

Articles
What Is A Line Set In HVAC
Modified: August 17, 2024
Learn all about lineset in HVAC systems with our informative articles. Discover the importance of linesets and how they contribute to efficient cooling and heating.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, there are various components that work together to create a comfortable indoor environment. One crucial element of an HVAC system is the lineset, which plays a vital role in transporting refrigerant between the indoor and outdoor units.
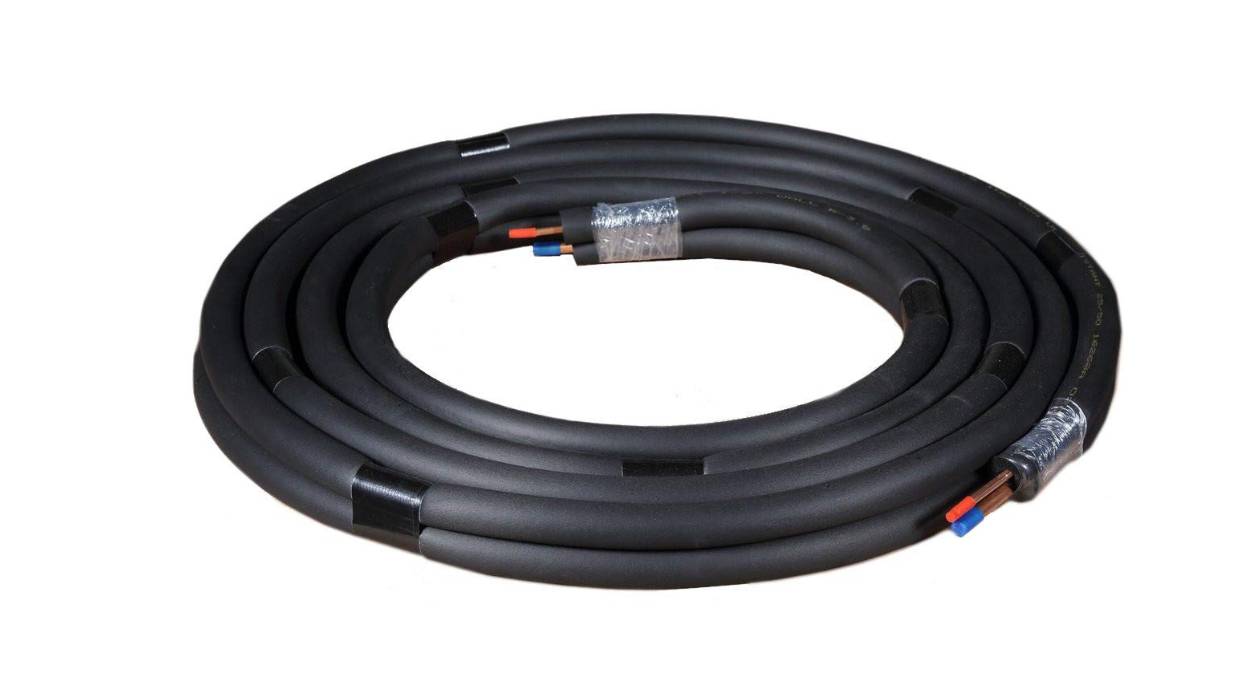
A lineset is essentially a pair of copper pipes that connect the condenser unit, located outside the building, to the evaporator unit, typically found indoors. These pipes allow for the passage of refrigerant, which is responsible for cooling or heating the indoor space. Understanding the construction, function, and benefits of lineset HVAC systems is essential for homeowners, HVAC technicians, and anyone interested in the mechanics of indoor climate control.
In this article, we will explore the definition of a lineset HVAC, the components that make up the system, its purpose and function, the installation process, common issues and troubleshooting, maintenance and cleaning tips, and the advantages and disadvantages of using a lineset HVAC system.
By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of lineset HVAC systems and their importance in maintaining a comfortable and controlled indoor environment.
Key Takeaways:
- Efficient and Reliable Climate Control
Lineset HVAC systems offer efficient heat transfer, reliable performance, and energy efficiency, making them a cost-effective and visually appealing option for maintaining comfortable indoor environments. Proper installation and maintenance are crucial for optimal functionality. - Considerations for Installation and Maintenance
When considering a lineset HVAC system, it’s important to assess building requirements, potential limitations, and the need for professional installation and regular maintenance. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages will help make an informed decision.
Read more: How To Clear HVAC Drain Line
Definition of Lineset HVAC
A lineset HVAC, also known as a refrigerant lineset or simply a lineset, is a pair of copper pipes that connect the outdoor condenser unit to the indoor evaporator unit in an HVAC system. These pipes are responsible for transporting refrigerant, which is the substance that absorbs and releases heat, between the two units.
The lineset consists of two pipes: the larger one is called the suction line or the low-pressure line, while the smaller one is known as the liquid line or the high-pressure line. The suction line carries cool, low-pressure refrigerant vapor from the evaporator unit to the condenser unit where it is compressed and converted back into a high-pressure gas. The liquid line, on the other hand, carries the high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant liquid from the condenser unit to the evaporator unit, where it expands and evaporates to cool the indoor space.
Both pipes of the lineset are made of copper due to its excellent heat transfer properties and corrosion resistance. Copper is widely used in HVAC systems as it is a durable and efficient material for carrying refrigerant. The pipes are insulated to prevent condensation and maintain the temperature of the refrigerant as it travels between the units.
The length of the lineset can vary depending on the distance between the indoor and outdoor units. Longer linesets may require additional refrigerant charge and proper sizing of the pipes to ensure optimal system performance. It is important to follow manufacturer guidelines and consult with HVAC professionals to determine the appropriate lineset length for a specific installation.
In summary, a lineset HVAC is a pair of copper pipes that connect the indoor and outdoor units of an HVAC system, allowing for the transfer of refrigerant to cool or heat the indoor space. These pipes play a critical role in the operation and efficiency of the HVAC system.
Components of a Lineset HVAC
A lineset HVAC system consists of several components that work together to ensure the smooth and efficient transfer of refrigerant between the outdoor condenser unit and the indoor evaporator unit. Understanding these components is essential for proper installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of the lineset HVAC system. Let’s take a closer look at each component:
- Pipes: The lineset consists of two copper pipes, known as the suction line and the liquid line. The suction line carries cool, low-pressure refrigerant vapor from the evaporator unit to the condenser unit, while the liquid line carries the high-pressure refrigerant liquid from the condenser unit to the evaporator unit.
- Insulation: The pipes of the lineset are typically wrapped in insulation to prevent heat gain or loss and to reduce condensation. Insulation helps maintain the temperature of the refrigerant as it travels between the units, ensuring efficient operation and preventing energy wastage.
- Refrigerant: The refrigerant is the substance that circulates through the lineset, absorbing and releasing heat to cool or heat the indoor space. It undergoes phase changes from a low-pressure vapor to a high-pressure gas and back to a liquid, allowing for effective heat transfer.
- Fittings: Fittings, such as couplings, elbows, and valves, are used to connect and secure the lineset components. These fittings help maintain the integrity of the lineset and prevent leaks, ensuring the efficient flow of refrigerant.
- Flared Connections: Flared connections are commonly used for joining the lineset pipes to the indoor and outdoor units. Flaring the ends of the pipes creates a wider surface area for the connections, enhancing the seal and reducing the risk of leaks.
- Filter Drier: The filter drier is a crucial component installed in the liquid line of the lineset. Its purpose is to filter out contaminants, such as moisture and debris, that can harm the HVAC system and compromise its performance.
- Valves: Valves are used to control and regulate the flow of refrigerant in the lineset. They allow for proper charging, maintenance, and troubleshooting of the system, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
These components work in tandem to facilitate the transfer of refrigerant and maintain the functionality of the lineset HVAC system. Understanding their roles and functions is crucial for ensuring the proper installation, operation, and longevity of the system.
Purpose and Function of a Lineset HVAC
The lineset in an HVAC system serves a critical purpose and plays a crucial role in the overall functionality of the system. Let’s explore the purpose and function of a lineset in more detail:
Purpose:
The primary purpose of a lineset HVAC is to transport refrigerant between the outdoor condenser unit and the indoor evaporator unit. Refrigerant is the key substance responsible for cooling or heating the indoor space, making the lineset a vital component in achieving comfortable indoor temperatures. By connecting the two units, the lineset enables the continuous circulation of refrigerant, facilitating the heat transfer process.
Function:
The lineset plays a crucial function in the following ways:
- Refrigerant Transfer: The lineset facilitates the transfer of refrigerant between the condenser unit and the evaporator unit. The suction line carries low-pressure, cool refrigerant vapor from the evaporator unit to the condenser unit. In contrast, the liquid line carries high-pressure, compressed refrigerant liquid from the condenser unit to the evaporator unit. This transfer of refrigerant enables the cooling or heating of the indoor space.
- Heat Exchange: The lineset allows for the heat exchange process to occur. In cooling mode, warm indoor air is drawn into the evaporator unit, and the refrigerant absorbs the heat from the air, causing it to condense and cool down. This cooled air is then circulated back into the indoor space. In heating mode, the process is reversed, and the lineset facilitates the transfer of heat from the outdoor air to warm the indoor space.
- Pressure Regulation: The lineset helps regulate the pressure of the refrigerant. As the refrigerant flows through the lineset, it undergoes phase changes from a low-pressure vapor to a high-pressure gas in the condenser unit and back to a liquid in the evaporator unit. The lineset, along with other components like valves and fittings, helps maintain proper pressure levels throughout the system, ensuring efficient and reliable operation.
- Insulation: Another important function of the lineset is insulation. The pipes of the lineset are typically wrapped in insulation to prevent heat gain or loss during the refrigerant transfer process. Insulation helps maintain the temperature of the refrigerant, ensuring optimal efficiency and preventing energy waste.
Overall, the purpose of a lineset HVAC is to transport refrigerant, enable heat exchange, regulate pressure, and maintain efficient operation of the HVAC system. Understanding the function of the lineset is crucial for proper installation, operation, and maintenance, ensuring the system operates effectively and provides optimal comfort in indoor spaces.
Installation Process of a Lineset HVAC
Installing a lineset HVAC requires careful planning and attention to detail to ensure optimal performance and functionality of the system. Here is a step-by-step guide to the installation process:
- System Design: Begin by determining the appropriate size and capacity of the HVAC system based on the cooling or heating requirements of the space. Consider factors such as square footage, insulation levels, and climate conditions. Consult with HVAC professionals to design a system that meets your needs.
- Unit Placement: Choose suitable locations for the outdoor condenser unit and indoor evaporator unit. Ensure they have adequate clearance for airflow and maintenance. Follow manufacturer guidelines and local building codes for proper unit placement.
- Lineset Routing: Plan the routing of the lineset between the indoor and outdoor units. Consider factors such as distance, obstacles, and accessibility. The lineset should be as straight and direct as possible to minimize pressure drop and ensure efficient refrigerant flow.
- Pipe Sizing: Determine the appropriate size of the lineset pipes based on the manufacturer’s specifications and refrigerant requirements. Larger systems may require larger diameter pipes to accommodate higher refrigerant volumes. Proper pipe sizing is crucial for efficient system operation.
- Mounting and Insulation: Secure the lineset pipes using appropriate mounting brackets to prevent movement and vibration. Wrap the pipes with insulation to prevent heat gain or loss and to reduce condensation. Insulation helps maintain the temperature of the refrigerant, ensuring optimal efficiency.
- Connection and Sealing: Connect the lineset pipes to the condenser and evaporator units using flared connections or other approved methods. Ensure tight and secure fittings to prevent leaks. Properly seal all connections to maintain the integrity of the lineset system.
- Filter Drier Installation: Install a filter drier in the liquid line to capture and remove contaminants that can harm the HVAC system. The filter drier helps maintain the performance and longevity of the system by preventing debris and moisture from circulating.
- Vacuum and Pressure Test: After installation, the lineset should be vacuumed to remove any air and moisture. This is crucial for proper refrigerant flow and system efficiency. A pressure test should also be conducted to ensure there are no leaks in the lineset or connections.
- Refrigerant Charging: Once the lineset passes the vacuum and pressure test, the refrigerant is charged into the system following manufacturer guidelines and refrigerant specifications. Proper refrigerant charge is essential for system performance and efficiency.
- System Startup: Finally, the HVAC system can be started up and tested to ensure all components are functioning correctly. Check for proper refrigerant flow, temperature differentials, and overall system performance. Make any necessary adjustments or repairs as needed.
It is crucial to note that the installation process of a lineset HVAC system requires technical knowledge and expertise. It is recommended to consult with HVAC professionals who can ensure proper installation and adherence to local codes and regulations.
A lineset in HVAC refers to the pair of copper tubes that connect the indoor and outdoor units of a split system air conditioner or heat pump. It carries refrigerant between the two units, so it’s important to ensure proper installation and insulation to maintain system efficiency.
Read more: How To Clean HVAC Drain Line
Common Issues and Troubleshooting a Lineset HVAC
While lineset HVAC systems are designed to operate smoothly and efficiently, there are a few common issues that may arise. Understanding these issues and knowing how to troubleshoot them can help you identify and resolve problems with your lineset HVAC system. Here are some of the most common issues and troubleshooting tips:
- Refrigerant Leaks: One of the most common issues with lineset HVAC systems is refrigerant leaks. Leaks can occur at the connections, fittings, or even within the lineset itself. To troubleshoot a refrigerant leak, use a refrigerant leak detector to pinpoint the source of the leak. Once identified, repair or replace the faulty component and recharge the system with the proper amount of refrigerant.
- Insufficient Cooling or Heating: If your lineset HVAC system is not providing adequate cooling or heating, there may be a few potential causes. Check the filters to ensure they are clean and not obstructing airflow. Inspect the outdoor condenser unit for any debris or obstructions. Make sure the thermostat settings are correct and functioning properly. If the issue persists, consult with an HVAC professional to assess the system’s capacity and performance.
- Pressure Imbalances: Pressure imbalances within the lineset HVAC system can result in poor performance and reduced efficiency. If you notice uneven temperature distribution or fluctuating pressure readings, check for obstructions or restrictions in the lineset. Inspect the valves and fittings for any malfunctions and ensure they are properly adjusted. In some cases, it may be necessary to clean or replace components to restore balanced pressure.
- Condensation and Moisture: Excessive condensation or moisture buildup along the lineset may indicate an insulation problem. Inspect the insulation for any damages or gaps and replace if necessary. Ensure proper insulation coverage to prevent heat gain or loss and condensation formation. Be mindful of any sources of excess moisture near the lineset, such as leaks or high humidity levels, and address these issues promptly.
- Vibrations and Noises: Unusual vibrations or noises coming from the lineset HVAC system could be a sign of loose or faulty fittings, improper mounting, or worn components. Inspect the lineset for any loose brackets or connections and tighten them as needed. Check for any damaged or worn-out components and replace them. If the vibrations or noises persist, contact a qualified HVAC technician for further inspection and repair.
- Inadequate Insulation: Insufficient insulation along the lineset can lead to energy loss and decreased system efficiency. Check the insulation for any signs of damage, wear, or gaps. Make sure the insulation is properly installed and covers the entire length of the lineset. Replace or add insulation as necessary to maintain optimal performance and prevent thermal loss or gain.
It’s important to note that while troubleshooting some common issues can be done by homeowners, more complex issues may require the expertise of a qualified HVAC technician. Regular maintenance and prompt attention to any issues can help keep your lineset HVAC system running smoothly and efficiently.
Maintenance and Cleaning of a Lineset HVAC
Maintaining and cleaning your lineset HVAC system is essential to ensure its longevity, efficiency, and optimal performance. Regular maintenance can prevent issues and extend the life of your system. Here are some maintenance and cleaning tips for your lineset HVAC:
- Inspect the Lineset: Regularly inspect the lineset for any signs of damage, such as corrosion, leaks, or wear. Check the insulation for gaps or tears. Address any issues promptly to prevent further damage or efficiency loss.
- Clean the Outdoor Unit: Keep the area around the outdoor condenser unit clean and free from debris such as leaves, grass, and branches. Regularly clean the unit by gently hosing it down to remove dirt, dust, and debris that can obstruct airflow. Ensure the unit’s fins are straight and free from any bending or damage.
- Replace Air Filters: Regularly replace or clean the air filters in the indoor unit as per manufacturer recommendations. Dirty or clogged filters can restrict airflow and reduce system efficiency. Clean filters ensure better air quality and improve the overall performance of your HVAC system.
- Clean Vents and Registers: Clean the vents and registers in your home regularly to remove dust and debris. Blocked vents can reduce airflow and hinder system performance.
- Monitor Refrigerant Levels: Check the refrigerant levels regularly to ensure they are within the manufacturer’s recommended range. Low refrigerant levels can indicate a leak. If you suspect a leak, contact an HVAC technician to diagnose and repair the issue.
- Schedule Professional Maintenance: It is recommended to schedule professional maintenance at least once a year, preferably before the start of the cooling or heating season. An HVAC technician will perform a comprehensive inspection, cleaning, and tune-up of your system, identifying and resolving any potential issues.
- Keep the Lineset Insulation Intact: Ensure that the insulation covering the lineset remains intact and in good condition. Replace any damaged or deteriorated insulation to maintain optimal energy efficiency and prevent condensation issues.
- Check for Vibrations: Periodically check the lineset for vibrations or unusual noises while the system is running. If you notice any vibrations, tighten loose brackets or connections, and ensure that the lineset is properly secured.
- Trim Vegetation: Trim any overgrown vegetation near the outdoor unit to ensure proper airflow. Leaves or branches obstructing the unit can reduce its efficiency and lead to performance issues.
Remember, proper maintenance and cleaning will not only extend the life of your lineset HVAC system but also improve its efficiency and provide better indoor comfort. If you are unsure or uncomfortable performing any maintenance tasks, it is recommended to consult with a qualified HVAC professional for assistance.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using a Lineset HVAC
Lineset HVAC systems offer several advantages and disadvantages, which should be considered when deciding whether to install or use this type of system. Here are the key advantages and disadvantages of using a lineset HVAC:
- Advantages:
- Efficient Heat Transfer: Lineset HVAC systems, with their copper pipes, provide excellent heat transfer capabilities, allowing for efficient cooling or heating of indoor spaces.
- Flexible Installation: Lineset HVAC systems can be installed in various types of buildings, including residential homes, commercial spaces, and offices, making them a versatile option for climate control.
- Reliable Performance: When properly installed and maintained, lineset HVAC systems can provide reliable and consistent cooling or heating performance, ensuring comfort throughout the year.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Lineset HVAC systems offer a clean and neat installation, with the majority of the components hidden within the walls. This results in a visually appealing and unobtrusive indoor environment.
- Energy Efficiency: With proper insulation of the lineset pipes, lineset HVAC systems can minimize energy loss during refrigerant transfer, resulting in reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills.
- Cost-Effective: Lineset HVAC systems generally have lower installation and maintenance costs compared to other HVAC system types, making them an economical option for climate control.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited Distance: Lineset HVAC systems have a maximum distance limitation between the indoor and outdoor units due to pressure drop and refrigerant flow considerations. This can limit their suitability for large or complex buildings.
- Installation Complexity: The installation of lineset HVAC systems requires professional expertise to ensure proper sizing, routing, and connection of the lineset pipes. Improper installation can lead to performance issues or refrigerant leaks.
- Potential for Refrigerant Leaks: The lineset pipes can develop refrigerant leaks over time due to factors such as corrosion, vibration, or improper installation. Regular inspection and maintenance are required to ensure the integrity of the lineset system.
- Insulation Maintenance: Insulation covering the lineset pipes must be inspected and maintained regularly to prevent issues such as heat gain, condensation, or energy loss. Damaged or deteriorated insulation can compromise system efficiency.
- Noise and Vibration: If not properly installed or secured, lineset HVAC systems can produce noise or vibrations during operation. This can be mitigated through proper installation and regular maintenance.
- Not Suitable for All Building Types: Lineset HVAC systems may not be suitable for certain building designs, such as high-rise buildings, where long lineset runs are required. In such cases, alternative HVAC systems may be more suitable.
Considering the advantages and disadvantages, it is important to assess your specific needs, building requirements, and budget when determining whether a lineset HVAC system is the right choice for your climate control needs. Consulting with HVAC professionals can provide valuable insights and guidance in making an informed decision.
Conclusion
Lineset HVAC systems play a crucial role in maintaining a comfortable indoor environment by facilitating the transfer of refrigerant between the outdoor condenser unit and the indoor evaporator unit. The lineset, consisting of copper pipes, ensures efficient heat transfer, allowing for effective cooling or heating of indoor spaces.
Understanding the components, purpose, and function of a lineset HVAC system is essential for homeowners and HVAC technicians. The installation process requires careful planning, proper sizing, and secure connections to ensure optimal system performance. Regular maintenance, such as inspecting the lineset, cleaning the outdoor unit, and replacing filters, helps maintain efficiency and prevent issues.
Advantages of using a lineset HVAC system include efficient heat transfer, flexible installation options, reliable performance, and energy efficiency. These systems can also provide a visually appealing and cost-effective solution for climate control. However, there are several disadvantages to consider, such as limited distance capabilities, the complexity of installation, and the potential for refrigerant leaks.
Overall, lineset HVAC systems are a popular choice for many residential and commercial applications. They offer a balance of performance, convenience, and affordability. However, it is important to assess your specific needs, building requirements, and budget when determining whether a lineset HVAC system is the right choice for you.
Consulting with HVAC professionals is highly recommended to ensure proper installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of your lineset HVAC system. With proper care and attention, lineset HVAC systems can provide efficient and reliable climate control for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A Line Set In HVAC
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Is A Line Set In HVAC”