Home>Furniture>Bedroom Furniture>How Is A Mattress Made


Bedroom Furniture
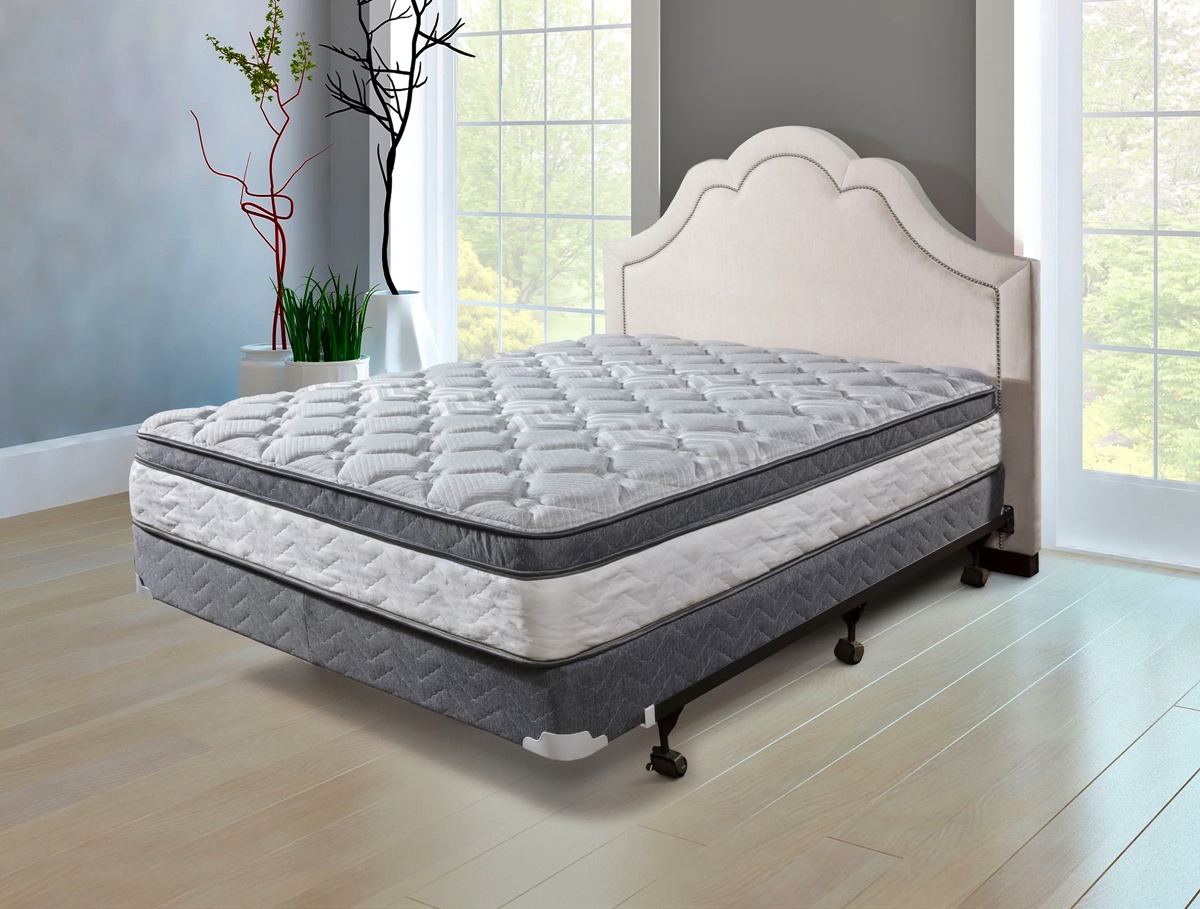
How Is A Mattress Made
Modified: March 2, 2024
Discover the fascinating process of how a mattress is made with our comprehensive guide. Explore the intricate details that go into crafting your essential bedroom furniture.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to creating a comfortable and relaxing bedroom, one of the most important elements to consider is the mattress. A good mattress can make all the difference in getting a good night’s sleep and waking up refreshed and rejuvenated. But have you ever wondered how a mattress is made? In this article, we will take a deep dive into the world of mattress construction, exploring the materials used and the manufacturing process.
Creating a high-quality mattress requires a careful selection of materials and a precise manufacturing process. Manufacturers strive to create a balance between support, durability, and comfort to ensure that the mattress meets the needs and preferences of a wide range of sleepers.
Before we delve into the manufacturing process, let’s first explore the materials commonly used in mattress construction.
Key Takeaways:
- The mattress manufacturing process involves precise cutting and shaping of foam, assembly of inner components, covering, quilting, and adding final touches. Each step contributes to creating a comfortable and supportive sleep surface.
- Different types of mattresses, such as hybrid, memory foam, innerspring, and latex, cater to diverse sleep preferences. Understanding the manufacturing process empowers consumers to make informed decisions about their sleep environment.
Read more: What Is The Purple Mattress Made Of
Materials Used in Mattress Construction
A well-constructed mattress is built with a combination of various materials that work together to provide optimal support and comfort. Here are some of the key materials commonly used in mattress construction:
- Innerspring Coils: Innerspring mattresses are known for their traditional design, which consists of a network of interconnected metal coils. These coils provide support and help distribute the weight of the body evenly across the mattress. They also allow for better airflow, promoting a cooler sleeping environment.
- Memory Foam Layers: Memory foam is a popular material in mattress construction due to its ability to contour to the body’s shape. It responds to heat and pressure, creating a customized level of support for each individual. Memory foam mattresses can provide excellent pressure relief, making them a great option for those with joint or back pain.
- Latex Layers: Latex is derived from the sap of rubber trees and is known for its natural elasticity and breathability. Latex mattresses offer a responsive and supportive sleeping surface, as they can conform to the body’s contours while bouncing back quickly. They are also resistant to dust mites and mold, making them a suitable choice for allergy sufferers.
In addition to these primary materials, mattresses may also incorporate other components such as foam encasements for edge support, gel-infused memory foam for enhanced cooling, or natural materials like wool for added softness and temperature regulation.
Now that we have a better understanding of the materials used in mattress construction, let’s explore the different types of mattress construction methodologies.
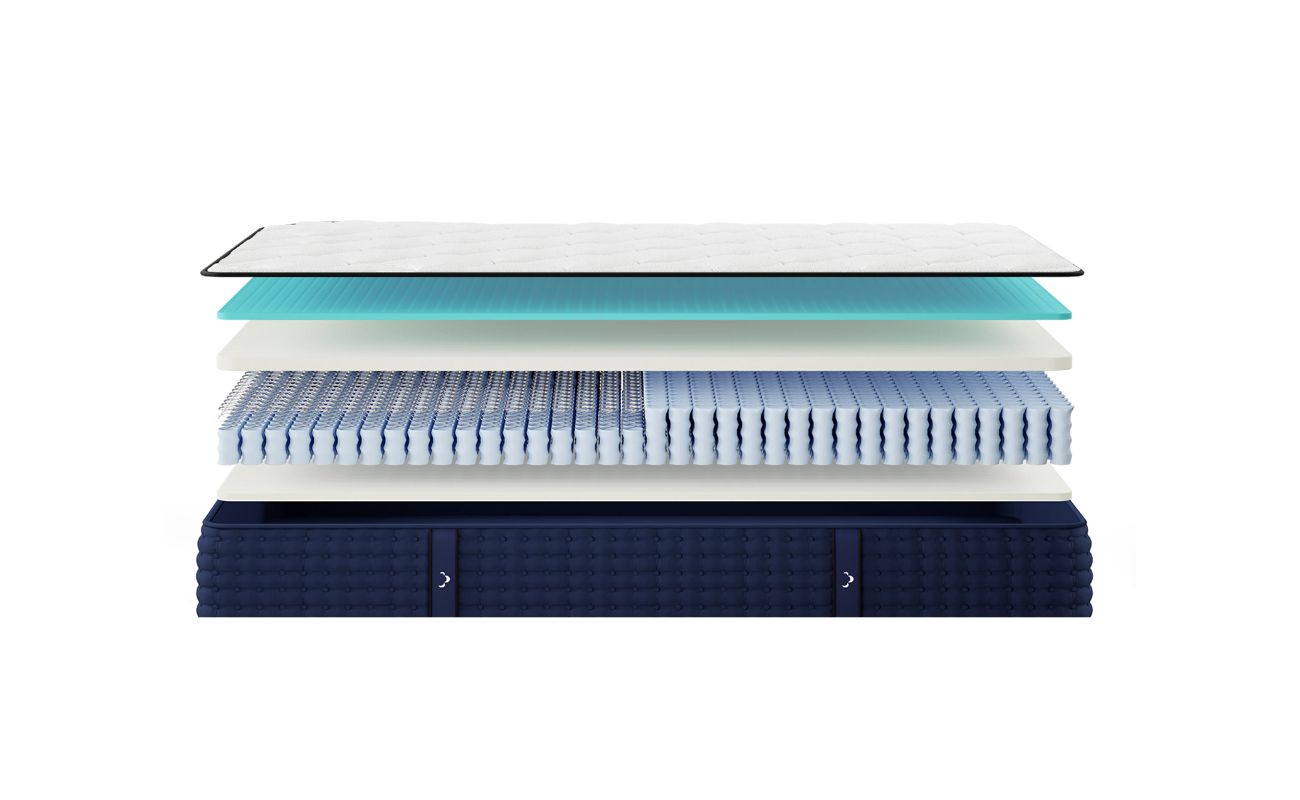
The Inner Components of a Mattress
Understanding the inner components of a mattress is essential to comprehend how each element contributes to its overall comfort and support. Here are the key components often found in mattresses:
- Innerspring Coils: Innerspring mattresses consist of a system of metal coils that provide support and help maintain the mattress’s shape. The number, thickness, and configuration of these coils can vary, affecting the level of support and motion isolation.
- Memory Foam Layers: Memory foam mattresses are designed with layers of viscoelastic foam that contour and adapt to the body’s shape, providing pressure relief and personalized support. The thickness and density of these foam layers can vary, influencing the mattress’s overall feel and responsiveness.
- Latex Layers: Latex mattresses are constructed with layers of natural or synthetic latex foam. This material offers elasticity and responsiveness, promoting a more supportive sleeping surface. The firmness and thickness of the latex layers can influence the mattress’s overall feel.
Combining different inner components can result in various types of mattresses that cater to different sleep preferences. Let’s explore some of the most common mattress construction types.
The Inner Components of a Mattress
– Innerspring Coils
Innerspring mattresses have been a popular choice for decades, known for their durability and support. The primary component of an innerspring mattress is the system of metal coils.
The coils in an innerspring mattress provide the foundational support and help distribute body weight evenly across the mattress surface. Typically made of steel, these coils come in different gauges (thickness) and shapes, such as Bonnell coils, offset coils, or pocketed coils.
Bonnell coils are the most common type of innerspring coil. These hourglass-shaped coils are connected with spiral wires, creating a network of interconnected coils. While they offer good support and are cost-effective, they may transfer motion more than other coil types.
Offset coils, on the other hand, have a more cylindrical shape and are hinged together by helical wires. This design helps to conform to the body’s shape and reduce motion transfer. Offset coils also provide more targeted support, making them a popular choice for those with specific pressure points or back issues.
Lastly, pocketed coils, also called individually wrapped coils, are individually encased in fabric. This design allows each coil to move independently, providing enhanced motion isolation and better contouring to the body’s shape. Pocketed coil mattresses are often recommended for couples as they minimize disturbances when one partner moves or changes positions during sleep.
It’s worth noting that innerspring mattresses usually include additional layers of padding on top of the coil system. These layers may consist of materials like foam, memory foam, or latex to enhance comfort and pressure relief.
Innerspring mattresses are known for their bouncy and responsive feel, with a good level of support. They also tend to offer better breathability compared to other mattress types, as the open coil design allows for improved airflow within the mattress.
Now that we’ve explored innerspring coils, let’s move on to the next component – memory foam layers.
The Inner Components of a Mattress
– Memory Foam Layers
Memory foam has gained tremendous popularity in mattress construction due to its ability to provide exceptional comfort and pressure relief. Memory foam mattresses are designed with layers of viscoelastic foam that respond to heat and pressure, conforming to the body’s shape.
Memory foam was originally developed by NASA to improve cushioning and shock absorption in spacecraft seats. The foam’s unique composition allows it to soften and mold when it comes into contact with body heat, distributing weight evenly and relieving pressure points.
In a memory foam mattress, multiple layers of varying densities of memory foam are often used. The top layer, known as the comfort layer, is typically made of a softer foam that provides the initial cushioning and contouring. This layer cradles the body and helps relieve pressure on areas such as the shoulders and hips.
Beneath the comfort layer, there may be additional layers of memory foam with different densities. These layers provide further support and responsiveness, ensuring proper spinal alignment and reducing the risk of sagging over time.
Memory foam mattresses offer several advantages. They are known for their ability to absorb motion, making them an excellent choice for light sleepers or those who share a bed. They also provide exceptional pressure relief, making them popular among individuals with chronic pain or conditions like arthritis.
However, some people find memory foam mattresses to retain heat due to their conforming nature. To address this, manufacturers often incorporate cooling technologies, such as gel-infused memory foam or open-cell foam, to promote better temperature regulation.
Now that you have an understanding of memory foam layers, let’s move on to the final inner component – latex layers.
The Inner Components of a Mattress
– Latex Layers
Latex is a natural or synthetic material derived from the sap of rubber trees. Latex mattresses are constructed with layers of latex foam, which offers unique properties that contribute to a comfortable and supportive sleep surface.
One of the primary advantages of latex is its exceptional elasticity, which allows it to bounce back quickly and provide consistent support throughout the night. Latex mattresses are known for their responsive feel, offering a combination of pressure relief and buoyancy.
Natural latex mattresses are made from 100% natural latex derived from rubber trees. They are highly durable, hypoallergenic, and resistant to dust mites and mold. Natural latex mattresses also tend to have a more breathable and cool sleeping surface, thanks to the latex’s open cell structure that allows for improved airflow.
Synthetic latex mattresses, also known as blended latex mattresses, combine natural latex with synthetic materials. Blended latex mattresses are more affordable than natural latex mattresses while still providing a supportive and comfortable sleep experience.
Latex mattresses are known for their excellent contouring ability, offering pressure relief without the sinking feeling associated with memory foam. The level of firmness can vary depending on the manufacturing process and the specific type of latex used. This makes latex mattresses suitable for a wide range of sleep preferences, from those who prefer a firmer surface to those who enjoy a softer feel.
In terms of durability, latex mattresses are often considered long-lasting and resilient, with an average lifespan of 8 to 10 years. They are less prone to sagging and indentations compared to other mattress types, which can contribute to a more comfortable and supportive sleep experience over time.
Overall, latex mattresses are a popular choice for sleepers who value both support and comfort. The combination of elasticity, pressure relief, and breathability makes latex an excellent material for creating a supportive and rejuvenating sleep surface.
Now that we have explored the inner components of a mattress, let’s move on to the next section, where we will discuss different types of mattress construction.
Read more: Where Is Simmons Mattress Made
Types of Mattress Construction
There are various types of mattress construction, each with its own unique characteristics and benefits. Understanding these different types can help you choose the mattress that best suits your sleep preferences. Let’s explore some of the most common mattress construction types:
- Hybrid Mattresses: Hybrid mattresses combine multiple support systems, typically a combination of innerspring coils and layers of foam or latex. By blending different materials, hybrid mattresses aim to provide the benefits of each component, such as the support of coils and the pressure relief of foam or latex. This combination can create a balanced and comfortable sleep surface that caters to a wide range of sleepers.
- Memory Foam Mattresses: Memory foam mattresses are constructed entirely or primarily with layers of memory foam. As mentioned earlier, memory foam conforms to the body’s shape, providing personalized support and pressure relief. Memory foam mattresses are known for their ability to minimize motion transfer and alleviate discomfort caused by pressure points, making them a popular choice for individuals with chronic pain or sleep disturbances.
- Innerspring Mattresses: Innerspring mattresses have a traditional construction consisting primarily of metal coils. These mattresses offer a classic and bouncy feel, with varying levels of firmness depending on the coil type and padding used. Innerspring mattresses are often preferred by individuals who enjoy a more traditional sleep surface and appreciate strong edge support.
- Latex Mattresses: Latex mattresses are made entirely or primarily of latex foam. They offer a responsive and supportive sleep surface with natural elasticity. Latex mattresses are known for their durability, breathability, and hypoallergenic properties. They can be a great choice for sleepers who prefer a resilient and buoyant feel.
While these are the main types of mattress construction, it’s important to note that there are also specialty mattresses available, such as adjustable air mattresses and organic mattresses, that cater to specific needs and preferences.
When choosing a mattress, consider factors such as your preferred sleep position, personal comfort preferences, and any specific needs or conditions you may have. Additionally, don’t forget to consider the quality and durability of the materials used in the construction to ensure a long-lasting and comfortable sleep surface.
Now that we have explored the types of mattress construction, let’s move on to the next section, where we will dive into the manufacturing process of mattresses.
Read more: Where Is Simmons Mattress Made
Types of Mattress Construction
– Hybrid Mattresses
Hybrid mattresses have gained popularity in recent years as they offer the benefits of multiple mattress constructions in one. These mattresses combine the support of innerspring coils with the contouring comfort of foam or latex layers, providing a balanced and luxurious sleep surface.
The core of a hybrid mattress is the innerspring coil system, which typically comprises individually wrapped coils. These coils provide excellent support and help maintain proper spinal alignment. The individual wrapping allows each coil to move independently, reducing motion transfer and promoting undisturbed sleep for couples.
To enhance the comfort and pressure relief, hybrid mattresses incorporate layers of foam or latex above the coil system. The top layers are often made of memory foam, latex foam, or gel-infused foam, offering contouring support and relieving pressure on the body’s pressure points.
By combining the resilience of innerspring coils with the plush comfort of foam or latex layers, hybrid mattresses aim to cater to a wide range of sleep preferences. These mattresses can provide the bounce and support of coils while offering the cushioning and pressure relief associated with foam or latex.
One of the advantages of hybrid mattresses is their ability to balance comfort and support. The coil system helps distribute body weight evenly, while the foam or latex layers contour to the body’s shape and alleviate pressure points. This combination can provide excellent support for different sleep positions and body types.
Additionally, hybrid mattresses often offer enhanced breathability compared to mattresses made entirely of foam. The coil system allows for increased airflow, which helps dissipate body heat and regulate temperature during sleep.
When shopping for a hybrid mattress, it’s important to consider factors such as the thickness and density of the foam or latex layers, as well as the coil gauge and quality. These factors can contribute to the overall comfort, durability, and longevity of the mattress.
Now that we have explored hybrid mattresses, let’s move on to the next type of mattress construction – memory foam mattresses.
Read more: Where Is Simmons Mattress Made
Types of Mattress Construction
Read more: Where Is Nolah Mattress Made
– Memory Foam Mattresses
Memory foam mattresses have revolutionized the sleep industry with their unique ability to contour and adapt to the body’s shape. These mattresses are constructed entirely or primarily with layers of viscoelastic memory foam, offering a personalized and pressure-relieving sleep surface.
Memory foam, also known as viscoelastic foam, is highly responsive to heat and pressure. When you lie on a memory foam mattress, the foam softens and conforms to your body, distributing weight evenly and relieving pressure points. This contouring effect helps promote proper spinal alignment and can alleviate discomfort caused by conditions such as arthritis or chronic pain.
The top layer of a memory foam mattress, often called the comfort layer, is typically made of a soft and plush foam that provides initial cushioning and contouring. Beneath the comfort layer, there are additional layers of memory foam with varying densities, intended to provide support and distribute weight evenly across the mattress surface.
One significant advantage of memory foam mattresses is their ability to minimize motion transfer. When one person moves or changes positions during sleep, the foam absorbs and isolates the motion, preventing disturbances for the other person. This makes memory foam mattresses an ideal choice for couples or light sleepers.
Another benefit of memory foam is its ability to reduce pressure points. By conforming to the body’s curves and supporting natural alignment, memory foam helps alleviate aches and pains that can result from sleeping on mattresses with less contouring ability.
One consideration when choosing a memory foam mattress is the foam’s density. Higher-density memory foam provides more support and durability, while lower-density foam tends to be softer and may have a shorter lifespan. It’s also worth noting that memory foam mattresses can retain heat, leading to a warmer sleep surface. However, many manufacturers now incorporate cooling technologies, such as gel-infused foam or open-cell foam, to enhance breathability and regulate temperature.
In summary, memory foam mattresses offer exceptional pressure relief, motion isolation, and personalized support. If you prefer a contouring and enveloping sleep surface that adapts to your body, a memory foam mattress may be an excellent choice.
Now, let’s move on to the next type of mattress construction – innerspring mattresses.
Read more: Where Is Simmons Mattress Made
Types of Mattress Construction
– Innerspring Mattresses
Innerspring mattresses have long been a staple in the mattress industry. These mattresses are constructed with a system of metal coils that provide support and resilience, making them a popular choice for those who prefer a more traditional sleep surface.
The core component of an innerspring mattress is the coil system. The coils, typically made of steel, are interconnected in various configurations to provide support and maintain the mattress’s shape. They help distribute body weight evenly, preventing excessive pressure on specific areas of the body.
The most common type of innerspring coil system is the Bonnell coil system. These hourglass-shaped coils are connected with spiral wires, creating a network of interconnected coils. Bonnell coils offer good support, durability, and affordability. However, they may transfer motion more compared to other coil types.
Another type of coil system is the offset coil system. These coils have a cylindrical shape and are hinged together with helical wires. The offset design allows for better conforming to the body’s contours, reduced motion transfer, and improved support. Offset coils are often recommended for individuals with specific pressure points or back issues.
Pocketed coils, also known as individually wrapped coils, are individually encased in fabric. This design allows each coil to move independently, conforming to the body’s shape and eliminating motion transfer. Pocketed coil mattresses provide excellent support, contouring, and motion isolation, making them popular for couples or those who value minimal disruption from their partner’s movements during sleep.
Innerspring mattresses often feature additional padding layers, such as foam, fiberfill, or pillow tops, to enhance comfort and cushioning. These layers can provide extra softness and contouring to the mattress’s surface.
Innerspring mattresses offer a range of firmness options to suit different sleep preferences. They are known for their responsiveness and bouncy feel, making them an excellent choice for those who prefer a more traditional and supportive sleep surface. In addition, the open coil design of innerspring mattresses allows for better airflow, promoting a cooler sleep environment.
It’s important to consider factors such as coil gauge, coil count, and quality of materials when choosing an innerspring mattress. Higher coil count and lower gauge generally indicate better support and durability.
In summary, innerspring mattresses provide a classic and supportive sleep surface. If you enjoy a bouncy feel and prefer a traditional mattress construction, an innerspring mattress may be a suitable choice for you.
Now, let’s move on to the final type of mattress construction – latex mattresses.
Read more: Where Is Simmons Mattress Made
Types of Mattress Construction
Read more: Where Are Simmons Mattresses Made
– Latex Mattresses
Latex mattresses are prized for their natural elasticity, comfort, and durability. These mattresses are constructed with layers of latex foam, derived from the sap of rubber trees, offering a supportive and resilient sleep surface.
Latex is available in two main types: natural and synthetic. Natural latex is made from the sap of rubber trees and is known for its eco-friendly and sustainable qualities. It is hypoallergenic, resistant to dust mites and mold, and offers excellent breathability, resulting in a cooler sleep experience.
Synthetic latex, also known as blended latex, is a petroleum-based product that mimics the properties of natural latex. Blended latex mattresses are typically more affordable than those made entirely of natural latex while still providing a comfortable and supportive sleep surface.
One of the key advantages of latex mattresses is their natural elasticity. Latex foam has a responsive bounce, allowing the mattress to quickly regain its shape after being compressed. This feature facilitates ease of movement during sleep and prevents the feeling of sinking that is commonly associated with other mattress types.
Latex mattresses provide a combination of support and contouring. The foam is able to conform to the body’s curves, providing pressure relief and proper spinal alignment. This makes latex mattresses a suitable choice for individuals with back or joint pain.
Latex is available in different firmness levels, ranging from soft to firm. This variety allows for customization and the ability to choose a mattress that suits your preference and sleep style. Additionally, latex mattresses have a natural ability to resist sagging and indentations, resulting in increased durability and longevity.
In terms of motion isolation, latex mattresses perform well. They absorb and minimize movement, reducing the risk of disturbances from a sleep partner’s movements during the night. This feature is beneficial for light sleepers or couples who value a peaceful sleep environment.
When choosing a latex mattress, consider factors such as the thickness and density of the latex layers, as they can affect the overall feel and support. Additionally, check for certifications such as Oeko-Tex® Standard 100 or GOLS (Global Organic Latex Standard) to ensure the latex used is of high quality and free from harmful chemicals.
In summary, latex mattresses provide a resilient and supportive sleep surface with natural breathability. Whether you prefer a softer or firmer feel, latex mattresses offer options to accommodate a variety of sleep preferences.
Now that we have explored different types of mattress construction, let’s move on to the manufacturing process of mattresses.
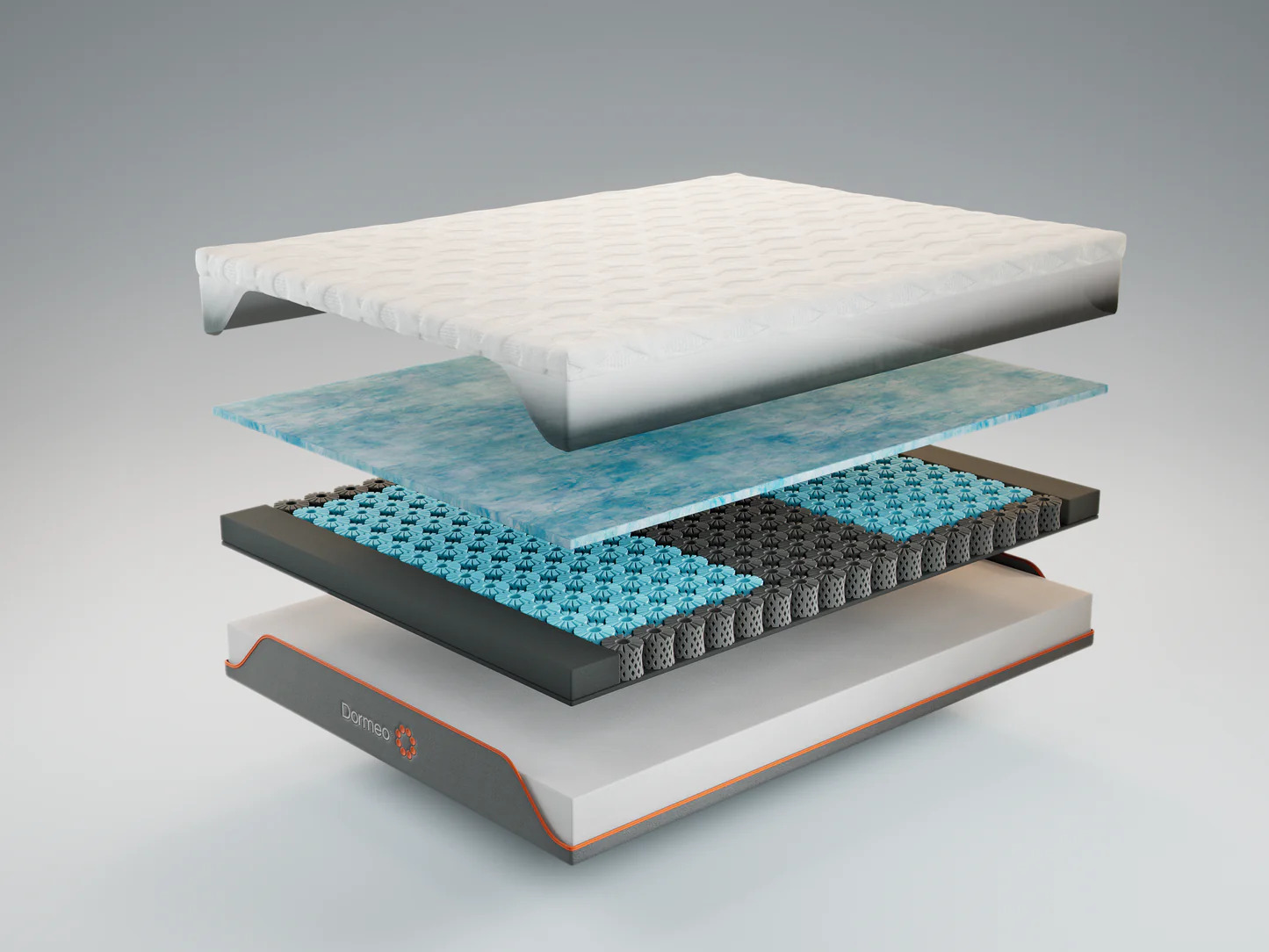
The Manufacturing Process of Mattresses
The manufacturing process of mattresses involves several steps and careful attention to detail to ensure the production of high-quality and comfortable sleep surfaces. Here is an overview of the typical manufacturing process:
Cutting and Shaping the Foam
The first step in the manufacturing process is cutting and shaping the foam layers. Whether it’s memory foam, latex foam, or other types of foam, machines are used to cut the foam into the desired sizes and shapes. This ensures the foam layers fit perfectly within the mattress structure and provide the intended comfort and support.
Assembling the Inner Components
After the foam layers are cut, the next step is to assemble the inner components of the mattress. In an innerspring mattress, the coil system is attached to a frame or encasement. Foam layers, such as comfort layers or insulating layers, are added on top of the coil system to provide cushioning and support.
In memory foam or latex mattresses, the foam layers are stacked on top of each other, with the softer or thicker layers typically placed closer to the surface for enhanced comfort. These layers are carefully aligned and adhered to ensure proper integration and stability within the mattress.
Read more: What Is An Organic Mattress Made Of
Covering and Quilting the Mattress
Once the inner components are assembled, the mattress is ready to be covered and quilted. A fabric cover, often made of materials like polyester or cotton, is stitched around the mattress to encase the foam layers and coil system. The cover serves as a protective barrier and provides a smooth and finished surface for the mattress.
In some cases, mattresses may have additional quilting layers added to enhance comfort and provide extra padding. These layers can include materials like fiberfill or foam, which are stitched or sewn into the mattress cover to create a quilted pattern.
Adding the Final Touches
After the mattress is covered and quilted, it goes through a final stage where finishing touches are added. This can include adding edge support systems, such as foam encasements, to provide stability and prevent sagging along the sides of the mattress.
Labels, tags, and handles may also be attached to the mattress during this final stage. These features provide important information about the mattress, such as its size, material composition, and care instructions, as well as making it easier to move and rotate the mattress as needed.
Once the manufacturing process is complete, the mattresses undergo thorough quality checks to ensure they meet industry standards for comfort, durability, and safety. They are then packaged and prepared for distribution to retailers or directly to consumers.
By following these steps and maintaining strict quality control measures, mattress manufacturers can produce mattresses that offer exceptional comfort, support, and longevity, allowing individuals to enjoy a restful and rejuvenating sleep experience.
Now that we’ve explored the manufacturing process, let’s conclude our journey into the world of mattresses.
The Manufacturing Process of Mattresses
– Cutting and Shaping the Foam
The first step in the manufacturing process of mattresses is cutting and shaping the foam. This step is crucial to ensure that the foam layers fit perfectly within the mattress structure and provide the intended comfort and support.
Various types of foam are used in mattress construction, including memory foam, latex foam, and polyurethane foam. Each type of foam has its unique properties and characteristics that contribute to the overall feel and performance of the mattress.
Specialized machines are used to cut the foam into the desired sizes and shapes. The foam sheets are carefully measured and marked before being fed into the cutting machines. The machines use sharp blades or water jets to precisely cut the foam according to the specifications provided.
Cutting the foam involves creating different layers with varying thicknesses, depending on the mattress design. The top comfort layer is often thicker to provide the desired level of softness and cushioning. Subsequent layers may have different thicknesses to provide support and transition between different foam densities.
Once the foam has been cut, it undergoes shaping processes to create contours, curves, or specific designs. These shapes can enhance the mattress’s ergonomics, allowing for better support and pressure relief in different areas of the body.
Shaping the foam can be done using techniques such as die-cutting, which uses specialized dies to cut the foam into specific shapes or patterns. Additionally, heat and pressure can be applied to mold the foam into various contours and designs, giving it the desired shape and firmness.
The cut and shaped foam layers are then ready to be assembled as part of the mattress’s inner components. They play a crucial role in providing comfort, pressure relief, and support, working in conjunction with other materials like coils or additional foam layers.
Manufacturers invest in precision cutting and shaping processes to ensure consistency in the final product. Accurate cutting and shaping of the foam layers contribute to a well-constructed mattress that delivers optimal performance and meets the expectations of consumers.
Now that we’ve covered the cutting and shaping of foam, let’s move on to the next step in the manufacturing process – assembling the inner components of the mattress.
The Manufacturing Process of Mattresses
– Assembling the Inner Components
After the foam layers have been cut and shaped, the next step in the manufacturing process of mattresses is assembling the inner components. This step involves carefully layering and integrating the various materials that make up the core of the mattress.
The specific composition of the inner components depends on the type of mattress being produced, such as innerspring, memory foam, or latex. However, the general process of assembling these components follows a similar pattern.
In an innerspring mattress, the coil system forms the foundation of the mattress. The coils, typically made of tempered steel, are connected to each other with wires or clips to create a sturdy network. The coil system is then attached to a frame or encasement that provides stability and support.
In memory foam and latex mattresses, the foam layers are stacked atop the support core. The foam layers may have different densities and firmness levels to provide a combination of comfort and support. The layers are carefully aligned to ensure proper integration and to achieve the desired feel and performance of the mattress.
In some cases, additional components such as transition layers, insulating layers, or lumbar support zones are integrated into the mattress during this assembly process. These components further enhance the mattress’s comfort, support, and overall performance.
The layers are typically affixed together using a combination of adhesives, heat-bonding, or stitching techniques. Manufacturers utilize specialized tools and machinery to ensure precise alignment and secure attachment of the layers.
During assembly, manufacturers also pay special attention to edge support. This involves reinforcing the mattress’s perimeter to prevent sagging and promote enhanced durability. Various methods, such as foam encasements or additional coils, are utilized to provide structural integrity and edge-to-edge support.
Throughout the assembly process, quality control measures are implemented to ensure that each mattress meets specific standards for comfort, durability, and performance. Random checks are conducted to verify the proper alignment of materials, the consistency of firmness, and the overall construction quality.
By carefully assembling the inner components, manufacturers ensure that the mattress provides the intended level of comfort and support to deliver a restful sleep experience for consumers. The attention to detail in this step is crucial to create a well-constructed mattress that meets or exceeds customer expectations.
Now that we’ve covered the assembly of the inner components, let’s move on to the next step in the manufacturing process – covering and quilting the mattress.
The Manufacturing Process of Mattresses
– Covering and Quilting the Mattress
Once the inner components of the mattress have been assembled, the next step in the manufacturing process is covering and quilting the mattress. This step involves encasing the mattress with a fabric cover and adding quilting layers for enhanced comfort and aesthetics.
The fabric cover serves as a protective barrier, enclosing the inner components and ensuring their longevity. It also provides a smooth and aesthetically pleasing surface for the mattress, giving it a finished look.
The fabric cover used in mattress manufacturing is typically made of polyester, cotton, or a blend of these materials. These fabrics are chosen for their durability, breathability, and ability to withstand regular use and washing.
The fabric cover is carefully measured and cut to the dimensions of the mattress. Skilled workers or specialized machinery then sew or stitch the cover tightly around the mattress, ensuring a snug fit. The edges and corners of the mattress are carefully sewn or reinforced to prevent the cover from shifting or coming loose over time.
Once the mattress is covered, the next step is the quilting process. Quilting involves adding additional layers of padding for extra comfort and cushioning. These layers are typically made of foam, fiberfill, or other materials chosen for their softness and ability to provide a plush surface.
Quilting layers can be attached to the fabric cover through a variety of techniques, including stitching or sewing. The quilting pattern can vary, ranging from simple straight lines to intricate designs. This step adds visual appeal to the mattress while also enhancing comfort and support.
The quilting layers help evenly distribute the padding and provide a consistent feel across the mattress surface. They also aid in preventing the migration of materials and maintaining the overall integrity of the mattress over time.
During the covering and quilting process, manufacturers pay close attention to quality control. Inspections are conducted to ensure that the cover is properly aligned, the stitching is secure and neat, and the quilting layers are evenly distributed.
Overall, the covering and quilting process gives the mattress its final appearance and ensures that it is ready for use. The attention to detail in this step not only enhances the visual appeal of the mattress but also contributes to its overall comfort, durability, and performance.
Now that we’ve covered the covering and quilting of the mattress, let’s move on to the final step in the manufacturing process – adding the final touches.
The Manufacturing Process of Mattresses
– Adding the Final Touches
After the mattress is covered and quilted, it goes through the final stage of the manufacturing process where the finishing touches are added. These final touches enhance the functionality, aesthetics, and overall appeal of the mattress.
One important aspect of adding the final touches involves incorporating edge support systems. These systems are designed to provide stability and prevent sagging along the sides of the mattress. Foam encasements or reinforced coils are often used to create a sturdy perimeter, increasing the usable surface area of the mattress and ensuring edge-to-edge support.
The mattress may also undergo tufting, a traditional technique that involves strategically stitching the top and bottom layers of the mattress using tufts or buttons. This process helps secure the layers in place and prevents shifting over time. Tufting contributes to the overall durability and stability of the mattress.
Additionally, labels, tags, and handles are added to the mattress during this stage. These features provide important information about the mattress, such as its size, material composition, and care instructions. Handles make it easier for consumers to move and rotate the mattress when necessary, ensuring even wear and prolonging its lifespan.
Once all the final touches are in place, the mattress undergoes a thorough quality check. Manufacturers inspect the mattress to ensure that it meets their strict quality standards for comfort, durability, and safety. Random checks are conducted to verify proper stitching, alignment of components, and adherence to industry regulations.
Once the quality checks are complete, the mattress is carefully prepared for packaging and distribution. It may be compressed, rolled, or folded for easy shipping and handling. Packaging materials, such as plastic wrap or cardboard boxes, are used to protect the mattress during transportation, ensuring that it arrives in pristine condition for the end consumer.
By adding the final touches, manufacturers ensure that the mattress delivers a complete and satisfying experience for consumers. These touches not only provide functional benefits like edge support and easy handling, but they also give the mattress a polished and professional appearance.
Now that we have covered the process of adding the final touches, we have completed our journey through the manufacturing process of mattresses. From cutting and shaping the foam to covering and quilting, every step is carefully executed to create a comfortable and durable sleep surface for individuals to enjoy night after night.
When learning about how a mattress is made, it’s important to understand the different layers and materials used, such as memory foam, latex, coils, and fabric. Each component contributes to the overall comfort and support of the mattress.
Conclusion
The manufacturing process of mattresses is a precise and meticulous endeavor that involves careful attention to detail and the use of high-quality materials. From cutting and shaping the foam to assembling the inner components, covering and quilting, and adding the final touches, each step plays a crucial role in creating a comfortable and supportive sleep surface.
Materials such as innerspring coils, memory foam, and latex are skillfully integrated to provide a balance of support, pressure relief, and durability. The specific combination of these materials, along with the design and construction techniques, determines the unique characteristics and feel of each type of mattress.
Hybrid mattresses combine the benefits of different components, while memory foam mattresses offer superior pressure relief and motion isolation. Innerspring mattresses provide a classic and bouncy feel, and latex mattresses offer natural elasticity and support. Each type caters to different sleep preferences and needs.
The manufacturing process involves precise cutting, shaping, and layering of foam, as well as the assembly of inner components such as coils. The meticulous process ensures proper alignment, durability, and structural integrity.
Covering and quilting the mattress provide protection and aesthetics, with careful stitching and attachment of quilting layers to enhance overall comfort and support. The addition of edge support systems and other finishing touches further enhance functionality and longevity.
Throughout the manufacturing process, rigorous quality control measures are implemented to ensure that each mattress meets high standards for comfort, performance, and safety. Random checks and inspections guarantee that the final product is of impeccable quality.
By understanding the intricacies of mattress manufacturing, consumers can make informed decisions about their sleep environment and choose a mattress that suits their individual needs and preferences. The craftsmanship and attention to detail that go into the creation of a mattress result in a restful and rejuvenating sleep experience night after night.
So, the next time you lay on your mattress, appreciate the careful craftsmanship and intricate manufacturing process that went into creating a comforting and supportive haven for your sleep.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Is A Mattress Made
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.