Home>Technology>Smart Home Devices>What Is The Drum In A Printer


Smart Home Devices
What Is The Drum In A Printer
Modified: August 17, 2024
Learn about the drum in a printer and its role in producing high-quality prints. Explore how smart home devices are revolutionizing printing technology.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
**
Introduction
**
Welcome to the fascinating world of printers, where cutting-edge technology meets the art of producing crisp, vibrant documents. At the heart of a printer lies a crucial component known as the drum. This often-overlooked element plays a pivotal role in the printing process, contributing to the high-quality output that we have come to expect from modern printers.
Understanding the drum’s function, history, types, and maintenance is essential for anyone seeking to delve deeper into the realm of printing technology. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the drum in printers, shedding light on its significance and the key factors that contribute to its optimal performance.
**
Key Takeaways:
- The drum in printers is a crucial component that helps create high-quality prints by transferring toner onto the printing surface using electrostatic forces and precise mechanical processes.
- Understanding the history, function, types, and maintenance of printer drums is essential for optimizing printer performance and achieving exceptional print quality.
Read more: How To Clean A Printer Drum
History of Drum in Printers
**
The history of the drum in printers is a tale of innovation and evolution, intricately woven into the fabric of printing technology. The concept of the drum dates back to the early days of printing, where manual processes such as etching and woodblock printing were prevalent. However, the integration of drums into modern printers marks a significant milestone in the advancement of printing technology.
The inception of the modern drum in printers can be traced back to the development of electrophotography, commonly known as xerography, by the legendary inventor Chester Carlson in the late 1930s. This groundbreaking invention laid the foundation for the creation of the first commercial xerographic copier, the Xerox 914, which revolutionized the way documents were reproduced.
As printing technology continued to evolve, the drum played a pivotal role in the transition from analog to digital printing. With the advent of laser printers in the 1970s, the drum became an indispensable component, enabling the precise transfer of toner onto the printing surface. This marked a paradigm shift in the printing industry, leading to the widespread adoption of laser printing technology in both commercial and consumer markets.
Over the years, advancements in materials science and manufacturing processes have led to the development of high-performance drums capable of delivering exceptional print quality and durability. Today, the drum remains a fundamental element in a wide range of printing devices, including laser printers, photocopiers, and multifunction printers, contributing to the seamless reproduction of text, images, and graphics.
The rich history of the drum in printers reflects the relentless pursuit of excellence in printing technology, driving innovation and setting new standards for print quality and reliability. As we delve deeper into the function and significance of the drum, it is essential to appreciate its evolution and the transformative impact it has had on the world of printing.
**
Function of the Drum in a Printer
**
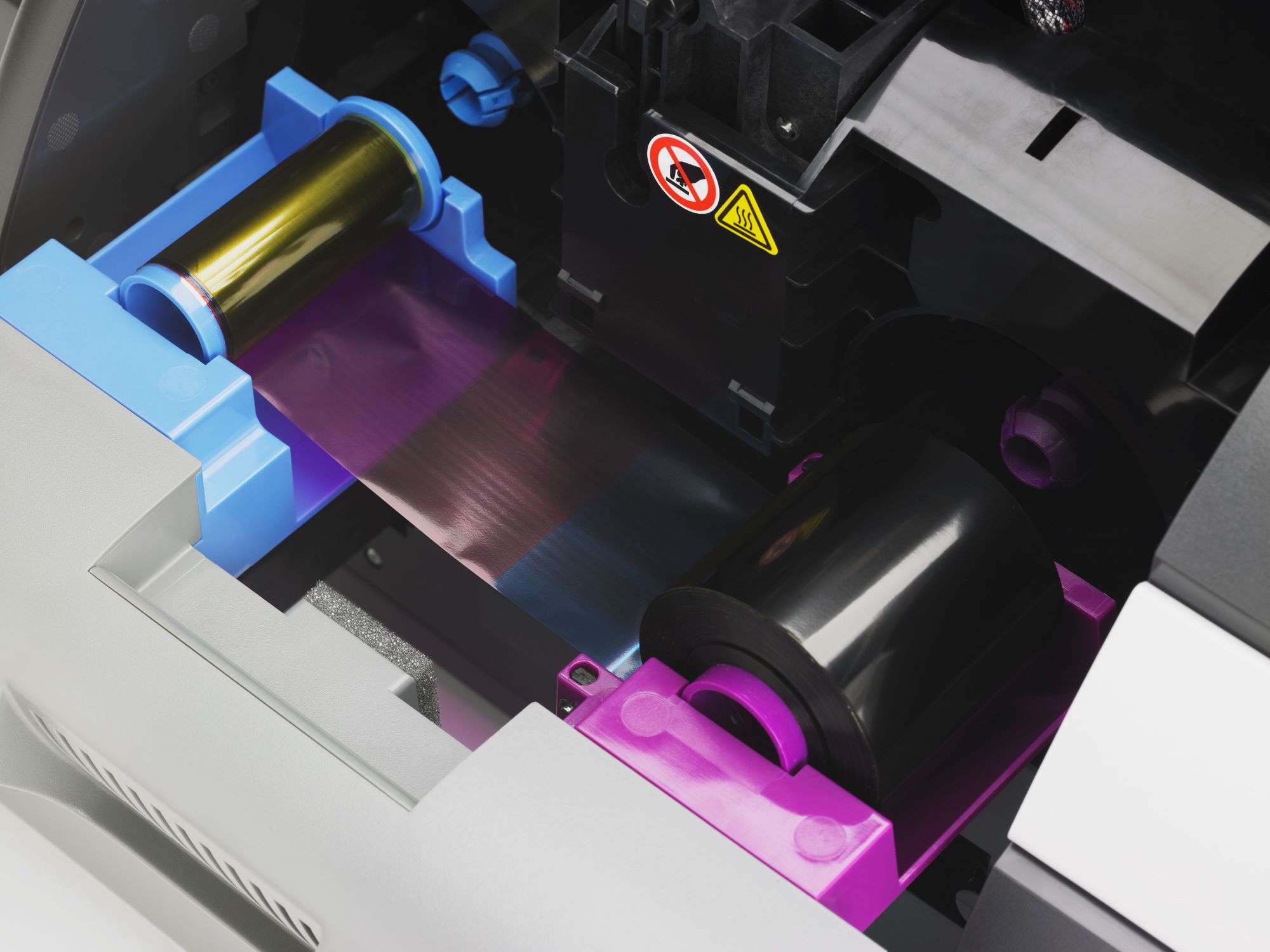
The drum in a printer serves as a critical component in the electrostatic reproduction of text and images onto various types of media. Its primary function is to facilitate the precise transfer of toner particles onto the printing surface, resulting in the creation of high-quality printed documents.
At the core of the drum’s function lies the principle of electrostatic attraction and repulsion. In a laser printer, the drum is initially charged with a uniform electrostatic charge. As the printing process commences, a laser beam selectively discharges specific areas of the drum, creating an electrostatic image of the content to be printed. This process, known as laser-induced electrostatic discharge, forms the basis for the creation of the latent image on the drum surface.
Subsequently, the charged toner particles are attracted to the discharged areas of the drum, adhering to the electrostatic image. This transfer of toner onto the drum is facilitated by a combination of electrostatic forces and the rotation of the drum, ensuring precise deposition of the toner particles in accordance with the desired content.
Once the toner particles have been deposited on the drum, the next stage involves transferring the toner from the drum onto the printing surface, typically paper. This is achieved through a series of electrostatic and mechanical processes, culminating in the fusion of the toner onto the paper, resulting in the final printed output.
It is important to note that the function of the drum is intricately linked to the overall printing process, playing a crucial role in ensuring the accurate reproduction of text and images with exceptional clarity and detail. The precision and reliability of the drum’s function directly impact the quality of the printed output, making it an indispensable component in modern printing technology.
As we delve deeper into the function of the drum, it becomes evident that its role extends beyond mere mechanical transfer, embodying the convergence of scientific principles and engineering ingenuity to deliver unparalleled printing performance.
**
Types of Drums in Printers
**
Printers employ various types of drums, each tailored to specific printing technologies and applications. Understanding the distinct characteristics and functionalities of these drums is essential for optimizing printing performance and achieving superior output quality.
1. Organic Photoconductor (OPC) Drums:
OPC drums are commonly utilized in laser printers and multifunction devices. These drums feature a photosensitive coating composed of organic compounds, which exhibit excellent photoconductivity when exposed to light. OPC drums are renowned for their durability and consistent performance, making them a popular choice for high-volume printing environments.
2. Seamless Drums:
Seamless drums, also known as continuous surface drums, are characterized by their smooth, uniform surface, which eliminates the need for seams or joints. This design minimizes image distortion and enhances print quality, making seamless drums ideal for precision printing tasks that demand exceptional clarity and detail.
3. Differential Charge Development (DCD) Drums:
DCD drums feature a specialized design that enables the precise control of toner deposition, resulting in enhanced image resolution and tonal accuracy. These drums are particularly well-suited for applications that require the reproduction of intricate graphics and fine details, delivering exceptional print fidelity across a wide range of media types.
4. Conductive Drums:
Conductive drums utilize a conductive surface to facilitate the controlled transfer of toner particles during the printing process. This design ensures uniform toner distribution and efficient toner transfer, contributing to consistent print quality and reliable performance in diverse printing environments.
5. Long-Life Drums:
Long-life drums are engineered to withstand extended usage without compromising print quality or reliability. These drums are designed to endure the rigors of high-volume printing, offering exceptional longevity and consistent performance, making them an ideal choice for demanding printing applications.
By understanding the unique characteristics and advantages of each type of drum, users can make informed decisions when selecting printers that align with their specific printing requirements. The diverse array of drum technologies available in modern printers underscores the continuous innovation and refinement in printing technology, empowering users to achieve exceptional results across a broad spectrum of printing tasks.
**
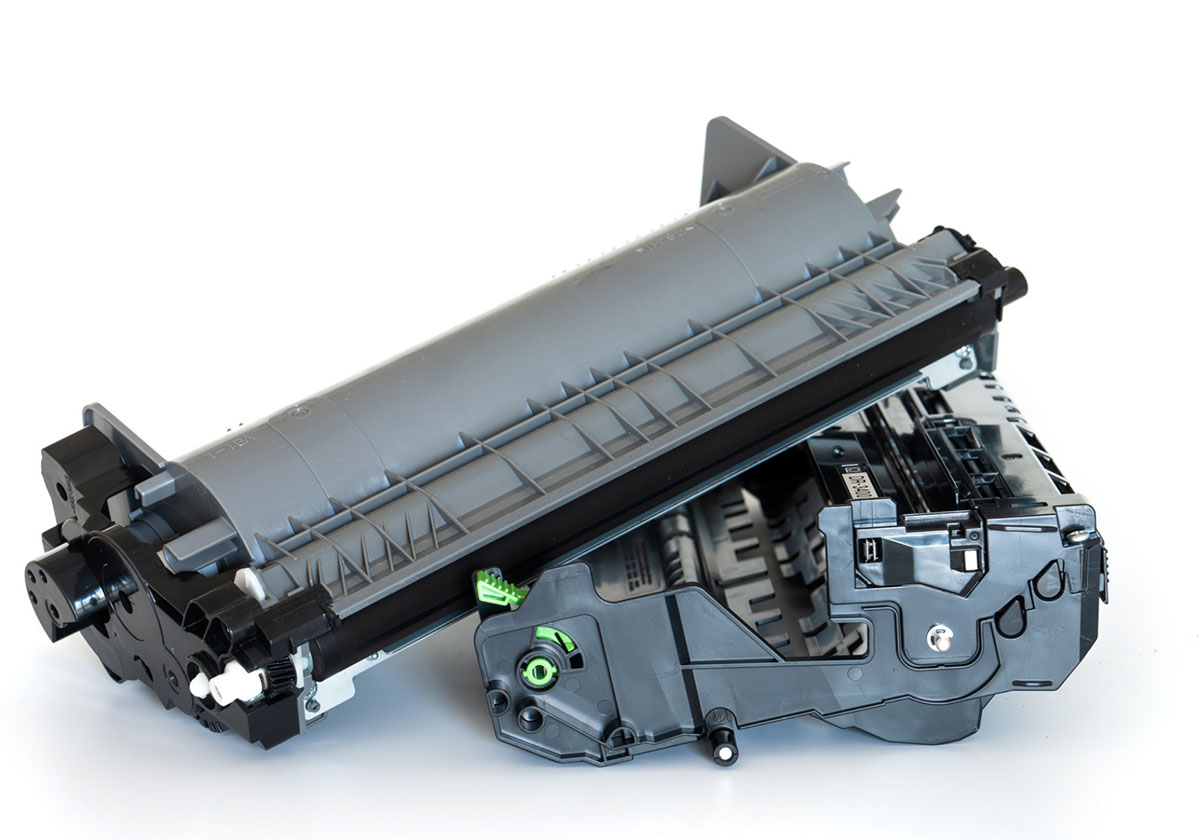
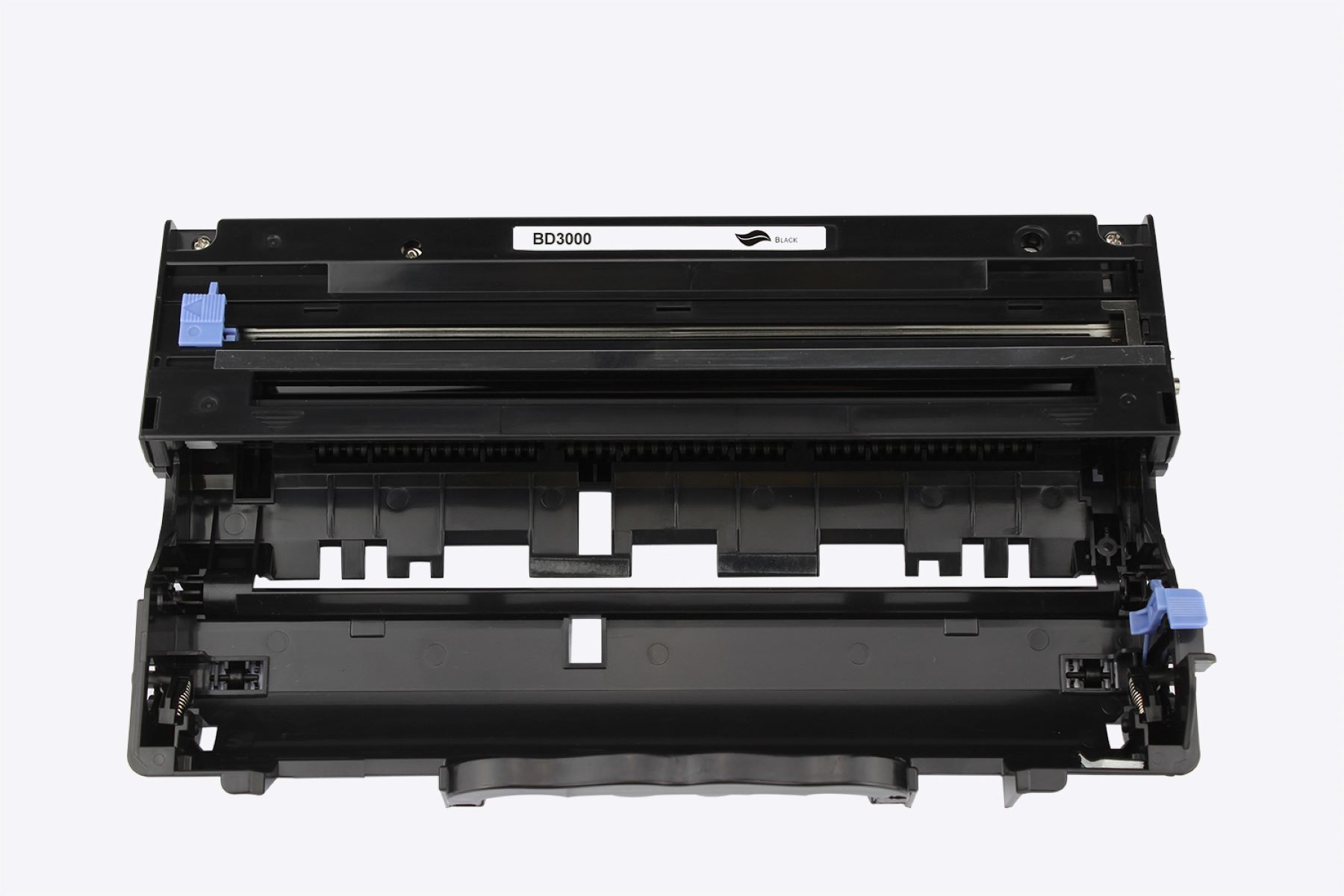
The drum in a printer is a cylindrical component that transfers toner onto the paper. It is important to keep the drum clean and free of debris to ensure high-quality prints.
Importance of the Drum in Printer Performance
**
The drum in a printer plays a pivotal role in determining the overall performance and print quality of the device. Its significance extends beyond being a mere component, as it directly influences the precision, reliability, and longevity of the printing process. Understanding the importance of the drum is essential for optimizing printer performance and achieving exceptional output quality.
1. Image Reproduction:
The drum is instrumental in faithfully reproducing text, images, and graphics with exceptional clarity and detail. Its precise transfer of toner particles onto the printing surface ensures that the intended content is accurately rendered, resulting in high-quality printed output that meets the exacting standards of professional and personal printing needs.
2. Consistency and Reliability:
A high-quality drum contributes to consistent print performance, ensuring that each document produced maintains uniformity in print density, sharpness, and color accuracy. This consistency is essential for professional documents, marketing materials, and creative projects, where reliable print quality is paramount.
3. Longevity and Durability:
An efficient drum is designed to withstand the rigors of continuous printing, offering exceptional longevity and durability. This longevity ensures that the printer can maintain optimal performance over an extended period, minimizing downtime and maintenance requirements while delivering consistent print quality.
4. Compatibility with Diverse Media:
The drum’s performance directly impacts its compatibility with various types of media, including plain paper, envelopes, labels, and specialty papers. A high-quality drum is engineered to accommodate diverse media types, enabling users to produce professional-grade prints on a wide range of materials.
5. Optimized Toner Usage:
An efficient drum maximizes the utilization of toner, ensuring that toner particles are accurately transferred onto the printing surface without waste or excess consumption. This optimized toner usage contributes to cost savings and environmental sustainability, making efficient drums an essential component for eco-conscious printing practices.
Understanding the pivotal role of the drum in printer performance underscores the importance of selecting printers equipped with high-quality drums. Whether for personal, professional, or commercial use, the drum’s influence on print quality, reliability, and efficiency cannot be overstated, making it a critical consideration for anyone seeking exceptional printing results.
**
Maintenance and Care of the Drum in Printers
**
Maintaining the drum in a printer is essential for preserving its performance, extending its lifespan, and ensuring consistent print quality. Proper care and maintenance practices contribute to the longevity and reliability of the drum, ultimately enhancing the overall printing experience. Here are key maintenance and care guidelines for the drum in printers:
1. Regular Cleaning:
Periodic cleaning of the drum surface helps remove accumulated toner particles, debris, and other contaminants that may affect print quality. Use a lint-free cloth or specialized cleaning materials recommended by the printer manufacturer to gently wipe the drum surface, ensuring that it remains free from residue and foreign particles.
2. Avoiding Physical Damage:
Handle the drum with care to prevent physical damage, scratches, or abrasions that can compromise its functionality. When accessing the drum for maintenance or replacement, follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations to minimize the risk of damage during handling.
3. Optimal Storage Conditions:
If storing replacement drums or spare parts, ensure that they are kept in a clean, dry environment with moderate temperature and humidity levels. Exposure to extreme environmental conditions can adversely affect the drum’s performance and longevity.
4. Using Genuine Replacement Parts:
When replacing the drum or related components, use genuine replacement parts recommended by the printer manufacturer. Genuine parts are engineered to meet the specific requirements of the printer and ensure compatibility, performance, and reliability.
5. Following Maintenance Schedule:
Adhere to the recommended maintenance schedule provided by the printer manufacturer. This may include periodic drum replacement, cleaning routines, and diagnostic checks to ensure that the drum and associated components are functioning optimally.
6. Avoiding Exposure to Light:
Minimize the drum’s exposure to direct light, especially ultraviolet (UV) light, as prolonged exposure can degrade the drum’s photosensitive surface. When accessing the drum for maintenance or inspection, work in a well-lit environment without exposing the drum to excessive light sources.
By following these maintenance and care practices, users can safeguard the integrity and performance of the drum in printers, contributing to consistent print quality, extended longevity, and reliable operation. Incorporating these guidelines into regular printer maintenance routines helps optimize the printing experience and ensures that the drum continues to deliver exceptional results.
**
Conclusion
**
The drum in printers stands as a testament to the seamless fusion of scientific innovation and engineering precision, playing a pivotal role in the electrostatic reproduction of text and images with exceptional clarity and detail. Its evolution from the early days of printing to the modern era of advanced printing technology reflects a relentless pursuit of excellence and a commitment to delivering superior print quality.
As we have explored the history, function, types, and maintenance of the drum, it becomes evident that its significance extends far beyond being a mere component within a printer. The drum’s influence on printer performance, print quality, and longevity underscores its indispensable role in the seamless creation of professional documents, vibrant graphics, and captivating visuals.
Understanding the diverse types of drums available in modern printers empowers users to make informed decisions when selecting printing devices that align with their specific needs and preferences. Whether it is the durability of organic photoconductor drums, the precision of differential charge development drums, or the versatility of long-life drums, each type offers unique advantages tailored to diverse printing requirements.
Moreover, the maintenance and care of the drum emerge as essential practices for preserving its performance, ensuring consistent print quality, and maximizing its lifespan. By following recommended maintenance guidelines, users can optimize the longevity and reliability of the drum, ultimately enhancing the overall printing experience.
In conclusion, the drum in printers exemplifies the harmonious convergence of technology and artistry, enabling the seamless transformation of digital content into tangible, vibrant prints. Its enduring legacy as a cornerstone of printing technology continues to shape the landscape of modern printing, setting new benchmarks for precision, reliability, and print fidelity.
As we embark on a journey through the ever-evolving realm of printing technology, let us acknowledge the drum’s unwavering contribution to the art of printing, inspiring us to pursue excellence and innovation in every document we create.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is The Drum In A Printer
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Is The Drum In A Printer”