Home>Technology>Smart Home Devices>What Does The Extruder Do In A 3D Printer

Smart Home Devices
What Does The Extruder Do In A 3D Printer
Published: January 21, 2024
Learn how the extruder functions in a 3D printer and its role in creating smart home devices. Explore the key features and benefits.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the fascinating world of 3D printing, where innovation and creativity converge to redefine manufacturing and prototyping processes. In this article, we will delve into the intricate workings of 3D printers, focusing specifically on the pivotal role of the extruder. Understanding the function and significance of the extruder is crucial for comprehending the 3D printing process as a whole.
As 3D printing continues to revolutionize various industries, from aerospace to healthcare, the demand for comprehensive knowledge about this technology is steadily increasing. Whether you are a seasoned enthusiast or a curious novice, exploring the intricacies of the extruder will provide valuable insights into the capabilities and limitations of 3D printing.
By unraveling the mysteries of the extruder, we aim to demystify the magic behind 3D printing and empower you to harness this cutting-edge technology with confidence and creativity. So, let’s embark on this enlightening journey into the heart of 3D printing and discover the indispensable role of the extruder.
Key Takeaways:
- The extruder in a 3D printer is like the conductor of an orchestra, orchestrating the precise melting and deposition of filament material to bring digital designs to life with incredible accuracy and finesse.
- Different types of extruders, like the Bowden, direct drive, dual, paste, and pellet extruders, offer unique capabilities for diverse printing needs, from intricate designs to sustainable and multicolor creations.
Read more: What Is An Extruder On A 3D Printer
Understanding 3D Printing
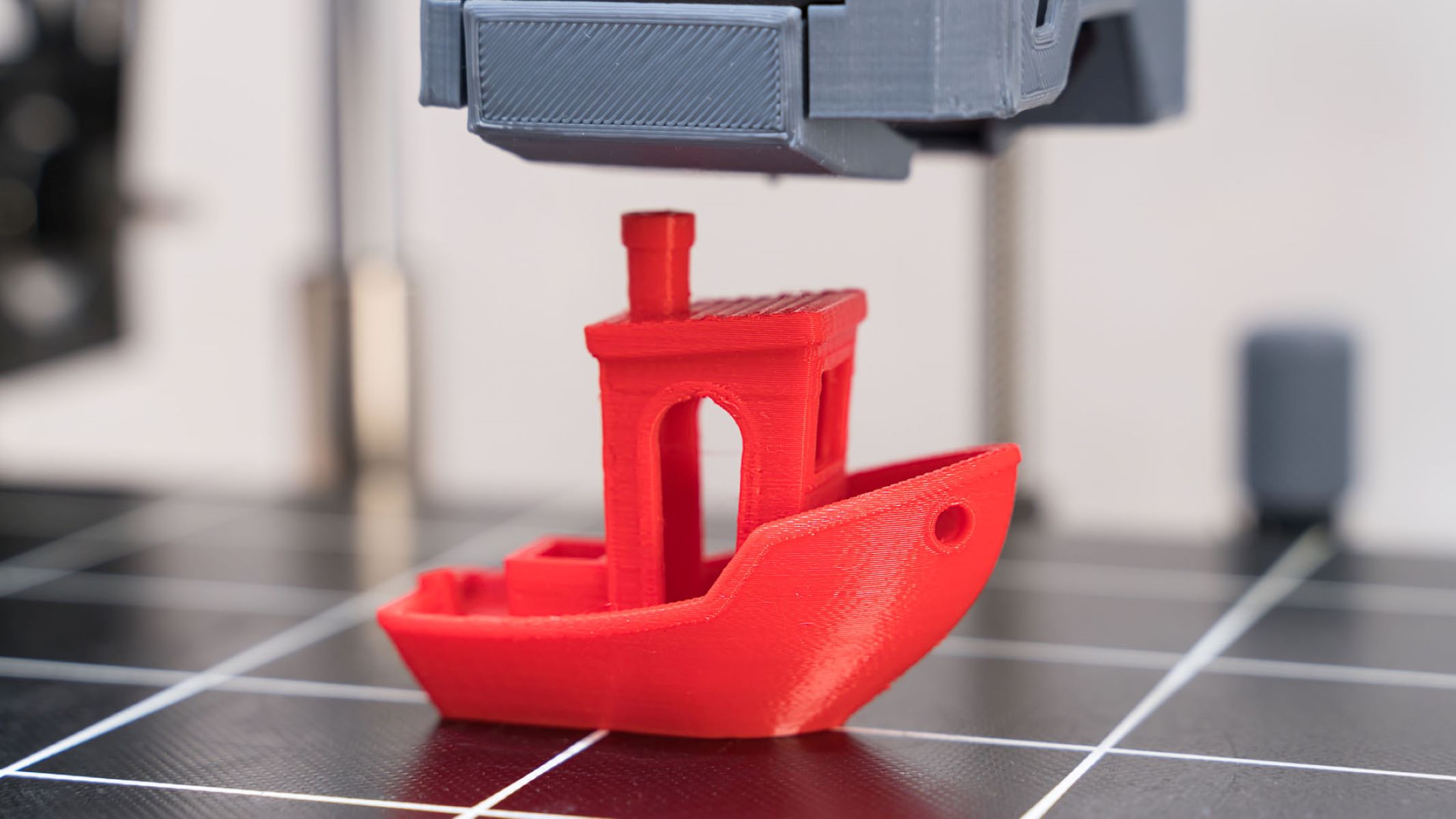
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a revolutionary process that fabricates three-dimensional objects by layering material in a precise and controlled manner. This innovative technology has transcended traditional manufacturing methods by enabling the creation of complex geometries and intricate designs with unparalleled efficiency and precision.
At the core of 3D printing lies the concept of layer-by-layer construction, where a digital model is translated into a physical object through a sequence of additive processes. This transformative approach to manufacturing has unleashed a wave of creativity and ingenuity, empowering individuals and industries to materialize their concepts with unprecedented speed and flexibility.
One of the defining features of 3D printing is its versatility, as it accommodates a diverse range of materials, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and even biomaterials. This adaptability has paved the way for a myriad of applications, spanning from rapid prototyping and custom tooling to personalized medical implants and architectural models.
Furthermore, the accessibility of 3D printing technology has catalyzed innovation across various domains, democratizing the production of prototypes, spare parts, and bespoke creations. The seamless integration of digital design software and 3D printers has democratized the production of prototypes, spare parts, and bespoke creations, fostering a culture of experimentation and iteration.
As 3D printing continues to evolve, its impact on traditional manufacturing, supply chains, and product development processes is becoming increasingly profound. Embracing the principles of sustainability and customization, 3D printing has emerged as a disruptive force that transcends the boundaries of conventional production methodologies.
By comprehending the fundamental principles and capabilities of 3D printing, individuals and businesses can harness this transformative technology to unlock new frontiers of innovation and efficiency. Now that we have gained a foundational understanding of 3D printing, let’s delve into the pivotal role of the extruder in this groundbreaking process.
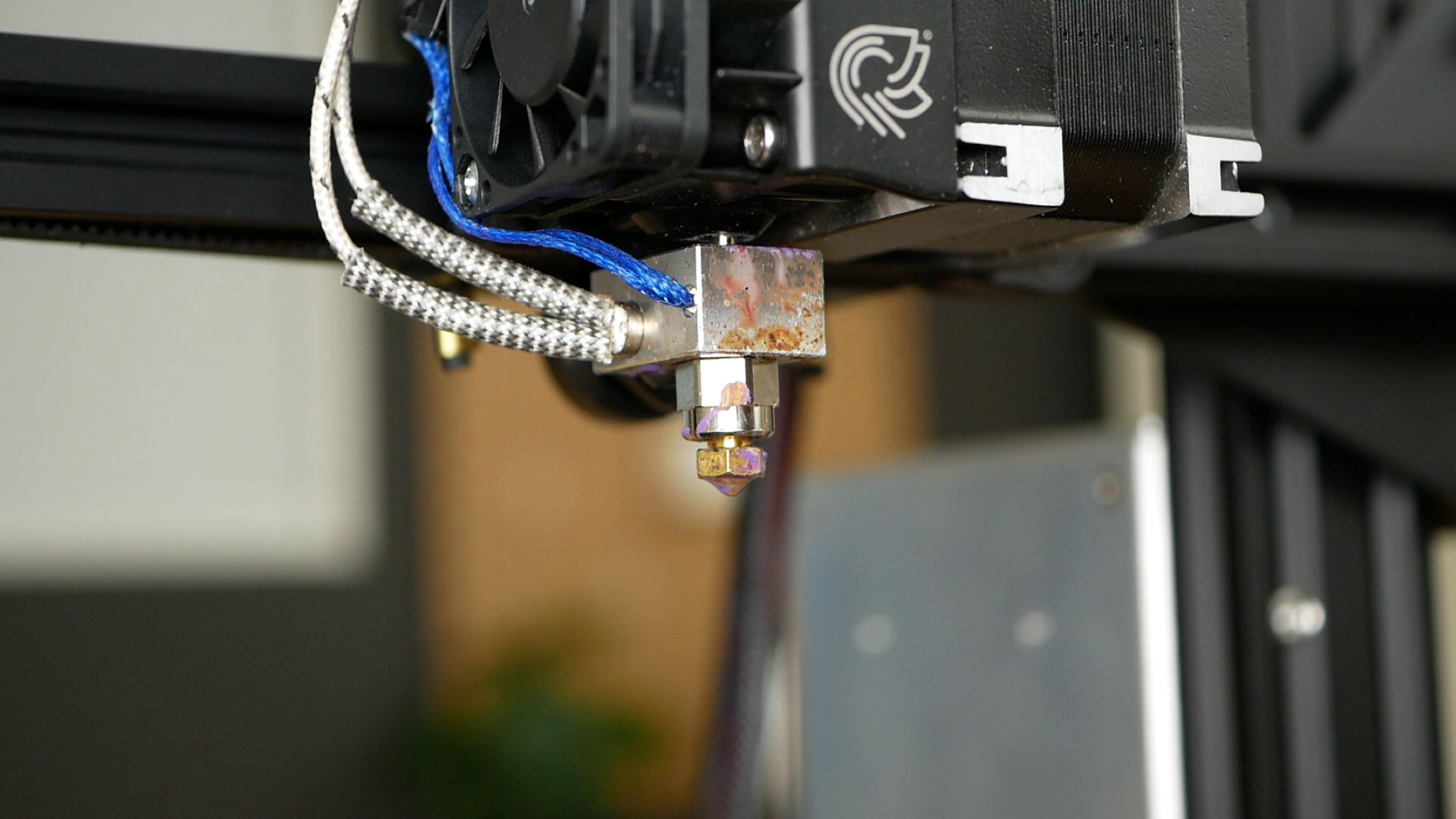
The Role of the Extruder
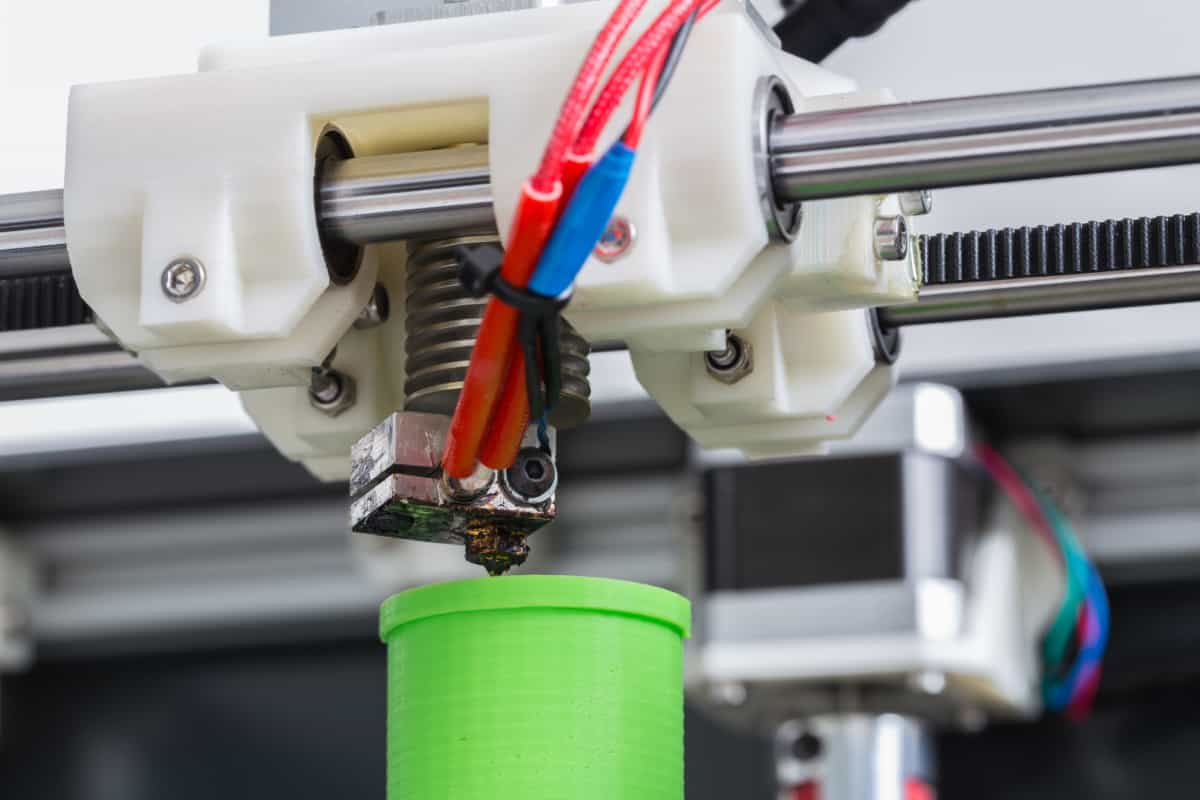
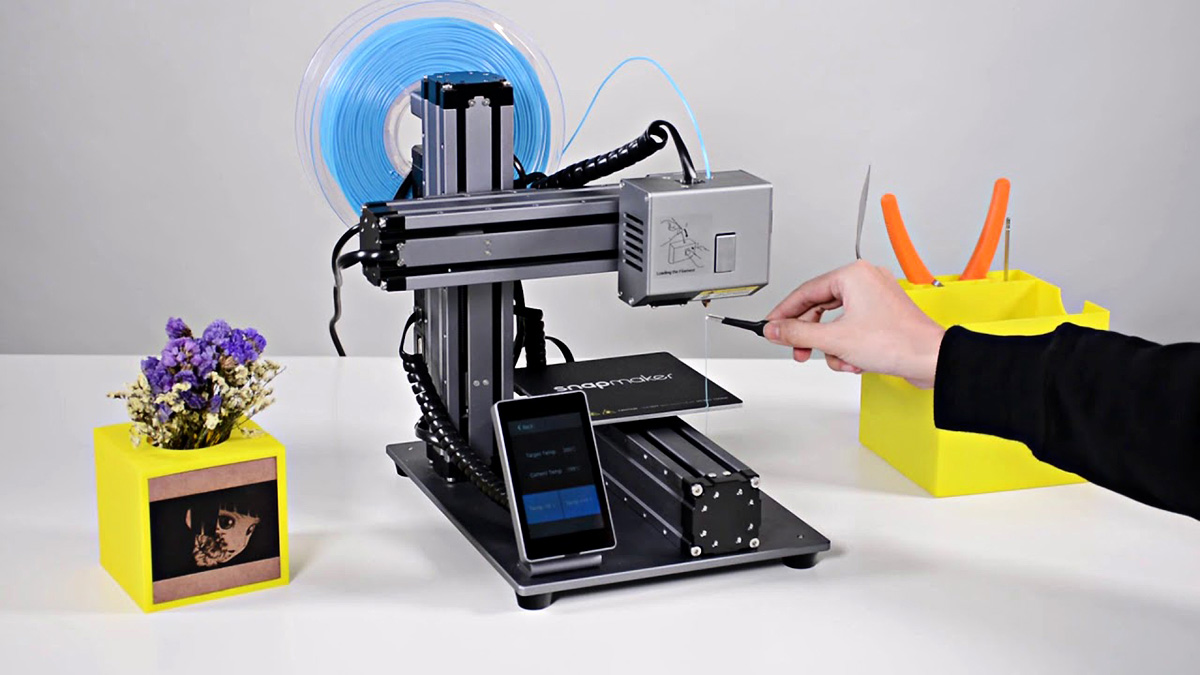
Central to the 3D printing process, the extruder plays a critical role in transforming raw material into intricate three-dimensional objects. Essentially, the extruder functions as the gateway through which filament, the primary printing material, is melted and precisely deposited layer by layer to construct the desired object.
At its core, the extruder is responsible for maintaining a consistent flow of filament and regulating its deposition with remarkable precision. This pivotal component ensures that the molten filament is extruded in a controlled manner, adhering to the predefined pathways dictated by the digital model.
Moreover, the extruder serves as a conduit for material versatility, accommodating an array of filament types, including PLA, ABS, PETG, and specialized composite materials. This adaptability empowers users to explore diverse material properties and harness them to materialize their creative visions with unparalleled flexibility.
Furthermore, the extruder’s ability to seamlessly transition between different filament colors and types facilitates the incorporation of intricate designs and multicolor elements within a single printed object. This capability expands the creative horizons of 3D printing, enabling the fabrication of visually captivating and functionally diverse creations.
As a fundamental component of the 3D printing ecosystem, the extruder embodies the precision and control that underpin the additive manufacturing process. Its role in regulating the flow and deposition of filament material is indispensable, ensuring the faithful translation of digital designs into physical reality.
By recognizing the pivotal role of the extruder, 3D printing enthusiasts and industry professionals can appreciate the intricacies of this transformative technology and harness its capabilities to realize innovative concepts with unparalleled precision and efficiency.
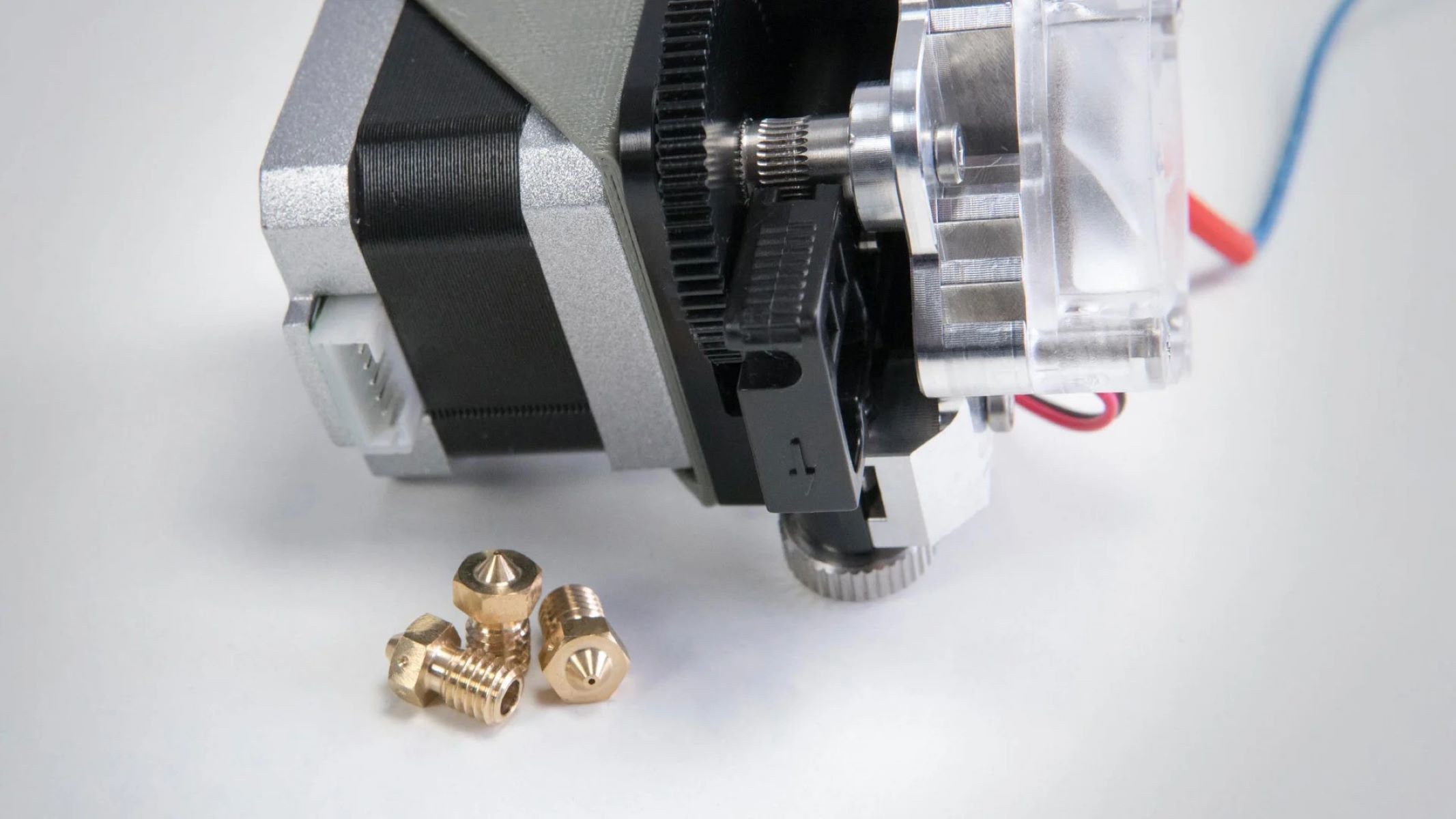
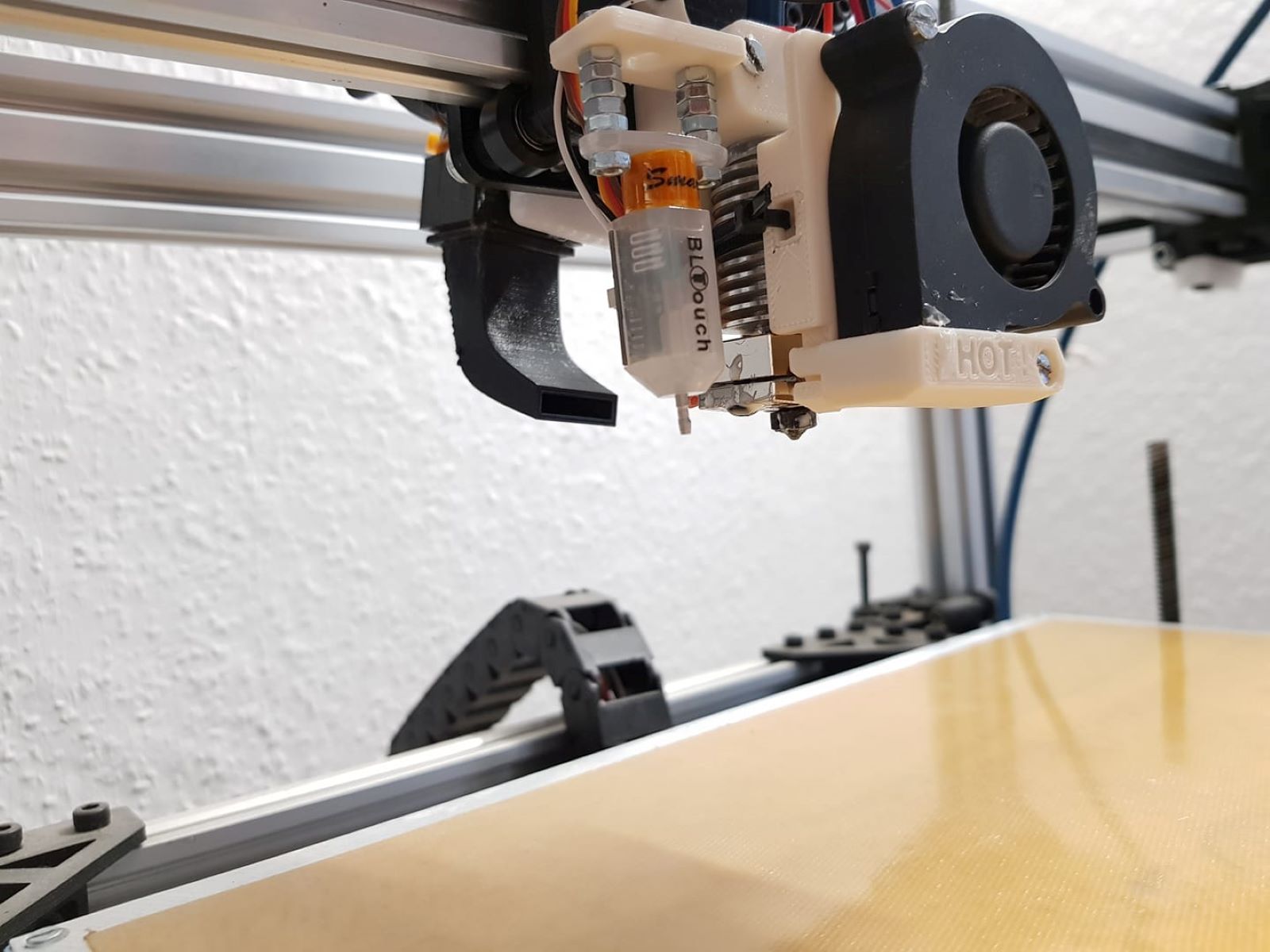
Components of the Extruder
The extruder, a complex yet meticulously engineered component of a 3D printer, comprises several essential elements that collectively facilitate the precise deposition of filament material. Understanding the intricate interplay of these components is crucial for comprehending the functionality and capabilities of the extrusion process.
1. Hotend: At the heart of the extruder, the hotend is responsible for heating the filament material to its melting point, thereby enabling its controlled extrusion. Equipped with a heating element and a temperature sensor, the hotend ensures that the filament undergoes a seamless transition from solid to molten state, ready for precise deposition.
2. Nozzle: Serving as the outlet through which the molten filament is extruded, the nozzle plays a pivotal role in determining the layer height and overall resolution of the printed object. The diameter of the nozzle dictates the precision and intricacy with which the filament is deposited, thereby influencing the surface finish and structural integrity of the final print.
3. Filament Drive: This component is responsible for gripping and advancing the filament material, ensuring a consistent and reliable supply to the hotend. By exerting controlled pressure on the filament, the filament drive mechanism regulates the flow of material, thereby facilitating precise extrusion and deposition.
4. Cooling System: To maintain optimal printing conditions and prevent filament deformities, the extruder incorporates a cooling system that rapidly solidifies the molten filament upon deposition. This crucial element ensures that each layer solidifies promptly, preserving the structural integrity and dimensional accuracy of the printed object.
5. Extruder Motor: Driving the filament drive mechanism, the extruder motor provides the necessary torque and precision to ensure consistent filament advancement. By synchronizing with the printer’s control system, the motor orchestrates the seamless movement of filament, aligning with the digital model’s specifications.
Understanding the intricate synergy of these components within the extruder illuminates the meticulous orchestration of processes that underpin the 3D printing workflow. By comprehending the functionality and significance of each element, enthusiasts and professionals can optimize their printing parameters and unleash the full potential of additive manufacturing technology.
The extruder in a 3D printer is responsible for melting and pushing the filament through the nozzle to create the printed object layer by layer. Make sure to keep the extruder clean and well-maintained for optimal printing results.
How the Extruder Works
The extruder operates as the beating heart of a 3D printer, orchestrating a symphony of precise movements and controlled processes to transform filament material into tangible creations. Understanding the inner workings of the extruder unveils the intricate choreography that underpins the additive manufacturing process.
The journey of filament material through the extruder commences with the filament drive mechanism, which grips the spooled filament and steadily advances it towards the hotend. As the filament approaches the hotend, the heating element within the hotend elevates its temperature to the melting point, transitioning it from a solid state to a molten form ready for extrusion.
Upon reaching the molten state, the filament material is propelled through the nozzle, a precision-engineered aperture that governs the flow and deposition of the molten material. The nozzle’s diameter dictates the layer height and intricacy of the printed object, influencing its surface finish and structural integrity.
Simultaneously, the extruder motor coordinates the precise advancement of the filament, synchronizing its movement with the digital model’s specifications. This orchestrated dance ensures that the molten material is extruded with unwavering precision, adhering to the predefined pathways delineated by the digital design.
As the molten filament is extruded layer by layer, the cooling system swiftly solidifies each deposition, preserving the structural integrity and dimensional accuracy of the printed object. This rapid solidification process is pivotal in ensuring that each layer seamlessly integrates with the preceding ones, culminating in a cohesive and meticulously crafted final product.
The harmonious interplay of these components within the extruder encapsulates the essence of additive manufacturing, where meticulous control and precision converge to materialize digital designs with unparalleled accuracy and finesse. By comprehending the intricacies of the extruder’s operation, enthusiasts and professionals can optimize their printing parameters and unleash the full potential of 3D printing technology.
Read more: How To Calibrate A 3D Printer Extruder
Types of Extruders
Within the realm of 3D printing, various types of extruders have emerged, each designed to cater to specific printing requirements and material characteristics. Understanding the diverse array of extruder types is pivotal for navigating the expansive landscape of additive manufacturing and harnessing the optimal technology for each application.
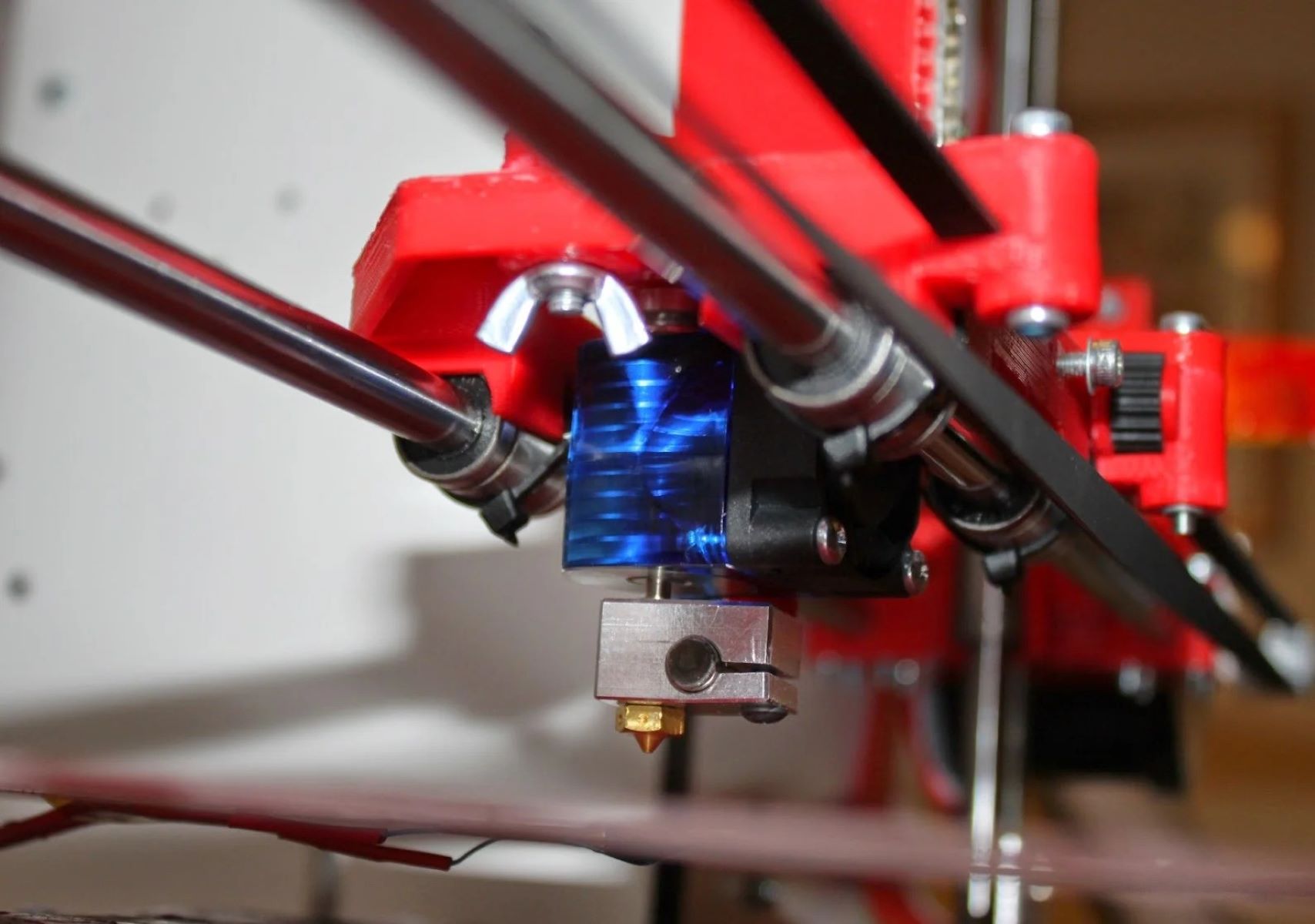
1. Bowden Extruder: Distinguished by its remote filament feeding mechanism, the Bowden extruder separates the filament drive mechanism from the hotend, enabling a lighter and more agile print head. This configuration minimizes the moving mass of the print head, facilitating swifter and more precise movements during printing, particularly for intricate designs and rapid prototyping.
2. Direct Drive Extruder: In contrast to the Bowden extruder, the direct drive extruder integrates the filament drive mechanism within the print head, affording greater control over the filament’s movement and deposition. This proximity enhances the extruder’s ability to handle a diverse range of filament materials, including flexible and abrasive filaments, while maintaining precise extrusion and consistent flow.
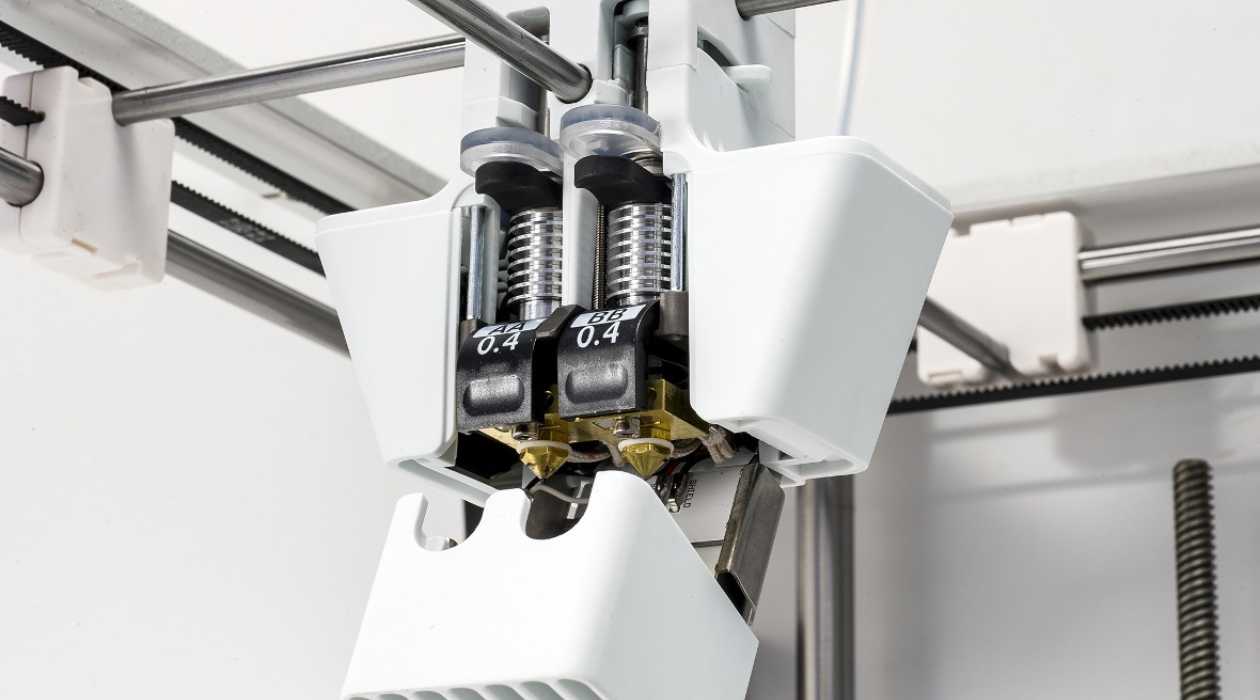
3. Dual Extruder: Catering to the burgeoning demand for multicolor and multimaterial printing, the dual extruder configuration incorporates two independent extruders within a single print head. This setup enables the simultaneous deposition of different filament colors or materials, fostering the creation of visually captivating and functionally diverse printed objects with seamless transitions between materials.
4. Paste Extruder: Tailored for applications that extend beyond traditional filament-based printing, the paste extruder is engineered to handle viscous materials such as clay, silicone, and food-grade substances. This specialized extruder broadens the horizons of 3D printing, empowering users to explore the realm of customized textures, culinary creations, and architectural prototypes with unprecedented versatility.
5. Pellet Extruder: Embracing a sustainable and cost-effective approach to 3D printing, the pellet extruder eschews traditional filament spools in favor of raw plastic pellets. By directly extruding these pellets, this extruder type offers enhanced material flexibility and cost efficiency, catering to environmentally conscious and budget-conscious printing endeavors.
By acquainting oneself with the diverse spectrum of extruder types, 3D printing enthusiasts and industry professionals can align their printing objectives with the most suitable extrusion technology, thereby unlocking new frontiers of creativity and functionality within the additive manufacturing landscape.
Conclusion
Embarking on this exploration of the extruder’s pivotal role in 3D printing has unveiled the intricate mechanisms and diverse configurations that underpin additive manufacturing. From the precise orchestration of filament deposition to the diverse array of extruder types, the extruder stands as a cornerstone of innovation and creativity within the 3D printing ecosystem.
By comprehending the multifaceted role of the extruder, enthusiasts and professionals can harness its capabilities to materialize their creative visions with unparalleled precision and flexibility. The seamless integration of diverse filament materials, intricate designs, and multicolor elements underscores the transformative potential of the extruder in unlocking new frontiers of additive manufacturing.
Moreover, the evolution of extruder technology continues to catalyze innovation across various domains, democratizing the production of prototypes, spare parts, and bespoke creations. The adaptability and precision of modern extruders have transcended traditional manufacturing boundaries, empowering individuals and industries to push the boundaries of creativity and functionality.
As 3D printing continues to redefine manufacturing and prototyping processes, the extruder remains a beacon of precision and control, guiding the transformation of digital designs into tangible realities. Embracing the nuances of extruder operation and the diverse array of extruder types equips individuals and businesses to navigate the expansive landscape of additive manufacturing with confidence and ingenuity.
In essence, the extruder encapsulates the spirit of innovation and precision that defines the 3D printing revolution, ushering in a new era of creativity and manufacturing prowess. By embracing the transformative potential of the extruder, we embark on a journey of limitless possibilities, where imagination converges with technology to reshape the fabric of production and creativity.
As we conclude this exploration, let us carry forth the insights gleaned from the realm of extrusion and 3D printing, empowering ourselves to embark on a transformative journey of innovation and creation, fueled by the boundless potential of additive manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Does The Extruder Do In A 3D Printer
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “What Does The Extruder Do In A 3D Printer”