Home>Furniture & Design>Interior Design Trends>How To Read A Glass Thermometer

Interior Design Trends
How To Read A Glass Thermometer
Published: February 4, 2024
Learn how to read a glass thermometer and stay updated on the latest interior design trends. Master the art of temperature measurement and design aesthetics.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
A glass thermometer is a simple yet essential tool used to measure temperature accurately. Whether you're monitoring the temperature of a feverish child, checking the ambient temperature in a room, or ensuring the ideal temperature for a scientific experiment, understanding how to read a glass thermometer is a valuable skill.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of reading a glass thermometer, providing you with the knowledge and confidence to interpret temperature readings with precision. From understanding the various parts of a glass thermometer to mastering the art of taking accurate readings, this article will equip you with the expertise needed to navigate the world of temperature measurement.
As we embark on this journey, it's important to note that the ability to read a glass thermometer extends beyond mere practicality. It offers a glimpse into the fascinating realm of thermal dynamics, where the behavior of substances is intimately tied to their temperature. By mastering the art of reading a glass thermometer, you gain insight into the fundamental principles that govern the physical world around us.
So, let's embark on this enlightening exploration of glass thermometers, unraveling the nuances of temperature measurement and empowering you with the skills to interpret temperature readings with confidence and accuracy.
Key Takeaways:
- Mastering the art of reading a glass thermometer helps you understand temperature better and make accurate measurements for things like fever, room temperature, and science experiments.
- To use a glass thermometer safely, handle it with care, be patient when taking readings, and follow proper disposal and storage guidelines to prevent accidents and exposure to hazardous substances.
Read more: How To Read A Glass Barometer
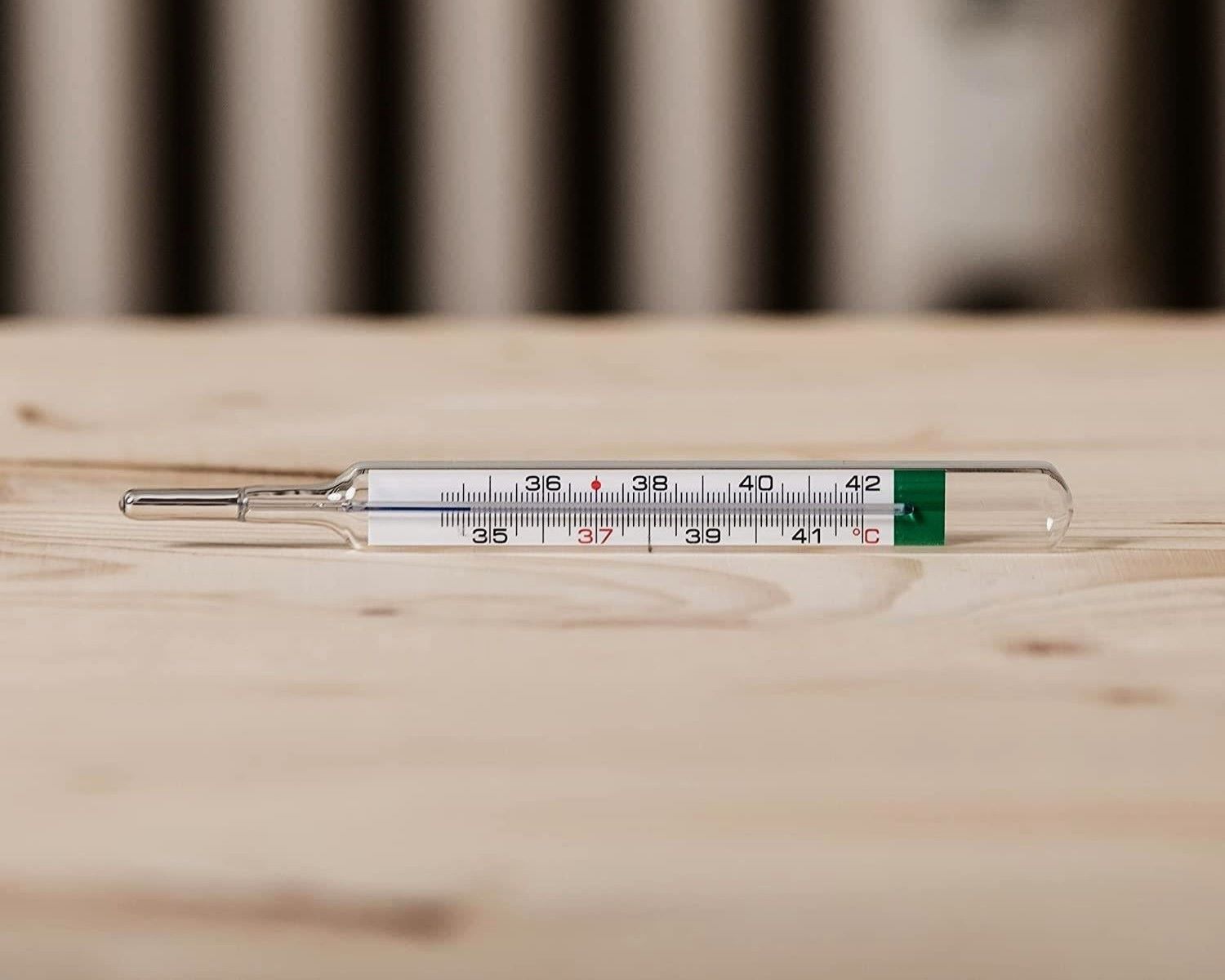
Understanding the Parts of a Glass Thermometer
A glass thermometer comprises several essential components that collectively enable accurate temperature measurement. Understanding these parts is crucial for interpreting temperature readings effectively. Here's a detailed overview of the key elements:
-
Bulb: The bulb, located at the base of the glass thermometer, contains a specialized liquid, typically mercury or colored alcohol. This liquid expands and contracts in response to temperature changes, facilitating precise temperature measurement.
-
Capillary Tube: Extending from the bulb, the capillary tube is a narrow, elongated channel within the glass thermometer. The capillary tube allows the liquid to rise and fall in response to temperature variations, providing a visual indication of the temperature.
-
Temperature Scale: Running parallel to the capillary tube, the temperature scale is marked with numerical increments that correspond to specific temperature values. This scale allows for the precise measurement and interpretation of temperature readings.
-
Meniscus: When taking temperature readings, it's essential to observe the meniscus, which refers to the curved surface of the liquid within the capillary tube. The position of the meniscus relative to the temperature scale indicates the current temperature.
-
Markings and Graduations: The temperature scale is adorned with markings and graduations that denote specific temperature intervals. These markings enable accurate temperature interpretation and ensure consistency in readings.
By familiarizing yourself with these fundamental components, you gain a comprehensive understanding of how a glass thermometer functions and how to interpret temperature measurements effectively. This knowledge forms the cornerstone of accurate temperature assessment, laying the groundwork for precise and reliable readings in various settings.
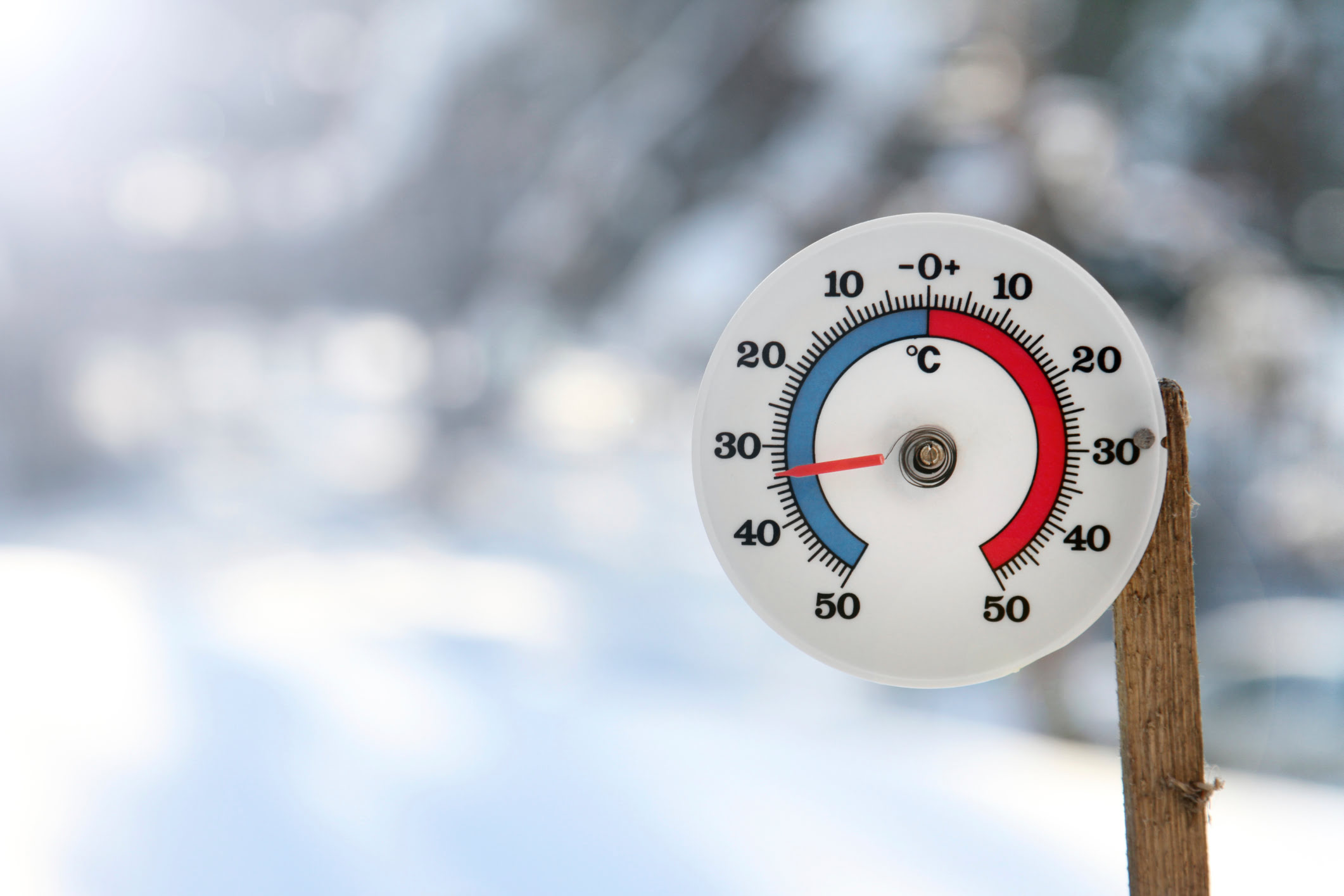
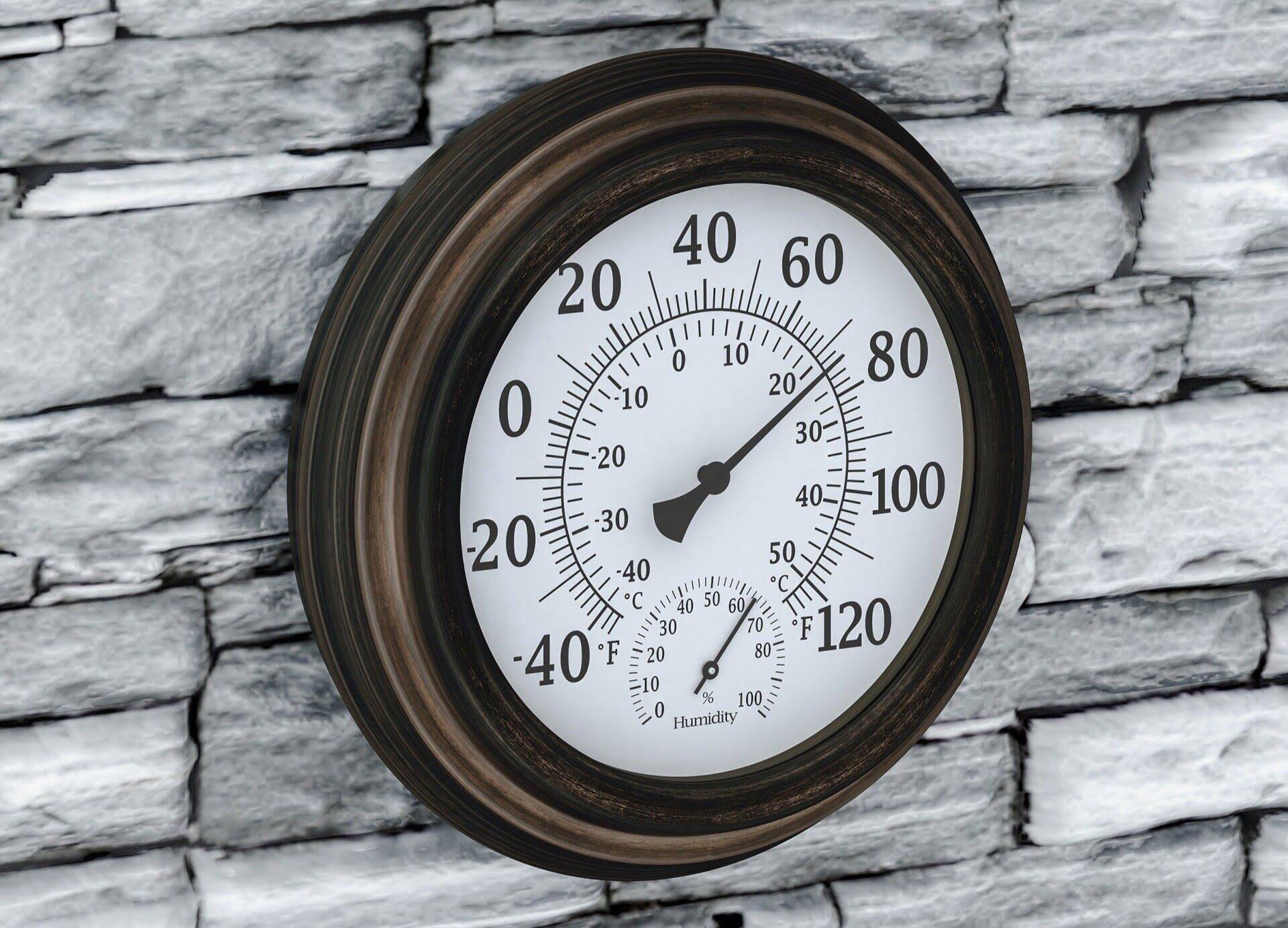
Reading the Temperature Scale
Reading the temperature scale on a glass thermometer is a fundamental aspect of accurately interpreting temperature measurements. The temperature scale, typically marked with numerical increments, provides a visual representation of the current temperature based on the position of the liquid within the capillary tube. Mastering the art of reading the temperature scale is essential for obtaining precise temperature readings in diverse scenarios.
When reading the temperature scale on a glass thermometer, it's crucial to observe the meniscus, which refers to the curved surface of the liquid within the capillary tube. The meniscus plays a pivotal role in determining the exact temperature, as its position relative to the markings on the temperature scale indicates the current temperature value. To ensure accuracy, it's important to view the thermometer at eye level when assessing the position of the meniscus. This perspective minimizes parallax errors and facilitates more precise temperature readings.
The temperature scale is adorned with markings and graduations that denote specific temperature intervals. These markings enable users to identify the temperature with a high degree of accuracy. Whether the thermometer employs the Celsius or Fahrenheit scale, each numerical increment corresponds to a specific temperature value, allowing for precise temperature assessment.
In the case of a Celsius thermometer, the temperature scale typically ranges from -10°C to 110°C, with each small increment representing one degree Celsius. The larger markings, often denoting five-degree intervals, serve as convenient reference points for quick temperature assessment. Similarly, a Fahrenheit thermometer features a scale spanning from 0°F to 220°F, with each small division representing one degree Fahrenheit. The prominent markings at ten-degree intervals offer a quick gauge of the temperature.
When reading the temperature scale, it's essential to identify the exact position of the meniscus in relation to the markings on the scale. By aligning the meniscus with the appropriate numerical increment, you can accurately determine the temperature. This precision is particularly crucial in scenarios where minute temperature differentials hold significant implications, such as in scientific experiments, medical applications, or culinary endeavors.
Mastering the art of reading the temperature scale empowers individuals to gauge temperature variations with confidence and precision. Whether it's discerning subtle changes in ambient temperature or monitoring critical thermal conditions, the ability to interpret the temperature scale effectively is a valuable skill that transcends diverse domains.
By honing your proficiency in reading the temperature scale, you elevate your capacity to navigate the intricate world of temperature measurement, unlocking a realm where precision and insight converge to unveil the mysteries of thermal dynamics.
Taking Accurate Readings
Taking accurate readings with a glass thermometer is a meticulous process that demands precision and attentiveness. Whether you're measuring body temperature, monitoring environmental conditions, or conducting scientific experiments, the ability to obtain precise temperature readings is paramount. Here's a comprehensive guide to mastering the art of taking accurate readings with a glass thermometer.
Proper Handling and Placement
To ensure accurate readings, it's essential to handle the glass thermometer with care and precision. When using a clinical thermometer to measure body temperature, position the individual in a comfortable and relaxed state. Place the thermometer under the tongue, in the armpit, or rectally, ensuring proper contact with the body to facilitate an accurate temperature assessment. For environmental temperature measurements, position the thermometer in the desired location, allowing it to acclimate to the surroundings for a few minutes before taking the reading.
Read more: How To Read A Storm Glass
Observation and Patience
Upon placing the glass thermometer in the designated location, it's crucial to observe the thermometer diligently and exercise patience. The thermometer requires sufficient time to register the temperature accurately. For clinical thermometers, it's recommended to wait for at least three minutes to obtain a precise body temperature reading. During this period, maintain a steady gaze on the thermometer, ensuring that it remains undisturbed to prevent inaccuracies in the temperature assessment.
Eye-Level Assessment
When the designated time has elapsed, it's time to read the temperature indicated on the glass thermometer. To ensure accuracy, position yourself at eye level with the thermometer, aligning your line of sight with the temperature scale. This perspective minimizes parallax errors and facilitates a clear view of the meniscus, enabling you to interpret the temperature reading with precision.
Recording and Interpretation
Upon obtaining the temperature reading, record the value promptly to prevent any discrepancies. Whether documenting body temperature for medical purposes or noting environmental temperature variations, accurate record-keeping is essential for future reference and analysis. Additionally, interpret the temperature reading based on the specific scale used, whether Celsius or Fahrenheit, and consider any relevant contextual factors that may influence the temperature assessment.
Calibration and Maintenance
Regular calibration and maintenance of the glass thermometer are crucial for ensuring accurate readings. Periodically verify the accuracy of the thermometer by comparing it with a certified reference thermometer or calibration device. Additionally, store the thermometer in a protective case and handle it with care to prevent damage or inaccuracies that may compromise its performance.
By adhering to these guidelines and practicing diligence in taking temperature readings, individuals can master the art of obtaining accurate and reliable measurements with a glass thermometer. Whether in clinical, environmental, or scientific settings, the ability to take precise temperature readings is a valuable skill that underpins numerous applications and contributes to informed decision-making based on reliable temperature data.
Read more: Why Are Glass Thermometers Rarely Used Today
Safety Precautions
When using a glass thermometer, it is essential to prioritize safety to prevent accidents and ensure the well-being of individuals involved in temperature measurement processes. Implementing the following safety precautions is paramount in promoting a secure and controlled environment for utilizing glass thermometers effectively.
-
Handling and Storage: Exercise caution when handling glass thermometers to avoid breakage or exposure to hazardous substances, such as mercury. Store thermometers in designated protective cases to prevent damage and minimize the risk of accidental exposure to the liquid contents.
-
Proper Disposal: In the event of a broken glass thermometer, adhere to established protocols for safe disposal of the glass fragments and any spilled liquid. Exercise care to prevent direct contact with the liquid contents, especially in the case of mercury-based thermometers, and utilize appropriate protective equipment during cleanup procedures.
-
Supervision for Children: When using glass thermometers for pediatric temperature measurements, ensure close supervision to prevent accidental ingestion or mishandling of the thermometer. Educate children on the proper use of thermometers and the importance of seeking adult assistance when utilizing these instruments.
-
Avoiding Glass Fragmentation: Take precautions to prevent glass thermometers from being subjected to sudden impacts or extreme temperature differentials, which may lead to breakage. Handle thermometers with care and avoid exposing them to conditions that could compromise their structural integrity.
-
Mercury Exposure Awareness: In the case of mercury-based thermometers, raise awareness about the potential hazards of mercury exposure and educate users on the proper handling and disposal of these instruments. Encourage the use of alternative, non-mercury thermometers where feasible to minimize the risk of mercury-related incidents.
-
Protective Gear: When handling glass thermometers in laboratory or industrial settings, utilize appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves and eye protection, to mitigate potential risks associated with accidental breakage or exposure to hazardous substances.
-
Training and Education: Provide comprehensive training on the safe handling and usage of glass thermometers to individuals tasked with temperature measurement responsibilities. Emphasize the importance of adhering to safety protocols and equip users with the knowledge to respond effectively in the event of accidents or emergencies involving glass thermometers.
By integrating these safety precautions into the utilization of glass thermometers, individuals and organizations can foster a culture of safety and responsibility, mitigating potential risks and promoting secure practices in temperature measurement activities. Prioritizing safety not only safeguards the well-being of individuals but also contributes to the efficient and reliable utilization of glass thermometers across various applications and settings.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the art of reading a glass thermometer is a valuable skill that transcends diverse domains, from healthcare and scientific research to everyday temperature monitoring. By understanding the fundamental components of a glass thermometer, including the bulb, capillary tube, temperature scale, meniscus, and markings, individuals gain a comprehensive insight into the intricacies of temperature measurement. This knowledge forms the cornerstone of accurate temperature assessment, empowering users to interpret temperature readings with confidence and precision.
Reading the temperature scale on a glass thermometer is a fundamental aspect of obtaining precise temperature measurements. By observing the meniscus and aligning it with the markings on the temperature scale, individuals can discern temperature variations with accuracy, whether using the Celsius or Fahrenheit scale. This proficiency is essential for applications where minute temperature differentials hold significant implications, such as in medical diagnostics, environmental monitoring, and scientific experiments.
Taking accurate readings with a glass thermometer demands meticulous attention to proper handling, observation, and interpretation. Whether measuring body temperature or environmental conditions, adhering to established protocols for thermometer usage ensures reliable and consistent temperature assessments. Additionally, regular calibration and maintenance of glass thermometers are crucial for preserving their accuracy and performance over time.
Implementing safety precautions when using glass thermometers is paramount in promoting a secure and controlled environment for temperature measurement activities. By prioritizing safe handling, storage, and disposal of glass thermometers, individuals can mitigate potential risks and safeguard against accidents or exposure to hazardous substances, particularly in the case of mercury-based thermometers.
In essence, the proficiency in reading a glass thermometer extends beyond mere practicality; it offers a glimpse into the fascinating realm of thermal dynamics, where the behavior of substances is intimately tied to their temperature. By honing the skills to interpret temperature readings accurately, individuals gain insight into the fundamental principles that govern the physical world around us. This knowledge not only contributes to informed decision-making but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the intricate interplay between temperature and the properties of matter.
In conclusion, the ability to read a glass thermometer with precision and confidence is a valuable asset, empowering individuals to navigate the complexities of temperature measurement with proficiency and insight.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Read A Glass Thermometer
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How To Read A Glass Thermometer”