Home>diy>Architecture & Design>What Does CAD Stand For


Architecture & Design
What Does CAD Stand For
Modified: January 9, 2024
Discover what CAD stands for and its significance in architecture design. Gain insights into the world of computer-aided drafting and the tools used in this field.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
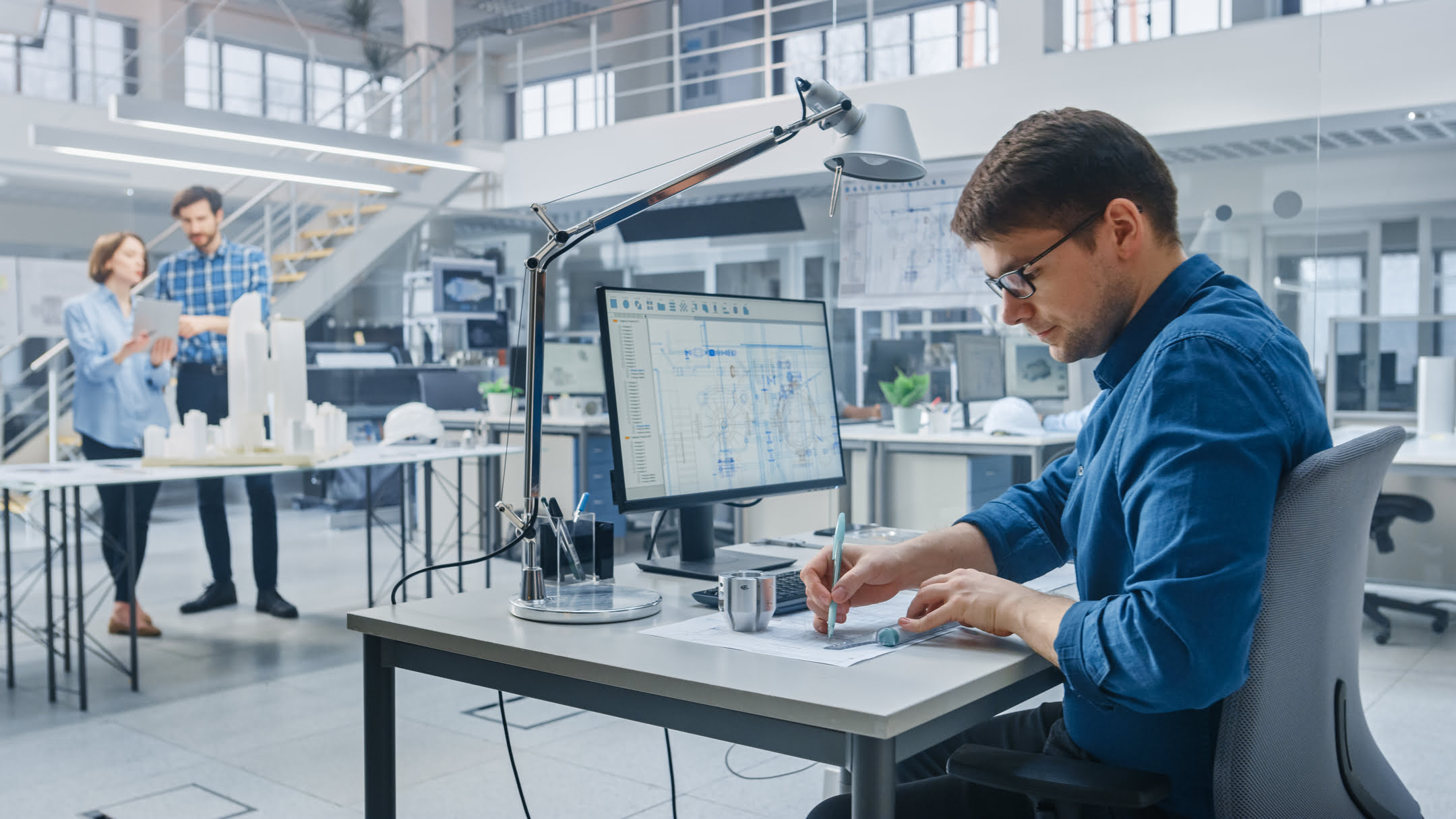
When it comes to architecture and design, precision and accuracy are of utmost importance. Designers and engineers need tools that can assist them in creating intricate and detailed designs while also streamlining the workflow. This is where Computer-Aided Design (CAD) comes into play.
CAD is a revolutionary technology that has completely transformed the way architectural and design projects are executed. By leveraging the power of computers, CAD software allows designers to create, edit, and manipulate intricate designs with ease, increasing efficiency and reducing errors.
In this article, we will explore the world of CAD, delving into its definition, history, applications, advantages, and disadvantages. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of this game-changing technology and how it has revolutionized the architecture and design industry.
Key Takeaways:
- CAD, or Computer-Aided Design, revolutionizes the architecture and design industry by offering precision, efficiency, and collaboration, leading to better design decisions and cost savings.
- While CAD offers numerous benefits, such as precision, efficiency, and visualization, it also comes with limitations like high initial costs, a learning curve, and potential compatibility issues.
Read more: What Does The Abbreviation CAD Stand For
Definition of CAD
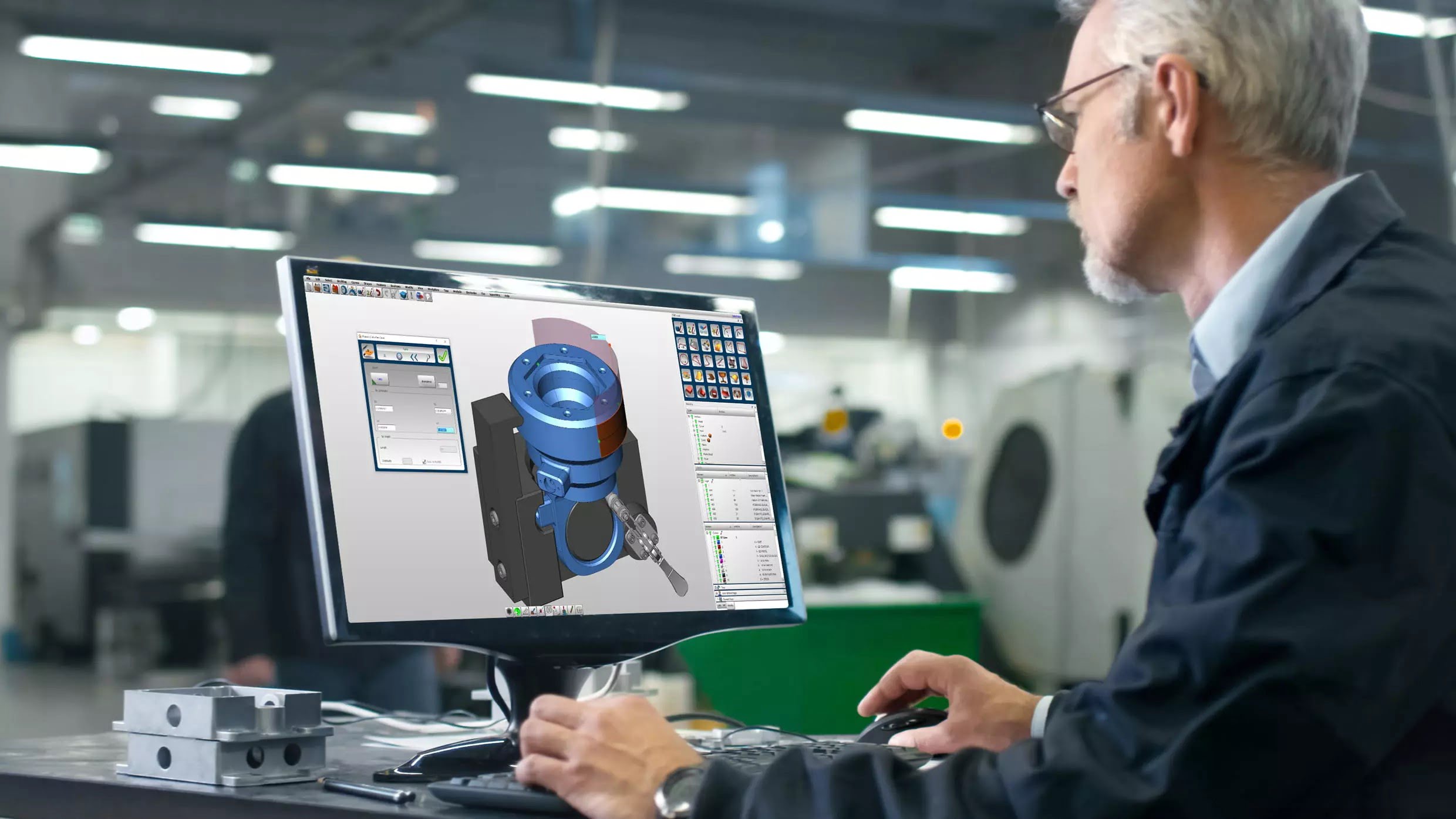
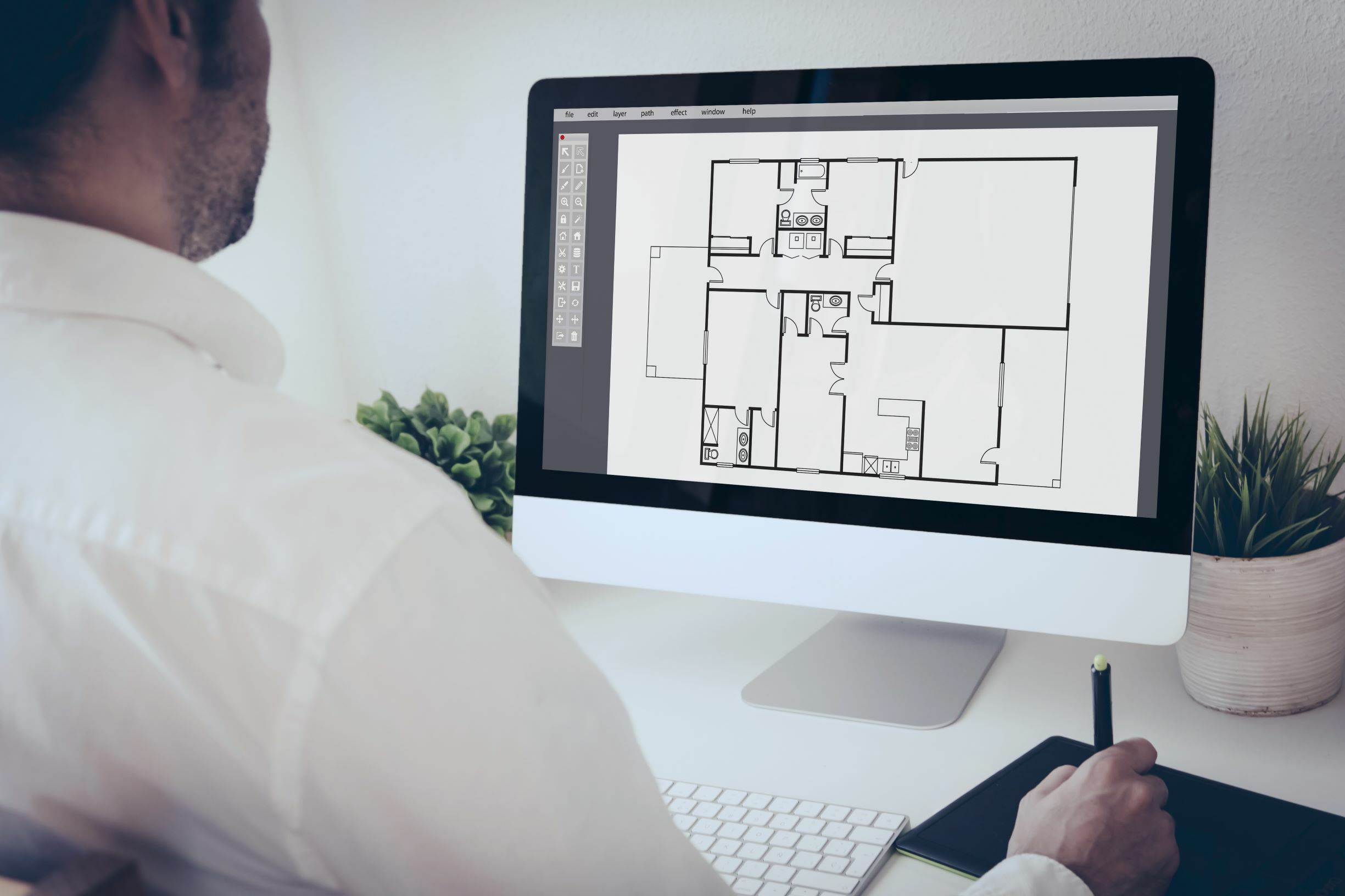
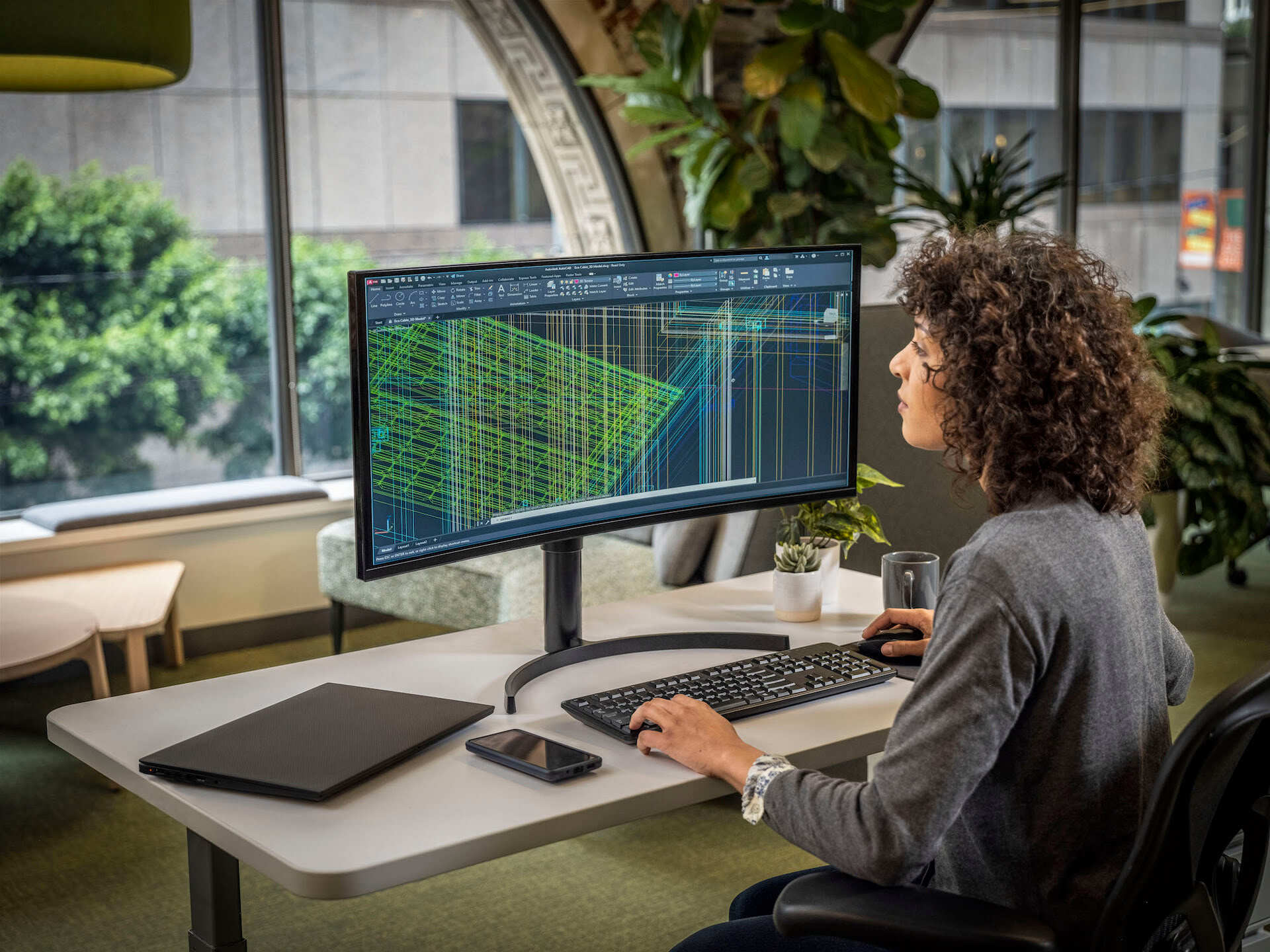
CAD stands for Computer-Aided Design. It refers to the use of computer software applications that enable architects, engineers, and designers to create, modify, analyze, and optimize designs for various industries. CAD software provides a digital platform where professionals can develop precise and accurate 2D and 3D models of objects, buildings, and structures.
The core principle behind CAD is the automation of manual drafting processes. In the past, architects and designers would create their designs manually using pencils, rulers, and drafting boards. This manual approach was time-consuming, prone to errors, and limited in terms of modifications and iterations. CAD software revolutionized this process by offering a digital medium where designs could be created, modified, and visualized in real-time.
CAD software offers a wide range of tools and features that enable designers to create detailed and complex designs. These tools include drawing tools, modeling tools, rendering capabilities, and analysis features. They allow designers to create precise blueprints, generate 3D renderings, simulate real-world conditions, and perform detailed analysis on the designs.
CAD is not limited to architecture and design; it is widely used across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, manufacturing, and construction. It has become an indispensable tool for professionals who rely on accurate and efficient design processes.
History of CAD
The origins of CAD can be traced back to the 1960s when the first computer-based drafting systems were developed. These early systems were primarily used for creating technical drawings and blueprints. The early versions of CAD software were limited in functionality and required expensive mainframe computers to run.
With the advancement of computer technology, CAD software became more powerful and accessible. In the 1970s, the introduction of interactive graphical user interfaces (GUI) revolutionized the CAD industry. This allowed designers to interact with the software using a mouse, making the design process more intuitive and user-friendly.
In the 1980s, CAD software started to gain widespread adoption as personal computers became more affordable and powerful. This led to the development of CAD software for specific industries, tailored to the unique needs and requirements of architects, engineers, and designers.
Throughout the 1990s and 2000s, CAD software continued to evolve, incorporating advanced features such as 3D modeling, parametric design, and simulation capabilities. These advancements further enhanced the design process, enabling designers to create highly complex and realistic models.
Today, CAD software has become an integral part of the design and manufacturing process. It has evolved into a multi-billion dollar industry, with numerous software providers offering a wide range of CAD applications. The software has become more user-friendly, powerful, and accessible, allowing designers to bring their ideas to life with unprecedented precision and efficiency.
Looking ahead, CAD software is expected to continue evolving, driven by advancements in technologies such as virtual reality (VR) and artificial intelligence (AI). These emerging technologies will further enhance the capabilities of CAD software, enabling designers to push the boundaries of creativity and innovation.
Applications of CAD
CAD software finds application in various industries, playing a crucial role in streamlining the design process and improving overall productivity. Here are some key industries where CAD is widely used:
- Architecture: CAD has revolutionized architectural design, allowing architects to create detailed 2D and 3D models of buildings, interiors, and landscapes. It facilitates better visualization, collaboration, and accuracy in the design process.
- Engineering: CAD is extensively used in engineering disciplines such as mechanical, civil, electrical, and industrial engineering. It assists engineers in designing components, systems, and infrastructure, optimizing performance and reducing manufacturing costs.
- Manufacturing: CAD software is essential for product design and manufacturing. It aids in creating 3D models of products, generating accurate manufacturing specifications, and facilitating efficient production processes.
- Automotive: CAD is heavily utilized in the automotive industry for designing vehicles, components, and systems. It enables engineers to simulate and analyze various vehicle aspects, such as aerodynamics, structural integrity, and ergonomics.
- Aerospace: CAD plays a critical role in aerospace engineering, allowing designers to develop complex aircraft designs, simulate flight conditions, and analyze structural integrity. It enables the creation of lightweight and efficient aircraft.
- Electronics: CAD software is essential for designing electronic circuits and printed circuit boards (PCBs). It facilitates schematic design, component placement, and routing, ensuring efficient and optimized electronic systems.
- Construction: CAD is used in the construction industry for creating detailed architectural plans, producing accurate quantity takeoffs, and facilitating better coordination between various stakeholders.
These are just a few examples of how CAD is applied across industries. Its versatility and flexibility make it an invaluable tool for designers, engineers, and architects, enabling them to bring their ideas to life with precision and efficiency.
CAD stands for Computer-Aided Design. It is a technology that allows engineers, architects, and designers to create and modify designs digitally, improving accuracy and efficiency in the design process.
Advantages of CAD
CAD software offers several advantages over traditional manual drafting methods. Here are some key benefits of using CAD in the design process:
- Precision: CAD allows for highly accurate and precise design, ensuring that measurements and dimensions are exact. This eliminates the risk of human error common in manual drafting, resulting in higher quality and more reliable designs.
- Efficiency: CAD significantly reduces design time compared to manual drafting. It offers a range of tools and features that automate repetitive tasks, enabling designers to work faster and more efficiently. Modifications and iterations can also be done quickly and easily.
- Visualization: CAD provides realistic, 3D visualizations of designs, allowing designers and clients to better understand and visualize the final product. This enhances communication and decision-making during the design process.
- Collaboration: CAD software facilitates collaboration between various stakeholders involved in the design process. Design files can be easily shared, reviewed, and modified, allowing for seamless communication and coordination.
- Simulation and Analysis: CAD software enables designers to simulate real-world conditions and perform detailed analysis on designs. This allows for optimization, testing, and evaluation of design performance, leading to better and more informed design decisions.
- Documentation: CAD software generates accurate and comprehensive documentation, including drawings, specifications, and Bills of Materials (BOM). This simplifies the manufacturing and construction processes, ensuring accuracy and reducing errors.
- Cost Savings: CAD streamlines the design process, reduces errors, and minimizes rework, resulting in significant cost savings. It also assists in optimizing material usage and manufacturing processes, further reducing costs.
The advantages of CAD make it an indispensable tool for designers and engineers in various industries. It improves productivity, accuracy, and overall design quality, leading to better and more efficient project outcomes.
Read more: What Does CAD Mean In TinkerCAD
Disadvantages of CAD
While CAD offers numerous benefits, it is not without its limitations. Here are some disadvantages of using CAD software:
- High Initial Cost: CAD software can be expensive, especially for premium versions that offer advanced features. Additionally, the hardware required to run CAD software, such as high-performance computers and graphics cards, can also add to the cost.
- Steep Learning Curve: CAD software can have a steep learning curve, especially for beginners. Mastering the various tools, functions, and workflows of the software may require extensive training and experience.
- Reliance on Technology: CAD software is heavily dependent on technology and can be vulnerable to technical glitches or system failures. This can lead to data loss, project delays, and disruption in the design process.
- Limited Creativity: While CAD software allows for precise and accurate designs, some argue that it can limit creativity compared to traditional hand-drawn methods. The software’s reliance on grids, measurements, and standardized shapes can restrict artistic freedom.
- Compatibility Issues: CAD software file formats may not always be compatible with other software applications, causing difficulties when sharing or collaborating with others who use different CAD software or tools.
- Dependency on Software Updates: CAD software continually evolves, with regular updates and new versions being released. Users may need to regularly upgrade their software to access new features, which can be costly and time-consuming.
- Potential for Design Errors: While CAD minimizes human error, design errors can still occur due to incorrect input or improper use of the software. It’s crucial to carefully review and validate designs to ensure accuracy.
Despite these disadvantages, CAD remains an essential tool in the design industry, offering significant advantages that outweigh the limitations. It is important for users to be aware of these limitations and take necessary precautions to mitigate their impact.
Conclusion
CAD has revolutionized the architecture and design industry, offering a powerful and efficient way to create, modify, and visualize intricate designs. It has become an indispensable tool for designers, engineers, and architects across various industries.
The advantages of CAD, including precision, efficiency, visualization, collaboration, and simulation, have significantly improved the design process. It has streamlined workflows, reduced errors, and enhanced communication among stakeholders. The ability to generate accurate documentation and perform analysis has led to better design decisions and cost savings.
However, CAD does have its limitations, such as high initial costs, a learning curve, reliance on technology, and potential compatibility issues. It is important for users to be aware of these limitations and take necessary precautions to overcome them.
Looking towards the future, CAD is expected to continue evolving with advancements in technologies such as virtual reality (VR) and artificial intelligence (AI). These advancements will further enhance the capabilities of CAD software, enabling designers to push the boundaries of creativity and innovation.
In conclusion, CAD has transformed the way designs are created and executed. It has improved efficiency, precision, and collaboration in the design industry. With its continued development and integration of new technologies, CAD will continue to shape the future of architecture and design, driving innovation and pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Does CAD Stand For
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Does CAD Stand For”