Home>Gardening & Outdoor>Plant Care & Gardening Tips>Which Insect Group Is Responsible For The Germination Of Many Wildflower Seeds In North America


Plant Care & Gardening Tips
Which Insect Group Is Responsible For The Germination Of Many Wildflower Seeds In North America
Modified: January 4, 2024
Discover the vital role of plant-care-and-gardening-tips in North America as they facilitate the germination of numerous wildflower seeds, contributing to the region's diverse flora. Explore the fascinating relationship between this insect group and the proliferation of native wildflowers.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Wildflowers are not only a sight to behold but also play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. Their vibrant colors and delicate petals not only beautify landscapes but also support a diverse range of wildlife. However, the process of wildflower seed germination is not solely reliant on soil, water, and sunlight; it also heavily depends on the assistance of various insect groups. In North America, these insects have a pivotal role in the germination of many wildflower seeds, contributing to the perpetuation of these beautiful blooms. Understanding the intricate relationship between insects and wildflower seed germination sheds light on the interconnectedness of nature and the delicate balance that sustains our ecosystems. In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of wildflower seed germination and the invaluable contribution of insect groups in this process.
Key Takeaways:
- Insects like bees, butterflies, ants, and beetles play a crucial role in helping wildflower seeds to grow and thrive in North America, supporting the beauty and balance of natural ecosystems.
- Wildflowers not only look beautiful but also support a diverse range of wildlife, and insects are essential partners in helping these vibrant blooms to grow and spread across North America’s landscapes.
The Role of Insects in Wildflower Seed Germination
Wildflower seed germination is a complex process that involves various natural elements, with insects playing a crucial role in this intricate dance of life. Insects contribute to wildflower seed germination through a series of interconnected actions that are essential for the successful propagation of these blooms.
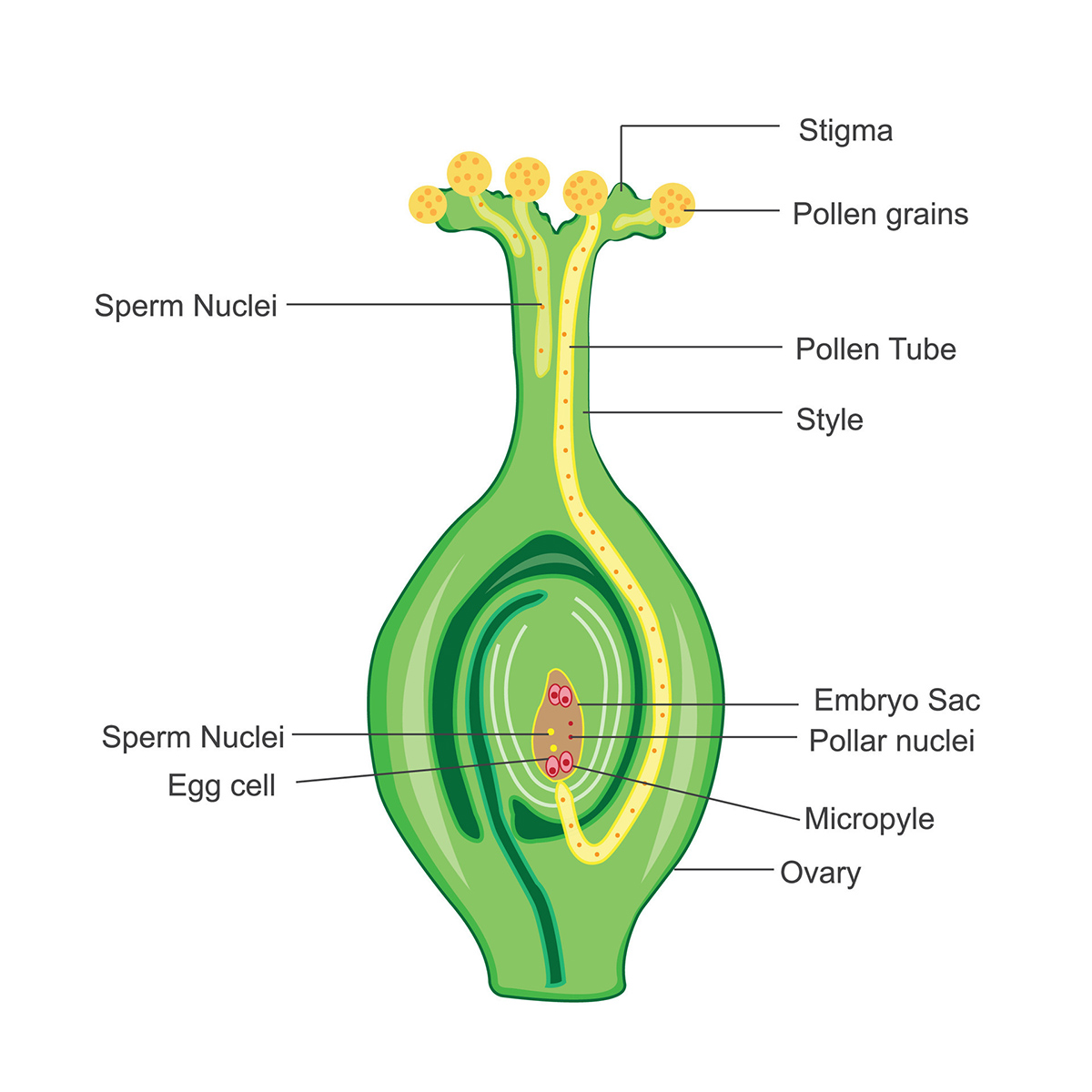
One of the primary ways in which insects facilitate wildflower seed germination is through pollination. As insects visit flowers in search of nectar and pollen, they inadvertently transfer pollen from one flower to another, facilitating the fertilization process. This pollen transfer is essential for the production of seeds, which are vital for the next generation of wildflowers. Without the diligent work of pollinating insects, many wildflower species would struggle to produce seeds, hindering their ability to propagate and thrive in their natural habitats.
Furthermore, certain insects play a direct role in seed dispersal, aiding in the distribution of wildflower seeds across diverse landscapes. Insects such as ants and beetles are known to carry and bury seeds, inadvertently aiding in their germination. This process, known as myrmecochory, not only assists in seed dispersal but also provides the seeds with a protective environment for germination, increasing their chances of successful growth.
Additionally, some insects contribute to wildflower seed germination through their feeding behaviors. Certain seeds have evolved to rely on specific insects to aid in their scarification or the breaking of seed dormancy. For example, the hard coatings of some wildflower seeds may require the mechanical action of insects’ mandibles or digestive tracts to weaken and break, allowing the seeds to germinate more effectively.
The intricate relationship between insects and wildflower seed germination highlights the interdependence of these organisms within ecosystems. By fulfilling various roles such as pollination, seed dispersal, and scarification, insects play a vital part in ensuring the continued proliferation of wildflowers, contributing to the biodiversity and resilience of natural habitats.
Insect Groups Responsible for Wildflower Seed Germination
Several diverse insect groups actively participate in the facilitation of wildflower seed germination, each contributing to the process in unique and indispensable ways. Understanding the specific roles of these insect groups provides insight into the intricate mechanisms that drive the germination and propagation of wildflowers across North America.
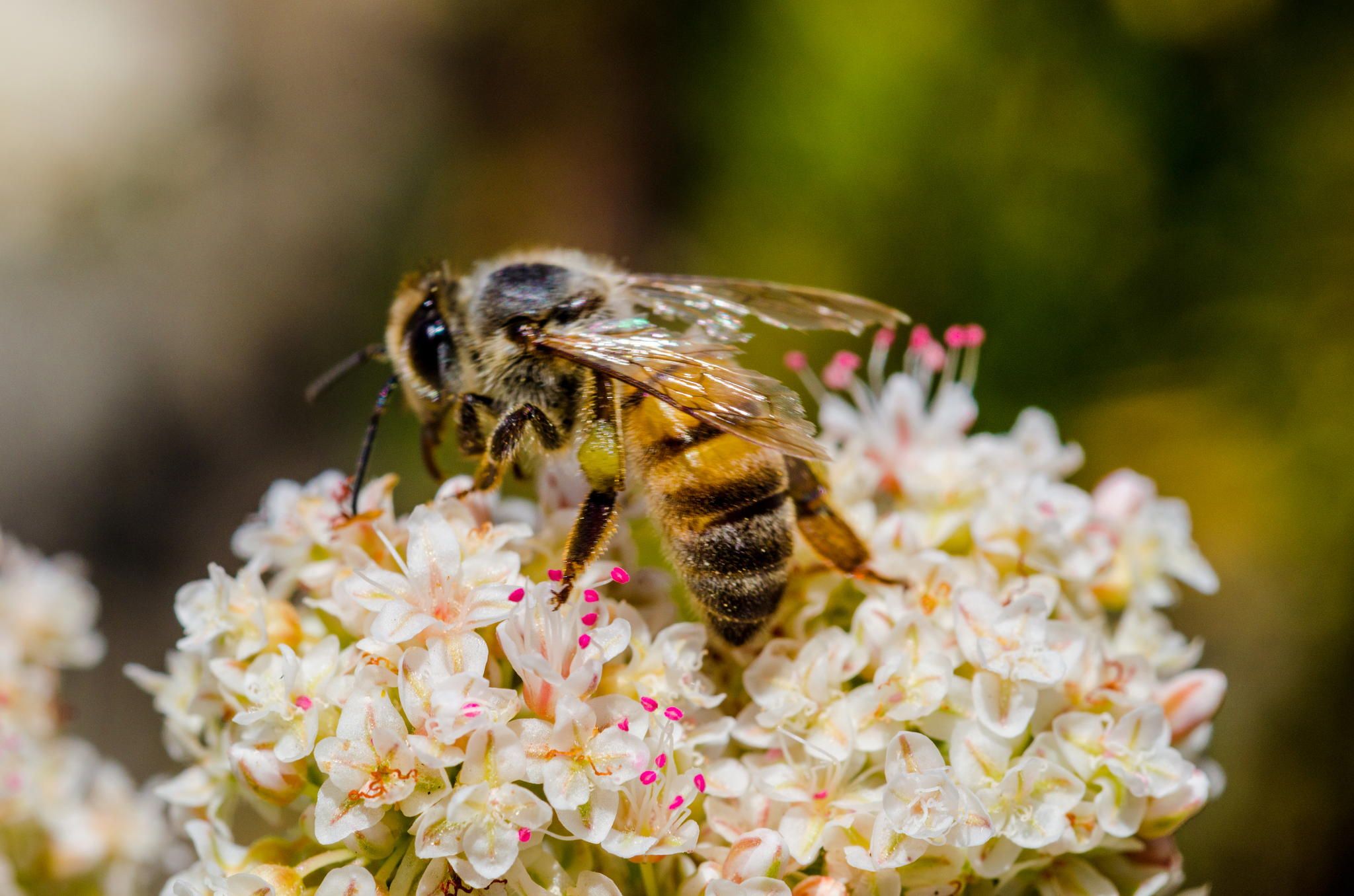
Bees:
Bees are among the most prominent and effective pollinators of wildflowers. Their foraging activities result in the transfer of pollen between flowers, promoting fertilization and seed production. In addition to their role in pollination, certain bee species engage in a behavior known as “buzz pollination,” where they use sonic vibrations to release pollen from flowers, further aiding in the reproductive success of wildflower species. The indispensable contribution of bees to wildflower seed germination underscores the critical role of these industrious insects in sustaining floral diversity.
Butterflies:
Butterflies, with their graceful flight and delicate beauty, are not only a captivating sight but also essential pollinators of numerous wildflower species. As they flit from flower to flower in search of nectar, butterflies inadvertently transfer pollen, facilitating the fertilization process. Their role in wildflower seed germination highlights the interconnected relationship between these ethereal insects and the vibrant blooms that adorn meadows and woodlands.
Read more: How Long Do Wildflowers Take To Germinate
Ants:
Ants play a unique role in wildflower seed dispersal through a process known as myrmecochory. Certain wildflower seeds have specialized structures, called elaiosomes, which attract ants. The ants carry these seeds to their underground nests, where they consume the elaiosomes and discard the seeds in nutrient-rich chambers. This process not only aids in seed dispersal but also provides an optimal environment for germination, enhancing the chances of successful seedling establishment.
Beetles:
Beetles, with their diverse species and ecological roles, contribute to wildflower seed germination through their involvement in both pollination and seed dispersal. Some beetle species are known to visit flowers for nectar and inadvertently transfer pollen, while others aid in seed dispersal by carrying seeds to new locations. The varied interactions between beetles and wildflowers highlight the intricate web of ecological relationships that underpin the successful germination and proliferation of these blooms.
Flies:
Flies, often overlooked in discussions of pollination and seed dispersal, play a significant role in the germination of certain wildflower species. Their visits to flowers for feeding purposes result in the transfer of pollen, contributing to the reproductive success of diverse wildflower species. The diverse behaviors and ecological interactions of flies underscore their importance in supporting the germination and propagation of wildflowers in North America.
These insect groups, among others, contribute to the rich tapestry of interactions that underlie the germination and proliferation of wildflowers in North America. Their diverse roles in pollination, seed dispersal, and scarification collectively contribute to the perpetuation of these vibrant blooms, shaping the ecological landscapes and sustaining biodiversity.
Importance of Wildflower Seed Germination for Ecosystems
The germination of wildflower seeds plays a pivotal role in maintaining the health and resilience of ecosystems across North America. The presence of diverse wildflower species not only enhances the visual appeal of natural landscapes but also contributes to the overall ecological balance and the well-being of numerous organisms within these habitats.
Read more: How Many Days For Yarrow To Germinate
Biodiversity and Habitat Support:
Wildflower seed germination fosters biodiversity by providing essential habitats and food sources for a myriad of organisms. The diverse array of wildflower species supports a wide range of pollinators, including bees, butterflies, and other insects, ensuring the continued reproductive success of flowering plants. Additionally, the seeds, fruits, and nectar produced by wildflowers serve as vital food sources for birds, small mammals, and other wildlife, contributing to the intricate food webs that sustain ecological communities.
Erosion Control and Soil Health:
Wildflowers play a crucial role in preventing soil erosion and maintaining soil health. The extensive root systems of wildflowers help stabilize soil, reducing the risk of erosion caused by wind and water. Furthermore, the decomposition of wildflower plant material enriches the soil with organic matter, enhancing its fertility and supporting the growth of other plant species. By promoting soil stability and health, wildflower seed germination contributes to the overall resilience of ecosystems and their capacity to support diverse flora and fauna.
Pollination and Reproduction:
Wildflower seed germination is intrinsically linked to the process of pollination, which is essential for the reproduction of flowering plants. Pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and other insects facilitate the transfer of pollen between flowers, leading to the production of seeds and the perpetuation of wildflower species. The successful germination of wildflower seeds ensures the continued presence of these essential pollinator-attracting plants, supporting the reproductive success of numerous plant species and contributing to the overall stability of ecosystems.
Aesthetic and Cultural Value:
Beyond their ecological significance, wildflowers hold a profound aesthetic and cultural value. Their vibrant colors and delicate blooms enrich the visual tapestry of natural landscapes, providing inspiration and joy to those who encounter them. Additionally, wildflowers have been deeply intertwined with human cultures, serving as symbols of resilience, beauty, and the interconnectedness of all living beings. The successful germination of wildflower seeds ensures the perpetuation of these cultural and aesthetic treasures, enriching the human experience and fostering a deeper appreciation for the natural world.
The importance of wildflower seed germination for ecosystems cannot be overstated. By supporting biodiversity, promoting soil health, facilitating pollination, and enriching human experiences, wildflowers contribute to the vitality and interconnectedness of natural environments, underscoring the need for their conservation and sustainable management.
Read more: How Many Days For Marigolds To Germinate
Conclusion
The intricate relationship between insects and wildflower seed germination underscores the interconnectedness of nature and the vital role played by these vibrant blooms in sustaining ecosystems across North America. Insects, ranging from bees and butterflies to ants and beetles, contribute to the successful germination and propagation of wildflowers through their diverse roles in pollination, seed dispersal, and scarification. Their collective efforts support the biodiversity, habitat stability, and cultural significance of wildflowers, highlighting the far-reaching impact of these delicate blooms on the natural world and human experiences.
Understanding the importance of wildflower seed germination for ecosystems reveals the intricate web of ecological interactions that underpin the health and resilience of natural habitats. From providing essential habitats and food sources for diverse organisms to promoting soil stability and preventing erosion, wildflowers contribute to the overall balance and functionality of ecosystems. Their role in supporting pollinators and facilitating the reproduction of flowering plants further underscores their significance in maintaining the delicate balance of natural environments.
As we marvel at the beauty of wildflowers and witness the bustling activities of insects among their blooms, we are reminded of the interconnectedness of all living beings and the delicate dance of life that sustains our planet. The conservation and preservation of wildflower habitats, along with the protection of their insect allies, are essential for maintaining the ecological integrity and beauty of our natural landscapes. By recognizing the invaluable contribution of insects to wildflower seed germination and the broader implications for ecosystems, we can cultivate a deeper appreciation for the intricate and wondrous tapestry of life that surrounds us.
Ultimately, the partnership between insects and wildflowers serves as a poignant reminder of the harmonious relationships that define the natural world, inspiring us to cherish and protect the delicate balance that sustains the diverse array of life on our planet.
Frequently Asked Questions about Which Insect Group Is Responsible For The Germination Of Many Wildflower Seeds In North America
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “Which Insect Group Is Responsible For The Germination Of Many Wildflower Seeds In North America”