Home>Garden Essentials>How Can Green Space Address Health Inequalities In The Living Environment?
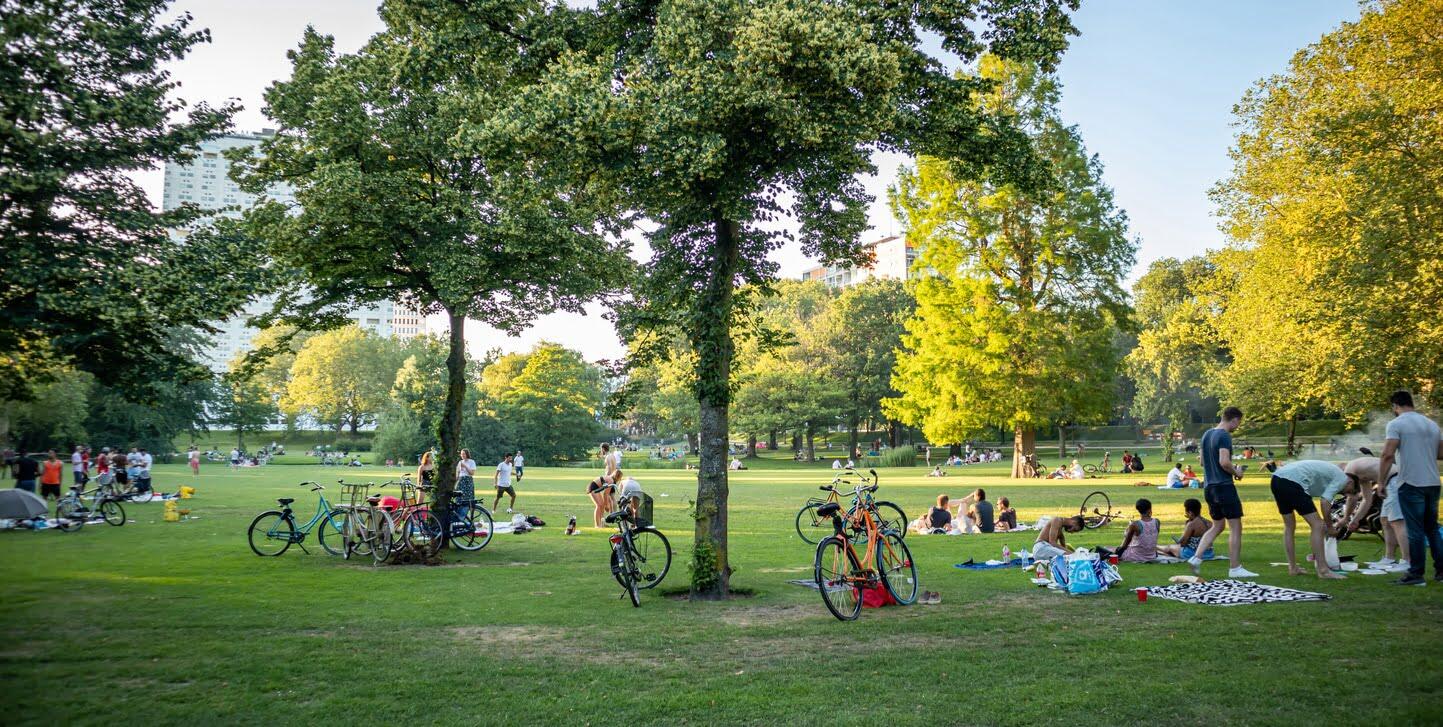
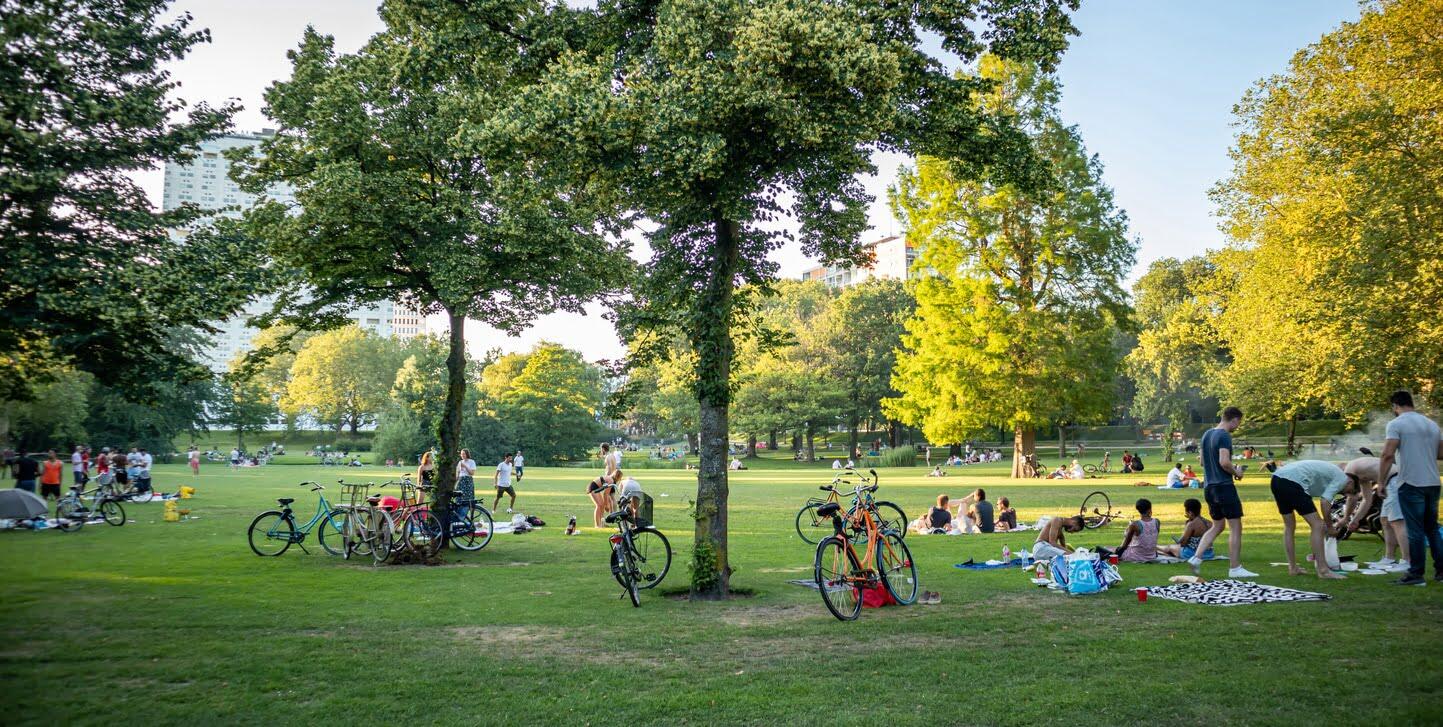
Garden Essentials
How Can Green Space Address Health Inequalities In The Living Environment?
Modified: March 7, 2024
Discover how creating a garden can help address health inequalities in the living environment, improving well-being and creating a healthier, greener space.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Green space, characterized by lush gardens, vibrant parks, and thriving landscapes, has long been recognized for its aesthetic appeal. However, beyond its visual beauty, green space also has the power to address health inequalities in the living environment. In recent years, there has been a growing body of research highlighting the numerous benefits that green space can offer to both physical and mental well-being.
But what exactly is green space? Green space refers to any area of land, whether in urban or rural settings, that is covered by vegetation and is accessible to the public. This can include parks, gardens, forests, and even street trees. It is a vital component of a healthy living environment, providing a range of ecological, social, and psychological benefits.
Despite the undeniable benefits of green space, health inequalities persist across different communities. These disparities in health outcomes are often closely linked to socio-economic factors, with individuals from lower-income backgrounds bearing the brunt of poor health conditions. However, green space offers a promising solution to bridge this gap and promote better health for all.
Throughout this article, we will explore the impact of green space on both physical and mental health, discuss the barriers to accessing green space, and delve into strategies that can be implemented to address health inequalities through the promotion of green spaces.
Key Takeaways:
- Green spaces, like parks and gardens, improve physical and mental health for everyone. But not all communities have equal access. We need to make sure everyone can enjoy the benefits of green spaces.
- Green spaces can reduce health inequalities by providing cleaner air, stress relief, and mental well-being. We must work together to make sure everyone has access to these valuable environments.
Defining Green Space
Green space, also referred to as open space or greenspace, is a term used to describe any area of land that is predominantly covered with vegetation, such as trees, grass, flowers, or other plants. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the ecological balance, improving air quality, and providing spaces for recreational activities.
Green spaces can take on various forms, ranging from public parks and gardens to urban street trees and community allotments. They can be found in both urban and rural areas, offering a respite from the concrete jungle and providing a place where individuals can connect with nature.
While the specific definition of green space may vary depending on the context, it generally encompasses areas that are accessible to the public and contribute to the overall quality of the environment. These spaces serve as essential components of urban planning, contributing to the creation of sustainable and livable communities.
Green spaces can be categorized into different types, including:
- Parks: These are designated areas of land specifically designed for recreational activities and leisure pursuits. Parks often include amenities such as playgrounds, sports fields, walking paths, seating areas, and picnic spots.
- Gardens: Gardens are cultivated spaces that can be privately owned, such as backyard gardens or communal gardens, or public spaces like botanical gardens. They provide opportunities for individuals to engage in gardening, appreciate the beauty of plants, and relax in a tranquil setting.
- Natural areas: These include forests, woodlands, nature reserves, and other undeveloped or minimally managed areas. They offer opportunities for hiking, birdwatching, wildlife observation, and other nature-based activities.
- Green corridors: These are linear green spaces that connect different areas, such as riverside paths, greenways, or tree-lined streets. Green corridors help promote biodiversity, improve air quality, and provide recreational opportunities for pedestrians and cyclists.
Overall, green spaces provide numerous benefits to individuals and communities, contributing to physical, mental, and social well-being. They not only enhance the aesthetics of the environment but also play a vital role in supporting a healthier and more sustainable living environment.
Health Inequalities in the Living Environment
Health inequalities refer to the disparities in health outcomes and access to healthcare that exist between different groups of people. These differences can be attributed to various factors, including socio-economic status, race/ethnicity, education level, and living environment.
Living environment plays a significant role in determining an individual’s health and well-being. Unfortunately, not all communities have equal access to resources and amenities that support good health. In many cases, marginalized and lower-income communities bear the brunt of health inequalities, facing greater challenges in maintaining good health.
Several factors contribute to health inequalities in the living environment:
- Socio-economic status: Individuals from lower-income backgrounds often face limited access to quality healthcare, nutritious food options, and safe housing. This can lead to higher rates of chronic diseases, such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular conditions.
- Physical infrastructure: The availability of essential infrastructure, such as clean water, sanitation facilities, and safe housing, significantly impacts health outcomes. Communities lacking these basic amenities are at a higher risk of diseases and poor health.
- Environmental hazards: Some communities are disproportionately exposed to environmental hazards, such as air and water pollution, hazardous waste sites, and industrial emissions. These exposures can have detrimental effects on health, increasing the risk of respiratory diseases, cancer, and other illnesses.
- Social determinants of health: Factors such as education level, employment opportunities, social support networks, and access to recreational resources also contribute to health inequalities. Communities with limited educational opportunities, high unemployment rates, and inadequate social support systems face greater challenges in achieving and maintaining good health.
Addressing health inequalities is crucial to promoting a fair and just society, and improving the overall well-being of individuals and communities. Green space has emerged as a powerful tool in reducing these disparities and creating healthier living environments.
Next, we will explore the impact of green space on physical and mental health, and how it can help alleviate health inequalities.
Impact of Green Space on Physical Health
Green space has a profound impact on physical health, providing numerous benefits that contribute to overall well-being and reducing the risk of various health conditions. The presence of green spaces in the living environment can directly and indirectly influence physical health outcomes in the following ways:
- Improved air quality: Green spaces, particularly trees and vegetation, play a vital role in improving air quality by absorbing harmful pollutants and releasing oxygen. This reduces the risk of respiratory illnesses and contributes to better lung function.
- Promotion of physical activity: Green spaces provide opportunities for physical activity, such as walking, jogging, cycling, and gardening. Engaging in regular physical activity can help prevent chronic diseases, maintain a healthy weight, strengthen muscles and bones, and enhance cardiovascular fitness.
- Stress reduction: The presence of natural elements in green spaces, including trees, plants, and water features, has a calming effect on individuals. Nature has been shown to reduce stress levels, lower blood pressure, and improve the body’s response to stress. This, in turn, can reduce the risk of stress-related health conditions.
- Support for healthy lifestyles: Green spaces can help promote healthy lifestyle choices by encouraging individuals to spend time outdoors, engage in physical activities, and connect with nature. This can lead to improved nutrition, better sleep patterns, and decreased rates of smoking and alcohol consumption.
- Enhanced immune system function: Spending time in green spaces has been linked to improved immune system function. The exposure to diverse microbes found in soil, plants, and the natural environment can strengthen the immune system, reducing the risk of allergies and autoimmune disorders.
It is important to note that the benefits of green space on physical health are not limited to individuals alone. The presence of green spaces in communities also encourages social interactions, fosters a sense of belonging, and promotes community engagement. These social connections and support systems further contribute to better overall health outcomes for individuals.
Overall, by providing cleaner air, promoting physical activity, reducing stress, supporting healthy lifestyles, and enhancing immune system function, green spaces have a significant impact on physical health. The accessibility and availability of green spaces in all communities play a crucial role in reducing health inequalities and ensuring that everyone has equal opportunities to enjoy these health benefits.
Increasing access to green spaces in urban areas can help address health inequalities by providing opportunities for physical activity, reducing stress, and improving air quality. This can lead to better overall health for all residents, regardless of their socioeconomic status.
Impact of Green Space on Mental Health
Green space not only benefits physical health but also has a profound impact on mental well-being. The presence of green spaces in the living environment can have a positive effect on mental health outcomes, promoting overall psychological well-being and reducing the risk of several mental health conditions. Here are some ways in which green space influences mental health:
- Stress reduction: Spending time in green spaces has been shown to significantly reduce stress levels. The calming effect of nature, coupled with the absence of urban noise and distractions, helps individuals unwind and relax, leading to a decrease in stress-related symptoms.
- Improved mood and happiness: Green spaces have a positive impact on mood and emotional well-being. Being in nature, surrounded by greenery and natural beauty, can boost mood, increase feelings of happiness, and reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety.
- Enhanced cognitive function: Interacting with green spaces, whether through activities like walking or simply enjoying the view, has been linked to improved cognitive function. Exposure to nature has been shown to enhance attention span, concentration, and memory.
- Relief from mental fatigue: The demands of modern life can lead to mental fatigue and burnout. Spending time in green spaces provides a respite from the constant stimulation of urban environments, allowing the mind to rest and recover.
- Increased social connections: Green spaces often serve as gathering places for communities, fostering social interactions and promoting a sense of belonging. Engaging in social activities and connecting with others in green spaces can combat feelings of loneliness and improve overall mental well-being.
- Nature as a therapy: Green spaces have been recognized as therapeutic environments, with nature-based therapies gaining popularity. Activities such as horticultural therapy and ecotherapy utilize the healing power of green spaces to improve mental health, reduce symptoms of trauma, and promote self-care.
Green spaces offer a sanctuary from the stresses of daily life, providing individuals with a retreat where they can relax, recharge, and reconnect with nature. The positive effects on mental health can be experienced by people of all ages, from children to older adults.
However, it is essential to ensure that green spaces are accessible and inclusive to all communities, especially those who may face barriers in accessing these environments. By providing equal opportunities for everyone to enjoy the mental health benefits of green spaces, we can work towards reducing mental health inequalities and creating healthier, happier communities.
Access to Green Space and Health Disparities
While green spaces have been shown to have numerous health benefits, not all communities have equal access to these environments. Access to green space can vary depending on factors such as socio-economic status, race/ethnicity, and geographic location, leading to health disparities among different populations.
Several factors contribute to the unequal access to green spaces:
- Socio-economic disparities: Lower-income communities often have fewer green spaces available compared to wealthier neighborhoods. This can be attributed to limited funding for green space development and maintenance, unequal distribution of resources, and historical disinvestment in marginalized areas.
- Racial and ethnic disparities: Minority communities, including Black, Indigenous, and People of Color (BIPOC), often face higher levels of environmental injustice, with limited access to green spaces. This can result from historical inequities, discriminatory housing policies, and the placement of hazardous facilities in these communities.
- Urban versus rural disparities: Rural areas may lack adequate green spaces due to limited resources and infrastructure. Conversely, urban areas face the issue of limited green spaces in densely populated areas, where land is scarce and prioritized for other uses.
- Transportation barriers: Lack of transportation options and the distance to green spaces can hinder access for individuals who do not have their own vehicles. This is particularly challenging for people with disabilities, older adults, and those living in communities with inadequate public transportation.
- Fear and safety concerns: Perceptions of safety and fear of crime can deter individuals, especially children and women, from utilizing green spaces. This may result in underutilization of these spaces and further exacerbate health disparities.
The lack of access to green spaces can have a detrimental impact on the health and well-being of communities. Individuals living in areas with limited green space may face higher rates of chronic diseases, increased stress levels, reduced opportunities for physical activity, and decreased access to the mental health benefits that green spaces provide.
Addressing health disparities requires implementing strategies to improve access to green spaces for all populations. Some approaches that can help bridge the gap include:
- Increasing the availability and accessibility of green spaces, particularly in underserved communities.
- Promoting equitable distribution of green spaces across neighborhoods and ensuring that every community has access to nearby parks, gardens, and recreational areas.
- Engaging community members in the planning and development of green spaces to ensure that their needs and preferences are considered.
- Investing in the maintenance and enhancement of existing green spaces to ensure their long-term viability and appeal.
- Improving transportation options to green spaces, including increasing public transportation routes and improving pedestrian and cycling infrastructure.
- Fostering partnerships between local governments, community organizations, and businesses to fund and support the development of green spaces.
- Addressing safety concerns through enhanced lighting, visible green space design, and community policing initiatives.
By addressing barriers to green space access and promoting equitable distribution, we can work towards reducing health disparities and ensuring that everyone has the opportunity to benefit from the positive impacts of green spaces on health and well-being.
Strategies to Address Health Inequalities through Green Space
To tackle health inequalities and promote equitable access to the benefits of green spaces, several strategies can be implemented. These strategies aim to increase the availability, accessibility, and inclusivity of green spaces in all communities. Here are some approaches that can help address health inequalities:
- Equitable distribution: Ensure that green spaces are distributed equitably across neighborhoods, with a focus on areas that are underserved or have limited access to nature. This can be achieved through strategic planning and allocation of resources to develop green spaces in marginalized communities.
- Community engagement: Involve community members in the planning, design, and management of green spaces. Engage with local residents, community organizations, and stakeholders to understand their needs and preferences, and incorporate their input into the development process.
- Adaptive design: Create green spaces that cater to the diverse needs of the community, including individuals of different ages, abilities, and cultural backgrounds. Consider incorporating features such as accessible pathways, seating areas, play spaces, and facilities for people with disabilities.
- Education and outreach: Conduct educational programs and outreach initiatives to raise awareness about the benefits of green spaces and promote healthy behaviors. Provide information on utilizing green spaces, engaging in physical activity, gardening, and connecting with nature for improved health and well-being.
- Urban greening: Implement urban greening initiatives to increase the presence of green spaces in densely populated areas. This can involve creating rooftop gardens, vertical gardens, and pocket parks to optimize available space and enhance the urban environment.
- Green infrastructure: Integrate green infrastructure, such as street trees, rain gardens, and green roofs, into urban planning and development. This helps maintain a healthy living environment, mitigate the effects of climate change, and improve neighborhood aesthetics.
- Multi-functional spaces: Design green spaces that serve multiple purposes to maximize their benefits and utility. Incorporate features such as community gardens, exercise equipment, gathering spaces, and areas for cultural activities to cater to a wide range of community needs.
- Collaboration and partnerships: Foster collaborations between local governments, community organizations, non-profit groups, and businesses to fund, develop, and maintain green spaces. Leverage public-private partnerships to ensure sustainable funding and shared responsibility for creating and enhancing green spaces.
- Accessibility improvements: Improve infrastructure and transportation options to facilitate better access to green spaces for all individuals. Enhance pedestrian and cycling infrastructure, increase public transportation options, and address safety concerns to encourage more people to utilize green spaces.
By implementing these strategies, we can work towards reducing health inequalities through the promotion of green spaces. Creating a more equitable and accessible environment will empower individuals and communities to enjoy the physical and mental health benefits that green spaces offer, regardless of their socio-economic status, race/ethnicity, or geographic location.
Conclusion
Green spaces have the power to address health inequalities in the living environment through their impact on physical and mental well-being. These vibrant oases of nature not only provide aesthetic pleasure but also offer numerous health benefits that contribute to a better quality of life. From improving air quality and promoting physical activity to reducing stress and enhancing social connections, green spaces play a vital role in creating healthier and more equitable communities.
However, it is important to acknowledge that not all communities have equal access to green spaces, which can perpetuate health disparities. Socio-economic status, race/ethnicity, and geographic location often play a significant role in determining who has access to these valuable environments. To address this issue, it is crucial to implement strategies that increase the availability, accessibility, and inclusivity of green spaces for all populations.
These strategies include equitable distribution of green spaces, community engagement in the planning and development process, adaptive design to cater to diverse needs, education and outreach programs, urban greening initiatives, and collaborations between various stakeholders. By working together, we can ensure that green spaces are not limited to privileged communities but are accessible to individuals from all walks of life.
When green spaces are accessible to everyone, regardless of socio-economic background or race, they become powerful tools for reducing health inequalities. They offer opportunities for individuals to engage in physical activity, connect with nature, improve mental well-being, and foster community ties. Green spaces become places of empowerment, where individuals can take control of their health and well-being.
In conclusion, green spaces have immense potential to address health inequalities in our living environment. They hold the key to creating healthier, happier, and more equitable communities for present and future generations. Let us continue to advocate for the development, maintenance, and accessibility of green spaces as we strive towards a society where everyone can thrive and enjoy the benefits of a greener world.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Can Green Space Address Health Inequalities In The Living Environment?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “How Can Green Space Address Health Inequalities In The Living Environment?”