

Articles
What Is Flux Used For In Plumbing
Modified: April 22, 2024
Learn about the uses and benefits of flux in plumbing with our informative articles. Discover how flux helps create a strong bond between pipes and fittings.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to plumbing, ensuring strong and durable connections is crucial. One key component that plays a vital role in achieving this is flux. If you’re unfamiliar with the term, let’s dive into the world of plumbing and explore what flux is and why it is used.
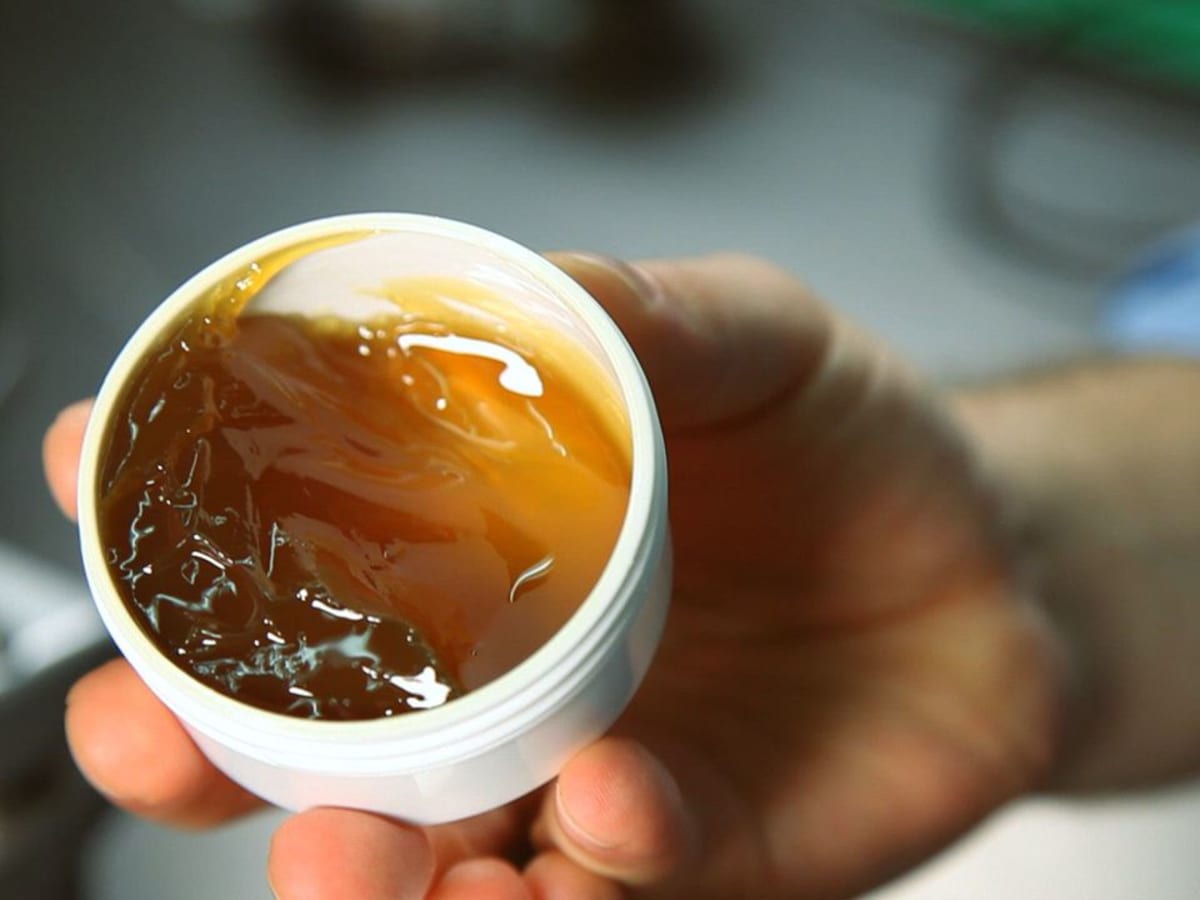
Flux is a substance that is commonly used in plumbing to facilitate the soldering process. Soldering involves joining two metal surfaces together by melting a filler metal, known as solder, and allowing it to flow into the joint. Flux is applied to the joint before soldering to promote proper bonding and prevent oxidation or contamination.
Flux acts as a cleaning agent, removing any dirt, grease, and oxidation from the metal surfaces. This ensures a clean and even surface for the solder to adhere to, resulting in a strong and secure connection. Moreover, flux also helps to prevent further oxidation during the soldering process, enhancing the longevity of the joint.
There are various types of flux available for plumbing purposes, each designed to suit different plumbing materials and applications. By choosing the right flux for your specific project, you can ensure optimal results.
In the next section, we will delve deeper into the different types of flux used in plumbing and their specific applications.
Key Takeaways:
- Flux is a crucial component in plumbing, serving as a cleaning agent, preventing oxidation, and promoting strong solder bonds. Choosing the right type of flux for specific materials is essential for achieving durable connections.
- Utilizing flux in plumbing offers benefits such as improved solder flow, clean surfaces, oxidation prevention, and stronger connections. However, it’s important to follow safety precautions and avoid common mistakes for optimal results.
Read more: What Is Plumbing Tape Used For
Definition of Flux
Flux, in the context of plumbing, refers to a chemical substance used to prepare metal surfaces for soldering. It serves as a cleaning and protective agent during the soldering process, ensuring strong and reliable connections between plumbing components.
The primary purpose of flux is to remove contaminants and impurities from the metal surfaces, such as dirt, grease, and oxidation. These impurities can hinder proper bonding between the solder and the metal, leading to weak joints or leaks. Flux acts as a cleaning agent, enabling the solder to adhere to the metal surface more effectively.
Furthermore, flux also helps to prevent oxidation during the soldering process. When metal surfaces are exposed to air, they can react with oxygen and form a layer of oxidation. This layer can interfere with the soldering process and weaken the joint over time. Flux creates a barrier between the metal and the air, preventing oxidation and ensuring a clean surface for the solder to flow.
In addition to cleaning and protection, flux also aids in the capillary action of the solder. Capillary action refers to the ability of a liquid, in this case, solder, to flow and fill in small gaps or crevices. Flux helps to improve the wetting ability of the solder, allowing it to spread evenly and penetrate tight joints. This results in stronger bonds and better overall soldering quality.
It is important to note that flux is not a permanent part of the solder joint. Once the soldering process is complete, the flux residue should be removed or neutralized to prevent corrosion. Leaving flux residue on the joints can lead to future issues, such as deterioration and blockages in the plumbing system.
Now that we understand the purpose and role of flux in plumbing, let’s explore the different types of flux commonly used in the industry.
Types of Flux Used in Plumbing
There are several types of flux available for plumbing applications, each specifically formulated to suit different metal materials and soldering processes. Here are some common types of flux used in plumbing:
- Acid Flux: Acid flux is a commonly used type of flux in plumbing. It contains acidic compounds, such as zinc chloride or hydrochloric acid, which are effective at removing oxidation and contaminants from copper and brass surfaces. Acid flux is typically used for soldering copper pipes and fittings. However, it is important to note that acid flux is corrosive and can attack certain metals, such as stainless steel or aluminum. Therefore, it should be used with caution and only on compatible materials.
- Water Soluble Flux: Water soluble flux is another popular option in plumbing. It is a non-corrosive flux that can be easily removed with water after soldering. This type of flux is often preferred for soldering stainless steel, chrome-plated pipes, or other sensitive metals that may be affected by acid flux. Water soluble flux is also environmentally friendly, as it does not contain harmful chemicals.
- Rosin Flux: Rosin flux, also known as resin flux, is made from natural pine sap. It is a mild flux that is commonly used for soldering electrical components, but can also be used in plumbing applications. Rosin flux is suitable for copper, brass, and even some stainless steel materials. It leaves minimal residue after soldering, but it is recommended to clean the joints thoroughly to prevent any long-term corrosion.
- Paste Flux: Paste flux is a thicker, gel-like flux that is easy to control and apply. It is often used in situations where precise application is required, such as small joints or tight spaces. Paste flux generally contains similar ingredients as other types of flux, such as acid or rosin, but in a thicker consistency. It provides excellent cleaning and fluxing properties and is suitable for various plumbing applications.
Before selecting a flux, it is essential to consider the specific material being soldered and the soldering process itself. Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations to ensure compatibility with the materials and to achieve the best results.
Now that we have explored the different types of flux used in plumbing, let’s move on to understand the soldering process itself and the importance of flux in achieving strong and reliable plumbing connections.
Soldering Process in Plumbing
The soldering process is a fundamental technique used in plumbing to join metal pipes, fittings, and other components. It involves the melting of a filler metal called solder, which then flows into the joint and creates a secure connection. Flux plays a crucial role in this process by ensuring proper bonding and preventing oxidation.
Here are the basic steps involved in the soldering process in plumbing:
- Cleaning the surfaces: Before soldering, it is essential to clean the surfaces to be joined. This involves removing any dirt, grease, or oxidation using a wire brush or emery cloth. Proper cleaning ensures better adhesion and improves the effectiveness of the flux.
- Applying flux: Once the surfaces are cleaned, the next step is to apply flux to the joint areas. Flux can be applied using a flux brush or a flux pen. It is important to apply a thin and even layer of flux, covering the entire joint area. The flux will serve as a cleaning agent, removing any remaining contaminants and preventing oxidation during the soldering process.
- Heating the joint: After applying flux, heat is applied to the joint using a propane torch, soldering iron, or a soldering gun. The heat source should be adjusted to provide enough heat to melt the solder without overheating the surrounding area. The joint should be heated evenly to ensure proper flow and bonding of the solder.
- Applying solder: Once the joint is sufficiently heated, solder is introduced to the joint. The solder should be applied to the heated joint, not directly to the heat source. The solder will melt and flow into the joint due to capillary action, filling any gaps and creating a strong bond between the surfaces. It is important to apply enough solder to ensure a fully filled joint, but excess solder should be avoided to prevent solder drips or excessive buildup.
- Cooling and cleaning: After the solder has flowed and formed the joint, it is necessary to allow the joint to cool naturally. Once the joint has cooled, any excess flux residue should be cleaned off using a damp cloth or sponge. Leaving flux residue on the joint can lead to corrosion over time, so thorough cleaning is essential.
It is important to note that proper safety precautions should be followed during the soldering process. This includes wearing protective gloves, goggles, and working in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhalation of toxic fumes from flux or solder.
Now that we understand the soldering process, let’s explore the importance of flux in plumbing and why it is a critical component in achieving secure and long-lasting plumbing connections.
Importance of Flux in Plumbing
Flux plays a crucial role in plumbing, as it is a key component in achieving strong, durable, and leak-free connections. Here are some reasons why flux is important in plumbing:
- Surface preparation: Flux acts as a cleaning agent, removing dirt, grease, and oxidation from the metal surfaces to be soldered. This ensures a clean and uniform surface, allowing the solder to adhere properly and form a strong bond. Without flux, contaminants on the metal surfaces can hinder the soldering process, leading to weak joints or leaks.
- Oxidation prevention: Metal surfaces, such as copper or brass, can quickly oxidize when exposed to air. Oxidation creates a thin layer of corrosion that can interfere with the soldering process and weaken the joint over time. Flux forms a protective barrier on the metal surfaces, preventing oxidation during the soldering process and ensuring a clean and conducive surface for the solder to flow.
- Enhanced wetting: Flux helps improve the wetting ability of solder. Wetting refers to the ability of the molten solder to flow and spread on the metal surfaces. The flux reduces the surface tension of the solder, allowing it to spread more evenly and penetrate tight joints. This results in improved contact between the solder and the metal, creating stronger bonds and better overall soldering quality.
- Capillary action: Flux promotes capillary action, which is the ability of the molten solder to flow into small gaps or crevices. This ensures that the solder can fill any imperfections in the joint, creating a solid and leak-free connection. The capillary action, coupled with the cleaning properties of flux, helps achieve a reliable and structurally sound joint.
- Longevity and reliability: By using flux during the soldering process, you are ensuring the longevity and reliability of the plumbing connections. Flux helps create a strong bond between the metal surfaces, minimizing the risk of leaks or separation. It also prevents future corrosion by removing contaminants and oxidation, ensuring that the joints remain secure and durable over time.
It is important to choose the right type of flux for your specific plumbing project to maximize its effectiveness. Different metals and soldering processes may require different types of flux. Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations to ensure compatibility and optimal results.
Next, let’s explore the many benefits of using flux in plumbing and how it can contribute to the overall success of your plumbing projects.
Flux is used in plumbing to clean and prepare metal surfaces for soldering. It helps the solder adhere to the pipes and fittings, creating a strong and leak-free joint. Always use the appropriate type of flux for the specific metal being soldered.
Read more: What Is ABS Used For In Plumbing
Benefits of Using Flux in Plumbing
Using flux in plumbing offers several benefits that contribute to the overall success and reliability of your plumbing projects. Here are some key advantages of using flux:
- Improved solder flow: Flux helps to improve the flow of solder by reducing its surface tension. This allows the molten solder to spread more evenly and penetrate tight spaces, ensuring better coverage and filling of the joint. The improved flow also facilitates the formation of strong bonds between the metal surfaces, creating secure and leak-free connections.
- Clean and uniform surfaces: Flux acts as a cleaning agent, removing contaminants such as dirt, grease, and oxidation from the metal surfaces. This ensures that the solder adheres properly to the metal, without any hindrance from impurities. The result is clean and uniform surfaces, which are essential for achieving strong and reliable plumbing connections.
- Prevention of oxidation: Metals like copper and brass are prone to oxidation when exposed to air. Flux creates a protective barrier on the metal surfaces, preventing oxidation during the soldering process. By eliminating the oxidation layer, flux ensures better adhesion and enhances the longevity of the joint.
- Stronger and more durable connections: The combination of improved solder flow, clean surfaces, and prevention of oxidation leads to stronger and more durable connections. Flux ensures that the solder penetrates into the joint and achieves maximum contact with the metal surfaces. This results in solid bonds that can withstand the stresses and pressures of daily use, reducing the risk of leaks or joint failures.
- Increased efficiency: Using flux in plumbing can increase the efficiency of the soldering process. Flux helps to reduce the time and effort required to achieve proper bonding by promoting the flow of solder and enhancing the wetting ability. This can lead to faster and more efficient completion of plumbing projects.
- Compatibility with different metals: Flux is available in various formulations to suit different types of metals and soldering processes. This makes it versatile and compatible with a wide range of plumbing materials, including copper, brass, and stainless steel. Choosing the right flux for your specific application ensures optimal performance and compatibility.
When using flux, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines. This includes applying the appropriate amount of flux, ensuring even coverage on the joint, and properly cleaning any flux residue after soldering.
Now that we understand the benefits of using flux in plumbing, let’s move on to discussing some safety precautions that should be taken when working with flux.
Safety Precautions When Using Flux in Plumbing
While flux is an essential component in plumbing, it is important to exercise caution and follow safety guidelines when working with it. Here are some important safety precautions to keep in mind when using flux in plumbing:
- Read and follow manufacturer instructions: Before using any flux product, carefully read and follow the manufacturer’s instructions. This includes information on proper application, storage, handling, and disposal.
- Use in a well-ventilated area: Flux can release fumes during the soldering process, which can be harmful if inhaled. Always work in a well-ventilated area, opening windows or using exhaust fans to ensure proper air circulation.
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE): When working with flux, it is important to wear protective equipment, such as gloves and safety goggles, to protect your skin and eyes from potential hazards.
- Avoid ingestion and skin contact: Flux can be toxic if ingested or if it comes into contact with your skin. Avoid touching your face or mouth with contaminated hands and take care to prevent any skin contact with the flux. If accidental ingestion or skin contact occurs, seek medical help immediately.
- Store flux properly: When not in use, store flux in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area away from heat sources, flammable materials, and direct sunlight. Always keep flux containers tightly sealed to prevent moisture or contamination.
- Dispose of flux properly: Follow local regulations for the proper disposal of flux and its packaging. Do not pour flux down the drain or dispose of it with regular household waste. Contact your local waste management authorities for guidance on safe disposal methods.
- Avoid open flames: When using flux, be cautious around open flames or heat sources. Flux is flammable, and it is crucial to avoid exposing it to direct flame or excessive heat, as it can ignite or release harmful gases.
- Keep away from children and pets: Store flux out of reach of children and pets to prevent accidental ingestion or exposure. Ensure that the work area remains inaccessible to them during the soldering process as well.
By following these safety precautions, you can ensure a safe working environment and minimize potential risks associated with using flux in plumbing projects.
Now that we have covered the safety precautions, let’s discuss some common mistakes to avoid when using flux in plumbing.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Flux in Plumbing
While using flux in plumbing is essential for achieving strong and reliable connections, there are some common mistakes that should be avoided to ensure optimal results. By being aware of these mistakes, you can enhance your soldering technique and maintain the integrity of your plumbing projects. Here are some common mistakes to avoid when using flux in plumbing:
- Insufficient flux application: Applying an inadequate amount of flux or unevenly distributing it on the joint can result in poor solder flow and weak connections. Be sure to apply an even and sufficient layer of flux to ensure optimal cleaning and bonding.
- Using the wrong type of flux: Different metals and soldering processes require specific types of flux. Using the wrong type of flux can lead to compatibility issues and compromised connections. Always choose the appropriate flux for your specific plumbing materials and soldering requirements.
- Failure to clean the surfaces properly: Flux is most effective when applied to clean and properly prepared surfaces. Failing to adequately clean the metal surfaces before applying flux can prevent proper adhesion and compromise the strength of the joint.
- Overheating the joint: Excessive heat can damage the joint or surrounding components, causing leaks or weakening the joint. It is important to apply heat evenly and avoid prolonged exposure to high temperatures, ensuring that the solder melts and flows smoothly without overheating the area.
- Applying solder directly to the heat source: Applying solder directly to the heat source instead of to the heated joint can result in insufficient bonding or incomplete filling of the joint. Always apply solder directly to the heated joint to achieve maximum adhesion and proper flow.
- Ignoring safety precautions: Working with flux involves potential hazards, such as toxic fumes or skin contact with harmful chemicals. Ignoring safety precautions, such as proper ventilation or wearing protective equipment, can increase the risk of health issues. Always follow safety guidelines to protect yourself and maintain a safe working environment.
- Leaving flux residue on the joint: Flux residue left on the joint can lead to corrosion or blockages in the plumbing system over time. After soldering, it is essential to clean and remove any flux residue using a damp cloth or sponge to ensure the longevity and reliability of the joint.
- Not checking for leaks: After soldering, it is crucial to carefully inspect the joints for any signs of leaks. Missing this step can result in undetected leaks, which can cause water damage and other issues. Always perform a thorough leak check to ensure the integrity of the soldered connections.
By avoiding these mistakes and following best practices, you can achieve strong, secure, and long-lasting plumbing connections with the help of flux.
Now that we have covered the common mistakes to avoid, let’s summarize the importance and benefits of using flux in plumbing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, flux plays a vital role in the world of plumbing by ensuring strong, reliable, and leak-free connections. It serves as a cleaning agent, preventing oxidation, improving solder flow, and promoting capillary action. By choosing the appropriate flux for your specific plumbing materials and following the proper soldering techniques, you can achieve secure and durable joints.
The different types of flux, such as acid flux, water soluble flux, rosin flux, and paste flux, offer versatility in catering to various plumbing needs and materials. Each type has its own advantages and considerations, so it is important to select the right flux for your specific application.
However, it is essential to exercise caution when working with flux. Following safety precautions, such as proper ventilation, wearing personal protective equipment, and storing and disposing of flux correctly, are crucial to ensure a safe working environment and to minimize health risks.
By using flux in plumbing, you can benefit from improved solder flow, clean surfaces, oxidation prevention, stronger connections, increased efficiency, and compatibility with different metals. These benefits contribute to the overall success and reliability of your plumbing projects.
Avoiding common mistakes, such as insufficient flux application or using the wrong type of flux, will help you achieve optimal results. Additionally, cleaning the surfaces properly, avoiding overheating, applying solder correctly, and performing a leak check will ensure the integrity of the soldered connections.
In the end, utilizing flux in plumbing projects is essential for creating strong and durable connections that will withstand the test of time. With proper techniques, safety precautions, and attention to detail, you can ensure the success of your plumbing projects and the satisfaction of your clients.
So, remember to choose the right flux, follow best practices, and prioritize safety as you utilize this important component in your plumbing endeavors.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is Flux Used For In Plumbing
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Is Flux Used For In Plumbing”