Home>Technology>Smart Home Devices>What Does A Thermal Printer Do


Smart Home Devices
What Does A Thermal Printer Do
Modified: January 24, 2024
Discover how thermal printers enhance smart home devices with efficient and reliable printing capabilities. Learn about their role in improving convenience and functionality at home.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
**
Introduction
**
In the realm of modern printing technology, thermal printers have emerged as a versatile and efficient solution for various industries and personal applications. These innovative devices utilize heat to produce high-quality images and texts on paper, offering a range of benefits such as speed, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Understanding the functionality, types, applications, and pros and cons of thermal printers is essential for anyone seeking to harness their potential in diverse settings. Let's delve into the fascinating world of thermal printers to uncover the intricacies of their operation, the scope of their utility, and the impact they have on our daily lives.
Key Takeaways:
- Thermal printers use heat to create images and text on paper, making them fast, reliable, and cost-effective for various industries and personal use. They come in different types for different printing needs.
- Thermal printers have advantages like high-speed printing and low maintenance, but they also have limitations such as media restrictions and print longevity. Understanding these factors helps in making informed decisions.
Read more: What Do Thermal Curtains Do
How Does a Thermal Printer Work?
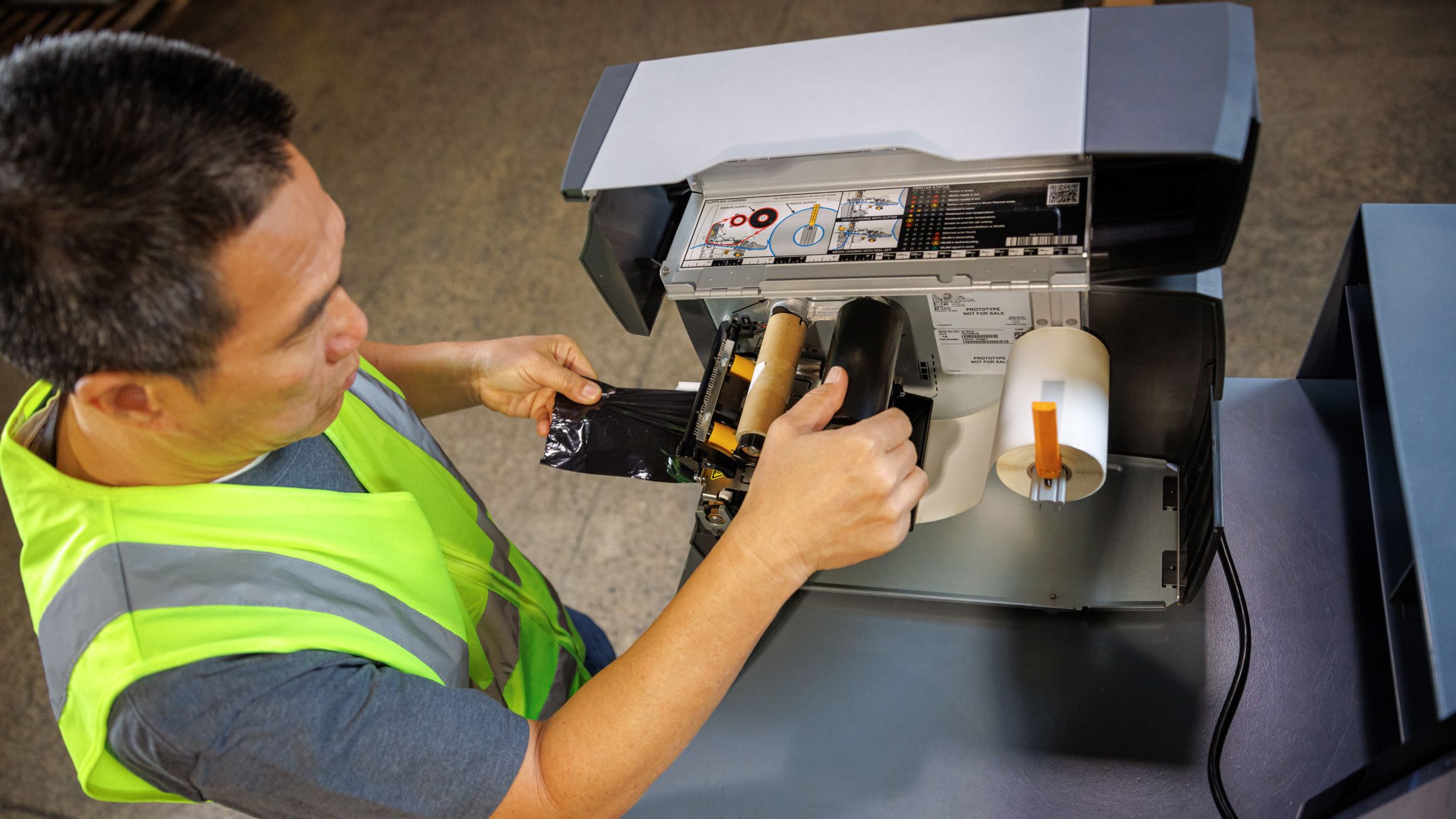
Thermal printers operate on a simple yet ingenious principle, harnessing the power of heat to create images and text on specially coated paper. There are two primary types of thermal printing technologies: direct thermal and thermal transfer.
Direct thermal printers utilize heat-sensitive paper that darkens when exposed to the thermal print head. This process is ideal for applications requiring high-speed printing, such as receipts, shipping labels, and barcode labels. The absence of ink or toner cartridges in direct thermal printers simplifies maintenance and reduces operational costs, making them a popular choice for businesses seeking efficient and economical printing solutions.
On the other hand, thermal transfer printers employ a different approach, using a heated ribbon to transfer ink onto the paper. This method enables the production of durable, long-lasting prints with enhanced resistance to environmental factors such as moisture and UV exposure. Thermal transfer printers are well-suited for applications demanding superior print quality, including product labeling, asset tagging, and industrial signage.
Both direct thermal and thermal transfer printing technologies rely on precise control of heat to create images and text with exceptional clarity and precision. By leveraging thermal energy, these printers offer reliable and consistent performance, making them indispensable tools in various sectors, from retail and logistics to healthcare and manufacturing.
Types of Thermal Printers
Thermal printers come in various configurations, each tailored to specific printing requirements and operational environments. Understanding the distinct characteristics of these types is crucial for selecting the most suitable option for a given application. The primary types of thermal printers include:
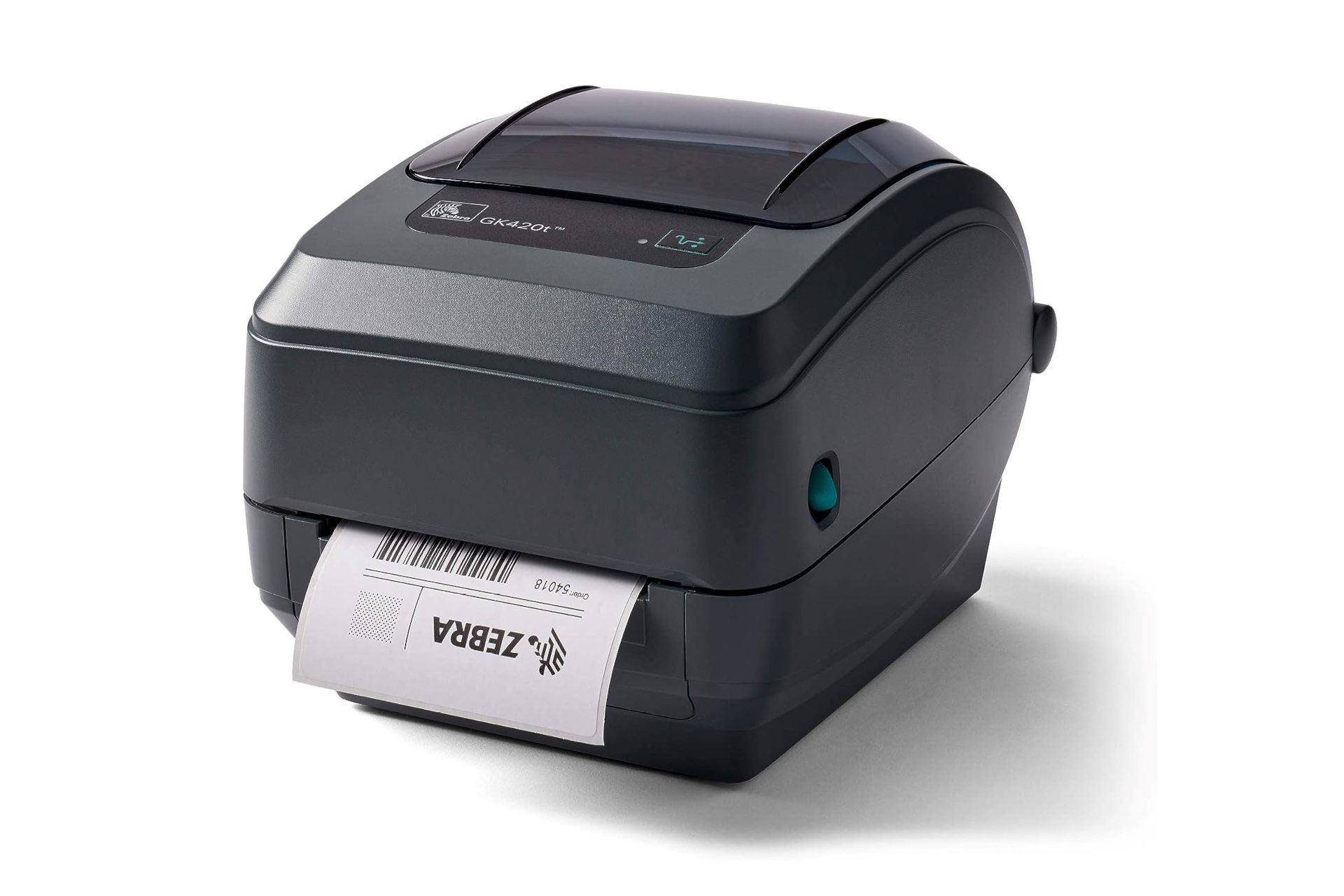
1. Direct Thermal Printers:
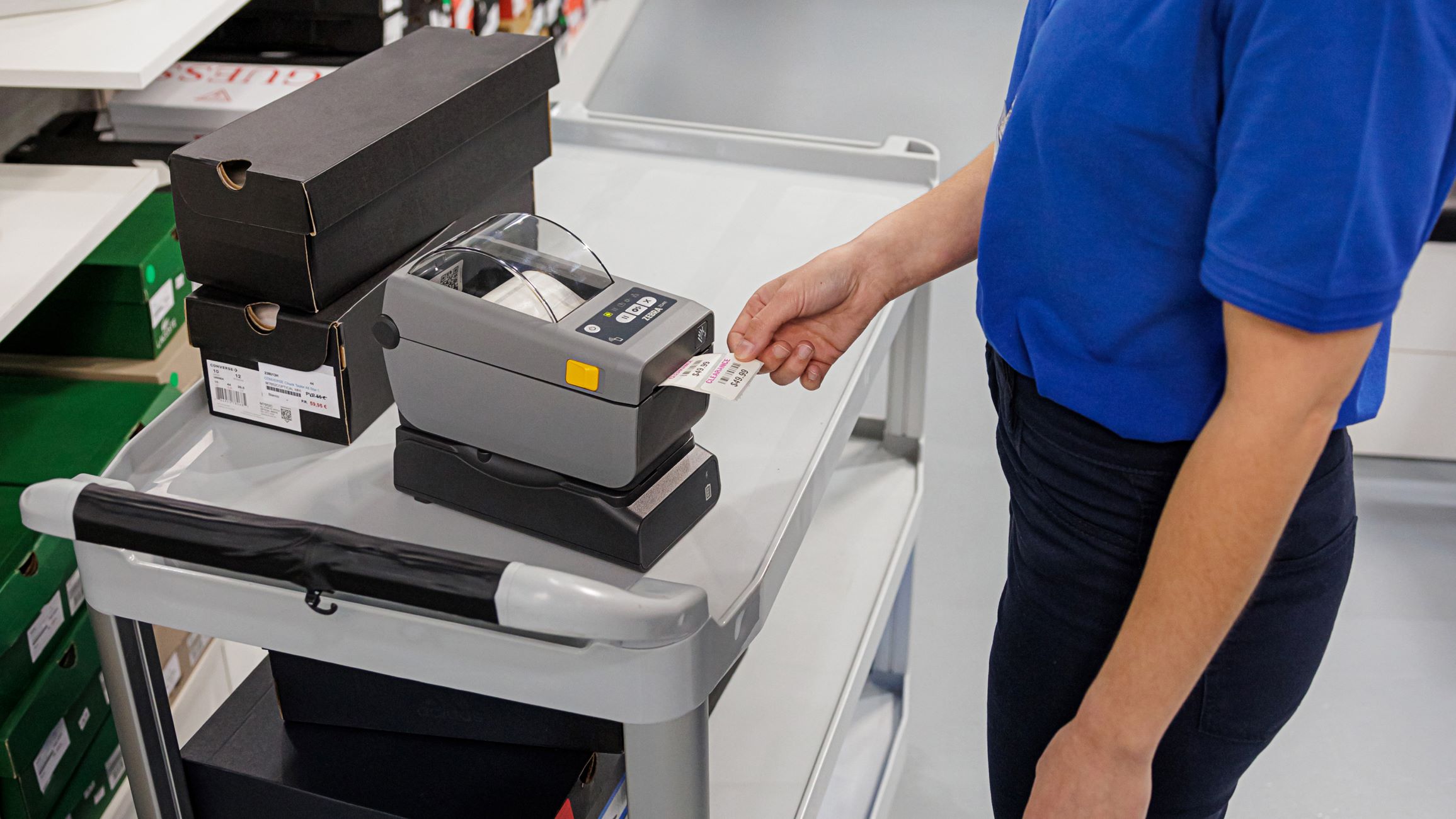
Direct thermal printers are designed for applications that prioritize speed and cost-efficiency. They utilize heat-sensitive paper that darkens when exposed to the thermal print head, eliminating the need for ink or toner cartridges. This simplicity makes direct thermal printers ideal for producing receipts, shipping labels, and barcode labels in high-volume settings, such as retail outlets, warehouses, and logistics centers.
2. Thermal Transfer Printers:
Thermal transfer printers employ a heated ribbon to transfer ink onto the paper, resulting in durable and long-lasting prints. This method is well-suited for applications requiring enhanced print quality and resistance to environmental factors. Industries such as manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and electronics utilize thermal transfer printers for product labeling, asset tagging, and compliance labeling, where durability and legibility are paramount.
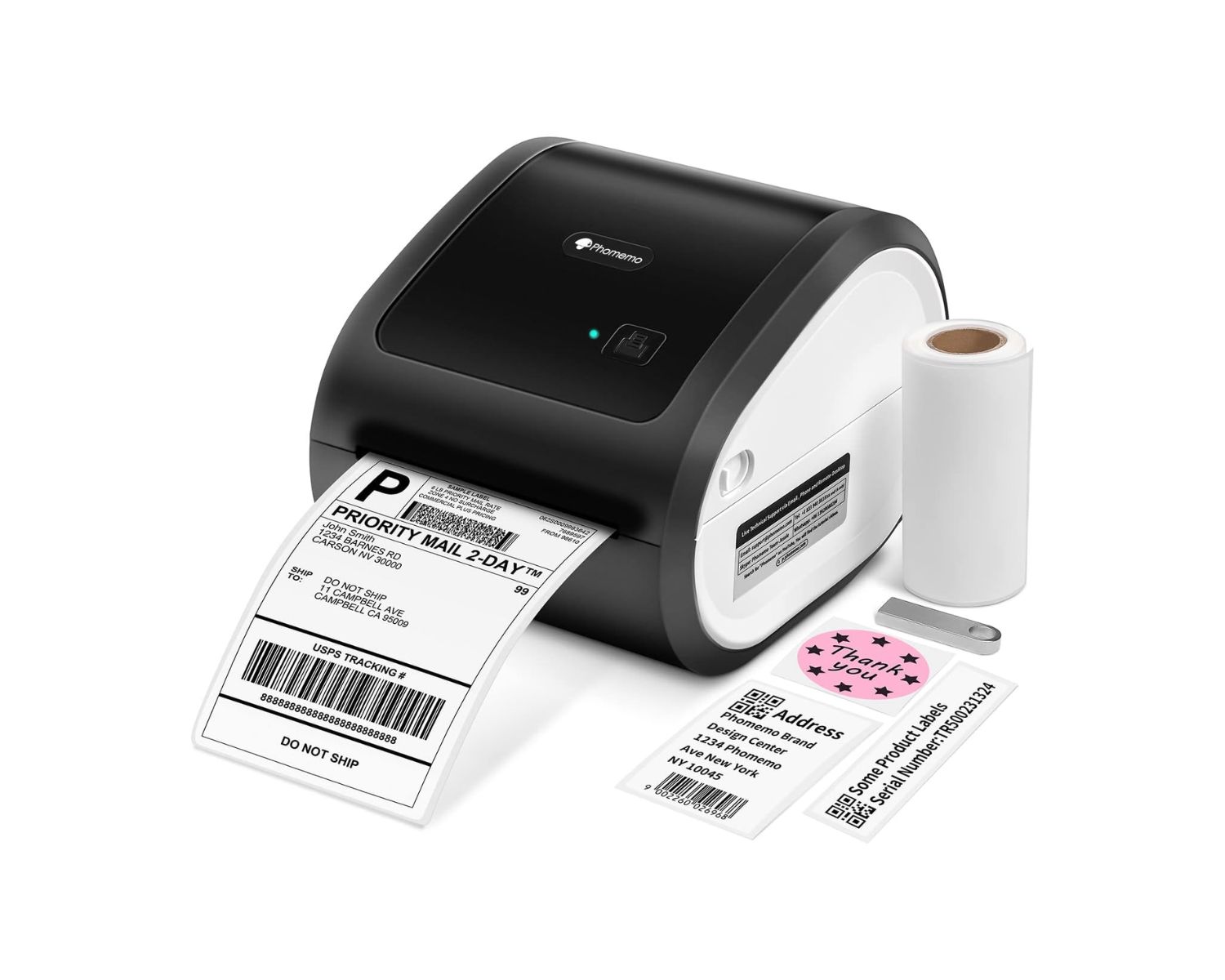
3. Desktop Thermal Printers:
Desktop thermal printers are compact, space-efficient devices commonly used in office settings, small businesses, and home offices. They offer versatility and convenience for printing shipping labels, receipts, and other essential documents. Their user-friendly design and ease of maintenance make them a practical choice for individuals and organizations with moderate printing needs.
4. Industrial Thermal Printers:
Industrial thermal printers are engineered for high-volume, demanding printing tasks in industrial and commercial environments. They are capable of handling large media rolls and are designed to withstand rigorous use, making them indispensable for applications such as manufacturing, distribution, and logistics. These robust printers deliver exceptional performance and reliability, catering to the stringent demands of industrial operations.
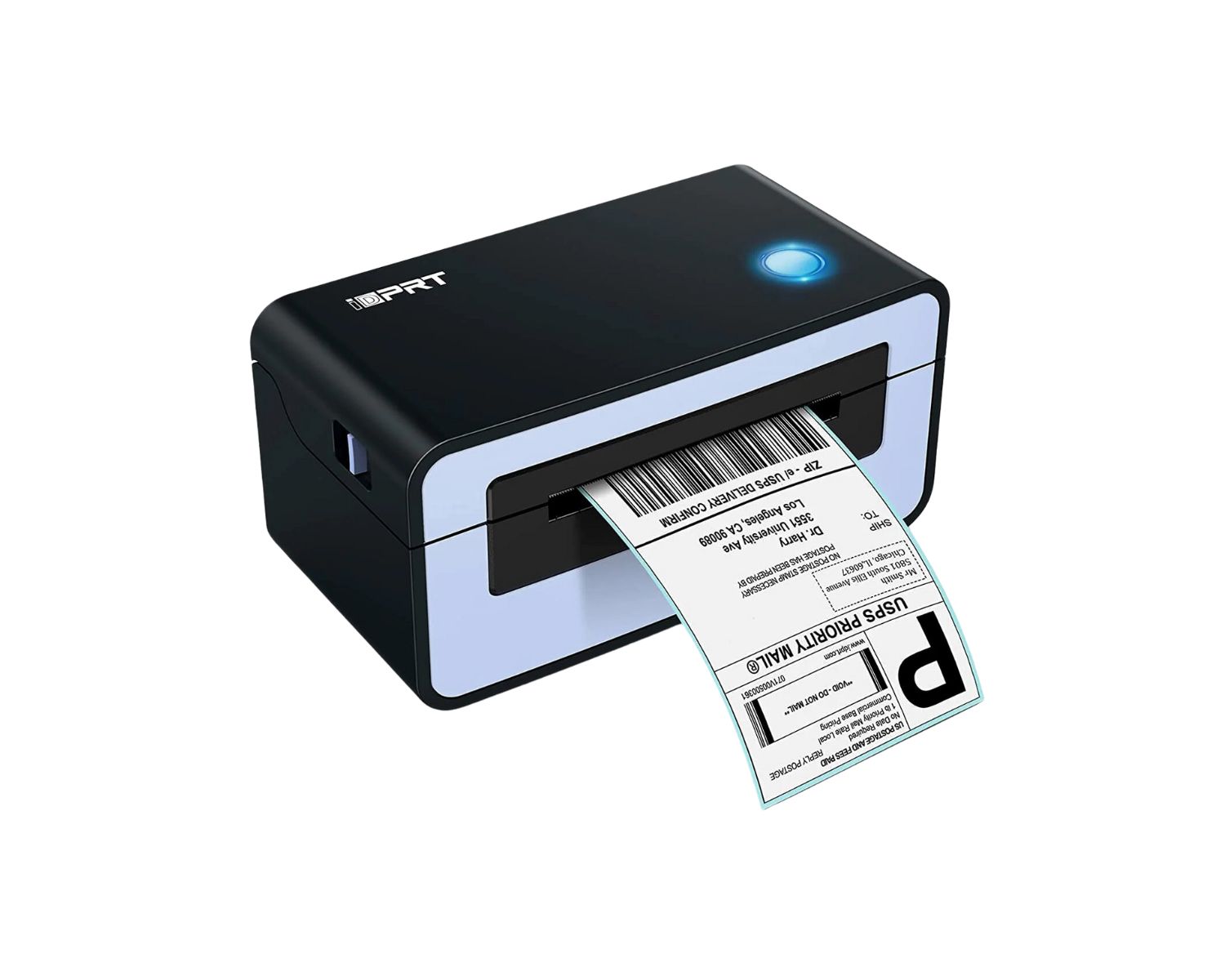
5. Mobile Thermal Printers:
Mobile thermal printers are compact, portable devices ideal for on-the-go printing requirements. They are commonly used in field service, transportation, and retail applications, enabling seamless printing of receipts, tickets, and invoices. The convenience and mobility offered by these printers make them valuable assets for professionals who require on-site printing capabilities.
Each type of thermal printer offers unique features and advantages, catering to diverse printing needs across industries and settings. Understanding the specific requirements of a given application is essential for selecting the most suitable thermal printer to optimize printing efficiency and quality.
A thermal printer uses heat to transfer ink onto paper, making it ideal for printing receipts, labels, and tickets. Make sure to use the correct type of thermal paper for best results.
Applications of Thermal Printers
Thermal printers find widespread use across diverse industries and applications, leveraging their unique capabilities to meet various printing needs. The versatility and efficiency of thermal printing technology make it an indispensable tool in the following key applications:
Retail and Point of Sale (POS):
In retail environments, thermal printers are commonly employed for printing receipts, product labels, and barcode labels. Their high-speed operation and cost-effective nature make them ideal for handling the demands of point-of-sale transactions, contributing to seamless and efficient customer service experiences.
Logistics and Shipping:
Thermal printers play a critical role in logistics and shipping operations, facilitating the printing of shipping labels, packing slips, and tracking labels. Their ability to produce clear, high-resolution prints at rapid speeds enhances the accuracy and efficiency of order fulfillment processes, streamlining the movement of goods within supply chains.
Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals:
In healthcare settings, thermal printers are utilized for printing patient wristbands, prescription labels, and laboratory specimen labels. Their ability to produce durable, smudge-resistant prints ensures the accurate identification and tracking of medical items and patient information, contributing to enhanced safety and operational efficiency.
Manufacturing and Industrial Labeling:
Thermal printers are essential for product labeling, asset tagging, and compliance labeling in manufacturing and industrial environments. Their capacity to produce durable, long-lasting prints with high resistance to environmental factors makes them well-suited for applications requiring robust labeling solutions in challenging operational conditions.
Hospitality and Entertainment:
In the hospitality and entertainment sectors, thermal printers are utilized for printing tickets, event passes, and receipts. Their compact size and fast printing capabilities make them valuable for on-demand printing requirements, enhancing guest experiences and operational efficiency in venues such as theaters, amusement parks, and event facilities.
Field Service and Mobile Applications:
For professionals in field service, transportation, and mobile sales, mobile thermal printers offer the convenience of on-the-go printing for invoices, receipts, and service reports. Their portability and wireless connectivity enable seamless integration with mobile devices, empowering professionals to generate essential documents efficiently while on-site.
The diverse applications of thermal printers underscore their adaptability and reliability across various industries, contributing to streamlined operations, improved accuracy, and enhanced customer experiences. By addressing a wide range of printing needs with precision and efficiency, thermal printers have become indispensable assets in modern business and operational environments.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Thermal Printers
Thermal printers offer a range of benefits that make them well-suited for specific applications, but they also come with limitations that warrant consideration. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of thermal printers is essential for informed decision-making when selecting printing solutions. Let’s explore the key pros and cons of thermal printers:
Advantages:
- High-Speed Printing: Thermal printers are renowned for their rapid printing capabilities, making them ideal for applications requiring efficient and timely production of documents, labels, and receipts.
- Low Maintenance: With no ink or toner cartridges to replace, thermal printers offer simplified maintenance, reducing operational downtime and associated costs.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Direct thermal printers eliminate the need for consumables such as ink and toner, resulting in lower operational expenses over time.
- Durable Prints: Thermal transfer printers produce durable, long-lasting prints that are resistant to environmental factors, ensuring the longevity and legibility of printed materials.
- Clarity and Precision: Thermal printing technology delivers clear, high-resolution prints with exceptional precision, contributing to the professional quality of printed output.
- Versatility: Thermal printers come in various configurations, including desktop, industrial, and mobile models, catering to diverse printing needs across industries and operational settings.
Disadvantages:
- Media Limitations: Thermal printers are often limited to specific types of media, such as heat-sensitive paper or specialized label stock, restricting the range of printing materials that can be used.
- Print Longevity: Direct thermal prints may be susceptible to fading over time when exposed to heat, light, or environmental factors, necessitating additional protective measures for archival purposes.
- Initial Investment: Thermal transfer printers and certain industrial models may require a higher initial investment compared to traditional inkjet or laser printers, impacting upfront costs for businesses.
- Maintenance Considerations: While thermal printers generally require minimal maintenance, the replacement of printheads or ribbons in thermal transfer printers may entail additional upkeep and associated expenses.
- Environmental Sensitivity: Direct thermal prints are sensitive to heat and light, requiring careful handling and storage to preserve print quality and longevity.
By weighing the advantages and disadvantages of thermal printers, businesses and individuals can make informed choices regarding the adoption of these printing solutions. While the speed, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of thermal printers offer compelling advantages for specific applications, it is essential to consider the limitations and operational considerations associated with their use.
Read more: How To Clean A Thermal Printer
Conclusion
Thermal printers have revolutionized the printing landscape, offering a compelling array of benefits and applications that cater to diverse industry needs. From the high-speed efficiency of direct thermal printers to the durability and quality of thermal transfer technology, these devices have become indispensable assets in retail, logistics, healthcare, manufacturing, and various other sectors.
The seamless integration of thermal printers into point-of-sale systems, shipping operations, healthcare facilities, and industrial environments underscores their adaptability and reliability. Their ability to produce clear, high-resolution prints with exceptional precision contributes to streamlined operations, improved accuracy, and enhanced customer experiences.
While thermal printers offer significant advantages such as rapid printing, low maintenance, and cost-effectiveness, it is crucial to consider the limitations associated with media compatibility, print longevity, and initial investment. By carefully evaluating the specific printing requirements and operational considerations, businesses and individuals can leverage the strengths of thermal printers while addressing potential challenges effectively.
As technology continues to evolve, the ongoing refinement of thermal printing solutions promises to further enhance their capabilities and versatility. The seamless integration of wireless connectivity, advanced print management features, and environmental sustainability initiatives will continue to shape the future of thermal printing, expanding its utility and impact across diverse applications.
In conclusion, the remarkable capabilities and diverse applications of thermal printers underscore their pivotal role in modern printing technology. By harnessing the advantages of thermal printing while addressing operational considerations, businesses and individuals can optimize their printing efficiency, quality, and overall productivity, ensuring that thermal printers remain at the forefront of the printing landscape for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Does A Thermal Printer Do
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “What Does A Thermal Printer Do”