Home>Technology>Home Entertainment Systems>How Is Data Transmitted By Television Companies?


Home Entertainment Systems
How Is Data Transmitted By Television Companies?
Modified: January 9, 2024
Learn how data is transmitted by television companies to enhance your home entertainment systems. Explore the technology behind seamless streaming and high-quality content delivery. Discover the latest advancements in home entertainment systems.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Home entertainment systems have evolved significantly over the years, and one crucial aspect of their operation is the transmission of data by television companies. Understanding how this data is transmitted is essential for consumers who want to make informed decisions about their home entertainment setups. In this article, we will explore the various methods used by television companies to transmit data, including analog and digital transmission, cable television, satellite television, and Internet Protocol Television (IPTV). By delving into these technologies, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and innovation that underpin modern home entertainment systems.
Key Takeaways:
- Television companies have evolved from using analog to digital transmission, offering better quality, more channels, and interactive features. This has revolutionized home entertainment systems, providing a diverse and immersive viewing experience.
- Cable, satellite, and IPTV data transmission methods have expanded the capabilities of home entertainment, offering high-quality programming, interactive features, and a versatile multimedia platform. These advancements continue to redefine the modern home entertainment experience.
Read more: How To Store Data In Database
Analog Data Transmission
In the early days of television, analog data transmission was the primary method used by television companies to deliver content to viewers’ homes. Analog signals are continuous waves that vary in amplitude and frequency to represent the audio and video information being transmitted. The most common form of analog transmission is through radio frequency signals, which are modulated to carry audio and video information. These signals are then received by television antennas and decoded by the television set to display the content.
One of the key characteristics of analog data transmission is its susceptibility to interference and degradation. External factors such as electromagnetic interference and signal attenuation can distort the transmitted signals, leading to poor image and sound quality. Additionally, analog signals are limited in the amount of information they can carry, which restricts the quality of the content that can be delivered to viewers.
While analog data transmission was once the standard for television broadcasting, technological advancements have paved the way for digital transmission, offering improved signal quality, increased channel capacity, and enhanced reliability. As a result, analog transmission has largely been phased out in favor of digital technologies, marking a significant shift in the way television companies deliver content to consumers.
Digital Data Transmission
With the advancement of technology, television companies have transitioned from analog to digital data transmission, revolutionizing the way content is delivered to home entertainment systems. Digital transmission involves encoding audio and video signals into binary data, which is then transmitted as discrete packets of information. This method offers several advantages over analog transmission, including improved signal quality, greater efficiency in spectrum usage, and the ability to deliver high-definition and even ultra-high-definition content.
One of the key benefits of digital data transmission is its resistance to signal degradation and interference. Unlike analog signals, digital signals can be accurately reconstructed at the receiving end, resulting in consistently high-quality audio and video output. Furthermore, digital transmission allows for the implementation of error correction techniques, ensuring that data integrity is maintained throughout the transmission process.
Another significant advantage of digital data transmission is its capacity for multiplexing, which enables multiple channels to be transmitted within the same frequency spectrum. This efficient use of bandwidth has expanded the range of programming available to viewers, offering a diverse selection of channels and content options.
Moreover, digital transmission has facilitated the integration of interactive features and additional data services, such as electronic program guides, on-screen displays, and interactive advertising. These enhancements have enriched the viewing experience and provided viewers with more control and customization options.
Overall, the transition to digital data transmission has elevated the quality, reliability, and versatility of television broadcasting, setting the stage for the next generation of home entertainment experiences.
Cable Television Data Transmission
Cable television, also known as cable TV, operates on a different principle compared to traditional broadcast television. Instead of relying on over-the-air transmission, cable TV utilizes a physical network of coaxial or fiber-optic cables to deliver audio and video signals directly to consumers’ homes. This infrastructure enables cable television companies to provide a wide range of channels and services, including high-speed internet access and digital telephone services, all through a single connection.
At the heart of cable television data transmission is the use of digital signals, which are modulated and transmitted over the cable network to subscribers’ set-top boxes or cable modems. This digital transmission allows for the delivery of high-quality audio and video content, including high-definition programming and on-demand services.
Furthermore, cable television systems employ a technique known as frequency division multiplexing (FDM) to allocate different channels within the available frequency spectrum. This method enables the simultaneous transmission of numerous channels over the same cable, providing viewers with a diverse selection of programming options.
One of the notable advantages of cable television data transmission is its ability to offer two-way communication, allowing viewers to interact with the content and access interactive services. This interactivity has paved the way for features such as video-on-demand, pay-per-view programming, and interactive television applications, enhancing the overall viewing experience for consumers.
Moreover, the integration of broadband internet services into cable television networks has expanded the capabilities of these systems, enabling high-speed internet access and the delivery of digital content over the same infrastructure. This convergence of services has transformed cable television into a comprehensive platform for entertainment, communication, and information dissemination.
Overall, cable television data transmission represents a sophisticated and versatile method of delivering audio and video content to consumers, offering a diverse array of programming options and interactive features that continue to shape the landscape of home entertainment.
Data is transmitted by television companies through a process called modulation, where the digital information is converted into analog signals for transmission through the airwaves. This allows the data to be received by television antennas and decoded by the TV set for viewing.
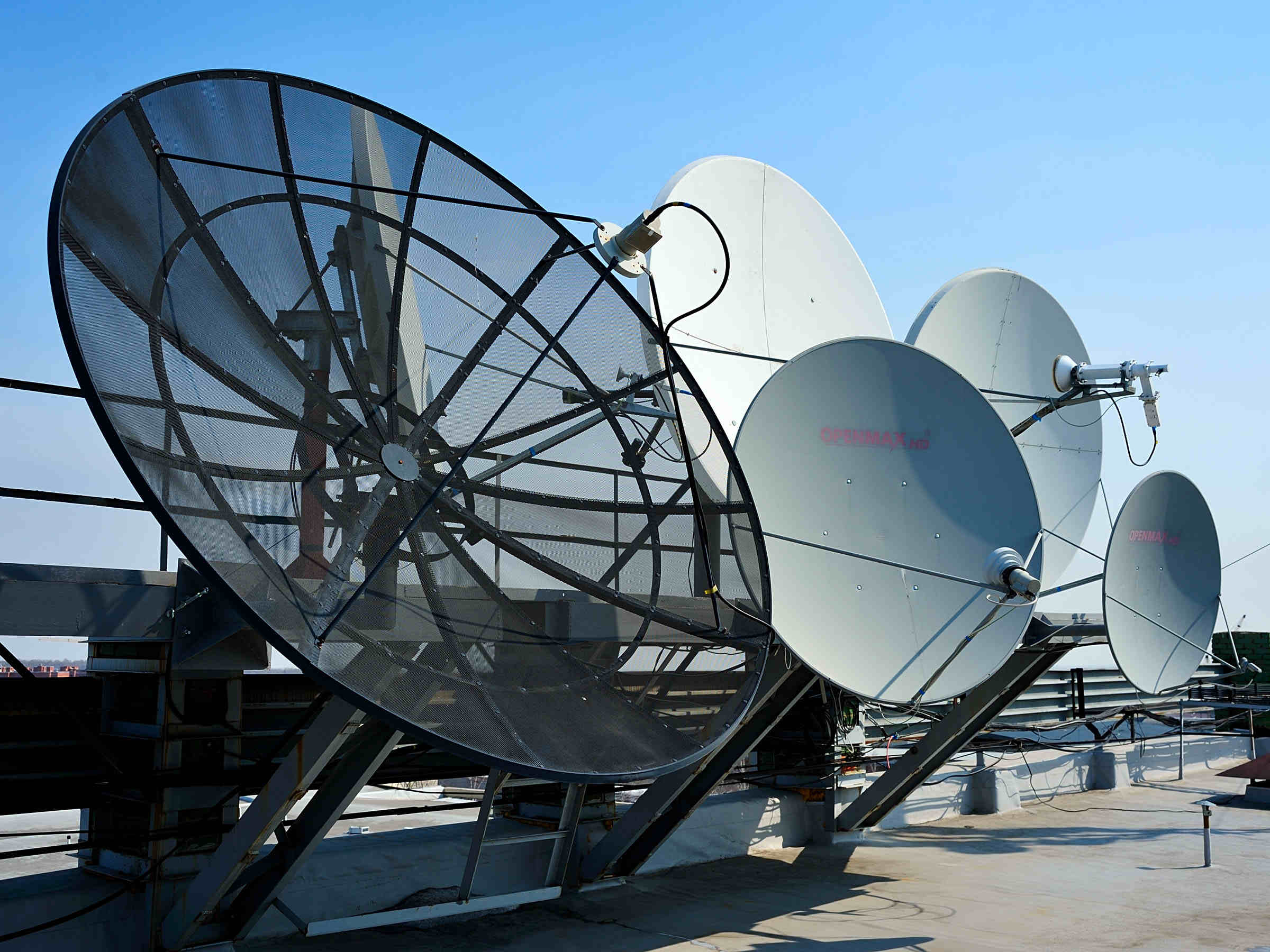
Satellite Television Data Transmission
Satellite television data transmission involves the delivery of audio and video content to consumers through the use of communication satellites orbiting the Earth. This method of content delivery offers widespread coverage, making it particularly valuable for reaching viewers in remote or geographically dispersed locations where traditional cable or terrestrial broadcasting may be impractical.
At the core of satellite television data transmission is the uplink process, where television content is transmitted from a ground station to the communication satellite. The satellite then receives, amplifies, and retransmits the signals back to Earth, where they are captured by satellite dishes installed at subscribers’ homes. This process enables the distribution of a wide range of programming, including local, national, and international channels, directly to viewers’ television sets.
One of the key advantages of satellite television data transmission is its ability to deliver high-quality audio and video content, including high-definition and ultra-high-definition programming. The digital signals transmitted via satellite ensure a reliable and consistent viewing experience for consumers, regardless of their geographic location.
Furthermore, satellite television systems can offer an extensive selection of channels and programming options, catering to diverse audience preferences. This expansive content offering, combined with the widespread coverage facilitated by satellites, has made satellite television a popular choice for consumers seeking a comprehensive and varied entertainment experience.
Moreover, satellite television data transmission has played a pivotal role in the globalization of media and entertainment, allowing viewers to access content from around the world. This has contributed to cultural exchange and the dissemination of diverse perspectives, enriching the viewing landscape for audiences worldwide.
Overall, satellite television data transmission represents a powerful and versatile method of delivering audio and video content to consumers, offering broad coverage, high-quality programming, and an extensive array of channels that continue to shape the landscape of home entertainment on a global scale.
Read more: How To Store Data In Python
Internet Protocol Television (IPTV) Data Transmission
Internet Protocol Television (IPTV) represents a modern and innovative approach to delivering audio and video content to consumers, leveraging the capabilities of internet protocol (IP) networks to transmit television signals. Unlike traditional broadcast, cable, or satellite television, IPTV operates through internet-based networks, enabling the seamless delivery of multimedia content to viewers’ homes.
At the heart of IPTV data transmission is the use of IP packets to transport audio, video, and control signals over the internet. This method allows for the efficient and flexible distribution of content, offering viewers access to an extensive range of programming, including live television, video-on-demand, and interactive media services.
One of the key advantages of IPTV is its ability to deliver high-quality audio and video content, including high-definition and ultra-high-definition programming, over IP networks. This ensures a superior viewing experience for consumers, characterized by crisp visuals, immersive audio, and seamless playback.
Furthermore, IPTV systems support interactive features and personalized content delivery, empowering viewers to engage with the programming, access on-demand services, and customize their entertainment preferences. This interactivity enhances the overall viewing experience, providing consumers with greater control and flexibility in accessing multimedia content.
Moreover, IPTV data transmission enables the integration of additional services such as electronic program guides, digital video recording, and multimedia applications, enriching the functionality and utility of the television viewing experience. These enhancements contribute to a more dynamic and engaging entertainment environment for consumers.
Additionally, IPTV has facilitated the convergence of television, internet, and telecommunications services, offering a comprehensive platform for entertainment, communication, and information dissemination. This convergence has expanded the capabilities of home entertainment systems, providing consumers with a versatile and integrated multimedia experience.
Overall, Internet Protocol Television (IPTV) data transmission represents a cutting-edge and dynamic method of delivering audio and video content to consumers, harnessing the power of IP networks to offer high-quality programming, interactive features, and personalized entertainment options that continue to redefine the modern home entertainment experience.
Conclusion
The transmission of data by television companies has undergone remarkable evolution, transitioning from analog to digital technologies and embracing innovative methods such as cable, satellite, and Internet Protocol Television (IPTV) data transmission. These advancements have revolutionized the delivery of audio and video content to home entertainment systems, offering consumers a diverse array of programming options, interactive features, and high-quality viewing experiences.
While analog data transmission laid the foundation for television broadcasting, digital transmission has emerged as the cornerstone of modern home entertainment, delivering superior signal quality, increased channel capacity, and enhanced reliability. The transition to digital technologies has empowered television companies to provide high-definition and ultra-high-definition content, interactive services, and personalized viewing experiences, setting a new standard for home entertainment.
Cable television data transmission has expanded the capabilities of home entertainment systems, offering a comprehensive platform for audio, video, and internet services over a single connection. The integration of broadband internet and interactive features has enriched the viewing experience, providing consumers with a versatile and dynamic entertainment environment.
Similarly, satellite television data transmission has played a pivotal role in global media dissemination, offering widespread coverage, high-quality programming, and an extensive array of channels. The use of communication satellites has facilitated the globalization of entertainment, allowing viewers to access content from around the world and contributing to cultural exchange on a global scale.
Internet Protocol Television (IPTV) data transmission represents a cutting-edge approach to delivering multimedia content, harnessing the capabilities of IP networks to offer high-quality programming, interactive features, and personalized entertainment options. The convergence of television, internet, and telecommunications services has redefined the modern home entertainment experience, providing consumers with a versatile and integrated multimedia platform.
In conclusion, the transmission of data by television companies continues to shape the landscape of home entertainment, offering consumers a wealth of options, interactivity, and high-quality content. As technology continues to advance, television companies are poised to further innovate and enhance the home entertainment experience, ensuring that consumers can enjoy immersive, personalized, and dynamic audio and video content in the comfort of their homes.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Is Data Transmitted By Television Companies?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “How Is Data Transmitted By Television Companies?”