Home>Garden Essentials>What Is R4 Infill Zoning

Garden Essentials
What Is R4 Infill Zoning
Modified: March 7, 2024
Discover what R4 infill zoning is and how it allows for garden-focused developments. Unlock the potential of your property with garden-friendly zoning regulations.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of R4 infill zoning! Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, this concept is worth exploring. Finding innovative ways to maximize your garden space and create a sustainable and flourishing environment has never been more important.
R4 infill zoning is an approach that has gained popularity in recent years. It offers numerous benefits for both urban and suburban areas, providing opportunities to turn underutilized spaces into lush green havens. By understanding the principles and possibilities of R4 infill zoning, you can transform your garden into a vibrant oasis.
In this article, we will delve into the definition, purpose, benefits, drawbacks, requirements, and case studies of R4 infill zoning. So grab your gardening gloves and let’s dig in!
Key Takeaways:
- R4 infill zoning helps cities use existing land wisely, making room for more homes and green spaces without spreading out too much. It’s like fitting more puzzle pieces into the same puzzle!
- R4 infill zoning can make neighborhoods more lively and diverse by adding different types of homes and improving access to cool stuff like parks and shops. It’s like giving the neighborhood a fun makeover!
Read more: What Does R4 Zoning Mean
Definition of R4 Infill Zoning
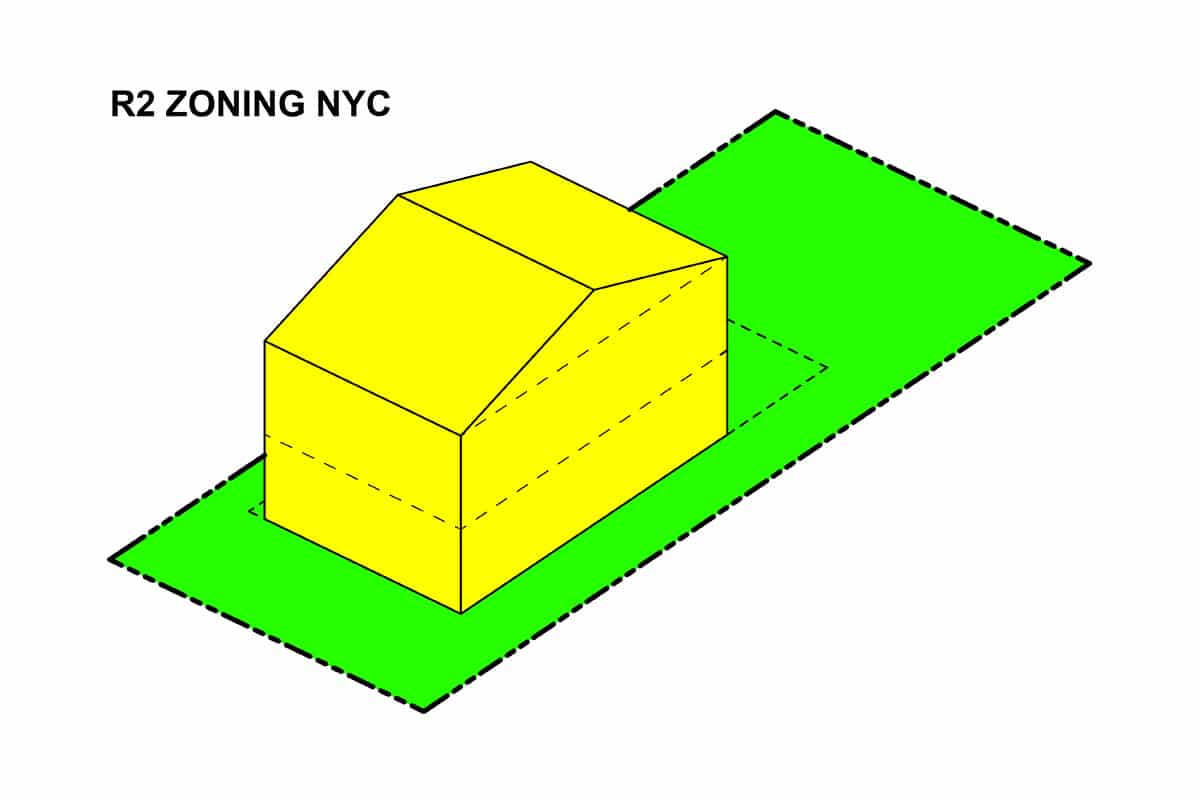
R4 infill zoning refers to a planning and regulatory measure aimed at efficiently using urban or suburban land by allowing increased density and development in specific areas. It is typically implemented in areas that are already built up, where there is limited vacant land available for traditional development.
The “R4” in the term represents the specific zoning designation assigned to these areas, signifying the regulations and guidelines that govern the type and scale of development allowed within the zone. Infill zoning acknowledges the need to accommodate population growth and urban revitalization without expanding into undeveloped or greenfield areas.
Under R4 infill zoning, existing properties and lots are divided into smaller units to create space for new construction. This can include building additional units on a single property or splitting larger lots into multiple smaller parcels to accommodate new structures.
The main objective of R4 infill zoning is to maximize the use of available land and promote sustainable development in already established neighborhoods. By utilizing vacant or underutilized spaces within urban or suburban areas, communities can avoid the negative impacts of sprawling development, such as increased traffic congestion and infrastructure demands.
With R4 infill zoning, there is a focus on integrating new development seamlessly into the fabric of the surrounding neighborhood. This means that new structures should complement the existing architectural style and character, ensuring a cohesive and visually appealing environment. Additionally, provisions may be in place to preserve green spaces and promote energy-efficient design practices.
It is important to note that R4 infill zoning regulations may vary depending on the location and jurisdiction. Local governments often determine the specific parameters, such as the maximum number of units allowed per lot, setbacks from property lines, height restrictions, and parking requirements. Adhering to these regulations is crucial to ensure compliance and avoid penalties or delays in the approval process.
Purpose of R4 Infill Zoning
R4 infill zoning serves several purposes that contribute to sustainable urban development and optimal land use. Let’s explore the key purposes of R4 infill zoning:
1. Increase Urban Density: One of the primary purposes of R4 infill zoning is to increase the density of urban areas. By allowing for the construction of additional units on existing properties or subdividing larger lots, infill zoning helps accommodate the growing population without encroaching on undeveloped land.
2. Utilize Underutilized Land: R4 infill zoning aims to make the most of underutilized or vacant land within built-up areas. By developing these spaces, communities can maximize land use efficiency and create vibrant, functional neighborhoods.
3. Revitalize Established Communities: Infill zoning plays a crucial role in revitalizing established communities. By encouraging new development and investment in older neighborhoods, R4 infill zoning helps breathe new life into these areas, attracting businesses, increasing property values, and improving overall quality of life.
4. Preserve Green Spaces: While infill zoning focuses on utilizing existing developed land, it also aims to preserve and enhance green spaces within urban areas. Through careful planning and design, R4 infill zoning can incorporate parks, gardens, and green infrastructure, promoting a more sustainable and environmentally-friendly urban environment.
5. Promote Transportation Efficiency: Concentrating development in infill areas helps support efficient transportation networks. By locating new residential units close to existing infrastructure and amenities, residents can have easier access to public transportation, reducing reliance on private vehicles and alleviating traffic congestion.
6. Foster Community Integration: R4 infill zoning encourages mixed-use development, creating opportunities for a diverse range of housing options, including affordable housing, townhomes, and apartment complexes. This promotes socio-economic diversity and allows for a more integrated and inclusive community.
7. Improve Walkability and Access to Amenities: By developing infill areas, communities can enhance walkability and provide residents with better access to amenities such as shops, schools, parks, and healthcare facilities. This promotes a more active and connected lifestyle while reducing the need for long commutes.
Overall, the purpose of R4 infill zoning is to create vibrant, sustainable, and well-planned urban environments. By increasing density, utilizing underutilized land, and revitalizing established communities, infill zoning helps accommodate growth while preserving the character and quality of existing neighborhoods. It supports transportation efficiency, fosters community integration, and enhances access to amenities, ultimately improving the overall livability of urban areas.
Benefits of R4 Infill Zoning
R4 infill zoning offers a multitude of benefits for communities, the environment, and individuals. Let’s explore some of the key benefits:
1. Optimal Land Use: R4 infill zoning maximizes the use of existing land within already developed areas, reducing the need for sprawling development. This leads to more efficient land use and prevents the loss of natural habitats and green spaces.
2. Preservation of Rural Areas: By promoting development in infill areas, R4 zoning helps preserve rural and undeveloped areas that would otherwise be at risk of urban expansion. This contributes to the conservation of agricultural land, wildlife habitats, and natural resources.
3. Revitalization of Communities: Infill zoning plays a vital role in revitalizing established communities by attracting new investment, improving property values, and fostering economic growth. It brings life back to underutilized areas and enhances the overall aesthetic appeal and livability of neighborhoods.
4. Improved Access to Amenities: Concentrating development in infill areas brings residents closer to existing amenities such as schools, shopping centers, parks, and public transportation. This improves accessibility and reduces the need for long commutes, enhancing the quality of life for individuals and reducing traffic congestion.
5. Sustainable Transportation: R4 infill zoning promotes a more sustainable transportation system by encouraging walkability and proximity to public transportation options. This reduces reliance on private vehicles, decreases greenhouse gas emissions, and improves air quality.
6. Increased Housing Options: Infill zoning creates opportunities for a diverse range of housing options, including affordable housing units. By increasing the availability of housing in desirable locations, infill zoning helps address housing shortages and promotes socio-economic diversity within communities.
7. Enhanced Community Connectivity: The development of infill areas fosters community connectivity and social interaction. By creating mixed-use developments with residential, commercial, and recreational spaces, infill zoning encourages a vibrant community atmosphere and supports local businesses.
8. Sustainable Design and Construction: R4 infill zoning often incorporates sustainable design practices, such as energy-efficient buildings, green infrastructure, and stormwater management systems. This reduces the environmental impact of new development and promotes sustainable living.
9. Preservation of Historic Character: Infill zoning strategies can include guidelines and regulations that protect the historic character and architectural heritage of established neighborhoods. This ensures that new development blends harmoniously with the existing built environment, preserving the unique charm and identity of the area.
Overall, R4 infill zoning benefits communities by promoting sustainable growth, revitalizing neighborhoods, increasing housing options, and improving access to amenities. It also has positive environmental impacts by preserving rural areas, reducing reliance on cars, and incorporating sustainable design principles. By utilizing infill opportunities, communities can create vibrant and resilient urban environments that balance economic, social, and environmental considerations.
When researching R4 infill zoning, be sure to understand the specific regulations and restrictions that apply to this zoning designation in your area. This will help you make informed decisions about property use and development.
Drawbacks of R4 Infill Zoning
While R4 infill zoning offers numerous benefits, it is important to also consider some of the potential drawbacks that can arise. Here are a few challenges associated with R4 infill zoning:
1. Community Resistance: Introducing new development in established neighborhoods can be met with resistance from existing residents. Concerns about increased traffic, parking issues, and changes to the neighborhood’s character can lead to opposition and conflicts within the community.
2. Limited Green Space: Although R4 infill zoning strives to balance development with the preservation of green spaces, the limited availability of land in built-up areas can lead to reduced open and recreational spaces. This may impact the quality of life for residents, especially in densely populated areas.
3. Strain on Infrastructure: Increasing density through infill development can put a strain on existing infrastructure, such as utilities, roads, and public services. The additional demand on these systems may require upgrades or expansion to accommodate the growing population in the area.
4. Disruption during Construction: The construction phase of infill development can cause temporary disruptions to the daily lives of residents, including noise, dust, and restricted access to roads or parking. This can lead to inconvenience and frustration among both existing and new residents.
5. Affordability Concerns: While infill zoning can provide opportunities for affordable housing, it is not always guaranteed. In some cases, developers may focus on high-end or luxury projects to maximize their return on investment, resulting in limited affordable housing options for low-income residents.
6. Loss of Neighborhood Character: Depending on the design and scale of infill development, there is a risk of losing the unique character and charm of established neighborhoods. In some instances, new structures may not blend harmoniously with the existing architectural style, potentially altering the neighborhood’s identity.
7. Inequality and Gentrification: Infill development can contribute to gentrification, as it often attracts higher-income residents and raises property values. This can lead to displacement of lower-income households and result in social and economic inequality within the community.
8. Regulatory Challenges: Implementing and enforcing infill zoning regulations can be complex, as local governments need to ensure compliance with building codes, design guidelines, and planning standards. In some cases, this may result in delays and additional administrative burdens for both developers and local authorities.
It is crucial for communities and policymakers to address these potential drawbacks and mitigate their impacts through effective planning, community engagement, and careful consideration of the specific needs and characteristics of the area. By addressing these challenges proactively, the negative consequences of R4 infill zoning can be minimized, while maximizing the benefits it offers for sustainable urban development.
Read more: What Does Zoning R Mean
Requirements and Restrictions of R4 Infill Zoning
R4 infill zoning comes with specific requirements and restrictions that dictate the type and scale of development allowed within the designated areas. These guidelines aim to ensure that new construction and redevelopment align with the objectives of sustainable and well-planned urban growth. Let’s take a closer look at some of the common requirements and restrictions of R4 infill zoning:
1. Density Limits: R4 infill zoning typically sets limits on the maximum number of units or dwellings allowed per lot or acre. These limits help control population density and prevent overcrowding in the designated areas.
2. Height and Setback Regulations: To maintain the visual and architectural harmony within established neighborhoods, R4 infill zoning often includes regulations regarding building height and setbacks from property lines. These restrictions ensure that new development fits appropriately within the existing built environment and does not obstruct sunlight or views for neighboring properties.
3. Design Guidelines: Many R4 infill zoning regulations include design guidelines to ensure that new construction adheres to specific aesthetic considerations. These guidelines may outline architectural styles, materials, and other design elements that should be followed to maintain the character and integrity of the neighborhood.
4. Parking Requirements: R4 infill zoning often dictates parking requirements to address the impact of increased density on parking availability. These requirements may specify the number of parking spaces required per unit or establishment, or provide standards for off-street parking facilities.
5. Open Space and Landscaping: To preserve greenery and promote a pleasant environment, R4 infill zoning often includes requirements for open space and landscaping. These requirements may mandate a minimum percentage of land to be dedicated to green space, specify types of vegetation to be planted, and establish guidelines for the maintenance of landscaping within the designated areas.
6. Affordable Housing Provisions: Some R4 infill zoning regulations may include provisions for affordable housing to address the need for diverse housing options. These provisions can require developers to allocate a certain percentage of units for affordable housing or payment of an in-lieu fee that supports affordable housing initiatives within the community.
7. Stormwater Drainage: In order to mitigate the impact of increased development on stormwater runoff, R4 infill zoning may have requirements for stormwater management. This can include the installation of retention ponds, green infrastructure, or the use of permeable surfaces to reduce the strain on local drainage systems.
8. Environmental Impact Assessments: Depending on the jurisdiction, R4 infill zoning may require developers to conduct environmental impact assessments to identify and mitigate potential environmental risks associated with the proposed development. This ensures that the project is conducted in an environmentally responsible manner.
It is important to note that the specific requirements and restrictions of R4 infill zoning can differ based on local regulations and the needs of the community. Developers and property owners must familiarize themselves with the zoning requirements and seek appropriate approvals from local planning authorities before proceeding with any infill development projects.
By adhering to these requirements and restrictions, developers can contribute to responsible and well-planned urban growth while maintaining the integrity and character of the surrounding neighborhoods.
Case Studies of R4 Infill Zoning Implementation
Examining real-world examples of R4 infill zoning implementation can provide valuable insights into the benefits and challenges of this approach. Let’s explore a few case studies that highlight successful R4 infill zoning projects:
1. Case Study 1: Portland, Oregon, USA
In Portland, the R4 infill zoning strategy has been instrumental in transforming underutilized spaces into vibrant communities. By encouraging the development of accessory dwelling units (ADUs), such as granny flats and converted basements, the city has increased affordable housing options while utilizing existing residential properties. This approach has not only provided additional housing units but has also contributed to improved neighborhood diversity and increased rental income for property owners.
2. Case Study 2: Vancouver, Canada
Vancouver has implemented innovative R4 infill zoning regulations to address housing affordability and sustainability. The city allows laneway housing, which involves building small, detached homes on existing lots facing back alleys. This approach maximizes land use in established neighborhoods and provides more affordable housing options for both homeowners and tenants. The laneway housing initiative has successfully revitalized neighborhoods and increased population density without compromising the overall character of the area.
3. Case Study 3: Melbourne, Australia
Melbourne has implemented R4 infill zoning to encourage urban regeneration and combat urban sprawl. The city’s strategy involves transforming underutilized industrial areas into mixed-use developments, incorporating residential, commercial, and recreational spaces. These developments have revitalized previously neglected areas, attracted investment, and boosted economic growth. By integrating new development with existing neighborhoods and enhancing urban amenities, Melbourne has created vibrant and livable communities.
4. Case Study 4: Stockholm, Sweden
Stockholm has utilized R4 infill zoning to address the growing demand for housing while promoting sustainable urban development. The city has implemented regulations that encourage the construction of energy-efficient and environmentally-friendly buildings. These developments prioritize sustainable design practices, such as green roofs, rainwater harvesting systems, and renewable energy sources. By combining increased housing density with sustainable features, Stockholm has created attractive, eco-friendly neighborhoods.
5. Case Study 5: Tokyo, Japan
Tokyo’s approach to R4 infill zoning has been focused on transforming older residential areas through redevelopment. The city aims to replace low-rise housing with taller, modern buildings to increase housing capacity and improve earthquake resistance. Through careful planning and design, Tokyo has successfully revitalized neighborhoods, enhanced accessibility to amenities and transportation, and created more resilient communities.
These case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of R4 infill zoning in various cities around the world. By utilizing existing land and maximizing density, these cities have addressed housing shortages, revitalized neighborhoods, and promoted sustainable growth. However, each case study also highlights the importance of careful planning, community engagement, and adherence to design guidelines to ensure that infill development aligns with the needs and characteristics of the specific area.
By learning from these examples, policymakers and communities can gain valuable insights into the implementation of successful R4 infill zoning projects and tailor their approach to suit their unique local context.
Conclusion
R4 infill zoning offers a promising approach to address the challenges of urban growth and sustainable development. By efficiently utilizing existing land within built-up areas, R4 infill zoning maximizes density, revitalizes neighborhoods, and promotes vibrant and resilient communities.
Throughout this article, we have explored the definition, purpose, benefits, drawbacks, requirements, and case studies of R4 infill zoning. It is clear that this zoning strategy provides a range of advantages, such as optimal land use, community revitalization, improved access to amenities, and sustainable transportation. However, we must also acknowledge the potential challenges, including community resistance, infrastructure strain, and affordability concerns.
Successful implementation of R4 infill zoning requires careful planning, community engagement, and adherence to design guidelines. It is essential to strike a balance between accommodating growth and preserving the character and integrity of existing neighborhoods. By incorporating principles of sustainability, affordability, and social inclusivity, R4 infill zoning can contribute to creating thriving, livable, and environmentally conscious urban environments.
As cities continue to face the pressures of population growth and urban expansion, R4 infill zoning offers a viable solution to accommodate increased density and address housing shortages without encroaching on undeveloped land. With thoughtful and sustainable infill development, we have the opportunity to create vibrant communities that promote social interaction, support local economies, and reduce environmental impacts.
In conclusion, R4 infill zoning presents a valuable tool for urban planners, policymakers, and communities to navigate the challenges of urban growth while fostering sustainable and inclusive development. By embracing the potential of underutilized spaces within our cities, we can build a future where vibrant communities thrive and open green spaces are preserved for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is R4 Infill Zoning
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.









0 thoughts on “What Is R4 Infill Zoning”