Home>Technology>Smart Home Devices>What Type Of Printer Has An Extruder As One Of Its Components?

Smart Home Devices
What Type Of Printer Has An Extruder As One Of Its Components?
Published: January 12, 2024
Discover the latest smart home devices with extruder components for efficient printing. Explore our range of printers designed for smart home integration.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of 3D printing, where innovation and creativity converge to revolutionize manufacturing and design. Among the myriad of 3D printers available, those equipped with extruders play a pivotal role in materializing intricate and customized creations.
The integration of extruders within 3D printers has significantly expanded the scope of what can be achieved in the realm of additive manufacturing. This article aims to delve into the nuances of printers with extruders, exploring their types, applications, advantages, and disadvantages.
As we embark on this journey, you will gain a comprehensive understanding of the capabilities and intricacies of printers with extruders, empowering you to harness their potential for a myriad of applications. Whether you are a seasoned enthusiast or a newcomer to the world of 3D printing, this exploration will provide valuable insights into the fascinating domain of printers with extruders.
Key Takeaways:
- 3D printers with extruders use precise layering to create intricate objects from materials like plastic, metal, and wood, revolutionizing industries from art to manufacturing.
- While printers with extruders offer versatility and customization, they may require post-processing for a smooth finish and have limitations in material availability and print speed.
Read more: What Is An Extruder On A 3D Printer
Understanding Printers with Extruders
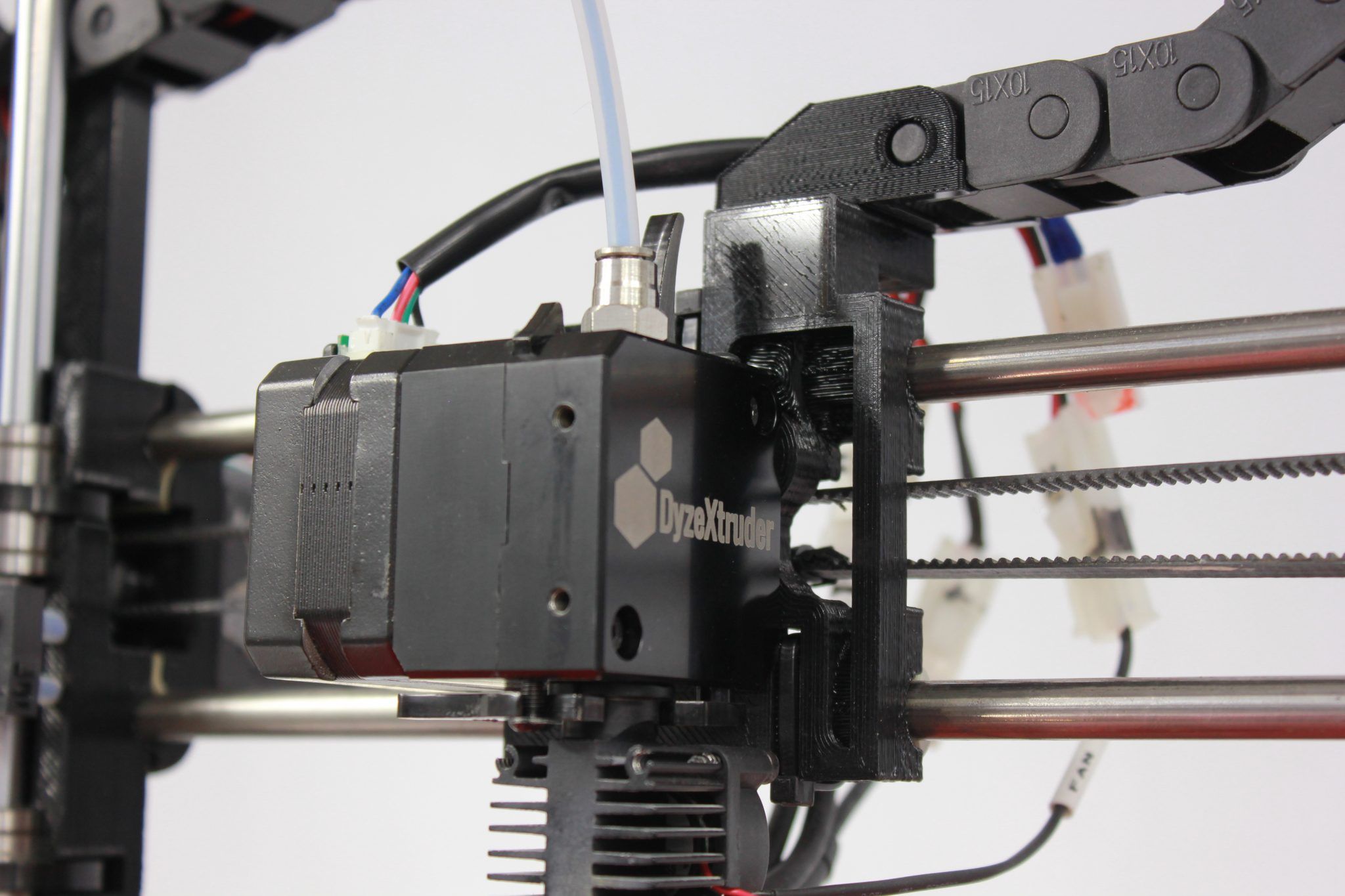
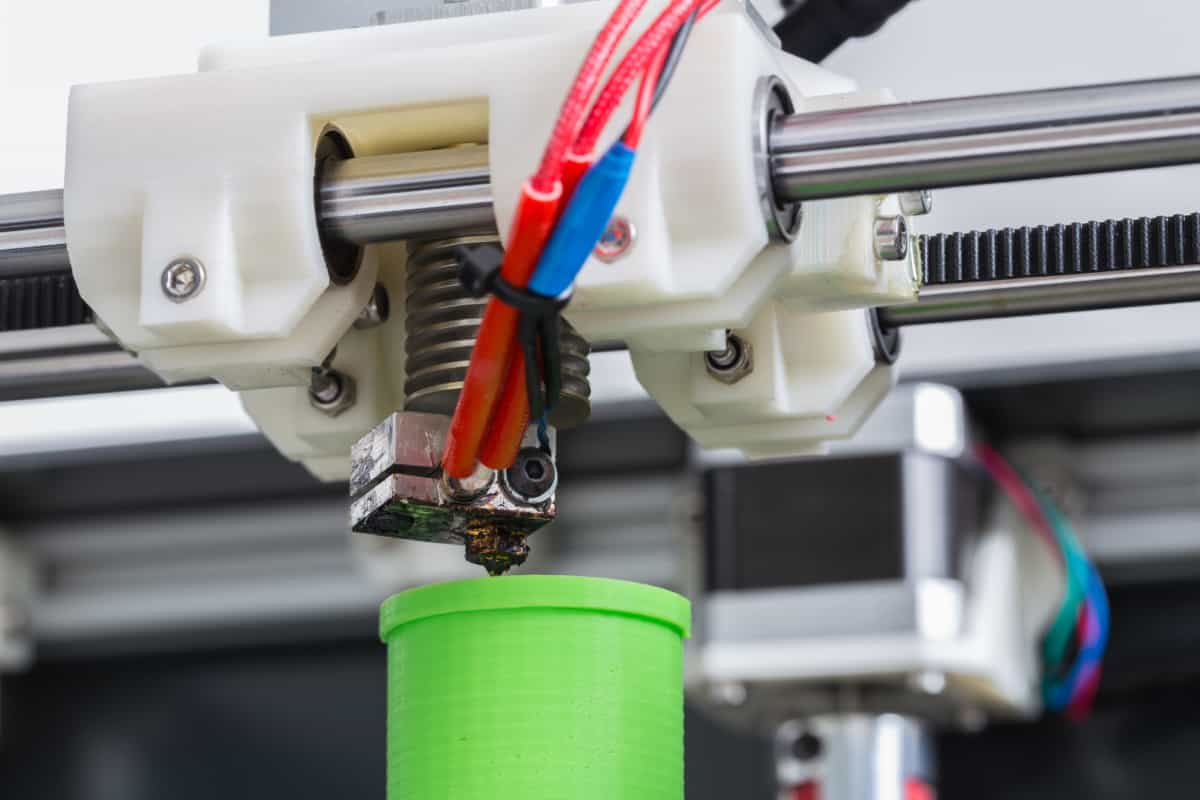
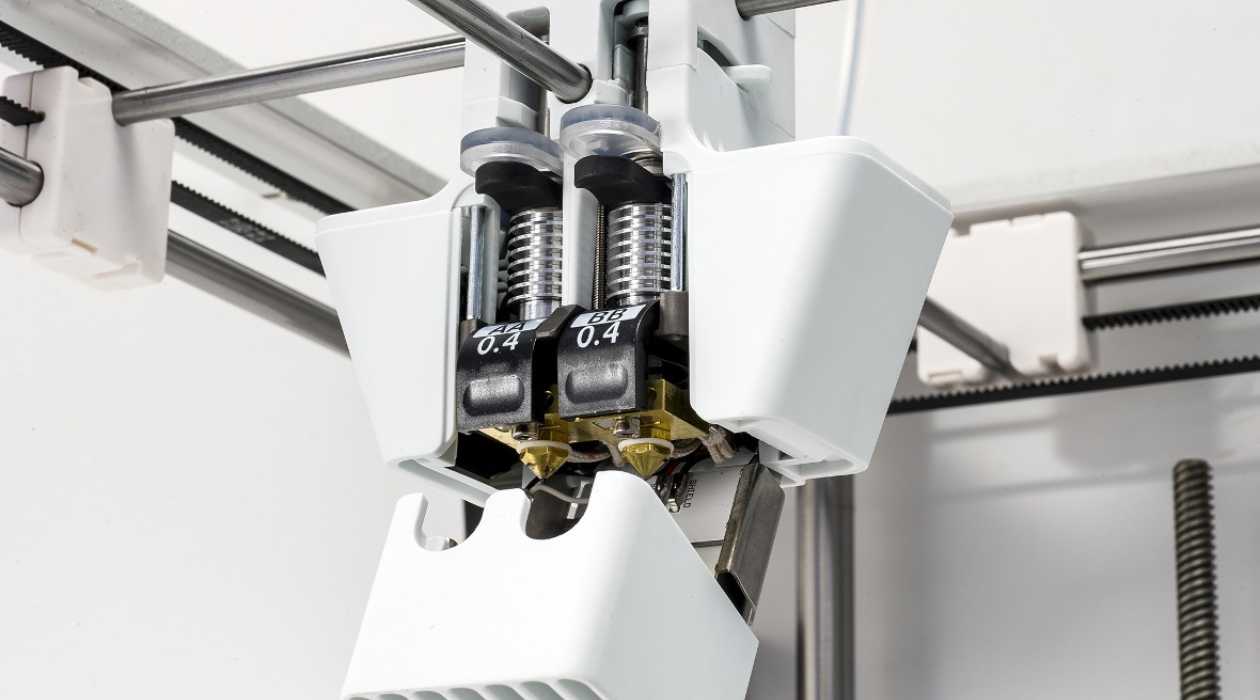
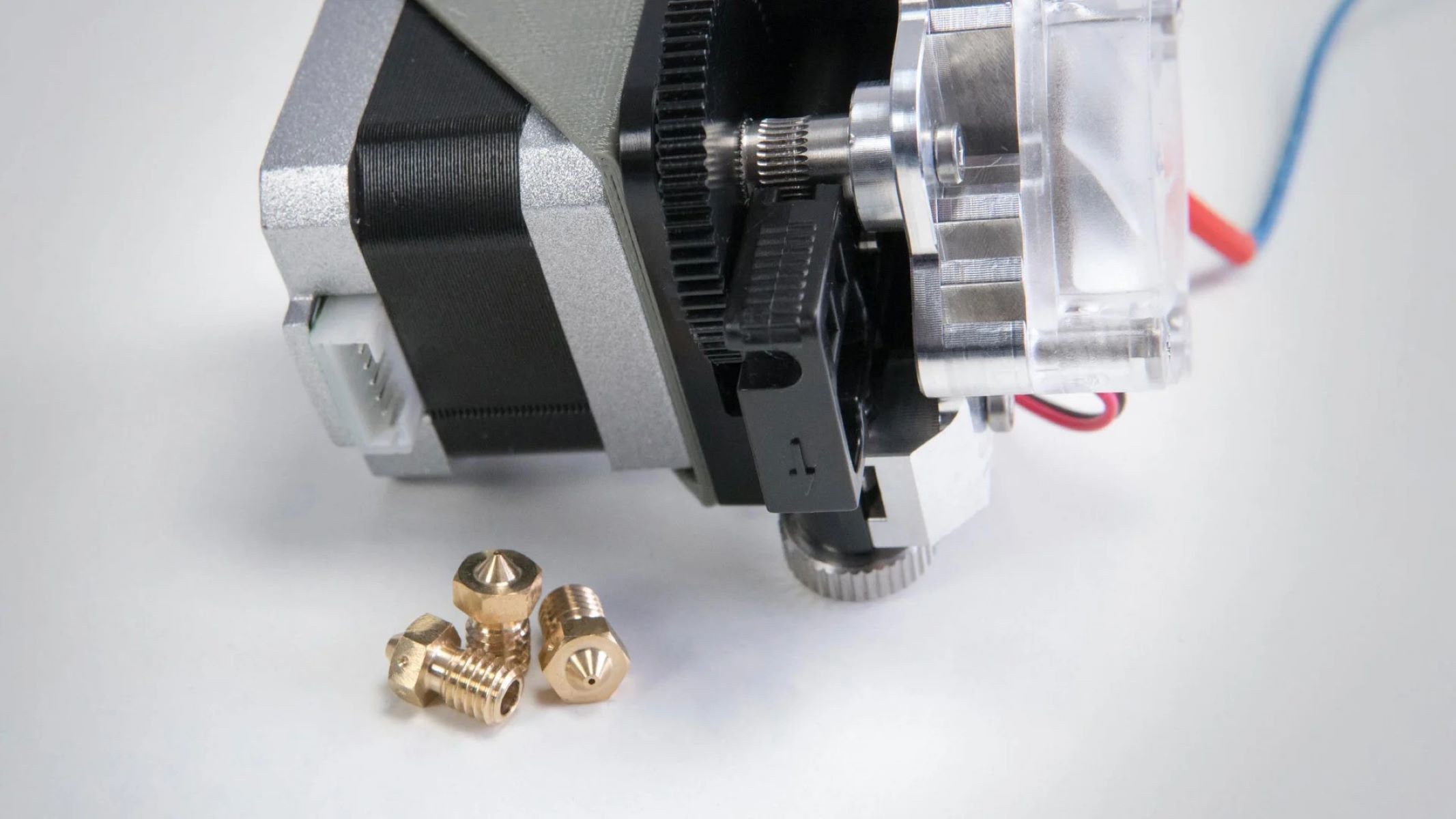
Printers equipped with extruders are at the forefront of additive manufacturing, boasting the capability to transform digital designs into tangible objects with remarkable precision. At the core of these printers lies the extruder, a fundamental component responsible for depositing and shaping the printing material layer by layer.
Extruders function by heating and melting the printing material, typically plastic filament, and depositing it onto the printing surface according to the specifications delineated by the digital design. This meticulous process enables the creation of three-dimensional objects with intricate geometries and fine details, making printers with extruders indispensable in various industries.
Furthermore, the extruder plays a crucial role in ensuring the structural integrity and dimensional accuracy of the printed objects. By meticulously controlling the extrusion process, printers with extruders can produce complex shapes and intricate patterns with unparalleled fidelity, catering to a diverse array of applications.
Moreover, the versatility of printers with extruders extends beyond traditional plastics, as they can accommodate an extensive range of printing materials, including composite filaments infused with metal, wood, or carbon fiber. This adaptability broadens the horizons of additive manufacturing, enabling the production of functional prototypes, artistic creations, and customized components with exceptional material properties.
By comprehending the pivotal role of the extruder within printers, one can appreciate the intricacies of additive manufacturing and the boundless potential it holds for materializing innovative designs and functional prototypes.
Types of Printers with Extruders
Printers with extruders encompass a diverse spectrum of configurations, each tailored to specific applications and user requirements. The two primary types of printers with extruders are Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) and Stereolithography (SLA) printers, each offering unique capabilities and advantages.
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) Printers: FDM printers are renowned for their accessibility, versatility, and robustness. These printers utilize a filament-based extrusion system, where a spool of thermoplastic filament is fed into the extruder, heated, and deposited layer by layer to construct the desired object. FDM printers are widely favored for their affordability, ease of use, and compatibility with a broad range of thermoplastics, making them ideal for rapid prototyping, educational purposes, and hobbyist endeavors.
- Stereolithography (SLA) Printers: In contrast, SLA printers employ a photopolymer resin as the printing material, which is meticulously cured layer by layer using a precise ultraviolet laser. This technology facilitates the creation of exceptionally detailed and high-resolution objects, making SLA printers a preferred choice for applications demanding intricate geometries, smooth surface finishes, and fine feature resolution. SLA printers excel in producing jewelry, dental models, and intricately detailed prototypes, catering to industries where precision and aesthetic appeal are paramount.
Furthermore, within the realm of FDM printers, variations exist based on the number of extruders incorporated. Single extruder FDM printers are suitable for monochromatic prints or those requiring a single material, while dual extruder FDM printers enable the fabrication of multi-material or multi-colored objects, enhancing the versatility and complexity of printed designs.
Understanding the distinctions between FDM and SLA printers, as well as the nuances within each category, empowers individuals and businesses to select the most suitable printer based on their specific requirements, budget, and intended applications.
Applications of Printers with Extruders
Printers equipped with extruders have permeated diverse industries, catalyzing innovation and streamlining production processes across a myriad of applications. The versatility and precision offered by these printers have rendered them indispensable in numerous fields, revolutionizing prototyping, manufacturing, and customization endeavors.
- Rapid Prototyping: 3D printers with extruders have redefined the landscape of rapid prototyping, enabling designers and engineers to swiftly materialize their concepts and iterate designs with unparalleled agility. These printers facilitate the creation of functional prototypes with intricate geometries, allowing for rigorous testing and validation of designs in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics.
- Customized Manufacturing: The customization capabilities of printers with extruders have found extensive utilization in the production of personalized consumer goods, bespoke jewelry, and tailored medical devices. By leveraging the precision and adaptability of these printers, manufacturers can fulfill niche demands and cater to individual preferences, fostering a new era of customized and on-demand manufacturing.
- Artistic Expression: Artists and designers harness the creative potential of printers with extruders to materialize intricate sculptures, artistic installations, and avant-garde creations that transcend the limitations of traditional artistic mediums. The ability to fabricate complex shapes and structures empowers artists to explore new dimensions of artistic expression, blurring the boundaries between art, technology, and craftsmanship.
- Educational Endeavors: Printers with extruders have become invaluable educational tools, enriching learning experiences and fostering innovation in academic settings. Students and educators alike benefit from the hands-on learning opportunities offered by these printers, delving into the realms of engineering, design, and material science while honing their creativity and problem-solving skills.
Moreover, the applications of printers with extruders extend to the realm of sustainable manufacturing, where the utilization of eco-friendly and recyclable materials in additive manufacturing processes contributes to the advancement of sustainable practices and circular economies.
By embracing the diverse applications of printers with extruders, industries and individuals are poised to unlock new frontiers of innovation, customization, and sustainable production, propelling the evolution of additive manufacturing into a ubiquitous and transformative force.
A 3D printer has an extruder as one of its components. The extruder heats and melts the printing material, then deposits it layer by layer to create a 3D object.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Printers with Extruders
Printers equipped with extruders offer a plethora of advantages that have propelled additive manufacturing to the forefront of modern production methodologies. However, they also present certain limitations and considerations that warrant careful assessment when determining their suitability for specific applications.
Read more: What Fruit Has Its Seeds On The Outside
Advantages:
- Versatility: Printers with extruders accommodate a wide array of printing materials, ranging from traditional thermoplastics to advanced composites, enabling the fabrication of objects with diverse material properties and functionalities.
- Precision and Detail: The meticulous layer-by-layer deposition facilitated by extruders results in objects with intricate geometries, fine details, and high dimensional accuracy, catering to applications necessitating precision and aesthetic appeal.
- Customization: These printers empower the production of customized and personalized objects, allowing for individualized designs, tailored components, and on-demand manufacturing, thereby fostering a paradigm shift towards mass customization.
- Rapid Prototyping: The agility and speed of printers with extruders expedite the prototyping process, enabling swift iteration of designs, accelerated product development cycles, and efficient validation of concepts and functionalities.
- Accessibility: Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) printers, in particular, are renowned for their affordability, user-friendly operation, and widespread availability, democratizing access to 3D printing technology across diverse user segments.
Disadvantages:
- Surface Finish: Objects produced by printers with extruders may exhibit visible layer lines and a textured surface finish, necessitating post-processing techniques to achieve a smooth and aesthetically pleasing appearance.
- Support Structures: Certain designs and geometries may require support structures during the printing process, which subsequently need to be removed and refined, adding complexity to the post-processing workflow.
- Material Limitations: While printers with extruders offer versatility, they may be constrained by the limited availability of certain specialized materials, hindering the realization of specific material requirements for certain applications.
- Print Speed: The layer-by-layer nature of extrusion-based printing can result in relatively longer print times for complex objects, necessitating patience and strategic planning for time-sensitive projects.
- Resolution and Detail: In comparison to other additive manufacturing technologies, the resolution and fine detail achievable with printers utilizing extrusion-based techniques may be relatively lower, impacting applications demanding exceptional surface finish and micro-scale features.
By comprehensively evaluating the advantages and limitations of printers with extruders, stakeholders can make informed decisions regarding their adoption, leveraging their strengths while mitigating potential challenges to maximize their utility and impact.
Conclusion
The pervasive influence of printers with extruders in the realm of additive manufacturing is undeniable, catalyzing a paradigm shift in prototyping, production, and customization across diverse industries. Their versatility, precision, and customization capabilities have redefined the boundaries of what can be achieved, empowering individuals and businesses to materialize their innovative visions with unprecedented fidelity.
As printers with extruders continue to evolve, advancements in material science, printing technologies, and post-processing techniques are poised to further enhance their capabilities, addressing current limitations and expanding their applicability to new frontiers.
Moreover, the democratization of 3D printing technology, particularly with the accessibility and affordability of Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) printers, has ushered in a new era of creativity, education, and entrepreneurial endeavors, fostering a vibrant ecosystem of makers, designers, and innovators.
It is imperative for stakeholders to embrace the opportunities presented by printers with extruders while acknowledging their inherent considerations, such as post-processing requirements, material constraints, and print speed, to effectively harness their potential for diverse applications.
Ultimately, the trajectory of printers with extruders is intertwined with the relentless pursuit of innovation and the convergence of digital design, material science, and manufacturing prowess. By embracing their advantages and addressing their limitations, we can propel additive manufacturing to unprecedented heights, ushering in an era of customized, sustainable, and intricately detailed creations that transcend the boundaries of traditional production methodologies.
As we traverse this dynamic landscape, the transformative impact of printers with extruders serves as a testament to the boundless potential of human ingenuity and technological advancement, inspiring a future where the line between imagination and materialization continues to blur, opening new horizons of creativity and possibility.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Type Of Printer Has An Extruder As One Of Its Components?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Type Of Printer Has An Extruder As One Of Its Components?”