

Articles
How To Store Biometric Data
Modified: October 27, 2024
Discover the best practices for storing biometric data in our informative articles. Safeguard your sensitive information and ensure compliance with data privacy regulations.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
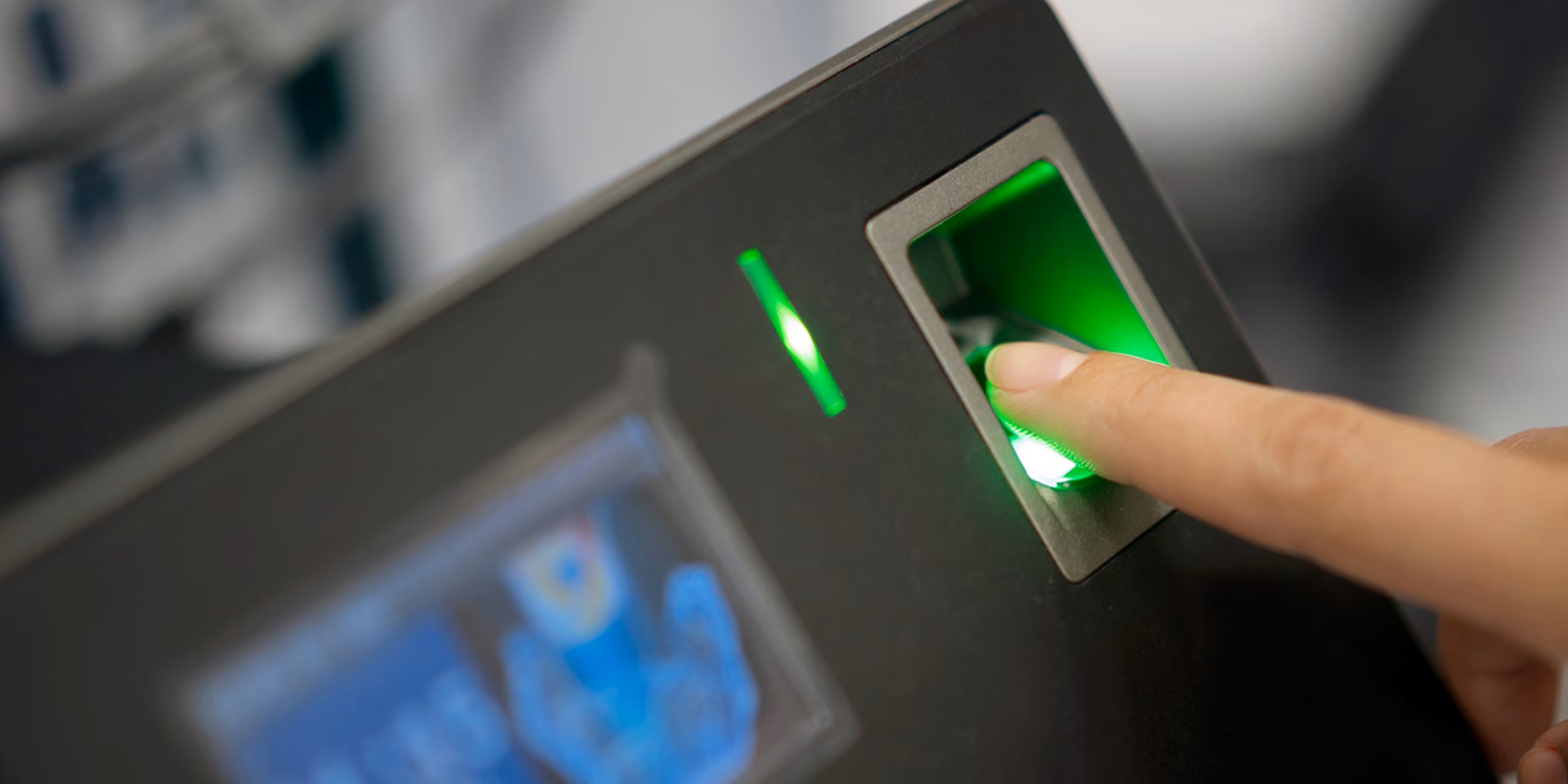
Biometric data refers to unique physiological or behavioral characteristics of an individual that can be used for identification or authentication. These characteristics include fingerprints, facial features, palm prints, iris patterns, voiceprints, and even DNA. With advancements in technology, organizations across various industries are increasingly relying on biometric data for a wide range of applications, from unlocking smartphones and accessing secure areas to verifying identities for financial transactions.
Storing biometric data securely is paramount to ensure the privacy and integrity of individuals’ personal information. In this article, we will explore the importance of biometric data storage, the legal and ethical considerations surrounding it, and the best practices and techniques for ensuring its security.
Subtitle: Importance of Biometric Data Storage
Effective storage of biometric data is crucial due to its sensitive nature. Biometric data, unlike traditional passwords or PINs, cannot be easily changed if compromised. It is inherently tied to an individual’s unique attributes and cannot be replicated or forged. As a result, it is essential to establish secure storage protocols to protect this valuable information from unauthorized access or misuse.
In recent years, the use of biometric data has expanded across industries, including banking, healthcare, government, and law enforcement. Financial institutions use biometrics as an added layer of security for authentication purposes, reducing the risk of identity theft and fraud. In healthcare, biometric data can be used to ensure patient safety and privacy, especially when accessing electronic medical records. Law enforcement agencies rely on biometrics to enhance criminal investigations by identifying suspects and linking evidence.
Subtitle: Legal and Ethical Considerations
When it comes to biometric data storage, organizations must navigate a complex landscape of legal and ethical considerations. Laws and regulations vary across jurisdictions, dictating how biometric data should be collected, stored, used, and shared. Compliance with these laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, is essential to avoid legal repercussions and maintain the trust of individuals.
In addition to legal obligations, organizations must address ethical concerns when handling biometric data. Transparency about the collection and storage of biometric information is crucial, ensuring individuals understand how their data will be used and protected. Consent must be obtained before collecting biometric data, and individuals should have the right to access, correct, and delete their data when necessary.
Key Takeaways:
- Secure storage of biometric data is crucial due to its sensitive nature, offering enhanced security, convenience, and accuracy. However, organizations must address legal, ethical, and technical challenges to ensure data integrity and privacy.
- Future trends in biometric data storage, such as blockchain-based storage and user-centric data control, promise to enhance security and privacy while adapting to evolving technological demands. Organizations must embrace these trends to safeguard individuals’ personal information effectively.
Read more: How To Store Data In Database
Importance of Biometric Data Storage
Effective storage of biometric data is crucial due to its sensitive nature. Biometric data, unlike traditional passwords or PINs, cannot be easily changed if compromised. It is inherently tied to an individual’s unique attributes and cannot be replicated or forged. As a result, it is essential to establish secure storage protocols to protect this valuable information from unauthorized access or misuse.
In recent years, the use of biometric data has expanded across industries, including banking, healthcare, government, and law enforcement. Financial institutions use biometrics as an added layer of security for authentication purposes, reducing the risk of identity theft and fraud. In healthcare, biometric data can be used to ensure patient safety and privacy, especially when accessing electronic medical records. Law enforcement agencies rely on biometrics to enhance criminal investigations by identifying suspects and linking evidence.
Biometric data storage provides several key benefits:
- Enhanced Security: Biometric data can significantly enhance security measures compared to traditional authentication methods. Using a unique physical attribute or behavior for identification makes it incredibly difficult for unauthorized individuals to gain access to sensitive information or restricted areas.
- Convenience: Biometric data offers a convenient and frictionless way to authenticate individuals. It eliminates the need to remember and input complex passwords or carry identification cards, making it faster and more user-friendly for authentication purposes.
- Accuracy: Biometric data provides a high degree of accuracy in identifying individuals. With advancements in technology, the margin of error has significantly decreased, making biometrics a reliable and efficient method for identification and authentication.
- Non-repudiation: Biometric data ensures non-repudiation, meaning an individual cannot deny their involvement or presence. This is crucial in legal and forensic contexts, where proving someone’s identity beyond a reasonable doubt is essential.
- Scalability: Biometric systems can easily scale to accommodate a large number of users. Whether it’s for a small organization or a national identification program, biometric data storage and matching algorithms can handle vast amounts of data efficiently and effectively.
However, it’s important to note that while biometric data storage offers numerous benefits, there are also potential risks associated with its use. Biometric data, if not properly protected, can be vulnerable to breaches and misuse. Therefore, implementing robust security measures and following best practices are critical to mitigate these risks and ensure the integrity and confidentiality of individuals’ biometric information.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
When it comes to biometric data storage, organizations must navigate a complex landscape of legal and ethical considerations. Laws and regulations vary across jurisdictions, dictating how biometric data should be collected, stored, used, and shared. Compliance with these laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, is essential to avoid legal repercussions and maintain the trust of individuals.
In addition to legal obligations, organizations must address ethical concerns when handling biometric data. Transparency about the collection and storage of biometric information is crucial, ensuring individuals understand how their data will be used and protected. Consent must be obtained before collecting biometric data, and individuals should have the right to access, correct, and delete their data when necessary.
Here are some key legal and ethical considerations related to biometric data storage:
- Data Protection Laws: Organizations must comply with data protection laws and regulations specific to their jurisdiction. These laws impose requirements on how biometric data should be collected, stored, and processed, including obtaining consent, informing individuals about data practices, and implementing appropriate security measures to protect the data.
- Consent: Before collecting biometric data, organizations must obtain clear and informed consent from individuals. Consent should be specific, freely given, and capable of being withdrawn at any time. Individuals should have the option to opt out of providing their biometric data without facing any negative consequences.
- Storage Limitation: Biometric data should only be stored for as long as necessary to fulfill the purpose for which it was collected. Organizations should establish data retention policies that align with legal requirements and regularly review and delete biometric data that is no longer needed.
- Data Security: Organizations must implement robust security measures to protect biometric data from unauthorized access, loss, or alteration. This includes implementing encryption, access controls, secure storage systems, and regular security audits. It is crucial to regularly assess and address vulnerabilities to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of the stored biometric data.
- Data Sharing: If biometric data needs to be shared with third parties, organizations must ensure that appropriate safeguards are in place to protect the data during transit and at the recipient’s end. Agreements should be in place to define the purpose, scope, and duration of data sharing, and individuals should be informed about the recipients of their data and any potential risks associated with the sharing.
- Data Breach Response: In the event of a data breach involving biometric data, organizations must have a robust incident response plan in place to promptly detect, contain, and mitigate the impact of the breach. They should also have a well-defined process to notify affected individuals and relevant authorities, as required by applicable laws.
By adhering to legal requirements and ethical principles, organizations can build trust with individuals and demonstrate their commitment to protecting their biometric data privacy. It is crucial to stay updated with any changes in relevant laws and regulations and continuously reassess and improve storage practices to ensure compliance and maintain data security.
Secure Biometric Data Storage Techniques
Securing biometric data is of utmost importance to protect individuals’ personal information from unauthorized access and potential misuse. Implementing robust storage techniques can help mitigate security risks and ensure the confidentiality and integrity of biometric data. Here are some secure biometric data storage techniques:
- Data Encryption: Encrypting biometric data before storage is a critical security measure. Encryption ensures that the data is converted into a coded form that can only be accessed with a decryption key. Advanced encryption algorithms, such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), are commonly used to protect biometric data during storage.
- Hashing: Hashing is a technique used to transform biometric data into a fixed-length string of characters, commonly known as a hash value. Unlike encryption, hashing is a one-way process, making it suitable for storing biometric templates. When a user’s biometric data is authenticated, the template is hashed and compared against the stored hash value to verify the identity.
- Salting: Salting is a technique used to enhance the security of hashed biometric data. It involves adding a random value, known as a salt, to the data before hashing. Salting prevents pre-computed attacks and rainbow table attacks, making it more difficult for attackers to reverse-engineer the original biometric data.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Adding an additional layer of authentication, such as a password or PIN, along with biometric data, can significantly enhance security. Multi-factor authentication ensures that even if the biometric data is compromised, unauthorized access is still prevented without the additional authentication factor.
- Secure Storage Infrastructure: The physical and virtual infrastructure where biometric data is stored should be secure. This includes implementing access controls, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular system updates. Limiting access to authorized personnel and implementing audit trails can help track any unauthorized access attempts.
- Redundancy and Backup: It is important to establish data redundancy and backup systems to prevent data loss due to hardware failures, natural disasters, or other unforeseen events. Regularly backing up biometric data and storing it in secure off-site locations ensures data availability and recovery in case of any incidents.
- Periodic Vulnerability Assessments: Conducting regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing helps identify and address any weaknesses in the biometric data storage system. By identifying and patching vulnerabilities proactively, organizations can stay one step ahead of potential security breaches.
It is essential to ensure that these techniques are implemented in conjunction with other security measures, such as strict access controls, employee training, and continuous monitoring of the storage environment. Regular security audits and updates to stay abreast of emerging threats and vulnerabilities are also crucial for maintaining the security of biometric data storage.
By implementing these secure storage techniques, organizations can protect biometric data from unauthorized access, maintain data integrity, and instill confidence in individuals that their personal information is handled with utmost care.
Encryption Methods for Biometric Data
Encryption plays a vital role in securing biometric data during storage and transmission. It ensures that the data is converted into an unreadable format that can only be decrypted with the appropriate key. There are several encryption methods commonly used for protecting biometric data:
- Symmetric Encryption: Symmetric encryption, also known as secret-key encryption, uses a single secret key to encrypt and decrypt data. The same key is used for both encryption and decryption processes. This method is efficient but requires secure key distribution to ensure the confidentiality of the data. Common symmetric encryption algorithms include AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and DES (Data Encryption Standard).
- Asymmetric Encryption: Asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key encryption, uses two different keys – a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. The public key can be freely distributed, allowing anyone to encrypt data, while the private key is kept secure and known only to the authorized recipient for decryption. Asymmetric encryption provides enhanced security and key management. RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) and ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography) are widely used asymmetric encryption algorithms.
- Hash-Based Encryption: Hash-based encryption, also known as keyed-hash message authentication code (HMAC), combines encryption and hashing techniques to ensure data integrity and authenticity. It uses a secret key and a cryptographic hash function to generate a hash value that is attached to the data. This hash value serves as a message authentication code, verifying the integrity and authenticity of the biometric data.
- Homomorphic Encryption: Homomorphic encryption is an emerging encryption technique that allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without the need for decryption. This enables processing and analysis of biometric data while preserving its confidentiality. Homomorphic encryption has the potential to revolutionize biometric data storage and processing by allowing secure data analysis without exposing the raw biometric data to third parties.
- Post-Quantum Encryption: As quantum computing advances, there is a need for encryption algorithms that can withstand attacks from quantum computers. Post-quantum encryption algorithms, such as lattice-based cryptography and code-based cryptography, are being developed to ensure the security of biometric data in a post-quantum computing era.
When choosing an encryption method for biometric data, several factors should be considered, including the level of security required, computational efficiency, key management, compatibility with existing systems, and compliance with industry standards and regulations.
It is important to note that encryption alone is not sufficient to ensure the security of biometric data. Proper key management, secure storage of encryption keys, regular updates, and adherence to best practices are crucial for maintaining data confidentiality and integrity. Additionally, encryption should be used in conjunction with other security measures, such as access controls, secure storage infrastructure, and regular vulnerability assessments, to provide comprehensive protection for biometric data.
By implementing robust encryption methods and following industry best practices, organizations can safeguard biometric data against unauthorized access and protect individuals’ privacy and security.
When storing biometric data, use encryption to protect the data from unauthorized access. Additionally, implement strict access controls and regularly update security measures to prevent data breaches.
Read more: How To Store Data In Python
Biometric Data Storage Best Practices
Proper storage of biometric data is essential to ensure its security and protect the privacy of individuals. Implementing best practices can help organizations mitigate risks and maintain the integrity and confidentiality of biometric data. Here are some key biometric data storage best practices:
- Data Minimization: Only collect and store the minimum amount of biometric data necessary to fulfill the intended purpose. Avoid unnecessary data retention to minimize the potential risks associated with storing sensitive information.
- Strong Authentication: Implement strong authentication measures to ensure that only authorized personnel can access the biometric data storage system. This can include multi-factor authentication, strong passwords, and regular access reviews to ensure that access privileges are up to date and appropriately assigned.
- Secure Storage Infrastructure: Establish a secure storage infrastructure that includes physical security measures, such as restricted access to storage locations and surveillance systems. Additionally, implement strong network security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion prevention systems, and regular security updates, to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Data Encryption: Implement encryption techniques to protect biometric data during storage. Use robust encryption algorithms and key management practices to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of the data. Regularly assess encryption practices and update them as needed to maintain the highest level of security.
- Regular Data Backups: Regularly backup biometric data and store backups in secure off-site locations. This ensures data availability and recovery in case of unexpected incidents or equipment failures. Test the restoration process periodically to ensure the integrity and reliability of the backup data.
- Monitor and Audit: Implement monitoring and auditing mechanisms to detect any unauthorized access attempts or suspicious activities in the biometric data storage system. Regularly review audit logs and implement real-time monitoring tools to promptly identify and respond to potential security incidents.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Educate employees about the importance of biometric data security and provide specific training on data handling, access control, and incident response. Promote a culture of security awareness to ensure that all employees understand their roles and responsibilities in protecting biometric data.
- Compliance with Regulations: Understand and comply with relevant regulations and data protection laws specific to the jurisdiction in which the organization operates. This includes obtaining necessary consents, informing individuals about data practices, and implementing appropriate security measures to protect biometric data.
- Regular Security Assessments: Conduct regular security assessments, penetration testing, and vulnerability assessments to identify any weaknesses in the biometric data storage system. Address any vulnerabilities promptly and establish a process for regular security updates and patches to ensure the continuous security of the system.
- Secure Disposal: Establish protocols for secure disposal of biometric data when it is no longer needed. Follow proper data destruction methods to ensure that the data cannot be recovered or accessed by unauthorized parties.
By following these best practices, organizations can minimize the risks associated with storing biometric data and ensure that proper safeguards are in place to protect the privacy and security of individuals’ personal information.
Challenges in Storing Biometric Data
Storing biometric data poses unique challenges compared to traditional forms of data. These challenges stem from the sensitive nature of biometric information and the need to ensure its security and privacy. Here are some of the key challenges organizations face when storing biometric data:
- Privacy Concerns: Biometric data is highly personal and sensitive, as it is directly tied to an individual’s unique physiological or behavioral characteristics. Storing this data requires organizations to handle it with the utmost care and implement robust security measures to protect individuals’ privacy from unauthorized access or misuse.
- Security Risks: The security of biometric data is a paramount concern. Breaches of biometric data can have severe consequences, as biometric information is irreplaceable. Organizations must continually evaluate and enhance their security measures to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and potential manipulation or replication of biometric data.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Storing biometric data requires compliance with various legal and regulatory frameworks, including data protection laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union. Organizations must ensure they meet legal obligations surrounding the collection, storage, and protection of biometric data. Failure to comply with these laws can result in severe penalties and damage to the organization’s reputation.
- Storage Capacity and Scalability: Biometric data storage often requires significant storage capacity due to the large amount of data associated with individual biometric templates. As the number of users and the size of biometric databases grow, scalability becomes a challenge. Organizations must plan for future storage needs and ensure their infrastructure can accommodate the increasing volume of biometric data.
- Interoperability: Biometric data is often used across various systems, applications, and platforms. Achieving interoperability between different systems and databases can be challenging due to differences in data formats, algorithms, and standards. Organizations must ensure that their biometric data storage systems can seamlessly communicate and integrate with other systems to facilitate efficient and accurate identity verification processes.
- Aging and Variation in Biometric Characteristics: Biometric characteristics, such as fingerprints or facial features, can change over time due to factors like aging or injuries. This poses challenges for long-term storage and accurate identification. Organizations must account for these variations and regularly update biometric data to ensure accuracy and prevent false rejections or false acceptances during the authentication process.
- Ethical Considerations: Storing biometric data raises ethical concerns regarding consent, transparency, and the potential for misuse. Organizations must be transparent about how biometric data is collected, stored, and used. They must obtain informed consent from individuals and provide clear information on the purposes and duration of data storage. Additionally, organizations should establish policies and procedures to address ethical considerations, such as data sharing and the rights of individuals regarding their biometric data.
Addressing these challenges requires organizations to adopt comprehensive security measures, comply with applicable laws and regulations, and maintain an ethical approach to biometric data storage. By doing so, organizations can mitigate the risks associated with storing biometric data and ensure the privacy, security, and integrity of individuals’ personal information.
Future Trends in Biometric Data Storage
The field of biometric data storage is constantly evolving as technology advances and new trends emerge. These trends have the potential to shape the future of biometric data storage, enhancing security and improving the user experience. Here are some future trends to watch out for:
- Biometric Cloud Storage: Cloud technology is becoming increasingly prevalent, offering flexible and scalable storage solutions. Biometric cloud storage allows organizations to store and manage biometric data securely, with the added benefits of accessibility, high availability, and reduced infrastructure costs. Cloud-based storage providers are expected to develop advanced security protocols and compliance measures to address the unique requirements of biometric data.
- Blockchain-based Storage: Blockchain technology offers a decentralized and immutable storage solution, making it a potential game-changer for biometric data storage. By leveraging blockchain technology, organizations can enhance the security and privacy of biometric data by creating transparent and tamper-proof storage systems. Blockchain-based storage also enables individuals to have greater control over their biometric data, allowing them to grant access and manage permissions more effectively.
- Post-Quantum Cryptography: As quantum computing continues to advance, there is a growing need for encryption algorithms that can withstand attacks from quantum computers. Post-quantum cryptography aims to develop encryption methods that are resilient against quantum attacks. In the future, biometric data storage systems may adopt post-quantum cryptographic algorithms to ensure the long-term security of stored biometric data.
- Biometric Fusion and Multi-Modal Systems: Biometric fusion involves combining multiple biometric modalities, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, and voice recognition, for more reliable and robust authentication. Multi-modal systems utilize multiple biometric characteristics simultaneously to increase accuracy and reduce the risk of spoofing or false acceptances. Future trends in biometric data storage will likely involve the integration of these fusion and multi-modal systems, providing enhanced security and accuracy for identity verification.
- Privacy-Preserving Techniques: With growing concerns about privacy and data protection, future trends in biometric data storage will likely focus on privacy-preserving techniques. These techniques aim to protect individuals’ privacy by minimizing the exposure of raw biometric data. Technologies such as secure enclaves and secure multiparty computation enable processing and analysis of biometric data without exposing the actual data, ensuring privacy while still allowing for successful identity verification.
- Distributed Biometric Systems: Distributed biometric systems distribute biometric data storage and processing across multiple devices or servers, reducing the vulnerability of data breaches and single points of failure. This approach enhances data security and availability, as the biometric data is stored and processed across different locations. Additionally, distributed systems can offer faster authentication response times by leveraging the processing power of multiple devices or servers.
- User-Centric Data Control: Future trends in biometric data storage will emphasize giving individuals more control over their biometric data. Users will have the ability to manage their data, grant permissions selectively, and easily revoke access to their biometric information. User-centric data control will empower individuals to make informed decisions about how their data is used and ensure their privacy preferences are respected.
These future trends in biometric data storage are driven by the need for increased security, privacy, and user experience. As technology continues to advance, organizations will need to adapt their storage systems to embrace these trends and meet the evolving demands of secure and efficient biometric data storage.
Conclusion
Biometric data storage is a critical aspect of utilizing biometric authentication and identification systems effectively. As the use of biometric data becomes more widespread across various industries, organizations must prioritize the secure storage of this sensitive information to protect individuals’ privacy, maintain data integrity, and comply with legal requirements.
Throughout this article, we have explored the importance of biometric data storage, the legal and ethical considerations surrounding it, and best practices for ensuring its security. We discussed various techniques such as data encryption, secure storage infrastructure, and multi-factor authentication that can enhance the protection of biometric data.
However, storing biometric data is not without challenges. Privacy concerns, security risks, legal compliance, and interoperability are all factors that organizations must address to safely store and manage biometric information. It is crucial to continually monitor and assess the storage systems, regularly update security measures, and adapt to emerging trends in technology to ensure the highest level of protection for biometric data.
Looking ahead, future trends in biometric data storage hold promise for even greater security and user-centric control. Innovations such as blockchain-based storage, post-quantum cryptography, and distributed biometric systems aim to address emerging security and privacy challenges. These advancements will likely reshape the landscape of biometric data storage, bringing enhanced security and privacy for individuals while maintaining efficient and accurate authentication processes.
In conclusion, the secure storage of biometric data is a critical responsibility for organizations that handle such information. By implementing best practices, adhering to legal and ethical considerations, and embracing emerging trends, organizations can create robust storage systems that safeguard biometric data effectively. This ensures the privacy, security, and integrity of individuals’ personal information and inspires confidence in the use of biometric technology.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Store Biometric Data
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How To Store Biometric Data”