Home>Technology>Smart Home Devices>What Is An Extruder On A 3D Printer

Smart Home Devices
What Is An Extruder On A 3D Printer
Published: January 14, 2024
Learn about the role of an extruder in 3D printing and how it contributes to the functionality of smart home devices. Explore the technology behind smart home devices and the significance of extruders in their production process.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the fascinating world of 3D printing! As the technology continues to evolve, it's crucial to understand the essential components that make this innovation possible. One of the most critical parts of a 3D printer is the extruder. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the extruder, exploring its functionality, types, and considerations for choosing the right one for your 3D printing needs.
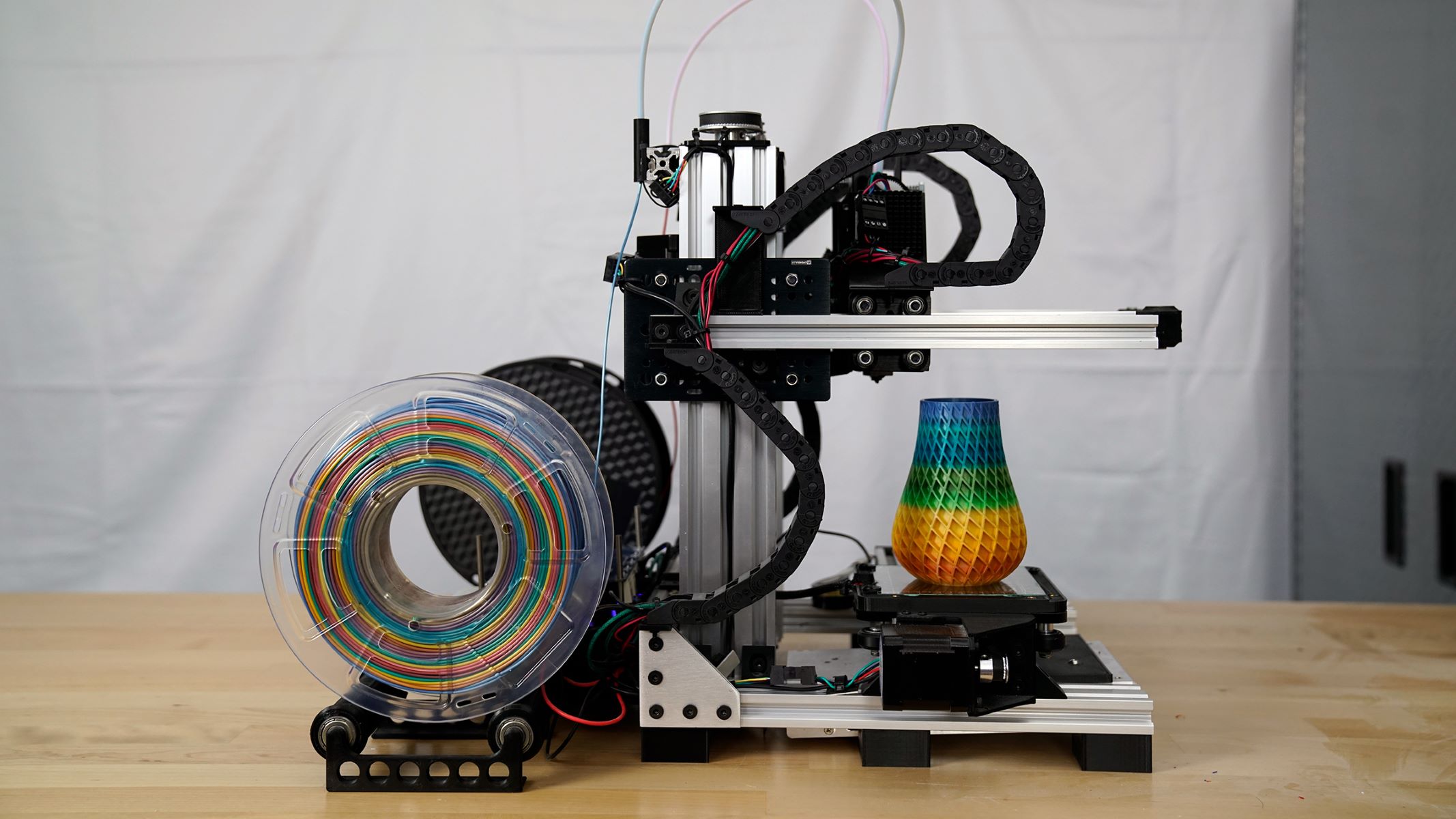
The extruder plays a pivotal role in the 3D printing process, as it is responsible for melting the filament and precisely depositing it layer by layer to create the desired three-dimensional object. Understanding the inner workings of the extruder is essential for anyone venturing into the world of 3D printing, whether as a hobbyist, a professional, or an enthusiast.
Throughout this article, we will unravel the mysteries of the extruder, shedding light on its significance and the various factors to consider when selecting the ideal extruder for your 3D printing endeavors. By the end of this exploration, you will have gained a comprehensive understanding of the extruder's function and its role in bringing your 3D printing projects to life. So, let's embark on this enlightening journey into the realm of extruders and their vital contribution to the captivating world of 3D printing.
Key Takeaways:
- The extruder is a crucial part of 3D printing, melting and depositing filament to create objects. It comes in different types, each with unique features for specific printing needs.
- When choosing an extruder, consider filament compatibility, printing speed, multi-material capabilities, specialized applications, and reliability to ensure optimal performance and creative flexibility in 3D printing projects.
Read more: What Does The Extruder Do In A 3D Printer
What Is an Extruder?
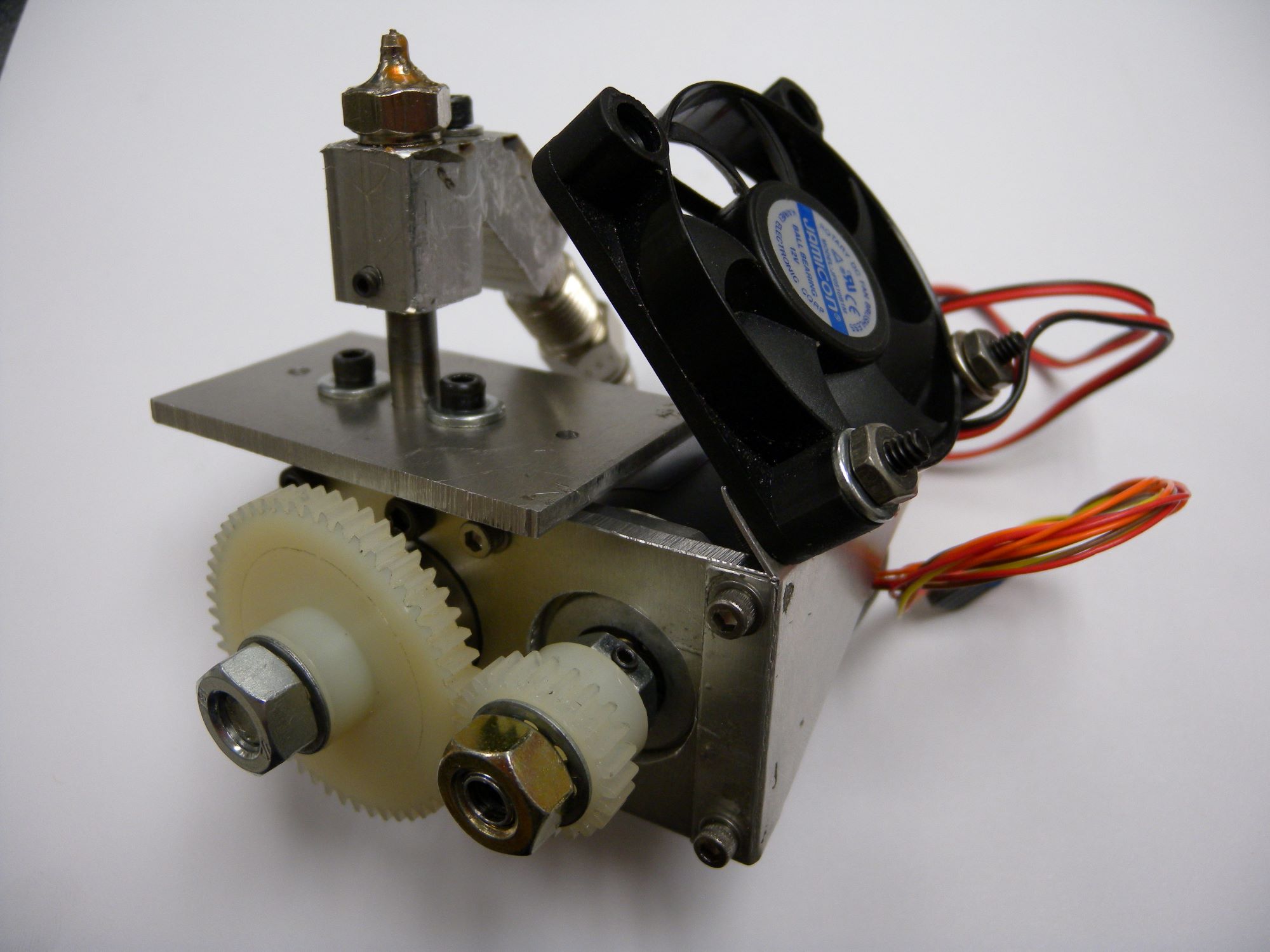
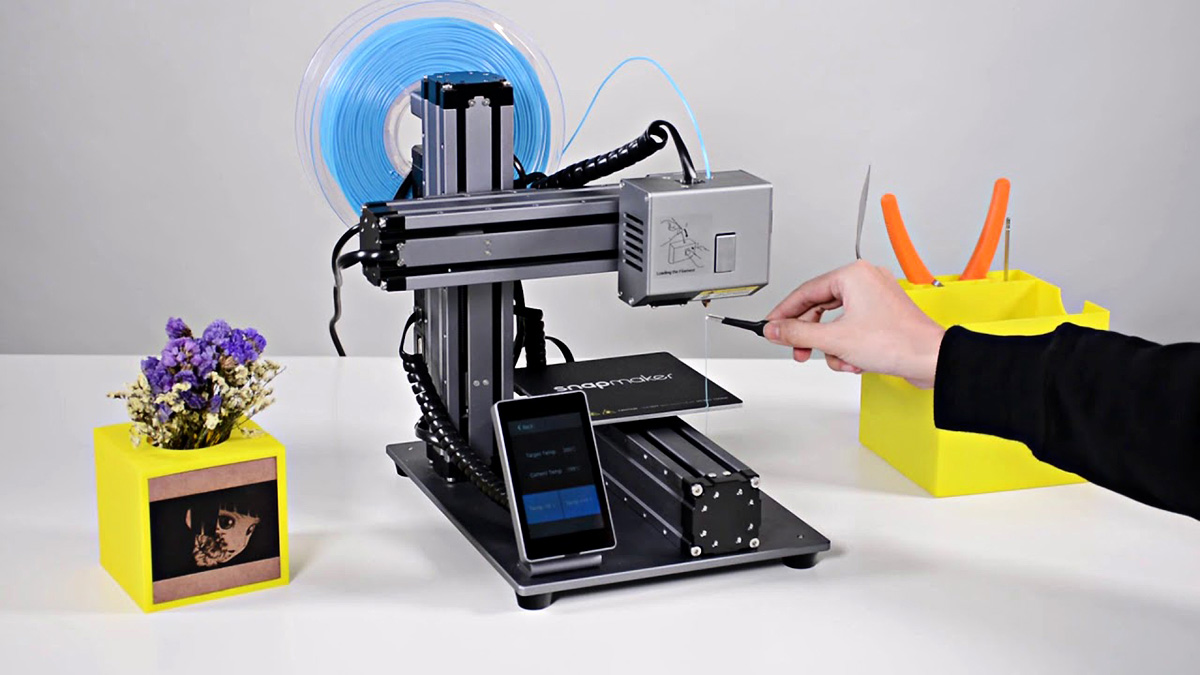
An extruder is a fundamental component of a 3D printer, serving as the mechanism responsible for feeding, heating, and depositing the filament material to create the printed object. Essentially, the extruder functions as a precision-controlled nozzle that melts the filament and precisely deposits it layer by layer, following the instructions from the 3D model. This process is crucial for achieving the desired shape and structure of the printed object.
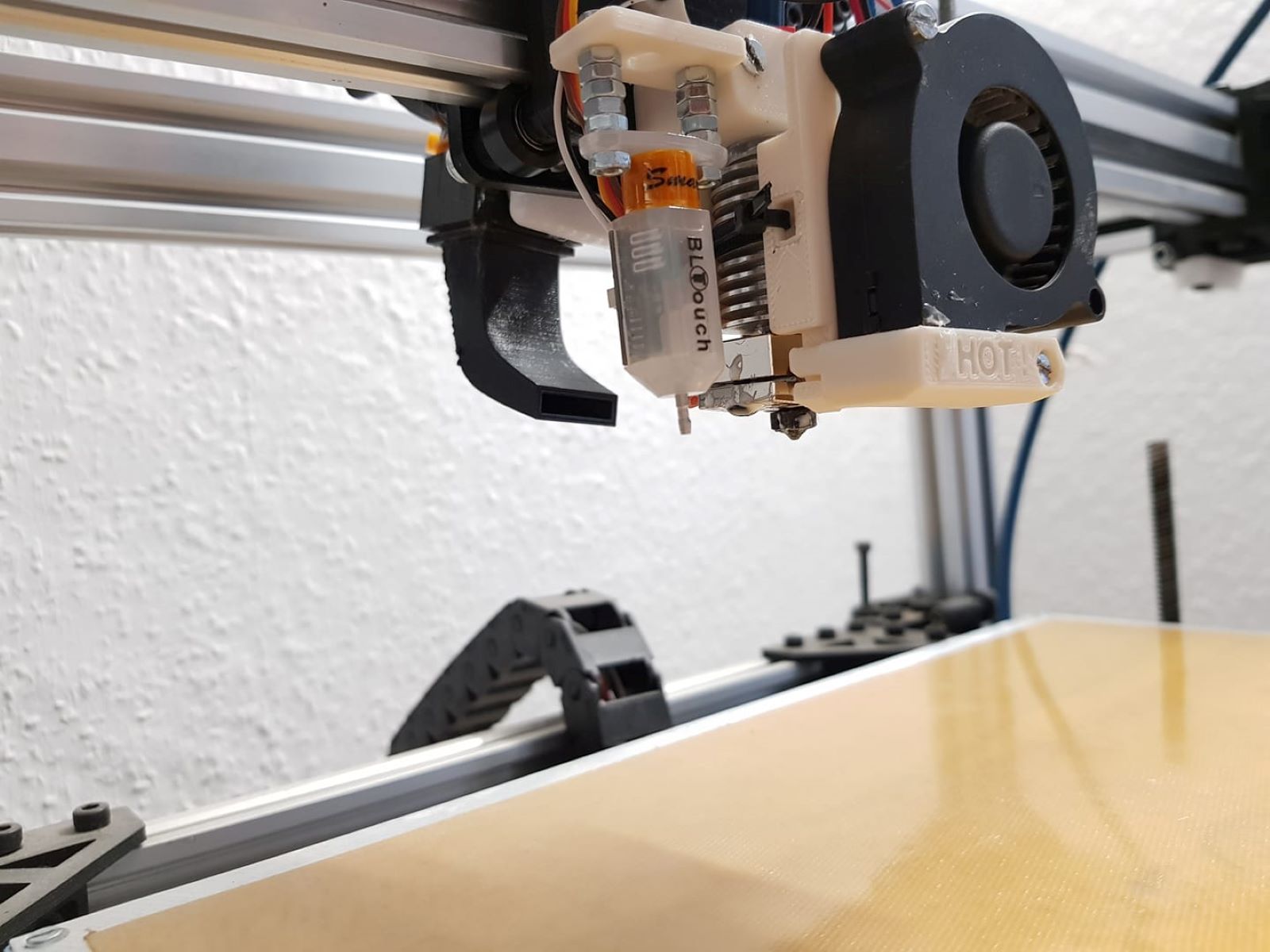
The extruder comprises several key elements, including a motor-driven gear mechanism to push the filament, a heating element to melt the filament, and a nozzle to deposit the molten material onto the print bed or the previously printed layers. Additionally, the extruder is equipped with a cooling system to ensure that the deposited material solidifies promptly, maintaining the integrity of each layer.
Furthermore, the extruder is often accompanied by a hot end, which is the assembly that includes the heating element and the nozzle. The hot end is designed to maintain a consistent and precise temperature to ensure the filament is melted uniformly and accurately deposited during the printing process.
It’s important to note that the extruder’s design and capabilities can vary significantly based on the type of 3D printer and the specific requirements of the printing project. Whether it’s a desktop FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) printer or an industrial-scale 3D printing system, the extruder’s functionality remains essential for translating digital designs into physical objects with remarkable precision and detail.
Overall, the extruder serves as the heart of the 3D printing process, playing a pivotal role in transforming raw filament material into intricate and complex three-dimensional structures. Its precision, reliability, and adaptability are crucial factors that contribute to the overall quality and success of 3D printing projects.
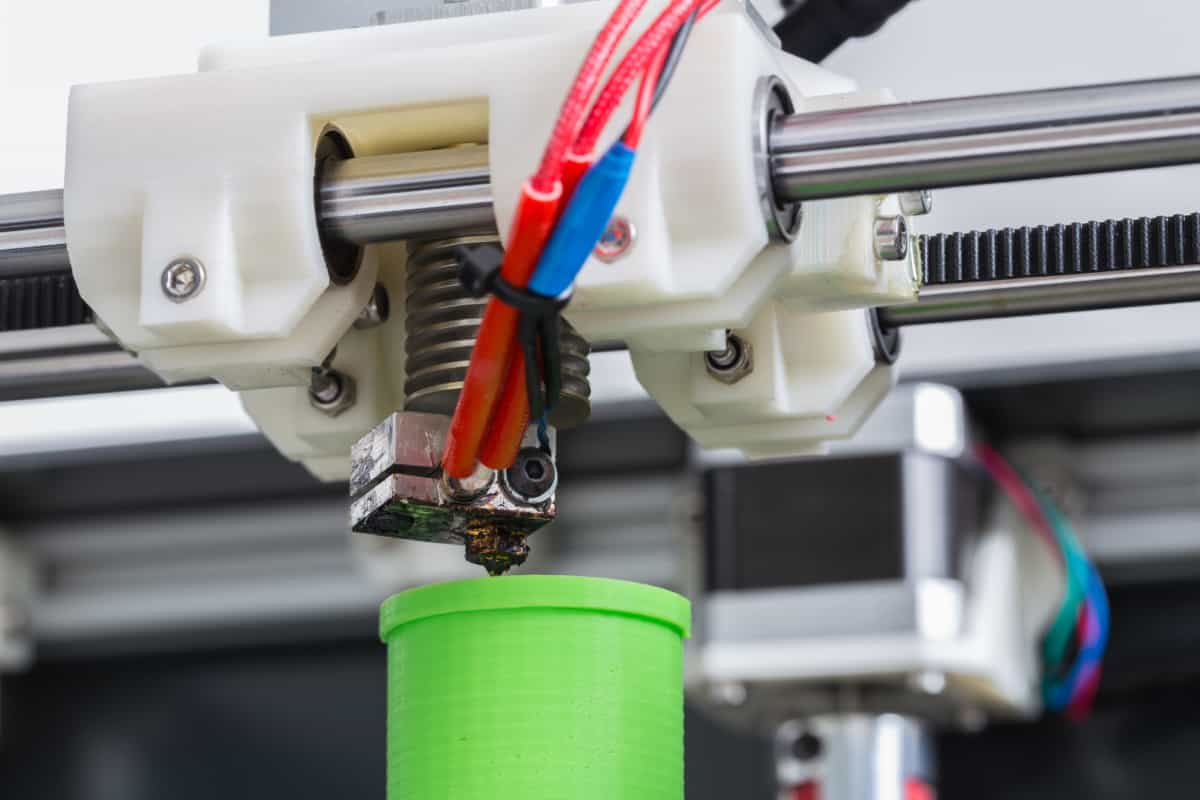
How Does an Extruder Work in a 3D Printer?
The functionality of an extruder in a 3D printer is a meticulously orchestrated process that involves several intricate steps, each crucial to the precise deposition of the filament material. The workflow of the extruder can be broken down into the following key stages:
- Filament Feeding: The process begins with the extruder’s motor-driven gear mechanism gripping the filament and steadily feeding it into the hot end. The gear mechanism ensures a consistent and controlled flow of filament, preparing it for the subsequent stages of the printing process.
- Filament Heating: As the filament enters the hot end, it encounters the heating element, which raises the temperature to the melting point of the material. This controlled heating process transforms the solid filament into a molten state, ready for precise deposition.
- Filament Deposition: Once the filament reaches the optimal molten state, the extruder’s nozzle carefully deposits it onto the print bed or the previously printed layers. The extruder’s precise control over the flow and deposition of the molten material ensures the accurate layering and shaping of the printed object, adhering to the specifications of the digital model.
- Cooling and Solidification: Following the deposition of each layer, the extruder’s cooling system comes into play, rapidly solidifying the molten material to maintain the structural integrity of the printed object. This cooling process is essential for achieving dimensional accuracy and preventing deformities in the printed layers.
The seamless coordination of these stages, facilitated by the extruder’s intricate design and precise control systems, is instrumental in translating digital designs into tangible, intricately detailed physical objects. The extruder’s ability to maintain consistent temperatures, regulate filament flow, and ensure precise deposition is paramount in achieving high-quality 3D prints with remarkable accuracy and fine details.
Furthermore, the extruder’s compatibility with various filament materials, including PLA, ABS, PETG, and specialized composite filaments, underscores its versatility and adaptability to a wide range of 3D printing applications. Whether producing prototypes, functional parts, artistic creations, or intricate models, the extruder plays a pivotal role in realizing diverse and innovative 3D printing projects.
Overall, the intricate interplay of the extruder’s components and functionalities underscores its indispensable role in the 3D printing process, embodying precision, reliability, and adaptability to bring digital designs to life in the physical realm.
The extruder on a 3D printer is the part that melts and pushes out the filament to create the 3D printed object. It’s important to keep the extruder clean and well-maintained for smooth printing.
Types of Extruders
Extruders come in various types, each tailored to specific 3D printing requirements and filament materials. Understanding the distinct characteristics of these extruder types is essential for selecting the most suitable option for a particular printing project. Here are some common types of extruders:
- Bowden Extruder: This type of extruder features a remote setup, where the motorized feeder is located away from the hot end. A long, flexible tube guides the filament from the feeder to the hot end. Bowden extruders are known for reducing the moving mass on the print head, resulting in improved printing speeds and reduced vibrations. However, they require precise calibration due to the filament’s elasticity within the feeding tube.
- Direct-Drive Extruder: In contrast to the Bowden extruder, the direct-drive extruder positions the motorized feeder directly above the hot end. This configuration minimizes filament slack and allows for more precise control over filament retraction, making it well-suited for printing flexible materials and achieving intricate details. Direct-drive extruders are favored for their versatility and compatibility with a wide range of filament types.
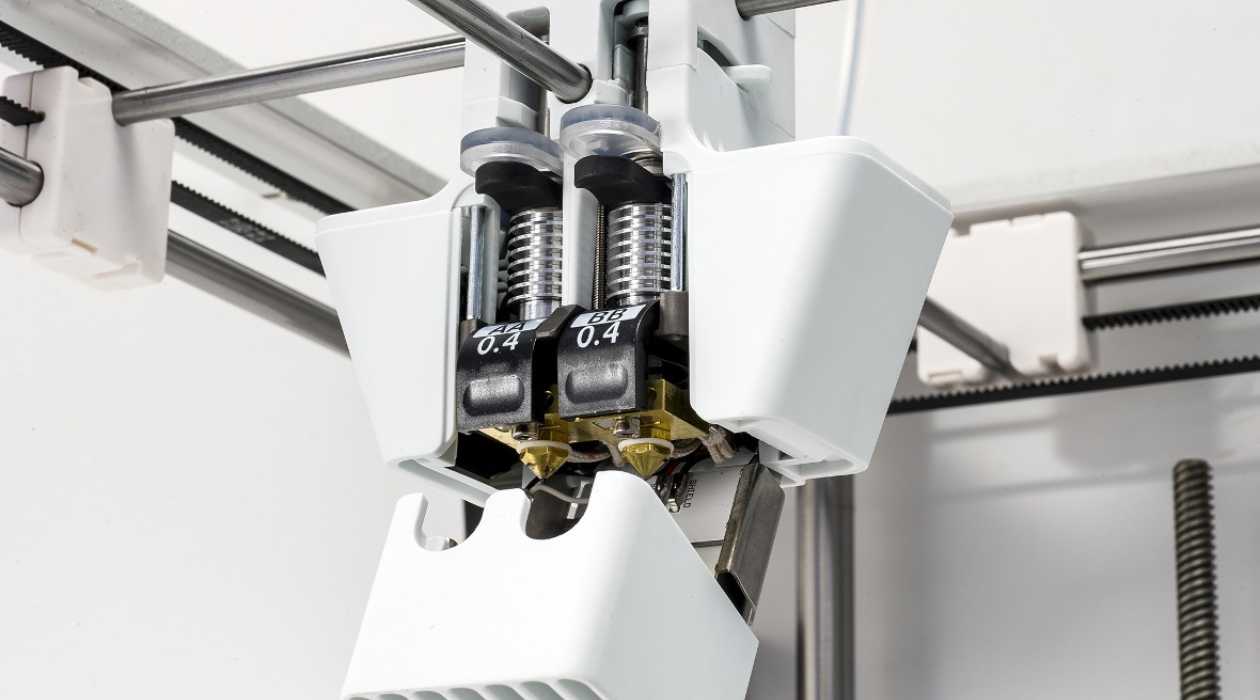
- Dual Extruder: As the name suggests, a dual extruder setup incorporates two extruders on the 3D printer, enabling the simultaneous use of two different filament materials or colors. This configuration is ideal for creating multi-material prints, intricate designs with soluble support structures, or colorful models with seamless transitions between filaments. Dual extruders offer enhanced flexibility and creativity in 3D printing projects.
- Paste Extruder: Unlike traditional filament-based extruders, paste extruders are designed to handle viscous materials such as silicone, clay, and food-based substances. These extruders are commonly used for experimental and specialized applications, including food printing, ceramic prototyping, and custom material extrusion. The ability to work with non-traditional materials expands the creative possibilities of 3D printing.
Each type of extruder offers unique advantages and considerations, catering to specific printing needs and material requirements. Whether prioritizing speed, precision, versatility, or specialized material compatibility, the diverse range of extruder types empowers 3D printing enthusiasts and professionals to explore a multitude of creative possibilities and applications.
By understanding the distinctions between these extruder types, individuals can make informed decisions when selecting the most suitable extruder for their 3D printing endeavors, ensuring optimal performance and exceptional results across a spectrum of printing projects.
Considerations When Choosing an Extruder
When selecting an extruder for a 3D printer, several crucial considerations come into play, influencing the performance, versatility, and compatibility of the extrusion system with specific printing requirements. By evaluating these factors, individuals can make informed decisions to ensure that the chosen extruder aligns seamlessly with their 3D printing goals. Here are key considerations when choosing an extruder:
- Filament Compatibility: Different extruders are designed to accommodate specific filament materials, including PLA, ABS, PETG, TPU, and composite filaments. It’s essential to ensure that the chosen extruder is compatible with the intended filament type, considering factors such as melting temperature, viscosity, and diameter range.
- Printing Speed and Precision: The extruder type and design can significantly impact printing speed and precision. For instance, direct-drive extruders are known for precise filament control, making them suitable for intricate details, while Bowden extruders may offer faster printing speeds due to reduced moving mass on the print head.
- Multi-Material Capabilities: Individuals seeking to explore multi-material printing or incorporate soluble support structures should consider extruders with dual or multi-extrusion capabilities. Dual extruders enable the simultaneous use of different filament materials, expanding creative possibilities and functional capabilities.
- Specialized Applications: For specialized applications such as food printing, ceramic prototyping, or custom material extrusion, individuals may need to explore paste extruders designed to handle viscous or non-traditional materials. Understanding the specific requirements of the printing project is crucial in selecting an extruder tailored to these applications.
- Printer Compatibility and Modifications: It’s important to consider the compatibility of the chosen extruder with the 3D printer’s design and specifications. Some extruders may require modifications or specific mounting systems to integrate seamlessly with the printer, necessitating careful assessment of the installation process and any potential adjustments.
- Reliability and Maintenance: Evaluating the reliability and maintenance requirements of the extruder is essential for long-term usability. Factors such as the durability of components, ease of cleaning, and accessibility for maintenance can influence the overall user experience and operational efficiency.
By carefully weighing these considerations and aligning them with the unique demands of 3D printing projects, individuals can make informed choices when selecting an extruder, ensuring optimal performance, material compatibility, and creative flexibility. Additionally, staying abreast of advancements in extrusion technology and innovative extruder designs can open doors to new possibilities and enhanced printing capabilities.
Ultimately, the selection of an extruder plays a pivotal role in shaping the 3D printing process, influencing the quality, versatility, and creative potential of each printing endeavor. By embracing these considerations, individuals can harness the power of advanced extrusion systems to bring their digital designs to life with precision, innovation, and remarkable intricacy.
Read more: How To Calibrate A 3D Printer Extruder
Conclusion
The extruder stands as a cornerstone of 3D printing technology, embodying precision, adaptability, and creative potential in the realm of additive manufacturing. Its role in melting, feeding, and depositing filament material is instrumental in transforming digital designs into tangible, intricately detailed physical objects. Throughout this exploration, we have unraveled the significance of the extruder and the diverse considerations that shape its selection and implementation in 3D printing projects.
From the distinct types of extruders, including Bowden, direct-drive, dual, and paste extruders, to the critical considerations of filament compatibility, printing speed, multi-material capabilities, specialized applications, and reliability, the extruder landscape offers a rich tapestry of options and factors to navigate. Understanding these nuances empowers 3D printing enthusiasts and professionals to make informed decisions, ensuring that the chosen extruder aligns seamlessly with their unique printing goals and material requirements.
As the 3D printing industry continues to evolve, so too does the landscape of extrusion technology, presenting innovative advancements and refined extruder designs that expand the horizons of additive manufacturing. Embracing these advancements and staying attuned to the dynamic extruder ecosystem enables individuals to unlock new creative possibilities, enhance printing capabilities, and push the boundaries of innovation in 3D printing.
Ultimately, the extruder’s precision, reliability, and adaptability serve as catalysts for transformative 3D printing experiences, enabling the realization of intricate prototypes, functional parts, artistic creations, and specialized applications with exceptional detail and quality. The journey into the realm of extruders illuminates the profound impact of this essential component, underscoring its indispensable role in bringing digital designs to life with precision, innovation, and boundless creativity.
As we continue to venture into the captivating world of 3D printing, the extruder remains an enduring symbol of precision and potential, driving the realization of diverse and extraordinary creations, layer by layer, with unwavering accuracy and ingenuity.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is An Extruder On A 3D Printer
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “What Is An Extruder On A 3D Printer”