Home>Technology>Smart Home Devices>What Does The Hot End Do In A 3D Printer

Smart Home Devices
What Does The Hot End Do In A 3D Printer
Modified: August 20, 2024
Learn about the hot end in 3D printers and its role in creating smart home devices. Understand how it functions and its importance in the 3D printing process.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
**
Introduction
**
Welcome to the fascinating world of 3D printing! In this article, we'll delve into the intricate workings of a crucial component of a 3D printer: the hot end. Whether you're a seasoned 3D printing enthusiast or a newcomer intrigued by this cutting-edge technology, understanding the hot end's role is essential for optimizing your printing experience.
As the name suggests, the hot end is responsible for heating and extruding the filament, a pivotal step in the 3D printing process. Its significance cannot be overstated, as the quality and precision of the final print depend largely on the hot end's performance. By comprehending the functions and intricacies of this component, you'll gain valuable insights into the inner workings of 3D printing technology.
Throughout this article, we'll explore the hot end's fundamental mechanisms, its various components, and the different types available. Additionally, we'll delve into essential maintenance practices and troubleshooting tips to ensure your hot end operates at its peak efficiency. Whether you're seeking to optimize your current 3D printing setup or are simply curious about the technology behind this innovative process, this comprehensive guide will provide valuable knowledge about the hot end's pivotal role in the world of 3D printing.
Key Takeaways:
- The hot end in a 3D printer is like the chef of the printing process, melting and extruding filament to create precise and detailed 3D objects. It’s crucial for maintaining consistent temperature and accommodating different filament materials.
- Regular maintenance and troubleshooting of the hot end are essential for ensuring high-quality 3D prints. Cleaning, inspection, and temperature calibration help prevent issues like extrusion problems, temperature fluctuations, and filament jamming, keeping the printing process smooth and reliable.
Read more: What Is An Extruder On A 3D Printer
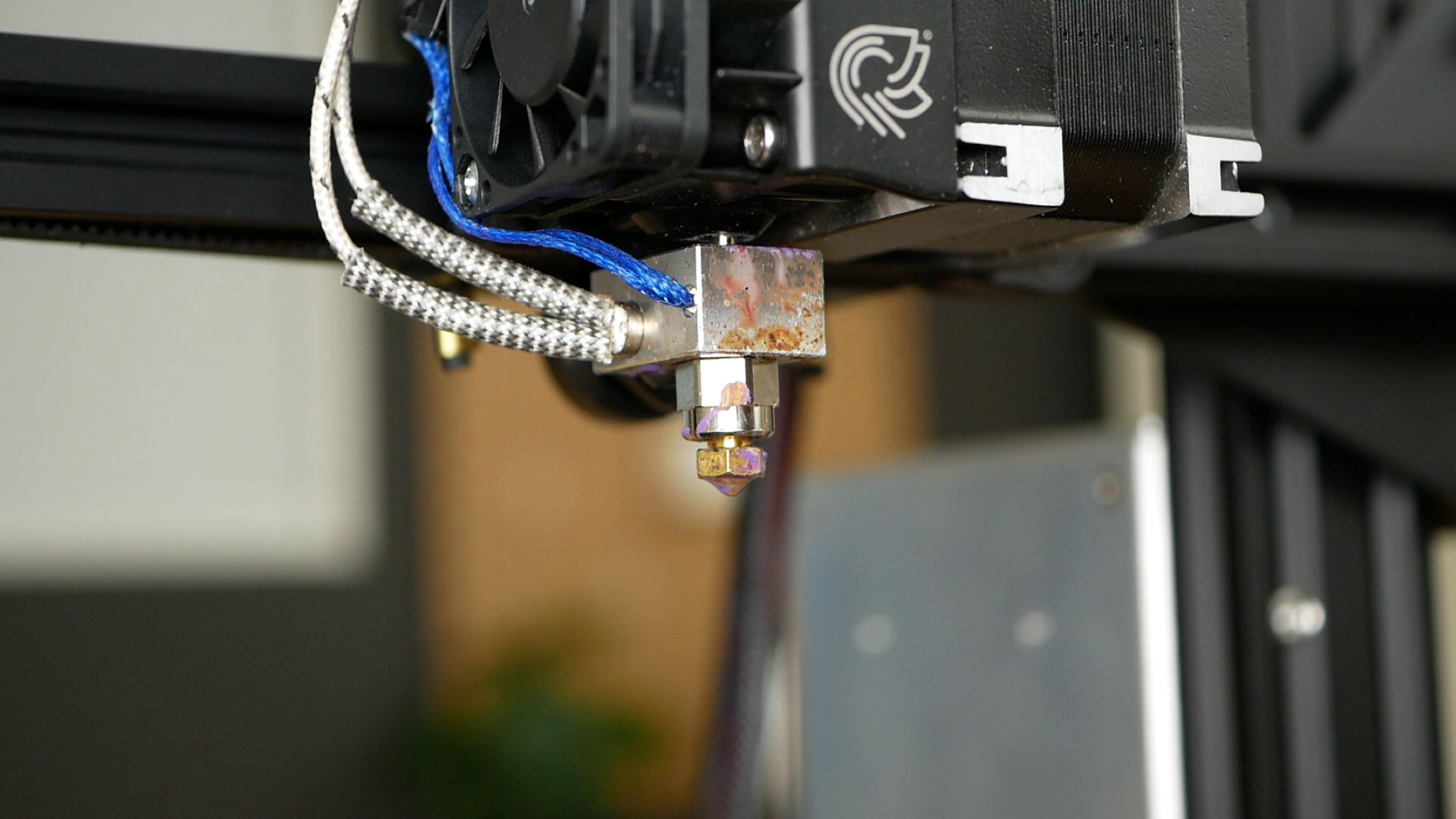
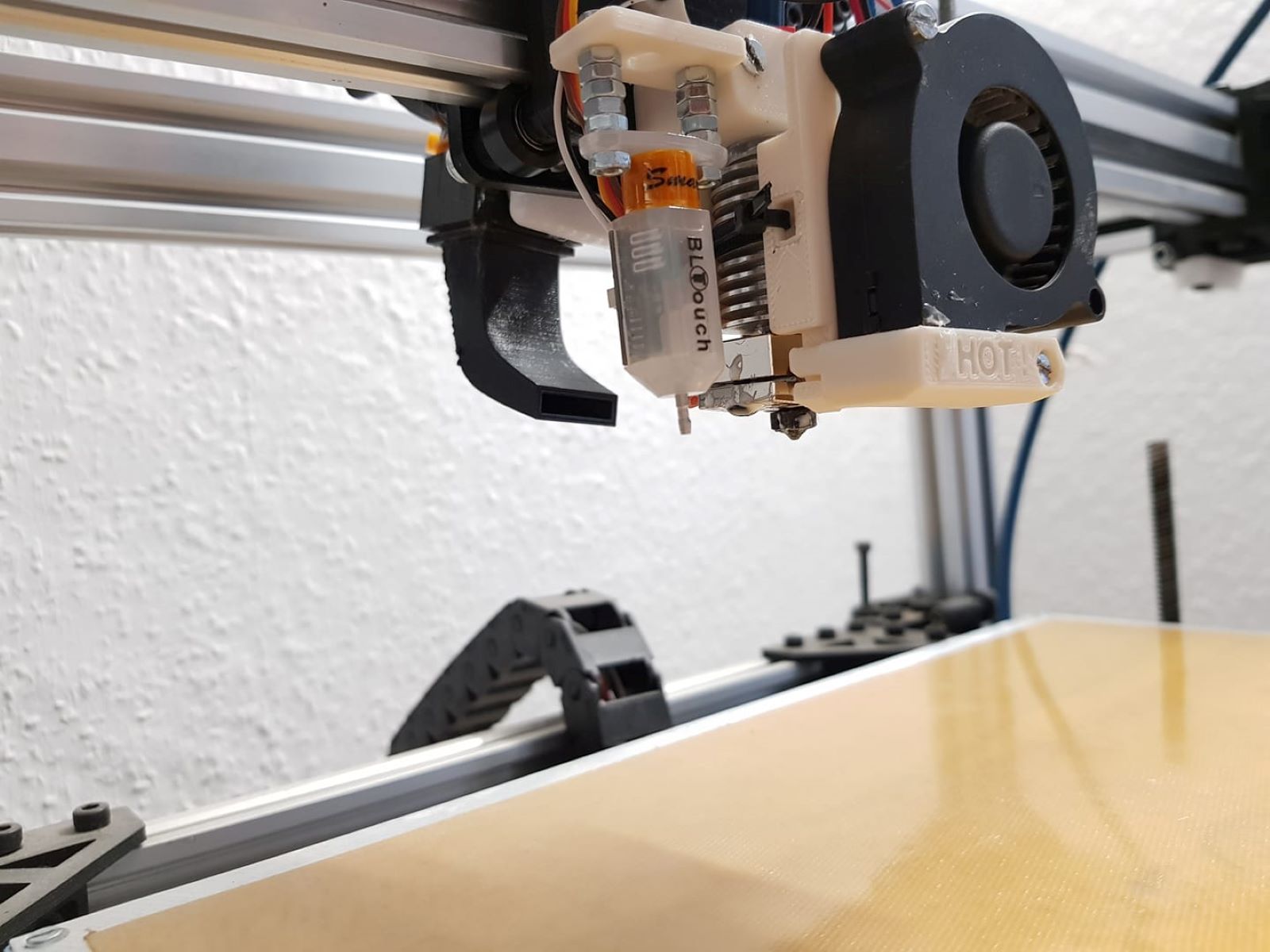
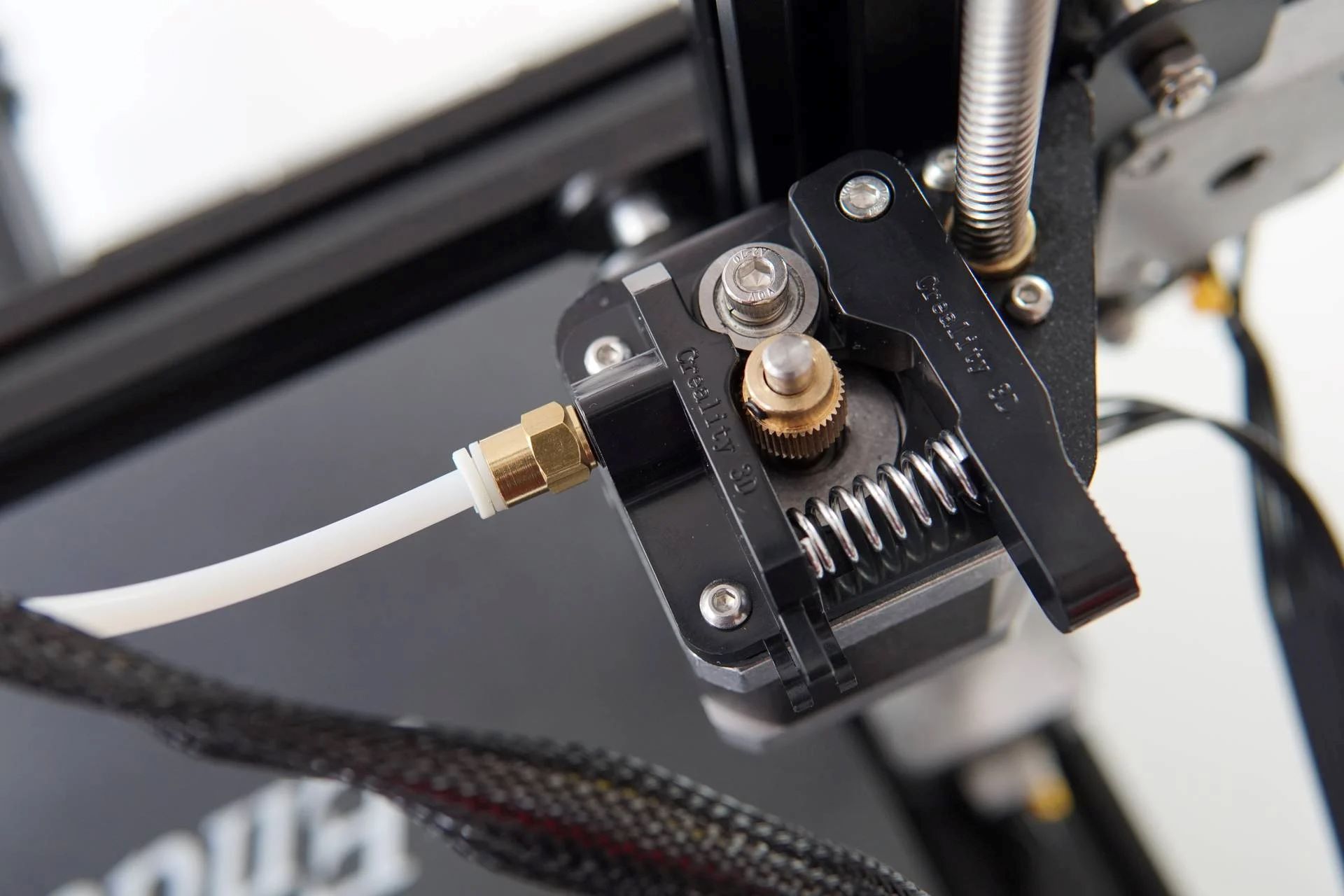
What is a Hot End?
At the heart of every 3D printer lies a crucial component known as the hot end. In simple terms, the hot end serves as the melting and extrusion point for the filament, which is the material used to create the printed objects. This process is fundamental to the entire 3D printing operation, as it dictates the precision and quality of the final output.
The hot end consists of a heating element, typically a resistor or a cartridge heater, which is responsible for heating the filament to its melting point. Once the filament reaches the desired temperature, it becomes pliable and can be extruded through a nozzle onto the print bed. This controlled extrusion process enables the layer-by-layer construction of the 3D object, ultimately resulting in the final printed product.
One of the key considerations when understanding the hot end is the type of filament it can accommodate. Different hot ends are designed to work with specific types of filament, such as PLA, ABS, PETG, and more. The ability to handle various filament materials is essential for accommodating diverse printing needs and ensuring compatibility with a wide range of projects.
Moreover, the hot end plays a critical role in maintaining a consistent temperature throughout the printing process. This temperature control is vital for achieving precise and accurate prints, as fluctuations can lead to imperfections and inconsistencies in the final output. Therefore, the hot end’s ability to regulate and sustain the filament’s temperature is paramount to the success of any 3D printing endeavor.
Overall, the hot end serves as the cornerstone of the 3D printing process, facilitating the controlled melting and extrusion of filament to bring digital designs to life. Its functionality, compatibility with various filament materials, and temperature regulation capabilities make it an indispensable component in the realm of 3D printing technology.
How Does the Hot End Work?
The hot end operates through a meticulously orchestrated process that begins with the heating of the filament to its optimal extrusion temperature. This temperature, which varies depending on the type of filament being used, is carefully maintained to ensure the filament remains in a molten state throughout the printing process.
When the 3D printer is in operation, the hot end’s heating element, typically a resistor or cartridge heater, initiates the filament’s heating process. As the filament reaches the designated temperature, it softens and becomes pliable, enabling it to be extruded through the nozzle onto the print bed. This controlled extrusion is precisely orchestrated to deposit the molten filament in a specific pattern, layer by layer, ultimately forming the desired 3D object.
The hot end’s nozzle plays a pivotal role in this process, as it determines the diameter of the extruded filament. Nozzle sizes can vary, with smaller diameters offering greater precision and finer details, while larger nozzles are suitable for faster printing and larger structures. The careful selection of the nozzle size is crucial for achieving the desired level of detail and speed in the printing process.
Furthermore, the hot end incorporates a cooling system to rapidly solidify the extruded filament once it is deposited onto the print bed. This rapid solidification is essential for maintaining the structural integrity of the printed layers and preventing deformation or warping. By swiftly solidifying the molten filament, the hot end ensures the accurate formation of each layer, contributing to the overall quality of the printed object.
Throughout the printing process, the hot end’s temperature regulation system diligently monitors and adjusts the filament’s temperature to accommodate variations in the printing environment. This meticulous temperature control is critical for preventing issues such as clogging, stringing, or inconsistent extrusion, which can compromise the print quality. By maintaining a consistent and precise temperature, the hot end upholds the integrity and accuracy of the 3D printing process.
Overall, the hot end’s intricate orchestration of heating, extrusion, nozzle control, and temperature regulation culminates in the precise layer-by-layer construction of 3D objects. Its seamless coordination of these essential functions is instrumental in producing high-quality, detailed prints while accommodating a diverse range of filament materials and printing requirements.
Components of the Hot End
The hot end comprises several key components that collectively facilitate the controlled melting and extrusion of filament, essential for 3D printing. Understanding the roles and interactions of these components provides valuable insights into the inner workings of this integral part of the 3D printer.
- Heating Element: At the core of the hot end is the heating element, typically a resistor or a cartridge heater. This component is responsible for elevating the filament’s temperature to its optimal extrusion point, enabling it to transition from a solid state to a molten form suitable for extrusion.
- Thermistor or Thermocouple: The hot end incorporates a temperature sensor, either a thermistor or a thermocouple, to monitor the filament’s temperature. This feedback mechanism enables the printer to regulate the heating element and maintain the filament at the desired temperature throughout the printing process.
- Nozzle: The nozzle serves as the point of extrusion, determining the diameter of the filament as it is deposited onto the print bed. Nozzles are available in various sizes, each suited for specific printing requirements, with smaller diameters offering finer details and larger nozzles enabling faster printing.
- Heat Sink: To prevent the heat generated by the heating element from traveling upward and affecting other components, the hot end features a heat sink. This component dissipates excess heat, safeguarding the printer’s overall functionality and preventing potential damage.
- Insulation: Insulation surrounding the heating element and the hot end assembly helps to retain and regulate the heat, ensuring consistent and efficient temperature control. By minimizing heat loss, insulation contributes to the hot end’s ability to maintain the filament at the required extrusion temperature.
- Fan: Many hot ends are equipped with a cooling fan that directs airflow to the printed layers, expediting the solidification of the extruded filament. This rapid cooling is essential for preserving the structural integrity of the printed object and preventing deformation or warping.
By comprehending the functions and interactions of these components, 3D printing enthusiasts can gain a deeper appreciation for the hot end’s intricate design and its pivotal role in the printing process. The seamless coordination of these components enables the hot end to deliver precise, controlled extrusion while accommodating diverse filament materials and maintaining consistent print quality.
Types of Hot Ends
The world of 3D printing encompasses a diverse array of hot end designs, each tailored to specific printing requirements and filament materials. Understanding the various types of hot ends enables enthusiasts to select the most suitable option for their projects, considering factors such as precision, speed, and material compatibility.
- Bowden Hot End: This design features a remote extruder located away from the hot end, connected by a PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) tube. Bowden hot ends are known for their lightweight extruder assemblies, enabling faster printing speeds and reduced inertia, resulting in precise and detailed prints.
- Direct Drive Hot End: In contrast to the Bowden setup, direct drive hot ends incorporate the extruder within close proximity to the hot end assembly. This configuration offers greater control over filament extrusion, making it suitable for a wide range of filament materials and intricate printing projects.
- All-Metal Hot End: Designed to withstand higher temperatures, all-metal hot ends are capable of accommodating a broader spectrum of filament materials, including those with elevated melting points such as nylon and polycarbonate. This versatility makes them well-suited for advanced and industrial-grade 3D printing applications.
- Paste Extruder: Specifically engineered for printing viscous materials such as clay, silicone, and food-based substances, paste extruders feature a specialized design that facilitates the controlled extrusion of non-traditional 3D printing materials. These hot ends cater to unconventional printing projects, expanding the creative possibilities of 3D printing technology.
- Hybrid Hot End: Combining the features of both Bowden and direct drive setups, hybrid hot ends offer a versatile solution for a wide range of printing requirements. This design provides the benefits of precise extrusion control while minimizing the weight and inertia associated with the extruder assembly, striking a balance between speed and accuracy.
Each type of hot end presents distinct advantages and considerations, catering to specific printing needs and material compatibilities. By selecting the appropriate hot end design, 3D printing enthusiasts can optimize their printing setups to achieve the desired level of precision, speed, and versatility, expanding the creative potential of this innovative technology.
The hot end in a 3D printer melts the filament and deposits it layer by layer to create the 3D object. Make sure to keep the hot end clean and at the right temperature for best results.
Read more: What Is The Cheapest 3D Printer
Hot End Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Ensuring the optimal performance of the hot end is essential for maintaining the quality and consistency of 3D prints. Implementing regular maintenance practices and troubleshooting techniques can mitigate potential issues and prolong the hot end’s functionality, ultimately enhancing the overall 3D printing experience.
Maintenance
Cleaning: Regularly cleaning the hot end and nozzle is crucial for preventing filament residue and debris from obstructing the extrusion process. This can be achieved by using a specialized nozzle cleaning tool or performing cold pulls to remove any accumulated contaminants.
Inspection: Periodically inspecting the hot end assembly for signs of wear, damage, or filament buildup is advisable. Identifying and addressing any issues promptly can prevent potential malfunctions and ensure consistent print quality.
Temperature Calibration: Calibrating the hot end’s temperature settings to align with the filament material being used is essential for achieving precise extrusion and preventing issues such as under-extrusion or overheating.
Troubleshooting
Extrusion Issues: If the hot end experiences inconsistent extrusion or clogging, it may be necessary to check for obstructions within the nozzle or perform a cold pull to clear any blockages. Additionally, adjusting the extrusion temperature and retraction settings can help alleviate extrusion-related issues.
Temperature Fluctuations: Fluctuations in the hot end’s temperature can lead to print imperfections. Troubleshooting temperature irregularities involves verifying the heating element’s functionality, inspecting the thermistor or thermocouple for accuracy, and ensuring proper insulation and heat dissipation.
Layer Adhesion Problems: In cases where printed layers exhibit poor adhesion, optimizing the hot end’s temperature and cooling settings can help address this issue. Additionally, ensuring the print bed is properly leveled and applying suitable adhesion aids can contribute to improved layer adhesion.
Filament Jamming: Addressing filament jams necessitates inspecting the extruder assembly for obstructions, adjusting the retraction settings to minimize filament pressure, and confirming that the filament path is unobstructed and properly aligned with the hot end.
By integrating these maintenance practices and troubleshooting techniques into their 3D printing routines, enthusiasts can uphold the hot end’s efficiency and address potential issues effectively, ultimately enhancing the reliability and quality of their 3D prints.
Conclusion
Exploring the hot end’s pivotal role in the realm of 3D printing unveils the intricate orchestration of heating, extrusion, and temperature regulation that underpins this innovative technology. As the cornerstone of the 3D printing process, the hot end’s ability to precisely melt and extrude filament material is fundamental to the creation of detailed and accurate 3D objects.
Understanding the components and functionalities of the hot end provides enthusiasts with valuable insights into the inner workings of their 3D printers, empowering them to optimize their printing setups and accommodate diverse filament materials and project requirements. From the heating element and nozzle to the cooling system and temperature regulation mechanisms, each aspect of the hot end plays a critical role in the seamless construction of 3D prints.
Furthermore, the diverse array of hot end designs, ranging from Bowden and direct drive setups to all-metal and paste extruders, offers enthusiasts the flexibility to tailor their 3D printing configurations to specific project needs, material compatibilities, and desired levels of precision and speed.
By incorporating regular maintenance practices and troubleshooting techniques, enthusiasts can uphold the hot end’s efficiency, mitigate potential issues, and ensure consistent print quality. Cleaning, inspection, and temperature calibration are essential maintenance steps, while addressing extrusion issues, temperature fluctuations, layer adhesion problems, and filament jamming can enhance the hot end’s reliability and performance.
Ultimately, the hot end stands as a testament to the meticulous engineering and precision required to bring digital designs to life through 3D printing. Its seamless coordination of heating, extrusion, and temperature control embodies the innovation and creativity that define the captivating world of 3D printing technology.
As 3D printing continues to evolve and expand its applications across various industries, the hot end remains an indispensable component, driving the precision, versatility, and transformative potential of this groundbreaking technology.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Does The Hot End Do In A 3D Printer
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.











0 thoughts on “What Does The Hot End Do In A 3D Printer”