Home>Technology>Smart Home Devices>How To Setup A Wi-Fi Router Without A Modem


Smart Home Devices
How To Setup A Wi-Fi Router Without A Modem
Modified: January 7, 2024
Learn how to set up a Wi-Fi router without a modem and connect smart home devices easily. Get step-by-step instructions for a seamless setup.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
**
Introduction
**
Setting up a Wi-Fi router without a modem is a common scenario in today's smart homes. With the increasing popularity of mesh Wi-Fi systems and the availability of standalone routers that offer advanced features, many users are opting to create their own Wi-Fi networks without relying on traditional modems. This approach allows for greater flexibility, improved performance, and enhanced control over the network.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of setting up a Wi-Fi router without a modem, exploring the technical aspects, potential challenges, and troubleshooting tips. Whether you are a tech enthusiast looking to optimize your home network or a novice seeking to understand the fundamentals of networking, this article will provide valuable insights to help you navigate the process with confidence.
We will begin by demystifying the role of Wi-Fi routers and their significance in modern households. Understanding the core functions and capabilities of these devices is essential for establishing a robust and reliable Wi-Fi network. Subsequently, we will delve into the step-by-step process of setting up a Wi-Fi router without a modem, addressing common misconceptions and offering practical guidance.
Furthermore, we will explore the crucial aspect of connecting various devices to the Wi-Fi router, encompassing smartphones, laptops, smart home gadgets, and other IoT (Internet of Things) devices. This section will elucidate the seamless integration of devices into the network, highlighting the convenience and versatility offered by standalone Wi-Fi routers.
Additionally, we will provide invaluable troubleshooting tips and recommendations to address potential issues that may arise during the setup process. By equipping readers with practical solutions and best practices, we aim to empower individuals to overcome technical hurdles and optimize their Wi-Fi networks effectively.
Ultimately, this guide aims to demystify the process of setting up a Wi-Fi router without a modem, catering to a diverse audience with varying levels of technical expertise. Whether you are embarking on this endeavor for the first time or seeking to refine your networking skills, this article will serve as a comprehensive resource, offering actionable insights and expert guidance.
Stay tuned as we unravel the intricacies of creating a robust and efficient Wi-Fi network without a modem, empowering you to harness the full potential of standalone routers in the digital age.
**
Key Takeaways:
- Setting up a Wi-Fi router without a modem offers more flexibility and control over your wireless network, allowing you to create a personalized and reliable Wi-Fi environment tailored to your specific needs.
- By understanding the role of Wi-Fi routers and following simple steps, you can seamlessly connect various devices to your standalone network, ensuring a smooth and interconnected digital experience within your home.
Read more: How To Connect A Wi-Fi Router To A Modem
Understanding Wi-Fi Routers
**
To embark on the journey of setting up a Wi-Fi router without a modem, it is imperative to grasp the fundamental role and functionality of these ubiquitous devices. Wi-Fi routers serve as the cornerstone of modern wireless networking, facilitating seamless connectivity and data transmission within homes, offices, and public spaces.
At its core, a Wi-Fi router acts as a central hub that enables wireless communication between various devices, such as smartphones, laptops, smart TVs, and IoT gadgets, utilizing the 802.11 standard for wireless networking. This pivotal device not only facilitates internet access but also enables inter-device communication, paving the way for the interconnected ecosystem of the Internet of Things (IoT).
One of the key functions of a Wi-Fi router is to create a local area network (LAN) within a specific physical space, allowing devices to communicate with each other and access shared resources, such as printers and network-attached storage (NAS) devices. Additionally, the router serves as a gateway to the internet, enabling devices within the network to access online services, streaming platforms, and web-based applications.
Furthermore, Wi-Fi routers employ advanced security protocols, such as WPA3 encryption and firewall capabilities, to safeguard the network from unauthorized access and cyber threats. This emphasis on security is paramount in the era of interconnected devices, where the protection of sensitive data and personal information is of utmost importance.
Moreover, modern Wi-Fi routers often integrate advanced features, including beamforming technology for optimized signal transmission, Quality of Service (QoS) settings for prioritizing specific types of network traffic, and parental control functionalities for managing internet access and content filtering.
As the demand for high-speed, reliable wireless connectivity continues to surge, Wi-Fi routers have evolved to support the latest wireless standards, such as Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax), which offers enhanced performance, increased capacity, and improved efficiency in handling multiple connected devices simultaneously.
In essence, understanding the multifaceted capabilities of Wi-Fi routers is essential for harnessing their full potential in creating robust, high-performance wireless networks. By comprehending the pivotal role of these devices in modern connectivity paradigms, individuals can embark on the journey of setting up a Wi-Fi router without a modem with clarity and confidence.
Now that we have unraveled the essence of Wi-Fi routers, let us delve into the intricacies of setting up a standalone Wi-Fi network, bypassing the conventional reliance on modems.
**
Setting Up a Wi-Fi Router Without a Modem
**
Setting up a Wi-Fi router without a modem entails a straightforward yet meticulous process that empowers users to establish a standalone wireless network with ease. While traditional networking setups often revolve around the integration of modems and routers, the standalone configuration offers unparalleled flexibility and customization options for optimizing wireless connectivity.
Before delving into the setup procedure, it is essential to ensure that the Wi-Fi router is equipped with the necessary features to operate independently, such as an integrated Ethernet WAN port or support for Ethernet-based internet connections. Additionally, verifying compatibility with the internet service provider (ISP) and understanding the specific network requirements is crucial for a seamless setup experience.
The following steps outline the process of setting up a Wi-Fi router without a modem:
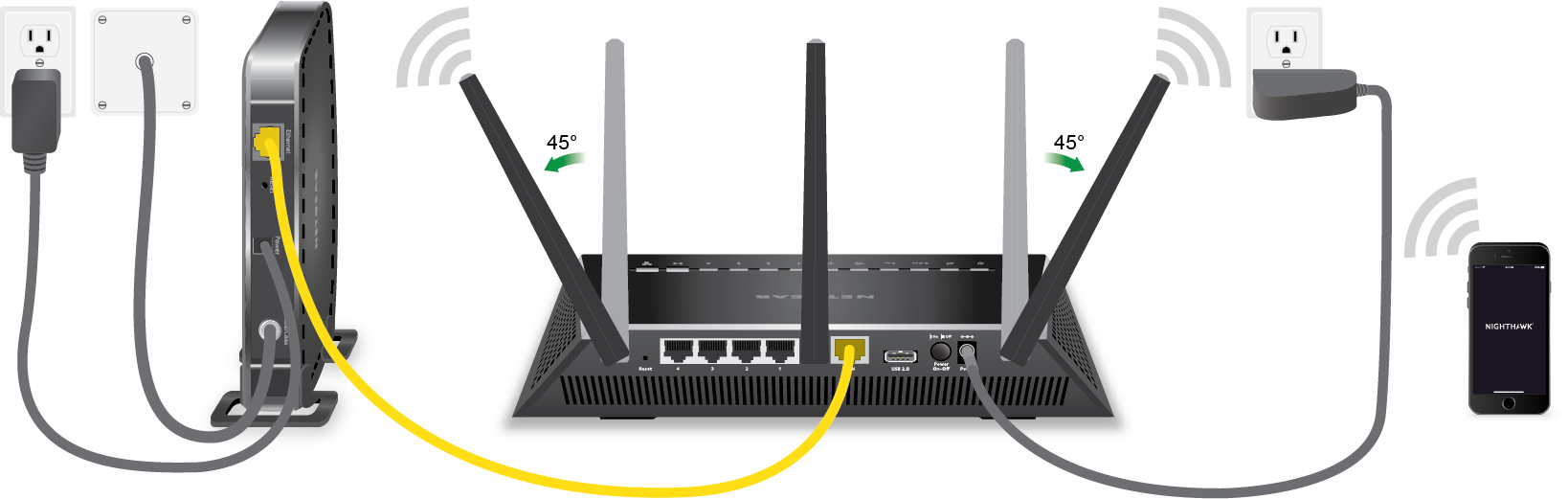
- Hardware Preparation: Begin by connecting the Wi-Fi router to a power source and ensuring that it is in close proximity to the primary Ethernet connection point, such as a wall outlet or Ethernet jack.
- Ethernet Connection: Using an Ethernet cable, establish a direct connection between the Ethernet WAN port of the Wi-Fi router and the Ethernet outlet or port provided by the ISP. This serves as the primary link for internet connectivity, bypassing the need for a traditional modem.
- Power On and Configuration: Power on the Wi-Fi router and access the router’s configuration interface via a web browser on a connected device, such as a laptop or smartphone. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to configure the router’s settings, including network name (SSID), security protocols, and administrative credentials.
- Internet Setup: Within the router’s configuration interface, navigate to the internet or WAN settings section and configure the connection type as “Ethernet” or “Static IP,” depending on the ISP’s specifications. Input the required network parameters provided by the ISP, such as IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and DNS server information.
- Network Optimization: Customize the Wi-Fi network settings, including Wi-Fi channel selection, security encryption (WPA2/WPA3), and network segmentation, to enhance performance and security.
- Verification and Testing: Once the configuration is complete, perform a thorough verification of the settings and conduct testing to ensure seamless internet connectivity and wireless network operation.
By diligently following these steps and leveraging the intuitive configuration interfaces provided by modern Wi-Fi routers, users can successfully establish a robust and self-contained wireless network without the need for a traditional modem.
This streamlined approach not only offers greater control and flexibility but also eliminates the reliance on external networking devices, empowering individuals to tailor their Wi-Fi networks to suit their specific requirements and preferences.
Now that the Wi-Fi router is set up and ready for operation, the next crucial step involves connecting various devices to the network, enabling seamless wireless access and interconnectivity.
**
You can set up a Wi-Fi router without a modem by connecting it to an Ethernet port on your existing internet connection, such as a DSL or cable modem. Then, follow the router’s setup instructions to configure the Wi-Fi network.
Connecting Devices to the Wi-Fi Router
**
Once the Wi-Fi router is successfully set up without a modem, the next pivotal phase involves connecting a diverse array of devices to the network, ranging from smartphones and laptops to smart home devices and IoT gadgets. This seamless integration of devices into the wireless network is essential for harnessing the full potential of the standalone Wi-Fi router and enabling ubiquitous connectivity within the designated physical space.
The following steps elucidate the process of connecting devices to the Wi-Fi router:
- Device Discovery: Ensure that the Wi-Fi router’s SSID (network name) is visible to the devices seeking to connect. This can be verified by accessing the list of available Wi-Fi networks on the device’s settings interface.
- Network Selection: From the list of available networks, select the Wi-Fi network associated with the router and input the network security key (password) if prompted. This initiates the connection process, enabling the device to establish a secure link with the Wi-Fi router.
- Authentication and Association: Upon entering the correct network security key, the device undergoes an authentication process to verify its credentials and establish an association with the Wi-Fi router. This pivotal step ensures secure and authorized access to the wireless network.
- IP Address Assignment: Once the device is successfully authenticated and associated with the Wi-Fi router, it receives an IP address from the router’s DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server, enabling seamless communication within the network and access to internet services.
- Network Validation: After the device is connected to the Wi-Fi network, perform a series of validation tests, such as accessing web pages, streaming media, and conducting network-intensive tasks, to ensure the stability and reliability of the wireless connection.
It is important to note that modern Wi-Fi routers often support advanced features, such as guest networks, device prioritization, and parental controls, which empower users to customize and manage the network according to their preferences and requirements. These capabilities enhance the overall user experience and enable efficient management of connected devices within the network ecosystem.
Furthermore, the seamless integration of smart home devices, such as smart speakers, thermostats, and security cameras, into the Wi-Fi network fosters a cohesive and interconnected ecosystem, enabling centralized control and synchronization of IoT devices for enhanced convenience and automation.
By following these steps and leveraging the advanced features offered by modern Wi-Fi routers, users can seamlessly connect a myriad of devices to the standalone network, fostering a harmonious and interconnected digital environment within their homes or workplaces.
With devices successfully integrated into the Wi-Fi network, it is essential to be equipped with troubleshooting tips and best practices to address potential challenges and optimize the network’s performance.
**
Troubleshooting and Tips
**
While setting up a Wi-Fi router without a modem offers unparalleled flexibility and control over the wireless network, it is essential to be prepared to address potential challenges and optimize the network’s performance. By leveraging troubleshooting tips and best practices, users can overcome technical hurdles and ensure a seamless and reliable wireless experience.
The following recommendations and insights encompass valuable troubleshooting tips and optimization strategies for standalone Wi-Fi networks:
- Signal Interference Mitigation: Identify potential sources of signal interference, such as neighboring Wi-Fi networks, electronic appliances, and physical obstructions, and position the Wi-Fi router in a central location to minimize signal degradation.
- Firmware Updates: Regularly check for firmware updates for the Wi-Fi router and ensure that the device is running the latest software version to benefit from performance enhancements, security patches, and feature improvements.
- Channel Optimization: Utilize Wi-Fi analyzer tools to identify the least congested Wi-Fi channels in the vicinity and configure the router to operate on the optimal channel for minimized interference and enhanced signal stability.
- Quality of Service (QoS) Configuration: Prioritize network traffic for specific devices or applications within the router’s settings to ensure a seamless and optimized user experience, particularly for bandwidth-intensive tasks such as streaming and online gaming.
- Security Best Practices: Implement robust security measures, including strong encryption (WPA2/WPA3), unique network passwords, and guest network isolation, to safeguard the wireless network from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
- Device Rebooting and Troubleshooting: In the event of connectivity issues, perform periodic reboots of the Wi-Fi router and connected devices to resolve potential network conflicts and restore optimal functionality.
- Range Extender Integration: Consider integrating Wi-Fi range extenders or mesh Wi-Fi systems to expand the coverage area and ensure consistent signal strength throughout the designated physical space, particularly in larger homes or multi-story buildings.
- Network Monitoring and Analytics: Leverage network monitoring tools and analytics platforms to gain insights into network performance, device connectivity, and bandwidth utilization, facilitating proactive troubleshooting and optimization.
By incorporating these troubleshooting tips and best practices into the management of the standalone Wi-Fi network, users can proactively address potential issues and fine-tune the network’s performance to meet their specific requirements and preferences.
Furthermore, staying informed about the latest advancements and best practices in wireless networking empowers individuals to adapt to evolving technological landscapes and harness the full potential of standalone Wi-Fi routers in the digital age.
With these invaluable insights and recommendations at their disposal, individuals can embark on the journey of setting up and optimizing a standalone Wi-Fi network with confidence and proficiency, fostering a seamless and high-performance wireless experience within their homes or workplaces.
**
Read more: What Is The Best Cable Modem Wi-Fi Router
Conclusion
**
As we conclude this comprehensive guide to setting up a Wi-Fi router without a modem, it is evident that the landscape of wireless networking has evolved to offer unprecedented flexibility, performance, and customization options for users seeking to establish robust and self-contained Wi-Fi networks.
By unraveling the intricate process of setting up a standalone Wi-Fi router, bypassing the traditional reliance on modems, we have empowered individuals to embark on this endeavor with confidence and clarity. The seamless integration of devices into the wireless network, coupled with troubleshooting tips and optimization strategies, ensures a seamless and reliable wireless experience within homes, offices, and public spaces.
It is imperative to recognize the pivotal role of Wi-Fi routers in modern connectivity paradigms, serving as the linchpin of interconnected ecosystems and facilitating ubiquitous wireless access for a myriad of devices, ranging from smartphones and laptops to smart home gadgets and IoT devices.
Furthermore, the emphasis on security best practices, signal optimization, and proactive network management underscores the importance of staying informed about the latest advancements and strategies in wireless networking, enabling users to adapt to evolving technological landscapes and safeguard their wireless environments from potential threats and performance challenges.
As technology continues to advance and connectivity becomes increasingly integral to our daily lives, the ability to set up and optimize standalone Wi-Fi networks represents a significant step towards embracing the potential of wireless networking and tailoring it to meet specific needs and preferences.
Ultimately, the journey of setting up a Wi-Fi router without a modem transcends technical configurations and enters the realm of empowerment, offering individuals the opportunity to craft personalized, high-performance wireless environments that seamlessly integrate with their digital lifestyles.
With the knowledge and insights gleaned from this guide, individuals are equipped to embark on this journey with confidence, harnessing the full potential of standalone Wi-Fi routers to create seamless, reliable, and secure wireless networks that cater to their unique connectivity requirements.
As we navigate the ever-evolving landscape of wireless connectivity, the ability to set up and optimize standalone Wi-Fi networks represents a significant step towards embracing the potential of wireless networking and tailoring it to meet specific needs and preferences.
By embracing the principles of flexibility, adaptability, and proactive network management, individuals can cultivate wireless environments that not only meet their current demands but also evolve to accommodate future technological advancements and connectivity paradigms.
With the knowledge and insights gleaned from this guide, individuals are poised to embark on this journey with confidence, harnessing the full potential of standalone Wi-Fi routers to create seamless, reliable, and secure wireless networks that cater to their unique connectivity requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Setup A Wi-Fi Router Without A Modem
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “How To Setup A Wi-Fi Router Without A Modem”