Home>Articles>What Was The Induction Electric Motor Used For


Articles
What Was The Induction Electric Motor Used For
Modified: October 20, 2024
Discover the history and applications of the induction electric motor in this informative article. Uncover how this innovative technology has transformed various industries.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
The induction electric motor, a key innovation in the field of electrical engineering, has revolutionized various industries and transformed the way we live and work. This remarkable invention, also known as the asynchronous motor, is widely used for its efficiency, reliability, and versatility.
Developed in the late 19th century, the induction electric motor has played a pivotal role in powering numerous applications, ranging from household appliances to industrial machinery. Its widespread adoption can be attributed to its simple design, cost-effectiveness, and ability to operate on alternating current (AC) power.
In this article, we will explore the history, principle of operation, applications, and advantages and disadvantages of the induction electric motor. By understanding the significance and applications of this groundbreaking invention, we can appreciate its impact on various aspects of our modern lives.
Key Takeaways:
- The induction electric motor, pioneered by Nikola Tesla, revolutionized industries with its efficient and reliable operation on AC power, powering everything from industrial machinery to household appliances.
- Despite limitations in starting torque and speed control, the induction electric motor’s high efficiency, reliability, and versatility make it a popular choice across industries, contributing to improved energy efficiency and reduced environmental impact.
Read more: What Electric Motor Does Tesla Use
History of the Induction Electric Motor
The development of the induction electric motor can be credited to the pioneering work of several inventors and engineers. The concept of electromagnetic induction, the fundamental principle behind this motor, was first discovered by Michael Faraday in the early 19th century. However, it was not until the late 1800s that practical induction motors were designed and produced.
One of the key figures in the development of the induction motor was Nikola Tesla. In the late 1880s, Tesla, along with his American rival Thomas Edison, engaged in the “War of Currents” in their quest to establish dominance in the field of electrical power distribution. Tesla’s invention of the polyphase AC system and his advancements in motor designs, including the induction motor, proved to be game-changing.
Tesla’s induction motor design was based on the principle of a rotating magnetic field. This concept involved the use of multiple phases of alternating current to create a magnetic field that would induce rotation in a rotor. In 1888, Tesla demonstrated the first practical AC induction motor, which was capable of driving industrial machinery efficiently and effectively.
Following Tesla’s breakthrough, the induction motor gained widespread recognition and was quickly adopted in various industries. The motor’s ability to operate on AC power made it especially advantageous, as it allowed for easy integration with the expanding AC power systems.
Over the years, advancements in materials, design, and manufacturing techniques have further improved the performance and efficiency of induction motors. Today, induction motors are available in a wide range of sizes and configurations, catering to the diverse needs of industries such as manufacturing, transportation, HVAC, and more.
The induction motor has truly stood the test of time and remains one of the most widely used electric motors in the world. Its invention and continuous development have played a significant role in revolutionizing the way we harness and utilize electrical power.
Principle of Operation
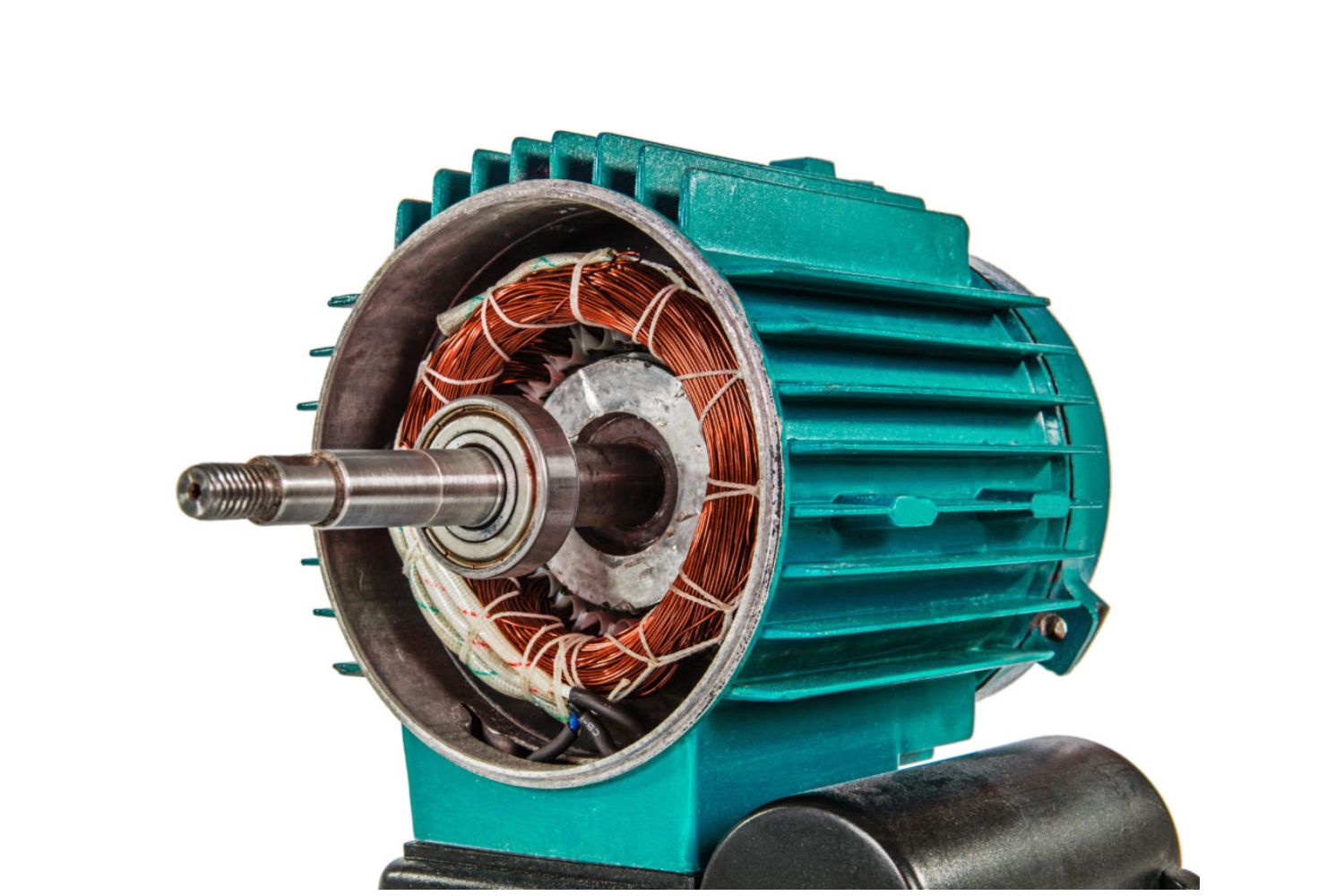
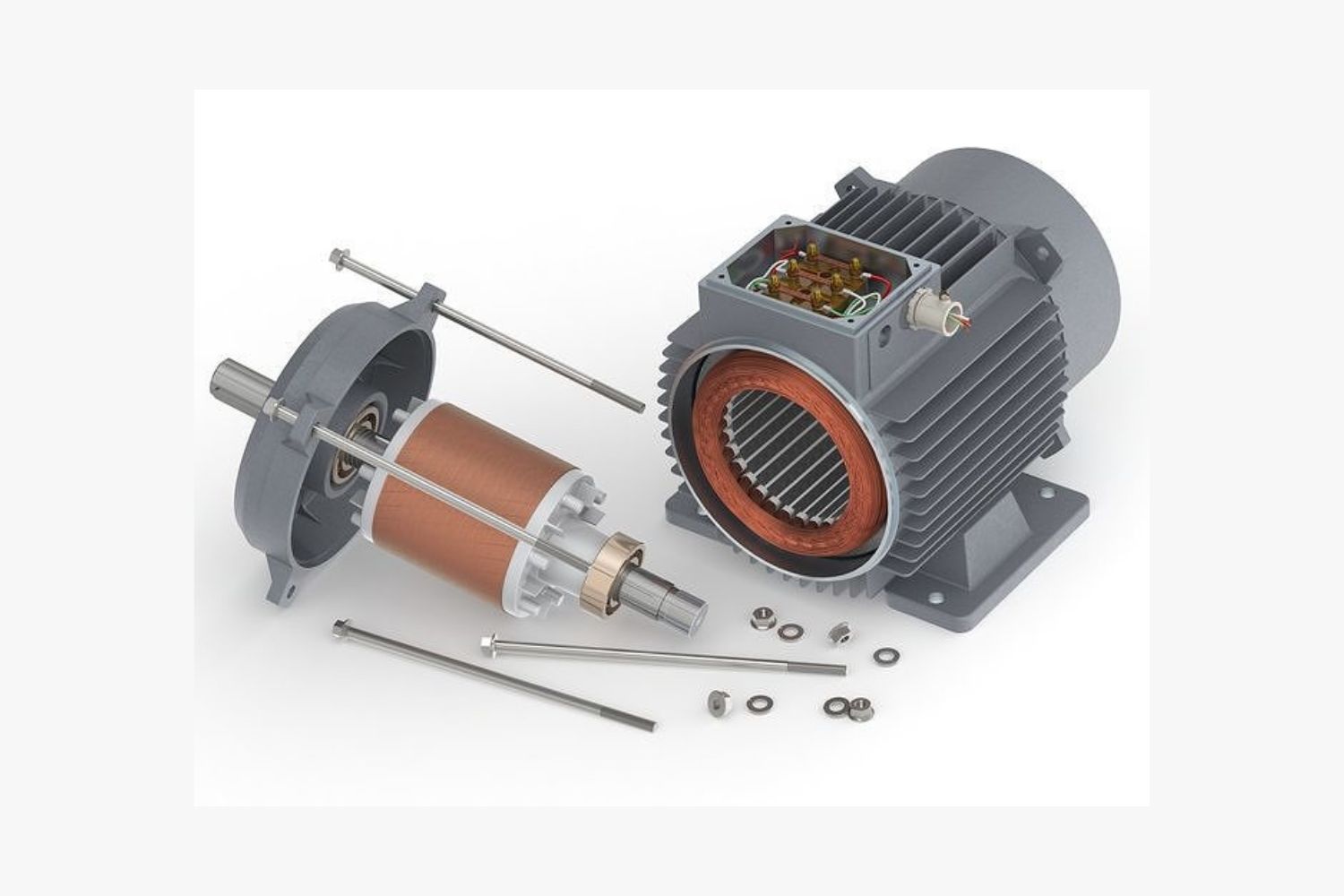
The operation of an induction electric motor is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. It consists of two main components: the stator and the rotor. The stator is the stationary part of the motor, while the rotor is the rotating part.
When an AC current is supplied to the stator windings, it creates a changing magnetic field. This magnetic field induces an electric current in the rotor, which in turn generates a magnetic field of its own. The interaction between the stator’s magnetic field and the rotor’s magnetic field causes the rotor to spin, initiating the motor’s rotation.
The rotating magnetic field produced by the stator windings is created by using multiple phases of AC power. In most induction motors, three-phase power is utilized, resulting in a three-phase motor. This three-phase power supply creates a rotating magnetic field with a specific frequency, depending on the frequency of the AC power source.
The speed at which the rotor rotates is determined by the frequency of the AC power supply and the number of poles on the motor. The synchronous speed of the motor can be calculated by dividing the frequency of the power supply by the number of poles. However, it’s important to note that due to slip, the rotor speed is always slightly lower than the synchronous speed.
The induction motor operates on the principle of asynchronous rotation, meaning the rotor speed is always slightly slower than the speed of the rotating magnetic field. This slip creates the torque necessary for the motor to perform useful work. The higher the load on the motor, the greater the slip, allowing for increased torque production.
The efficiency of an induction motor is influenced by various factors, including the design, construction, and quality of the motor. Factors such as stator and rotor material, winding configuration, and bearing quality can affect the overall performance and energy efficiency of the motor.
Overall, the principle of operation of an induction motor is simple yet effective. By harnessing the power of electromagnetic induction, these motors provide reliable and efficient rotational motion, making them a preferred choice for numerous applications across various industries.
Applications of the Induction Electric MotorThe induction electric motor finds widespread applications in various industries and sectors due to its versatility, reliability, and efficiency. Here are some of the key areas where these motors are commonly used:
- Industrial Machinery: Induction motors are extensively used in industrial machinery, such as pumps, compressors, conveyors, mixers, and fans. The motor’s ability to provide consistent torque and operate at different speeds makes it ideal for powering a wide range of equipment in factories and manufacturing facilities.
- HVAC Systems: Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems rely on induction motors for driving blowers, fans, and compressors. These motors are chosen for their energy efficiency, low noise levels, and long operating life, making them suitable for both commercial and residential HVAC applications.
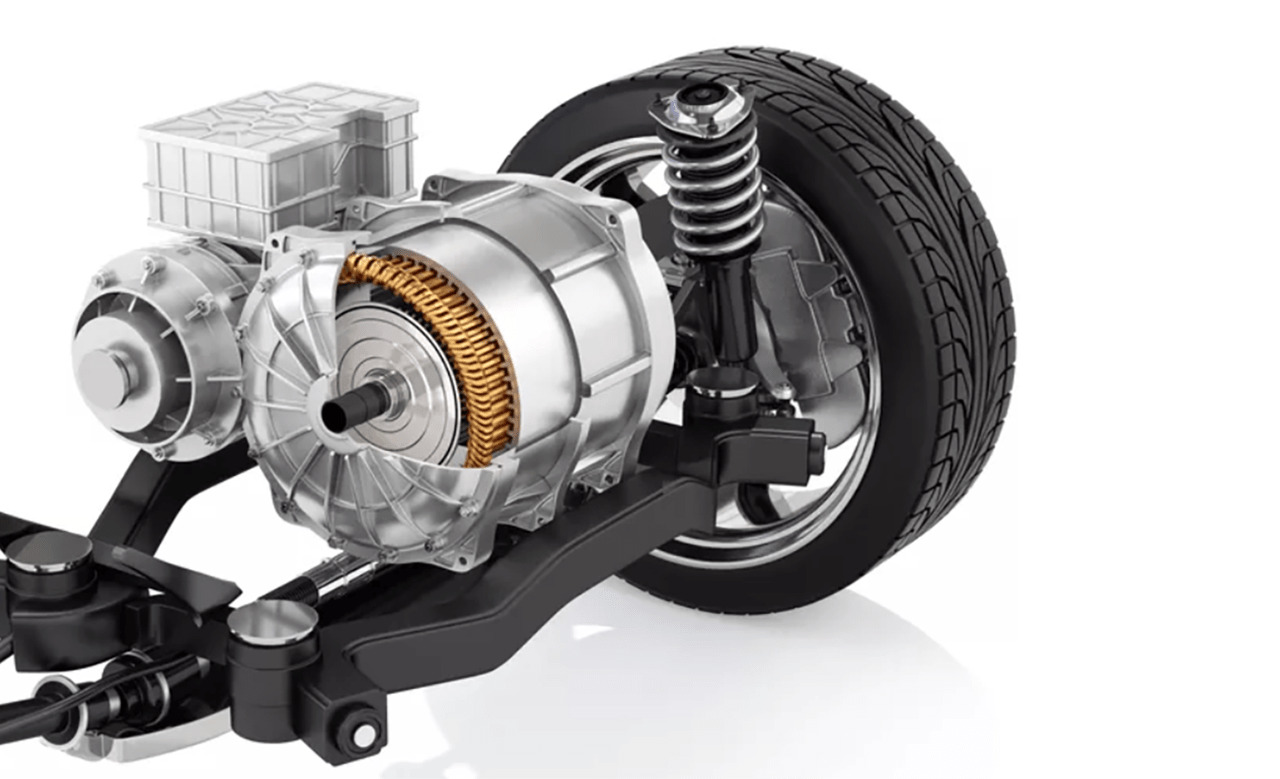
- Transportation: Induction motors are used in electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid vehicles, providing the required torque and power to propel the vehicle. Their high torque output and excellent reliability are key factors contributing to their adoption in the automotive industry.
- Power Tools: Many handheld power tools, such as drills, grinders, and saws, utilize induction motors for their compact size, high power-to-weight ratio, and durability. These motors enable efficient and precise operation of various power tools, enhancing productivity and user experience.
- Household Appliances: From refrigerators and washing machines to vacuum cleaners and ceiling fans, induction motors are widely used in numerous household appliances. Their efficient performance, low maintenance requirements, and quiet operation make them well-suited for everyday domestic use.
- Water Pumping Systems: Induction motors are commonly employed in water pumping systems for agricultural, residential, and commercial applications. These motors provide the necessary power to drive pumps and ensure reliable water supply for irrigation, municipal water distribution, and other purposes.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Induction motors are used in renewable energy systems, such as wind turbines and hydroelectric generators, to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. The robust and efficient nature of these motors allows for reliable power generation from renewable sources.
These are just a few examples of the diverse applications of induction electric motors. Their versatility and adaptability make them indispensable in various industries, playing a vital role in powering machinery, improving energy efficiency, and enhancing overall productivity.
The induction electric motor was used for a wide range of applications, including industrial machinery, household appliances, and electric vehicles. Its simple design and reliable performance made it a popular choice for many different uses.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The induction electric motor offers numerous advantages that contribute to its widespread use. However, it is not without its limitations. Let’s explore the advantages and disadvantages of induction motors:
Read more: What Is An Electric Motor Capacitor?
Advantages:
- Efficiency: Induction motors are highly efficient, with efficiency levels reaching up to 95%. This means that a large majority of the electrical energy is converted into mechanical energy, resulting in minimal energy losses during operation.
- Reliability: These motors are known for their robustness and reliability. They can withstand harsh operating conditions, such as high temperatures and vibration, without compromising performance. This reliability translates into lower maintenance requirements and longer operating life.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Induction motors are generally more cost-effective compared to other types of motors. Their simple design, easy manufacturing process, and availability of standardized components often make them a more economical choice for various applications.
- Versatility: These motors are suitable for a wide range of applications, from small household appliances to large industrial machinery. They can operate at different speeds and handle various load conditions, making them highly versatile in meeting different requirements.
- Compatibility with AC Power Systems: Induction motors are designed to operate on AC power, which is the most common form of electrical power distribution. This compatibility allows for seamless integration with existing power infrastructure in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
Disadvantages:
- Lower Starting Torque: Induction motors typically have lower starting torque compared to other motor types, such as DC motors. This can limit their use in applications that require high starting torque, such as heavy-duty machinery or equipment.
- Speed Control: Induction motors have limited speed control options, especially when compared to motors like DC or synchronous motors. While variable frequency drives (VFDs) can provide some speed control, it may not be as precise or flexible as with other motor types.
- Power Factor: Induction motors can have a lower power factor, which can lead to wasted energy and higher energy costs. However, power factor correction devices can be used to mitigate this issue and improve energy efficiency.
- Complex Motor Control: Controlling the speed, torque, and direction of induction motors can be more complex compared to other motor types. Additional equipment, such as VFDs or motor starters, may be required for precise motor control, adding complexity and cost to the system.
- Harmonics and Electromagnetic Interference: Induction motors can produce harmonic currents that may cause interference with other electrical equipment, affecting the overall power quality. Adding filters or incorporating proper grounding and shielding techniques can help mitigate this issue.
Despite these limitations, the advantages of induction motors outweigh the disadvantages in many applications. Their high efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness make them a popular choice for a wide range of industries and power systems.
Conclusion
The induction electric motor has had a profound impact on various industries and everyday life. Its development and widespread adoption have revolutionized the way we harness and utilize electrical power. From industrial machinery to household appliances, induction motors have become an integral part of numerous applications due to their efficiency, reliability, and versatility.
Throughout history, the induction motor has undergone continuous refinement and improvement, resulting in higher performance and energy efficiency. Its simple yet effective design, based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, allows for seamless integration with AC power systems and provides reliable rotational motion.
Induction motors offer several advantages, such as high efficiency, reliability, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with existing power infrastructure. They are known for their versatility, being able to operate at different speeds and handle various load conditions, catering to a wide range of applications.
While they have some limitations, including lower starting torque and limited speed control, these can often be mitigated by using additional components and control systems. Overall, the advantages of induction motors surpass their disadvantages in many situations.
The induction motor’s significance extends beyond industrial and commercial settings. It plays a vital role in powering household appliances, HVAC systems, transportation, and renewable energy systems, contributing to improved energy efficiency and reduced environmental impact.
In conclusion, the induction electric motor has been a game-changer in the field of electrical engineering. Its invention and subsequent advancements have transformed various industries, offering efficient and reliable motor solutions. As technology continues to evolve, the induction motor will continue to play an essential role in powering the world we live in.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Was The Induction Electric Motor Used For
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “What Was The Induction Electric Motor Used For”