A floor plan is a visual representation of a building or space, showing the layout of rooms, walls, and other architectural features. It is an essential tool in the design and construction process, as well as in real estate, interior design, and home remodeling. A well-designed floor plan provides an accurate and detailed depiction of a space, allowing individuals to visualize how it will look and function.
In this article, we will explore the purpose of a floor plan, its importance, how to create one, the components that make up a floor plan, its functionality, how to analyze it, the benefits of a well-designed floor plan, and the factors to consider when designing one.
Whether you are a homeowner planning a renovation, a real estate agent showcasing a property, or an architect designing a new building, understanding the significance of a floor plan is crucial. So, let’s dive in and discover why floor plans are an integral part of the architectural design process.
Key Takeaways:
- A floor plan is like a map for a building, showing where everything goes. It helps people make smart decisions about how to use the space efficiently and make it look great.
- When designing a floor plan, it’s important to think about how people will move through the space, where to put furniture, and how to make the space comfortable and practical for everyone.
Read more: What Is A Floor Plan
Definition of a Floor Plan
A floor plan is a scaled diagram that showcases the arrangement and organization of rooms, walls, doors, windows, and other architectural elements within a building or space. It provides a bird’s eye view of the layout, offering a clear understanding of how different areas connect and interact with one another.
Floor plans are typically drawn to scale, with each unit of measurement representing a certain distance in real life. They can be created for various types of buildings, including residential homes, apartments, office spaces, retail stores, and more. Floor plans can be simple, showing only the basic layout, or they can be detailed, including specific measurements, furniture placement, and other intricate features.
These diagrams are created by architects, interior designers, and engineers as part of the design process. They serve as a blueprint for constructing or remodeling a space, guiding contractors and builders in executing the project. Floor plans are also used in real estate to showcase properties to potential buyers or renters, helping them visualize the layout and flow of the space.
With the advancements in technology, floor plans can now be created using computer-aided design (CAD) software or online floor planning tools. This allows for greater precision, flexibility, and the ability to easily make changes or modifications to the design.
Overall, a floor plan acts as a visual representation of the architectural design, illustrating the spatial relationships and overall flow of a building or space. It is an essential tool in the construction and design industry, providing a foundation for effective communication and decision-making throughout the project.
Importance of a Floor Plan
A floor plan plays a crucial role in the architectural design process and has several key benefits. Let’s explore the importance of a floor plan:
- Visualizing Space: A floor plan allows individuals to visualize the layout and organization of a building or space. It provides a comprehensive overview of the size, shape, and arrangement of rooms, helping to understand how each area relates to one another. This visual representation helps architects, interior designers, and homeowners to make informed decisions about the design and functionality of the space.
- Efficient Use of Space: A well-designed floor plan ensures the efficient use of available space. It allows for effective utilization of every square foot, optimizing room sizes, circulation paths, and storage areas. By carefully planning the arrangement of rooms and their functions, unnecessary wasted space can be minimized, resulting in a more practical and functional layout.
- Workflow and Traffic Flow: A floor plan takes into account the flow of people within a space. It considers how individuals will move through the rooms and navigate through hallways, ensuring a logical and efficient flow of traffic. By strategically placing doors, windows, and hallways, a well-designed floor plan can enhance the overall traffic flow and improve the usability of the space.
- Furniture Placement and Spatial Arrangement: A floor plan helps in determining the placement of furniture and other furnishings within a space. By understanding the dimensions and layout of rooms, furniture can be arranged in a way that optimizes available space and creates balanced and inviting living or working environments. Additionally, a floor plan can assist in identifying areas where built-in furniture or storage solutions can be incorporated for added functionality.
- Effective Communication: Floor plans act as a common language between architects, designers, contractors, and clients. They provide a clear and standardized representation of the design intent, allowing for effective communication and collaboration among various stakeholders. With a visual reference, everyone involved in the project can better understand the design goals and requirements.
Overall, a floor plan is a vital tool in the architectural and design process. It not only helps in visualizing space and optimizing its functionality but also facilitates effective communication and decision-making. By investing time and effort into creating a well-designed and thoughtful floor plan, the end result is a harmonious and functional space that meets the needs and desires of its occupants.
Creating a Floor Plan
Creating a floor plan requires careful consideration and attention to detail. While it may seem like a daunting task, with the right tools and approach, anyone can create a basic floor plan. Here are the steps to guide you in creating your own floor plan:
- Measure and Sketch: Start by measuring the dimensions of the space you want to create a floor plan for. Use a tape measure to accurately measure the length and width of each room, as well as the positions of doors, windows, and other architectural features. Sketch a rough outline of the space on graph paper or use online floor planning software as a visual reference.
- Determine Scale: Choose a scale that will accurately represent your space on paper. For example, 1 inch on the paper can represent 1 foot in real life. This will ensure that your floor plan is to scale and provides an accurate representation of the space. Use a ruler or scale ruler to measure and draw the walls and other features of your space in the right proportions.
- Add Walls and Rooms: Start by drawing the walls of your space on the floor plan. Use straight lines to represent the walls and ensure they align with the measurements you took earlier. Next, add rooms by drawing internal walls to divide the space into separate areas. Keep in mind the flow and functionality of the rooms as you determine their positions and sizes.
- Include Doors and Windows: Indicate the positions of doors and windows on your floor plan. Draw them to scale and make sure they are accurately placed according to the dimensions you measured. Doors should open in the direction they do in reality, and windows should be drawn to reflect their size and shape. These elements are essential for understanding the flow and natural light of the space.
- Add Furniture and Fixtures: Once the basic structure of your floor plan is complete, you can start adding furniture and fixtures. Consider the purpose of each room and the necessary items that need to be included. Use simple shapes or symbols to represent furniture, such as rectangles for beds or sofas and circles for tables or chairs. Experiment with different furniture arrangements to find the best fit for your space.
- Label and Annotate: Label different rooms, doors, windows, and other notable features on your floor plan. Use clear and descriptive labels that will help others understand the layout of the space. Additionally, consider adding annotations or notes to highlight specific details or requirements that pertain to the design or functionality of the space.
- Review and Refine: Take the time to review your floor plan and make any necessary adjustments or refinements. Ensure that all measurements and proportions are accurate and that the layout makes sense functionally. Seek feedback from others, such as architects or interior designers, to further improve your floor plan.
Remember, creating a floor plan takes practice and patience. It’s important to start with a simple design and gradually increase its complexity as your skills develop. Additionally, there are various software options available that can simplify the process and provide additional features and functionality for creating detailed floor plans.
By following these steps and utilizing the right tools, you can create a floor plan that accurately represents the layout and design of your space, aiding in the visualization and planning of your architectural or interior design project.
Components of a Floor Plan
A floor plan consists of various components that work together to provide a comprehensive representation of a building or space. Understanding these components is essential for interpreting and analyzing floor plans. Let’s explore the key components of a floor plan:
- Walls: The walls of a floor plan are represented by straight lines that outline the different rooms and areas of the space. They indicate the division between rooms and define the overall layout and structure of the building.
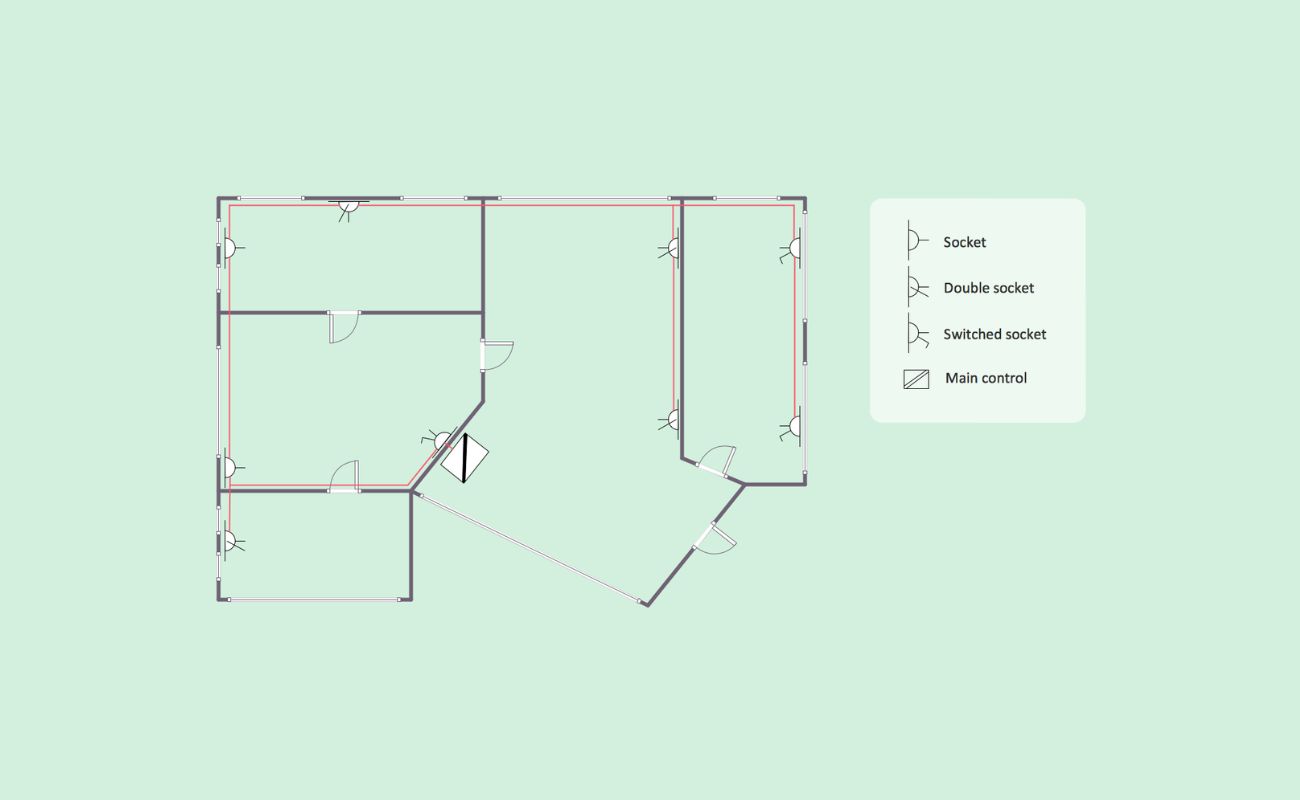
- Doors and Windows: Doors and windows are depicted with specific symbols or lines on the floor plan. They illustrate the entry and exit points of a room and the natural light sources within the space.
- Rooms and Areas: The floor plan shows the different rooms and areas within the building. Each room is labeled and may include dimensions to indicate its size. The arrangement of these rooms creates the overall functionality and flow of the space.
- Furniture and Fixtures: Furniture and fixtures are often included in a floor plan to showcase the placement and layout of these elements within a room. Symbols or simple shapes are used to represent items such as beds, sofas, tables, and chairs.
- Measurements and Dimensions: Floor plans include measurements and dimensions to provide an accurate representation of the space. These measurements indicate the length and width of rooms, the positions of walls, doors, and windows, and the overall size of the building.
- Text and Labels: Labels and text are used to provide additional information and context within the floor plan. This includes room labels, annotations for fixtures or special features, arrows for circulation paths, and other descriptive text that aids in understanding the layout and design of the space.
- Symbols and Legends: Floor plans often incorporate a legend or key that explains the symbols and markings used throughout the plan. This helps in understanding the meaning and representation of various elements, such as the symbols for doors, windows, furniture, or fixtures.
- Scale: The scale of a floor plan is represented by a ratio or fraction that indicates how much the drawing has been reduced in size from the actual measurements. This ensures that the floor plan accurately depicts the real-life dimensions and proportion of the space.
These components work together to create a comprehensive and informative floor plan. They help in understanding the layout, functionality, and overall design of a building or space, serving as a visual guide for architects, designers, and homeowners.
It’s important to note that not all floor plans include the same level of detail. Some may focus on the basic layout and structural elements, while others may provide more intricate details, such as plumbing or electrical fixtures. The level of detail depends on the purpose and intended use of the floor plan.
By familiarizing yourself with these components, you’ll be able to analyze and interpret floor plans effectively, gaining a deeper understanding of how a building or space is designed and organized.
A floor plan is a visual representation of a space, showing the layout and dimensions. It helps to understand the flow of a space, plan furniture placement, and visualize the overall design.
Read more: What Is An In-Law Floor Plan
Functionality of a Floor Plan
A floor plan serves as a crucial tool in understanding the functionality and usability of a building or space. It provides valuable insights into how the various elements work together to create a comfortable and efficient environment. Let’s explore the key aspects of the functionality of a floor plan:
- Space Organization: A well-designed floor plan organizes the space in a logical and efficient manner. It considers the flow of movement between rooms, the placement of furniture, and the arrangement of fixtures and amenities. By strategically organizing the space, a floor plan ensures that it is both pleasing to the eye and practical to navigate.
- Room Functionality: Each room within a floor plan has a specific purpose, and the layout and design of the space should reflect this functionality. For example, a kitchen should have easy access to a dining area and be equipped with the necessary appliances and storage. Similarly, bedrooms should have adequate space for a bed and storage and provide privacy from other areas of the home.
- Optimal Use of Space: A floor plan aims to make the most efficient use of available space. It considers the size and shape of rooms and ensures that there is minimal wasted space. By optimizing the layout, a floor plan enables individuals to utilize their space effectively, whether it’s for living, working, or entertaining.
- Natural Light and Ventilation: The placement of windows and doors within a floor plan plays a significant role in the functionality of a space. Natural light and ventilation are essential for creating a comfortable and healthy environment. A well-designed floor plan considers the position and size of windows to maximize natural light and provides adequate openings for ventilation.
- Accessibility: Accessibility is an important aspect of functionality in a floor plan. It ensures that the space is easily accessible to all individuals, regardless of their mobility limitations. A well-designed floor plan incorporates features such as wide doorways, ramps, and accessible bathrooms to accommodate individuals with disabilities or special needs.
- Storage and Organization: Adequate storage space is essential for maintaining a clutter-free and functional environment. A floor plan should consider the inclusion of closets, cabinets, and storage areas to provide ample room for belongings. By incorporating well-designed storage solutions, a floor plan helps individuals stay organized and promotes efficient use of space.
- Privacy: The functionality of a floor plan also accounts for privacy needs. It ensures that rooms requiring privacy, such as bedrooms or home offices, are appropriately positioned to minimize interruptions and external noise. Additionally, the layout should consider the placement of windows and doors to preserve privacy between different areas of the home.
By prioritizing functionality, a floor plan creates a harmonious and efficient living or working environment. It takes into account the specific requirements of the individuals using the space, offering a thoughtful and user-centered design.
When designing or reviewing a floor plan, it’s important to consider not only the aesthetics but also the functionality of the space. By striking a balance between form and function, a floor plan can enhance the overall usability and enjoyment of a building or space.
Analyzing a Floor Plan
Analyzing a floor plan is a crucial step in understanding the layout, functionality, and potential of a space. It allows individuals to assess the various components and features of the floor plan and make informed decisions about its design and utilization. Here are some key aspects to consider when analyzing a floor plan:
- Layout and Flow: Assess the overall layout and flow of the space. Consider how rooms are connected and the ease of movement between them. A well-designed floor plan will have a logical flow, with smooth transitions between different areas.
- Room Proportions and Sizes: Examine the proportions and sizes of individual rooms. Ensure that they are adequate for their intended purposes. Take note of any rooms that may be too small or excessively large, as this can impact the functionality and usability of the space.
- Natural Light and Views: Evaluate the placement of windows and doors to determine the potential for natural light and views. Consider the orientation of the building and how it may affect the amount of natural light that enters the space. Well-placed windows can enhance the overall ambiance of a room and provide pleasant views.
- Furniture Placement: Visualize how furniture will fit within the rooms. Consider the positioning of walls, doors, and windows in relation to furniture placement. Ensure that there is ample space for movement and that furniture can be arranged without obstructing walkways or blocking key elements.
- Functionality and Practicality: Evaluate how well the floor plan meets the functional needs of the occupants. Consider whether the layout is suitable for daily activities, such as cooking in the kitchen or entertaining in the living area. Determine if there are any areas that may pose challenges or require modifications for better practicality.
- Storage and Organization: Assess the availability of storage spaces within the floor plan. Consider if there are sufficient closets, cabinets, or built-in storage options to accommodate belongings. Adequate storage is essential for maintaining a tidy and organized living or working environment.
- Accessibility: Consider the accessibility of the space, especially for individuals with mobility limitations. Evaluate the width of doorways, the presence of steps or ramps, and the layout of bathrooms to ensure that the floor plan is inclusive and accessible to everyone.
- Flexibility for Future Changes: Think about the potential for future modifications or adaptations. Determine if the floor plan allows for flexibility and scalability, should the needs of the occupants change over time. A well-designed floor plan will accommodate potential modifications without compromising the overall functionality and flow of the space.
By analyzing these aspects of a floor plan, individuals can make informed decisions and identify areas for improvement or customization. It is important to consider personal preferences, lifestyle requirements, and specific needs when evaluating a floor plan. Seek advice from professionals such as architects or interior designers who can provide expert insights and suggestions throughout the analysis process.
Remember that a floor plan is a blueprint for the overall design and function of a space. By critically analyzing and evaluating the floor plan, individuals can ensure that the final design meets their needs, preferences, and aspirations.
Benefits of a Well-Designed Floor Plan
A well-designed floor plan can have a significant impact on the functionality, aesthetics, and overall enjoyment of a space. Whether it’s a residential home, office, or retail establishment, a thoughtfully designed floor plan offers several key benefits. Let’s explore some of the benefits of a well-designed floor plan:
- Optimized Use of Space: A well-designed floor plan ensures that every square foot of the space is utilized efficiently. It eliminates wasted areas, maximizes usable space, and provides practical solutions for storage, furniture placement, and circulation paths. This optimization allows for a more functional and comfortable living or working environment.
- Improved Flow and Traffic Patterns: A good floor plan considers the flow and traffic patterns within a space. It strategically positions rooms, doors, and hallways to create logical pathways and minimize congestion. With a well-designed floor plan, movement becomes effortless, and the space feels more open and inviting.
- Enhanced Natural Light and Views: A well-designed floor plan takes advantage of natural light and views. It incorporates large windows, skylights, or glass walls in areas where natural light is abundant. This not only reduces the need for artificial lighting but also brings in the beauty of the surrounding environment, creating a bright and uplifting atmosphere.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: A well-designed floor plan allows for flexibility and adaptability over time. It takes into consideration the potential changes in lifestyle, needs, or family size. Such a floor plan can be easily modified or customized to accommodate future renovations or modifications, offering long-term usability and value.
- Optimal Privacy and Noise Control: A well-designed floor plan considers privacy and noise control. It strategically places bedrooms and private areas away from high-traffic zones or noisy areas. This design approach ensures that individuals can enjoy a peaceful and undisturbed living or working environment.
- Efficient Energy Usage: A well-designed floor plan integrates energy-efficient features. It considers the positioning of windows to optimize natural ventilation and reduce the need for artificial cooling or heating. It may also incorporate efficient insulation and lighting solutions, reducing energy consumption and lowering utility costs.
- Enhanced Safety and Accessibility: A well-designed floor plan prioritizes safety and accessibility. It ensures clear and unobstructed pathways, adequate lighting in hallways and staircases, and adheres to building codes and regulations. Additionally, it can incorporate features such as ramps or wide doorways to accommodate individuals with mobility limitations.
- Increased Property Value: A well-designed floor plan enhances the value of a property. It attracts potential buyers or tenants, as it provides an appealing and functional living or working space. A property with a well-designed floor plan often commands a higher selling or rental price, making it a valuable investment.
Overall, a well-designed floor plan offers numerous benefits, from improved functionality and efficiency to enhanced aesthetics and value. It creates a harmonious and comfortable environment that aligns with the needs and preferences of the occupants. Whether it’s a residential, commercial, or institutional space, investing in a well-designed floor plan is a wise decision that pays off in the long run.
Factors to Consider in Designing a Floor Plan
Designing a floor plan is a complex task that requires careful consideration of various factors. It involves striking a balance between functionality, aesthetics, and the specific needs of the occupants. Whether you’re designing a new space or remodeling an existing one, here are some key factors to consider in the process of designing a floor plan:
- Functionality: Consider how the space will be used and design the floor plan to optimize functionality. Determine the number and size of rooms required and their relationships to one another. Prioritize the flow and efficiency of movement within the space to ensure that the layout meets the specific needs of the occupants.
- Space Requirements: Assess the space requirements of each room or area. Consider the intended use of the space and allocate adequate square footage accordingly. Determine the size and dimensions of rooms, ensuring that they are proportionate to their purpose and allow for comfortable movement and furniture placement.
- Natural Light and Views: Harness the power of natural light and views in your floor plan design. Position windows strategically to maximize the amount of daylight entering the space and to make the most of any desirable views. Consider the orientation of the building and the impact it will have on the availability of natural light throughout the day.
- Privacy and Noise Control: Incorporate appropriate measures to ensure privacy and minimize noise disturbances within the space. Strategically place bedrooms and areas that require privacy away from high-traffic zones or noisy areas. Consider using sound-absorbing materials, insulation, or structural design elements to minimize noise transmission between rooms.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Plan for future needs and potential changes within the space. Design the floor plan to allow for flexibility and adaptability, so that it can accommodate evolving requirements. Consider factors such as potential growth of the family, changing work-from-home trends, or the possibility of converting spaces for different purposes over time.
- Storage Solutions: Incorporate sufficient storage space within the floor plan. Evaluate the storage needs of the occupants and consider built-in storage options such as closets, cabinets, and shelving. Cleverly integrate storage solutions into the design to minimize clutter and maintain a clean and organized living or working environment.
- Accessibility: Ensure that the floor plan is accessible to all individuals, regardless of their mobility. Incorporate features such as wide doorways, ramps, or lifts to provide easy access for individuals with disabilities or mobility challenges. Consider the positioning of amenities such as bathrooms, kitchens, and laundry rooms to facilitate convenient and barrier-free use.
- Aesthetics: Balance functionality with aesthetics to create an appealing and visually pleasing space. Consider the overall design style, colors, materials, and finishes to achieve a cohesive and harmonious aesthetic. Incorporate architectural features and design elements that reflect the desired atmosphere and character of the space.
- Building Codes and Regulations: Ensure compliance with local building codes and regulations when designing the floor plan. Familiarize yourself with the relevant guidelines pertaining to room dimensions, clearances, egress requirements, and safety standards. This will help avoid costly design changes and ensure the project proceeds smoothly.
By carefully considering these factors during the floor plan design process, you can create a space that aligns with the functional needs, lifestyle preferences, and aesthetic goals of the occupants. Collaborating with professionals such as architects, interior designers, or builders can provide valuable insights and expertise throughout the design journey.
Remember, designing a floor plan is a creative and iterative process that requires attention to detail, open communication, and flexibility. By keeping these factors in mind, you can create a successful floor plan that fulfills both practical requirements and personal preferences.
Read more: What Is A Bunkhouse Floor Plan
Conclusion
A well-designed floor plan is a critical element in the architectural design process. It serves as a visual guide that presents the layout, organization, and functionality of a space. By taking into account factors such as functionality, space utilization, natural light, privacy, and accessibility, a floor plan can create a harmonious and efficient living or working environment.
Throughout this article, we have explored the various components and benefits of a well-designed floor plan. We have discussed how a floor plan helps with visualizing space, optimizing its functionality, and facilitating efficient traffic flow. We have also touched upon the importance of incorporating natural light, privacy considerations, and storage solutions within the floor plan.
Furthermore, we have highlighted the analytical aspect of floor plans, emphasizing the need to assess the layout, proportions, and functionality of the space. Understanding the functionality of a floor plan allows individuals to make informed decisions, ensuring their design meets their specific needs and preferences.
In conclusion, a well-designed floor plan offers a multitude of benefits, including optimized space usage, improved flow and circulation, enhanced natural light and views, increased privacy, and efficient energy usage. It provides a solid foundation for creating comfortable, practical, and visually appealing spaces.
When designing a floor plan, it is crucial to consider factors such as functionality, space requirements, natural light, privacy, adaptability, storage, accessibility, aesthetics, and compliance with building codes. By incorporating these considerations into the design process, you can create a floor plan that aligns with the needs, preferences, and aspirations of the occupants.
Whether you are designing your dream home, planning a renovation, or working on a commercial space, investing time and effort into creating a well-designed floor plan will undoubtedly result in a space that is functional, inviting, and tailored to your specific requirements.
So, take the time to carefully analyze, plan, and refine your floor plan to ensure it is a true reflection of your vision and a blueprint for an exceptional living or working environment.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is The Purpose Of A Floor Plan
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.







0 thoughts on “What Is The Purpose Of A Floor Plan”