Home>Articles>What Conduit Do I Use For Underground Electrical


Articles
What Conduit Do I Use For Underground Electrical
Modified: October 19, 2024
Find out the best conduit for underground electrical installations with our informative articles. Ensure a safe and efficient electrical system with the right choice of conduit.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to electrical installations, one crucial aspect that needs careful consideration is the selection of the right conduit for underground wiring. Underground electrical conduits serve as protective pathways that house and safeguard electrical wires from external elements, preventing damage and ensuring the safety and durability of the electrical system.
Choosing the correct conduit is essential as it determines the longevity and performance of the electrical infrastructure. Factors such as durability, resistance to environmental conditions, cost-effectiveness, and ease of installation play a significant role in the decision-making process.
In this article, we will explore the different types of conduits available for underground electrical wiring and discuss the factors you need to consider when selecting the appropriate conduit for your specific needs. We will also cover the installation process and safety guidelines to ensure a successful and secure electrical installation.
By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the various options available to you and be better equipped to make an informed decision about the conduit that best suits your underground electrical requirements.
Key Takeaways:
- Selecting the right conduit for underground electrical wiring involves considering factors such as durability, material compatibility, ease of installation, and cost-effectiveness. Each conduit type has unique benefits, making it essential to choose wisely for long-term performance and safety.
- The installation of underground electrical conduits requires careful planning, adherence to safety guidelines, and compliance with local electrical codes. Following proper installation practices, including trench safety, depth requirements, and grounding, is crucial for a successful and secure electrical infrastructure.
Read more: How To Run Electrical Conduit Underground
Factors to Consider for Underground Electrical Conduits
When choosing a conduit for underground electrical wiring, several factors need to be taken into consideration to ensure the longevity, safety, and efficiency of the electrical system. Here are the key factors to keep in mind:
Durability: Underground conduits are exposed to various environmental and external factors, such as moisture, temperature changes, soil conditions, and physical impact. It is important to select a conduit material that is durable and resistant to these elements to ensure long-term performance.
Material Compatibility: Consider the compatibility of the conduit material with the type of electrical cables or wires that will be installed. Different conduit materials are suitable for different types of wires, so make sure to choose a conduit that is compatible with the electrical wiring you are using.
Installation Ease: Opt for a conduit that is easy to install. Some conduits are more flexible and lightweight, making them easier to maneuver and install in tight spaces or challenging terrains.
Cost-effectiveness: The cost of the conduit, including both the material and installation, should be considered. Compare the cost of different conduit materials and installation methods to determine the most cost-effective option for your project.
Size and Capacity: Determine the appropriate size and capacity of the conduit based on the number and size of the electrical cables or wires that will be installed. Ensure that the conduit can accommodate any future expansion or additional wiring requirements.
Permit and Code Compliance: Familiarize yourself with local electrical codes and obtain the necessary permits before installing underground electrical conduits. Adhering to these regulations ensures that the installation is safe and compliant with the industry standards.
Maintenance and Repair: Consider the ease of maintenance and repair of the conduit. Some materials may require less maintenance while others may be more prone to damage and may require frequent repairs or replacements.
Longevity: Evaluate the expected lifespan of the conduit material. Choosing a conduit with a longer lifespan can save you from the hassle and cost of frequent replacements or repairs in the future.
By carefully considering these factors, you can make an informed decision and select the most suitable conduit for your underground electrical wiring needs. Next, let’s explore the different types of conduits commonly used for underground electrical installations.
Types of Conduits for Underground Electrical Wiring
There are several types of conduits available for underground electrical wiring, each with its own characteristics and advantages. Here are the most common types of conduits used for underground electrical installations:
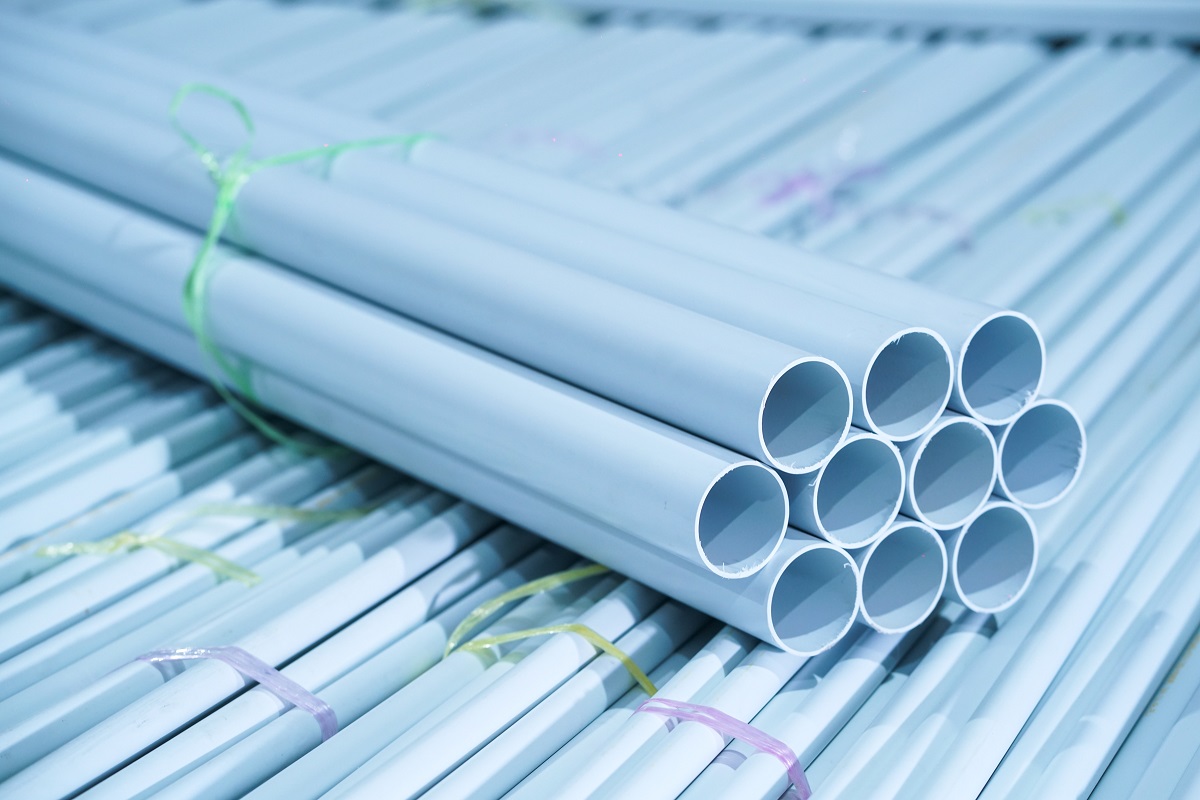
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) Conduit: PVC conduit is a popular choice for underground electrical wiring due to its affordability, durability, and ease of installation. It is resistant to moisture, corrosion, and chemicals, making it suitable for various environments. PVC conduits come in different sizes and can be easily cut and joined using PVC solvent cement.
- HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) Conduit: HDPE conduit is known for its high strength, flexibility, and resistance to impact. It is lightweight and easy to handle, making it ideal for underground installations that require flexibility. HDPE conduit is available in various sizes and can be joined using heat fusion or compression fittings.
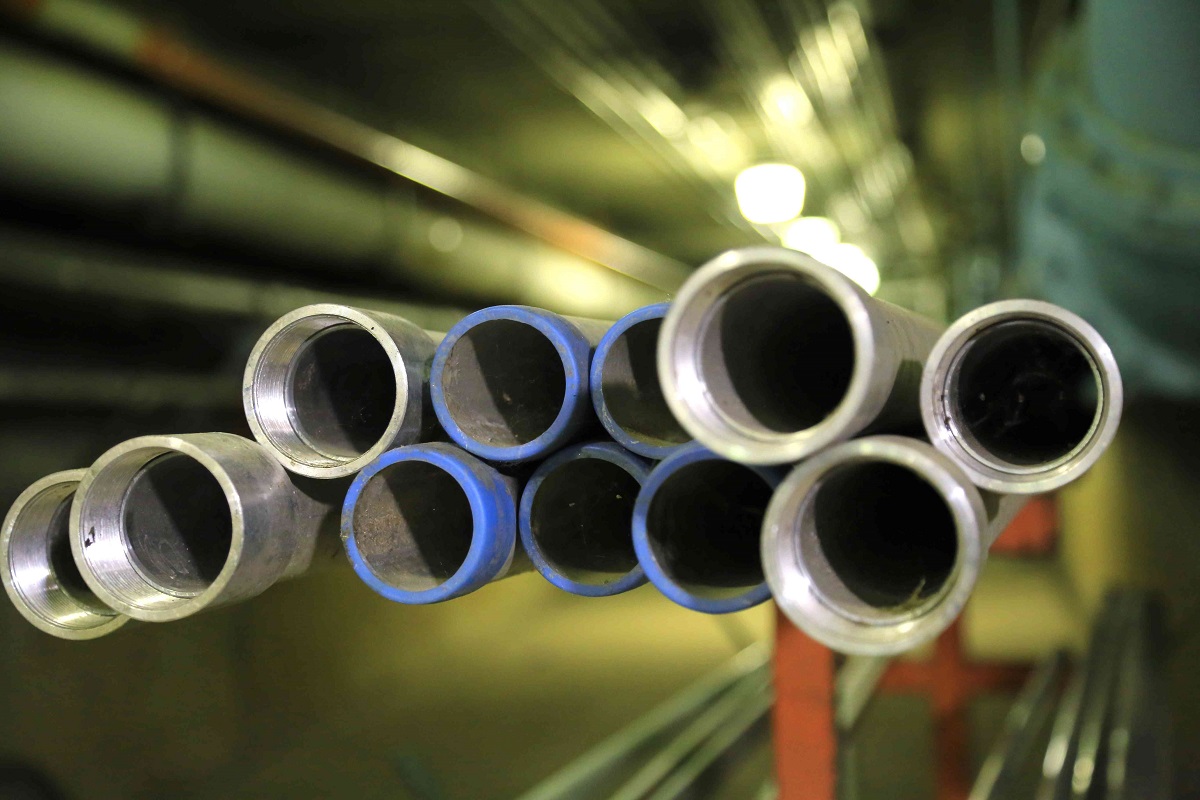
- Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC): RMC is a heavy-duty conduit made of steel. It provides excellent protection against physical damage, fire, and electromagnetic interference. RMC is typically used in areas where high-levels of protection are required, such as industrial or commercial applications. While it offers excellent durability, it can be more challenging to install due to its weight and rigidity.
- EMT (Electrical Metallic Tubing) Conduit: EMT conduit is made of galvanized steel or aluminum. It is lightweight, easy to bend, and cost-effective. EMT conduit is commonly used in residential applications or areas where flexibility is required. While it may not offer the same level of durability as RMC, it provides adequate protection for most underground electrical installations.
- Flexible Metal Conduit (FMC): FMC, also known as “Greenfield,” is a flexible conduit made of a spiral-wound metal strip. It is commonly used for short runs and in areas where flexibility is required. FMC is relatively easy to install and is suitable for underground applications that do not require heavy-duty protection.
Before selecting a conduit, consider the specific requirements of your project, including the environment, installation constraints, and budget. Be sure to consult local electrical codes and regulations to ensure compliance with the appropriate standards.
Now that you are familiar with the different types of conduits available, let’s move on to the types of conduit joints and fittings used in underground electrical installations.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) Conduit
PVC conduit is one of the most commonly used types of conduits for underground electrical wiring. It is preferred for its affordability, durability, and ease of installation. PVC conduit is made from polyvinyl chloride, a versatile and lightweight material known for its resistance to moisture, corrosion, and chemicals.
Here are some key features and benefits of PVC conduit:
- Affordability: PVC conduit is cost-effective compared to other types of conduits, making it a popular choice for both residential and commercial installations. It provides excellent value without compromising on performance.
- Durability: PVC is a durable material and can withstand various environmental conditions, including moisture, heat, and UV radiation. It is resistant to corrosion, making it a reliable option for long-term underground installations.
- Ease of Installation: PVC conduit is lightweight and easy to handle, making it simple to install even in tight spaces or challenging terrains. It can be easily cut and secured using PVC solvent cement, eliminating the need for complex fittings or connectors.
- Flexibility: While not as flexible as some other conduit materials, PVC conduit offers sufficient flexibility for most underground installations. It can be bent to accommodate corners or changes in direction, reducing the need for additional fittings.
- Size Variety: PVC conduits are available in a range of sizes to suit different wiring requirements. This allows for easy customization and ensures that the conduit can accommodate the desired number and size of electrical cables.
When installing PVC conduit, it is important to follow proper guidelines and adhere to local electrical codes. Here are a few tips to ensure a successful installation:
- Inspect the conduit for any defects or damage before installation.
- Plan the conduit routing and determine the appropriate length required for the installation.
- Ensure the conduit is properly supported and secured along its entire length.
- Use proper connectors and fittings to join sections of PVC conduit together.
- Seal all conduit joints and fittings using PVC solvent cement or appropriate sealing materials.
- Burial depth requirements should be followed to ensure the conduit is adequately protected underground.
- Consider using expansion fittings in areas where temperature fluctuations may occur.
By following these guidelines, you can maximize the benefits of PVC conduit and ensure a reliable and long-lasting underground electrical installation.
Next, let’s explore another popular type of conduit: HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) conduit.
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) Conduit
HDPE conduit, short for High-Density Polyethylene conduit, is a versatile and widely used option for underground electrical wiring. Made from a strong and flexible polymer, HDPE conduit offers several benefits that make it a popular choice for various applications.
Here are the key features and advantages of HDPE conduit:
- Strength and Flexibility: HDPE conduit is known for its high strength-to-density ratio, providing excellent durability and resistance to impact. It is flexible and can easily bend without requiring additional fittings or connectors, making installations more convenient and cost-effective.
- Corrosion and Chemical Resistance: HDPE conduit is highly resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for underground installations in diverse environments. It does not corrode when exposed to moisture, chemicals, or soil conditions commonly found in underground installations, ensuring long-term performance and reliability.
- Lightweight: HDPE conduit is lighter than many other conduit materials such as metal or PVC, making it easier to handle and install. The lightweight nature of HDPE conduit also reduces the strain on overhead structures and supports.
- UV Resistance: Unlike some other conduit materials, HDPE conduit is UV resistant, meaning it can withstand prolonged exposure to sunlight without degrading. This makes it an ideal choice for outdoor and above-ground installations where direct sunlight is a factor.
- Wide Temperature Range: HDPE conduit has a broad temperature range, allowing it to withstand both extremely cold and hot temperatures without losing its physical properties. This ability to perform in diverse temperature conditions makes it suitable for installations in various climates.
When installing HDPE conduit, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and local electrical codes. Here are a few tips for a successful installation:
- Measure and cut the HDPE conduit to the desired lengths, ensuring there is enough allowance for expansion and contraction.
- Prepare the conduit ends by chamfering or beveling them to facilitate smooth and secure joint connections.
- Use heat fusion or compression fittings specifically designed for HDPE conduit to create strong and watertight connections.
- Secure the conduit using appropriate supports, brackets, or hangers, ensuring proper spacing and alignment.
- Follow the recommended burial depth requirements to protect the HDPE conduit from any external damage or impact.
- Inspect the conduit regularly for any signs of damage or wear and promptly repair or replace any compromised sections.
By following these installation practices, you can ensure the longevity and reliability of your underground electrical system using HDPE conduit.
Now that we have explored HDPE conduit, let’s move on to another commonly used type: Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC).
Read also: 11 Best Underground Conduit for 2025
Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC)
Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC) is a heavy-duty and robust type of conduit commonly used for underground electrical wiring. Made from steel, RMC offers exceptional protection against physical damage, fire, and electromagnetic interference, making it suitable for demanding industrial and commercial applications.
Here are the key features and advantages of Rigid Metal Conduit:
- Durability and Protection: RMC is highly durable and provides a high level of protection for electrical wiring in challenging environments. It can withstand harsh conditions, physical impact, and extreme temperatures, ensuring the longevity and safety of the electrical system.
- Fire Resistance: RMC is fire-resistant, offering an added layer of protection in applications where fire safety is crucial. It helps prevent the spread of fire and provides a reliable conduit for electrical cables in critical locations.
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Shielding: Steel RMC provides effective shielding against electromagnetic interference, protecting sensitive electrical equipment and minimizing the risk of signal distortion or disruption.
- Secure and Stable: RMC is rigid and provides structural stability to the electrical installation. It is less prone to bending or shifting, ensuring the integrity of the wiring system over time.
However, there are a few considerations to keep in mind when working with RMC:
- Weight and Handling: RMC is heavier and more rigid than other types of conduits, making it more challenging to handle and install. Proper lifting and support techniques should be used to prevent injury and damage during installation.
- Specialized Tools: Working with RMC may require specialized tools such as pipe threaders and cutters. These tools are necessary to create threaded connections and cut the conduit to the desired lengths.
- Protection Against Corrosion: While RMC provides excellent protection against physical damage, it is susceptible to corrosion. Proper coating or painting should be applied to protect the conduit, especially in corrosive environments or areas with high humidity.
It is crucial to consult local electrical codes and regulations when using RMC for underground electrical wiring. Proper installation, including the use of approved fittings, secure fastening, and grounding, should be followed to ensure compliance and electrical safety.
Now that we are familiar with Rigid Metal Conduit, let’s move on to another commonly used conduit type: Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT).
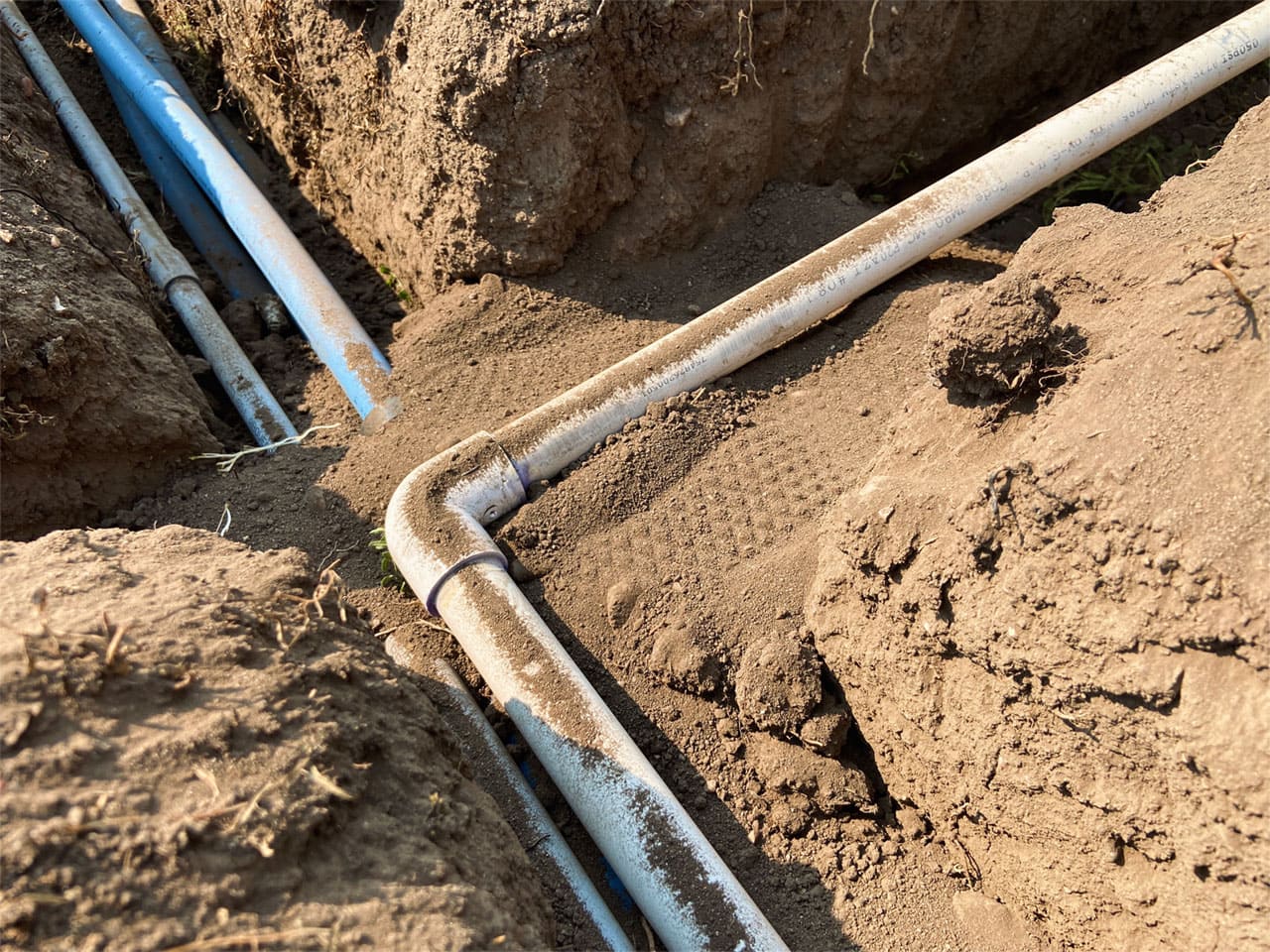
When installing underground electrical wiring, use a conduit made of PVC or rigid metal to protect the wires from moisture and physical damage. Make sure to bury the conduit at the proper depth according to local building codes.
EMT (Electrical Metallic Tubing) Conduit
EMT, also known as Electrical Metallic Tubing, is a commonly used type of conduit for underground electrical wiring installations. It is made of galvanized steel or aluminum and offers a balance between affordability, durability, and ease of installation.
Here are the key features and advantages of EMT conduit:
- Affordability: EMT conduit is a cost-effective option for both residential and commercial electrical installations. It provides reliable protection for the electrical wiring at a reasonable price.
- Strength and Durability: EMT conduit is manufactured from galvanized steel or aluminum, making it a sturdy and durable choice for protecting electrical cables underground. It can withstand rough handling, impact, and various environmental conditions.
- Flexibility and Ease of Installation: EMT conduit is lightweight and relatively flexible, allowing for easy handling and installation. It can be bent using a bending tool to fit around obstacles or follow the desired path, reducing the need for additional fittings.
- Corrosion Resistance: Galvanized EMT conduit is coated with a layer of zinc, providing excellent corrosion resistance. This makes it suitable for use in outdoor or underground applications where exposure to moisture and other corrosive elements is expected.
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Shielding: EMT conduit offers some level of electromagnetic interference shielding, protecting the electrical cables from external electrical noise or interference.
When working with EMT conduit, it is important to follow proper installation practices to ensure the integrity and safety of the electrical system. Here are a few tips:
- Measure and plan the conduit routing before installation to minimize the need for unnecessary bends or adjustments.
- Use an EMT bending tool to create accurate bends in the conduit as required by the installation design.
- Secure the conduit using appropriate straps or clamps at regular intervals to prevent movement or sagging.
- Install grounding bushings where necessary to ensure proper grounding of the conduit.
- Use EMT-specific connectors and fittings that provide secure connections and maintain the integrity of the conduit system.
- Follow local electrical codes and regulations regarding burial depths and any additional protective measures required for the specific installation.
By following these installation guidelines and using quality components, EMT conduit can provide reliable and long-lasting protection for your underground electrical wiring.
Now that we have covered EMT conduit, let’s move on to discussing the different types of conduit joints and fittings used in underground electrical installations.
Types of Conduit Joints and Fittings
Conduit joints and fittings are essential components of underground electrical installations. They provide secure connections, accommodate changes in direction, and ensure the integrity of the conduit system. Here are the most common types of conduit joints and fittings used:
- Coupling: Couplings are used to join two sections of the same type and size of conduit together. They typically have a threaded design that allows for a secure and watertight connection. Couplings are available in different materials such as steel, PVC, or aluminum, depending on the type of conduit being used.
- Connector: Connectors serve to connect conduits of different sizes or materials. They can also be used to connect conduit to electrical boxes, enclosures, or devices. Connectors come in various forms, including compression connectors, set-screw connectors, or snap-in connectors, depending on the specific application requirements.
- Elbow: Elbows, also known as bends, are used when there is a need to change the conduit’s direction. They provide a smooth and gradual change in direction without causing kinks or excessive stress on the conduit. Elbows are available in different angles, such as 90 degrees or 45 degrees, to suit various installation configurations.
- Coupling Reducer: A coupling reducer is used to transition between conduits of different sizes. It allows for a secure connection between two conduits with different diameters, ensuring a smooth and efficient transition in the conduit system.
- Bushing: Bushings are used to protect the wires or cables entering or exiting a conduit. They provide a smooth and safe transition from the conduit to the electrical box or equipment. Bushings also offer protection against sharp edges that could potentially damage the cables.
- Locknut: Locknuts are used to secure connectors or fittings to electrical boxes or enclosures. They provide a secure fastening and help prevent any unwanted movement or vibration that could loosen the connection. Locknuts are often made of metal, such as steel or zinc-plated steel.
- Strap or Clamp: Straps or clamps are used to secure the conduit to a supporting structure, such as walls or beams. They ensure that the conduit remains in the desired position and provides sufficient support to prevent sagging or movement. These straps or clamps can be made of metal, plastic, or nylon depending on the application requirements.
It is important to select appropriate joints and fittings that are compatible with the type and size of the conduit being used. Adhering to the manufacturer’s recommendations and local electrical codes is essential for ensuring safe and proper installation.
Now that we have covered the different types of conduit joints and fittings, let’s move on to discussing how to choose the right conduit for your underground electrical needs.
Choosing the Right Conduit for Your Underground Electrical Needs
Choosing the right conduit for your underground electrical needs is crucial for ensuring a safe, reliable, and efficient electrical installation. Here are some factors to consider when selecting the appropriate conduit:
- Environmental Conditions: Assess the environmental conditions in which the conduit will be installed. Consider factors such as moisture, temperature fluctuations, chemicals, and exposure to UV radiation. Choose a conduit material that is resistant to these conditions to ensure long-term performance and durability.
- Protection Level: Determine the level of protection required for your electrical wiring. If the installation is in an area prone to physical impact, fire hazards, or electromagnetic interference, consider using a conduit material that offers higher levels of protection, such as Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC).
- Application: Evaluate the specific application requirements. Different conduits may be more suitable for residential, commercial, or industrial applications. Consider factors such as the number and size of electrical cables, installation location, and expected future expansion needs.
- Cost-effectiveness: Consider the cost of the conduit material and the overall installation. Compare the prices of different conduit types, including any additional fittings or accessories required for the installation. Remember to factor in the long-term maintenance and repair costs as well.
- Installation Ease: Assess the ease of installation for the conduit. Some materials, such as PVC or HDPE conduits, are lightweight and flexible, making them easier to handle and install. Consider the available space, maneuverability requirements, and complexity of the installation when selecting a conduit type.
- Code Compliance: Ensure that the chosen conduit is compliant with local electrical codes and regulations. Familiarize yourself with the standards and requirements specific to your area to ensure a safe and legal installation.
- Future Expansion: Consider any potential future expansion needs. If there is a possibility of adding more electrical circuits or cables in the future, choose a conduit size that can accommodate these additions. Planning for future expansion can help save time and money on future modifications.
- Maintenance: Evaluate the maintenance requirements of the conduit material. Some materials may require regular inspections, cleaning, or repairs. Ensure that the selected conduit is easy to maintain and does not impose significant maintenance demands.
Taking all of these factors into account will help you make an informed decision and select the most suitable conduit for your underground electrical needs. Remember to consult with professionals and experts in electrical installations if you have any doubts or specific requirements.
Once you have selected the appropriate conduit, the next step is to understand the installation process. Let’s move on to discussing the installation process for underground electrical conduits.
Read more: What Electrical Wire To Run Underground
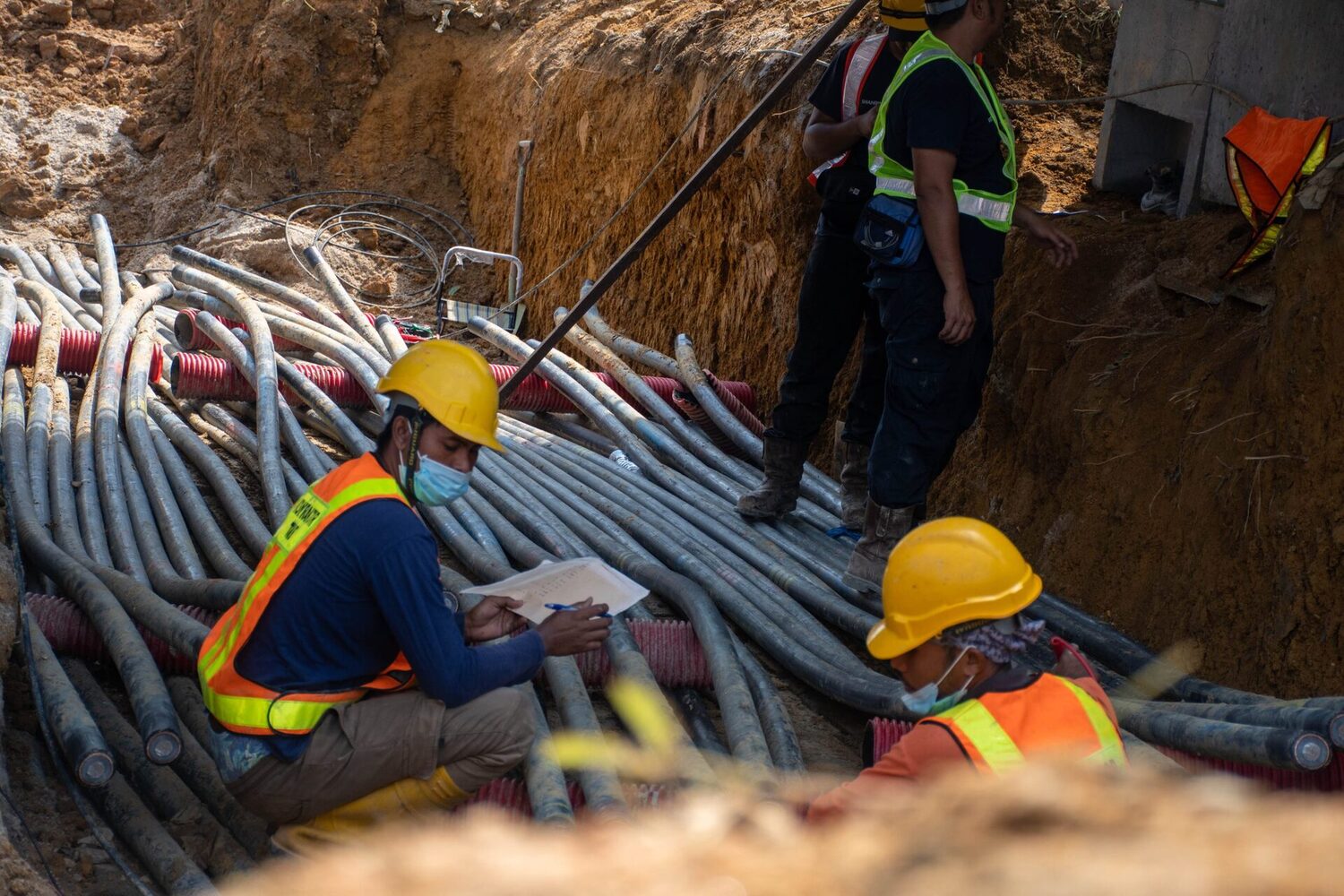
Installation Process for Underground Electrical Conduits
The installation process for underground electrical conduits requires careful planning, proper execution, and adherence to safety protocols. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you with the installation:
- Design and Planning: Start by evaluating the installation requirements and creating a detailed plan. Determine the route the conduit will take, ensuring it avoids obstacles such as trees, utility lines, or structures. Consider the burial depth requirements specified by local codes and regulations.
- Excavation: Once the route is determined, mark the area to be excavated. Use appropriate tools, such as a shovel or trencher, to dig a trench along the planned pathway. Ensure the trench is wide enough to accommodate the conduit and allows for the required burial depth.
- Prepare Conduit: Cut the conduit sections to the appropriate lengths based on the trench dimensions and installation plan. Remove any rough edges or burrs from the cuts. If necessary, add connectors or fittings at the ends of the conduit to ensure a secure and proper connection.
- Lay Conduit: Carefully place the conduit sections into the trench, ensuring they are aligned correctly along the planned route. Use caution to avoid bending or damaging the conduit during the installation process.
- Join Conduit Sections: Join the conduit sections together using the appropriate joints and fittings. Depending on the type of conduit, this may involve using couplings, connectors, or compression fittings. Ensure that the connections are secure, watertight, and comply with the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Secure Conduit: Use straps, clamps, or hangers to secure the conduit at regular intervals along the trench. This helps prevent excessive movement or sagging of the conduit and ensures its stability and support.
- Burial and Backfill: Once the conduit is secured in place, carefully backfill the trench with soil, ensuring it is evenly distributed around the conduit. Compact the soil gently to avoid damaging or shifting the conduit. Follow local codes and regulations regarding the appropriate burial depth for the conduit.
- Inspect and Test: After the installation is complete, thoroughly inspect the entire system to ensure there are no damaged or compromised areas. Test the conduit for continuity and use appropriate equipment to verify the integrity of the electrical wiring.
- Document and Cover: Document the installation details, including the route, depths, and any necessary information for future reference. Finally, cover the trench with a suitable material such as soil or gravel, ensuring the area is restored to its original condition.
It is crucial to follow safety guidelines and ensure compliance with local electrical codes throughout the installation process. If you are uncertain about any aspect of the installation, it is recommended to consult with a professional electrician or contractor who can provide guidance and assistance.
Now that you understand the installation process, it’s important to be aware of safety guidelines to ensure a secure installation. Let’s explore some safety guidelines for installing underground electrical conduits.
Safety Guidelines for Installing Underground Electrical Conduits
Installing underground electrical conduits requires strict adherence to safety protocols to ensure the protection of both the installer and the electrical system. Here are some essential safety guidelines to follow during the installation:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including safety glasses, gloves, and steel-toed boots, to protect against potential hazards such as debris, sharp edges, or electrical shocks.
- Utility Locates: Before digging the trench, contact the local utility companies to request utility locates. This will help identify any underground utilities or infrastructure in the area, preventing accidental damage or disruption of services.
- Shut Off Power: Ensure that the power to the area where the conduit will be installed is safely turned off. Consult with a licensed electrician to disconnect power if necessary. Treat all electrical lines as live until they are disconnected and verified as de-energized.
- Trench Safety: Take precautions to ensure the safety of those working in or near the trench. Use proper shoring, trench boxes, or barricades to prevent cave-ins. Keep a safe distance from the edges of the trench to avoid accidental falls.
- Depth and Clearance: Follow local codes and regulations regarding the minimum burial depth for the conduit. Ensure adequate clearance between the conduit and any other underground utilities or structures to prevent damage or interference.
- Electrical Grounding: Properly ground the conduit system to ensure electrical safety. Connect the conduit system to an appropriate grounding electrode, such as a grounding rod or water pipe, as per local electrical codes.
- Cable Pulling: Use proper techniques when pulling electrical cables through the conduit to prevent damage. Avoid sharp bends or excessive pulling force that could cause cable insulation or conductor damage.
- Proper Sealing: Seal all conduit joints, fittings, and entry points to prevent moisture or water infiltration. Choose suitable sealing materials, such as approved foams or sealing compounds, that are compatible with the conduit material.
- Electrical Inspections: Schedule electrical inspections as required by local authorities. This will ensure that the installed conduit and wiring comply with safety standards and regulations.
- Documentation and Accessibility: Keep thorough documentation of the installation, including conduit routes, depths, and any relevant notes. Ensure that access points, such as electrical boxes or enclosures, are easily accessible for future maintenance and repairs.
It is crucial to consult and comply with local electrical codes, regulations, and safety standards throughout the installation process. If you are unsure about any aspect of the installation, consult with a licensed electrician or an electrical professional who can provide guidance and assistance.
By following these safety guidelines, you can ensure a secure and successful underground electrical conduit installation.
Now that we have covered safety guidelines, let’s conclude our article with a summary of the key points.
Conclusion
When it comes to underground electrical installations, choosing the right conduit is critical to ensure the safety, durability, and efficiency of the electrical system. Factors such as durability, material compatibility, ease of installation, cost-effectiveness, and environmental resistance should be considered when selecting the appropriate conduit for your specific needs.
Popular conduit options for underground electrical wiring include PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) conduits, HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) conduits, Rigid Metal Conduits (RMC), and Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT) conduits. Each of these conduits has its own unique features and benefits, making them suitable for different applications and environments.
During the installation process, careful planning, proper conduit selection, and compliance with safety guidelines are essential. Follow the recommended steps, such as designing the conduit path, excavating the trench, laying and securing the conduit, and ensuring proper joint connections. Adhere to safety protocols and consider personal protective equipment (PPE), utility locates, trench safety, and grounding to minimize risks and ensure a successful installation.
By following these guidelines, you can achieve a reliable and efficient underground electrical conduit system. Regular inspections, adherence to maintenance requirements, and compliance with local electrical codes will help ensure the ongoing safety and performance of the electrical installation.
Remember, if you are unsure about any aspect of the installation or need assistance, it is always advisable to consult with a licensed electrician or electrical professional who can provide expert guidance.
Choosing the right conduit and installing it properly will ensure the longevity, reliability, and safety of your underground electrical system. With a well-planned and properly executed installation, you can have peace of mind knowing that your electrical infrastructure is protected and will meet your needs for years to come.
Ready to dig deeper into your underground electrical project? Don't stop at just choosing the right conduit. Understanding which electrical wires to use is equally vital for ensuring your system's safety and efficiency. Dive into our detailed guide on selecting the appropriate underground wiring for a robust and reliable setup. This next read is packed with practical advice and expert insights, perfect for anyone looking to enhance their electrical installation knowledge.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Conduit Do I Use For Underground Electrical
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Conduit Do I Use For Underground Electrical”