Home>diy>Architecture & Design>In Terms Of Engineering Software, What Does CAD Stand For


Architecture & Design
In Terms Of Engineering Software, What Does CAD Stand For
Modified: May 6, 2024
Discover the meaning of CAD in engineering software, specifically in the realm of architecture design. Get insights into this essential tool for professionals.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
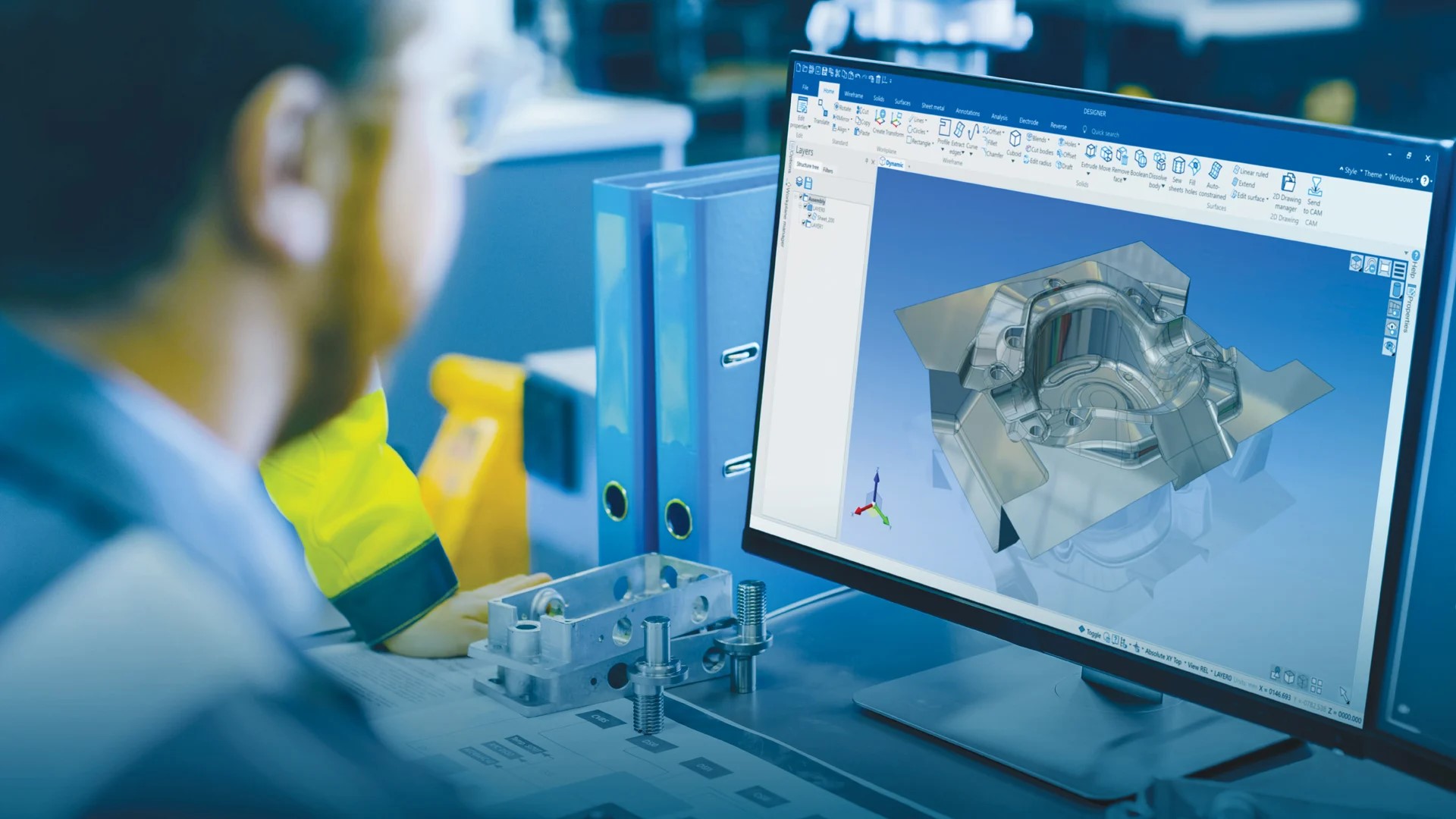
When it comes to engineering software, one term that is commonly heard is CAD. For those not familiar with the field, CAD may seem like just another acronym to decipher. But in the world of engineering design and architecture, CAD holds significant importance.
CAD, which stands for Computer-Aided Design, is a technology that has revolutionized the way architects, engineers, and designers create and develop their projects. This powerful software utilizes computer systems to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, and optimization of designs.
Over the years, CAD has become an indispensable tool, allowing professionals to generate precise and accurate drawings, 3D models, and prototypes. With its numerous capabilities and features, CAD has streamlined the design process, making it more efficient, cost-effective, and flexible.
In this article, we will delve into the world of CAD, exploring its definition, history, key features, different types of software, benefits, commonly used programs, and future trends.
Key Takeaways:
- CAD, or Computer-Aided Design, revolutionizes the design process by providing precise, efficient, and collaborative tools for architects, engineers, and designers. Its history, features, and future trends shape the future of design and engineering.
- The future of CAD technology holds exciting advancements, including AI integration, generative design, VR/AR, and sustainability focus. These innovations will reshape the design process, empower creativity, and enhance collaboration across industries.
Read more: What Are CAD Software
Definition of CAD
Computer-Aided Design, or CAD, is a technology that enables the creation, modification, and analysis of designs using computer systems. It provides a digital platform for architects, engineers, designers, and other professionals to draft, visualize, and simulate their ideas.
CAD software allows users to input design parameters and specifications, and then generates accurate and detailed drawings, models, and prototypes. These designs can range from simple 2D plans to complex 3D structures.
One of the key advantages of CAD is its ability to create precise and consistent designs. Manual drafting techniques often result in errors, whereas CAD eliminates these inconsistencies by providing tools for measurement, alignment, and geometric calculations. This precision is particularly valuable in fields where accuracy is critical, such as architecture, aerospace, and automotive engineering.
Additionally, CAD software enables quick iterations and modifications. Design changes can be implemented with a few clicks, eliminating the need to start from scratch. This not only saves time but also allows designers to explore different possibilities and refine their concepts.
Furthermore, CAD offers a range of tools and features to enhance design visualization and communication. Interactive 3D models, photorealistic renderings, and virtual simulations help stakeholders better understand the final product before construction or manufacturing begins.
In summary, CAD is a digital design tool that utilizes computer systems to create, modify, and analyze designs. It improves accuracy, efficiency, and communication, making it an essential tool in the field of engineering and design.
History of CAD
The history of CAD can be traced back to the early 1960s, when Ivan Sutherland developed the revolutionary software called Sketchpad. While Sketchpad was limited in its capabilities and could only produce simple drawings, it laid the foundation for computer-based design systems.
As computer technology advanced, CAD software became more powerful and accessible. In the 1970s, the emergence of minicomputers paved the way for CAD systems to be used in industries such as aerospace and automotive engineering.
By the 1980s, CAD software had evolved to include 2D drafting capabilities. This enabled engineers and designers to create detailed technical drawings with ease. The introduction of graphical user interfaces (GUIs) in CAD software further enhanced usability and productivity.
In the 1990s, the advent of 3D modeling revolutionized the way designs were conceptualized and visualized. With 3D CAD software, designers could create virtual models of objects or environments, allowing for more accurate representations and better analysis of designs.
Today, CAD software has become an integral part of various industries, including architecture, civil engineering, industrial design, and manufacturing. It has evolved to include advanced features such as parametric modeling, simulation, and collaboration tools.
Notably, the rise of cloud computing has enabled CAD systems to become more accessible and collaborative. Designers can now work seamlessly across different geographic locations, sharing and collaborating on projects in real-time.
Looking to the future, CAD technology is expected to continue advancing. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning is set to bring further automation and intelligence to the design process. Virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR) technologies are also poised to shape the future of CAD, offering immersive design experiences and enhanced project visualization.
In summary, the history of CAD spans several decades of innovation and technological advancements. From humble beginnings to sophisticated software systems, CAD has transformed the way designs are created, communicated, and realized.
Key Features of CAD Software
CAD software offers a wide range of features and tools that empower designers and engineers to create, modify, and analyze their designs with precision and efficiency. Here are some key features commonly found in CAD software:
- Drawing Tools: CAD software provides an extensive set of drawing tools that allow users to create accurate and detailed drawings. These tools include lines, arcs, circles, ellipses, and polygons.
- 3D Modeling: CAD software enables the creation of complex 3D models. Users can manipulate 3D objects, applying transformations, and adding textures, materials, and lighting effects to achieve realistic representations.
- Parametric Modeling: One of the most powerful features of CAD software is parametric modeling. It allows designers to define and control parameters such as dimensions, constraints, and relationships. Modifying one parameter automatically updates related elements, reducing the need for manual adjustments.
- Simulation and Analysis: CAD software often includes simulation and analysis capabilities. This allows designers to simulate real-world conditions and test the performance, functionality, and safety of their designs. Examples include stress analysis, fluid flow simulation, and thermal analysis.
- Assembly Design: CAD software facilitates the creation and management of assemblies, where multiple parts come together to form a larger structure. Designers can assemble components, define relationships, and check for interference or clearance issues.
- Collaboration: CAD software offers collaboration tools to foster teamwork and communication among design teams. Users can share design files, annotate, and provide feedback, ensuring smooth collaboration and reducing errors.
- Documentation and Annotation: CAD software allows designers to generate detailed documentation, including dimensioning, annotations, titles, and labels. This ensures that designs are accurately communicated to stakeholders and can be easily understood by manufacturers or construction teams.
- Customization and Automation: CAD software often provides customization options to tailor the software to specific workflows and requirements. Users can create macros, scripts, and custom commands to automate repetitive tasks and improve productivity.
- Compatibility: CAD software supports various file formats, allowing seamless integration with other software and compatibility with different design tools and equipment. This facilitates collaboration with stakeholders and suppliers using different software platforms.
These are just some of the key features that make CAD software an indispensable tool in engineering and design. The continuous advancements in CAD technology ensure that professionals can design and develop their projects with accuracy, efficiency, and innovation.
Different Types of CAD Software
CAD software comes in various forms, each tailored to specific industries, design requirements, and levels of complexity. Here are some of the different types of CAD software:
- 2D CAD: 2D CAD software focuses on creating and editing two-dimensional drawings. It is commonly used in fields such as architectural drafting, mechanical engineering, and electrical design. 2D CAD software provides tools for creating precise technical drawings, floor plans, schematics, and diagrams.
- 3D CAD: 3D CAD software allows designers to create and manipulate three-dimensional models. It is extensively used in industries such as product design, industrial engineering, and animation. With 3D CAD software, designers can visualize their concepts in realistic 3D representations, adding depth, textures, and lighting effects.
- Parametric CAD: Parametric CAD software enables designers to create models based on parameters and constraints. Changes made to one parameter automatically update related elements, streamlining the design process and facilitating design variations. Parametric CAD is particularly useful for complex designs and iterative workflows.
- Building Information Modeling (BIM): BIM software goes beyond traditional CAD by incorporating additional data and information about a building or infrastructure project. It allows for the creation of intelligent 3D models that store information about the components, materials, and specifications. BIM software is widely used in architecture, construction, and facility management.
- Rendering and Visualization Software: Rendering and visualization software enhances the visual representation of CAD models. It adds realistic lighting, textures, and shading to create photorealistic images or animations. This type of software is commonly used in industries like architecture, interior design, and marketing.
- Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) Software: CAE software focuses on analyzing and simulating the performance of designs under various conditions. It includes tools for finite element analysis (FEA), computational fluid dynamics (CFD), and other simulation techniques. CAE software helps engineers optimize designs for structural integrity, heat transfer, fluid flow, and other factors.
- Electronic Design Automation (EDA) Software: EDA software is specific to the field of electronic circuit design. It enables engineers to design and simulate electronic circuits, use integrated circuit (IC) layout tools, perform analysis, and generate manufacturing files. EDA software is integral to the development of electronic devices and systems.
- Industrial Design Software: Industrial design software focuses on creating aesthetically pleasing and ergonomic designs for products. It includes tools for creating concept sketches, rendering 3D models, and analyzing form and function. This type of software is commonly used in industries such as consumer product design, automotive design, and furniture design.
These are just a few examples of the different types of CAD software available in the market. The choice of software depends on the specific requirements of the industry, the complexity of the design, and the desired functionality and capabilities.
CAD stands for Computer-Aided Design. It is a software used by engineers to create, modify, analyze, and optimize designs for products and structures.
Read more: What Is NX CAD Software
Benefits of Using CAD Software
CAD software has revolutionized the field of design and engineering by providing numerous benefits that greatly enhance the design process. Here are some key advantages of using CAD software:
- Increased Productivity: CAD software allows designers to work more efficiently and accurately. With features such as parametric modeling and design automation, repetitive tasks can be automated, saving time and reducing errors.
- Improved Accuracy and Precision: CAD software enables precise and accurate designs. Measurement tools, snap-to-grid features, and geometric constraints ensure that designs meet exact specifications, minimizing potential errors and issues.
- Quick Iterations and Modifications: CAD software allows for easy modification and iteration of designs. Design changes can be made quickly, eliminating the need to start from scratch. This flexibility allows for exploration of multiple design options and rapid prototyping.
- Enhanced Visualization: CAD software provides powerful visualization capabilities. Designers can create realistic 3D models, renderings, and animations that help stakeholders visualize the final product before it is built. This enhances communication and understanding of the design intent.
- Better Collaboration: CAD software facilitates seamless collaboration among team members. Design files can be easily shared, reviewed, and commented on, enabling effective communication and coordination between designers, engineers, and stakeholders.
- Cost and Time Savings: CAD software can lead to significant cost and time savings in the design and development process. Design errors can be caught early through simulations and analysis, reducing the need for costly redesigns later on. Additionally, faster design iterations and streamlined workflows result in shorter project timelines.
- Improved Documentation: CAD software generates accurate and detailed documentation, including drawings, annotations, and specifications. This documentation provides a comprehensive and standardized record of the design, facilitating manufacturing, construction, and maintenance processes.
- Ease of Design Analysis: CAD software integrates analysis tools for various engineering disciplines. Designers can simulate and analyze factors such as structural integrity, thermal performance, and fluid flow. This allows for optimization and refinement of designs before they are physically constructed.
- Efficient Design Data Management: CAD software includes tools for managing and organizing design data. Versions, revisions, and changes can be tracked, ensuring that the most up-to-date design files are used. This streamlines the design process and minimizes confusion and errors caused by working with outdated information.
- Sustainability and Environmental Considerations: CAD software enables designers to optimize designs for energy efficiency, material usage, and environmental impact. By simulating and analyzing performance factors, designers can create more sustainable and environmentally-friendly designs.
These benefits highlight the tremendous advantages that CAD software brings to the design and engineering fields. From increased productivity and accuracy to improved collaboration and cost savings, CAD software has become an essential tool for professionals in various industries.
Commonly Used CAD Software Programs
There are several CAD software programs available in the market, each offering unique features and capabilities. Here are some of the commonly used CAD software programs:
- AutoCAD: AutoCAD is one of the most popular and widely used CAD software programs. Developed by Autodesk, it offers a comprehensive set of tools for 2D drafting, 3D modeling, and documentation. AutoCAD is widely used in architecture, engineering, and construction industries.
- SolidWorks: SolidWorks is a powerful 3D CAD software program known for its robust design and simulation capabilities. It is commonly used in mechanical design, product development, and manufacturing industries. SolidWorks offers a user-friendly interface and a wide range of tools for creating complex 3D models.
- CATIA: CATIA, developed by Dassault Systèmes, is a comprehensive CAD software program used in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and industrial design. It offers advanced capabilities for 3D modeling, simulation, and collaborative design.
- PTC Creo: PTC Creo, formerly known as Pro/ENGINEER, is a CAD software program that provides a complete suite of design, analysis, and manufacturing tools. It is widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer products. PTC Creo offers parametric modeling, simulation, and advanced assembly design capabilities.
- Revit: Revit, also developed by Autodesk, is a leading BIM (Building Information Modeling) software program. It is extensively used in the architecture, engineering, and construction industries for creating intelligent 3D models that store building data. Revit enables efficient collaboration and coordination among project stakeholders.
- Autodesk Inventor: Autodesk Inventor is a 3D CAD software program primarily used for mechanical design and product development. It offers powerful parametric modeling, simulation, and visualization tools. Autodesk Inventor is known for its ability to integrate with other design and manufacturing software.
- SketchUp: SketchUp is a user-friendly 3D CAD software program commonly used in architecture, interior design, and construction. It provides intuitive tools for quickly creating 3D models and visualizing design ideas. SketchUp is known for its ease of use and availability of a vast library of pre-built 3D models.
- Fusion 360: Fusion 360, also developed by Autodesk, is a cloud-based CAD software program that combines design, simulation, and manufacturing tools into a single platform. It is used in various industries, including product design, industrial machinery, and consumer goods.
- Siemens NX: Siemens NX is a comprehensive CAD/CAM/CAE software program known for its advanced capabilities and industry-specific solutions. It is widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and machinery. Siemens NX offers advanced 3D modeling, simulation, and manufacturing capabilities.
- Creo Parametric: Creo Parametric, developed by PTC, is a powerful parametric modeling software program used for mechanical design and product development. It offers a wide range of tools for 3D modeling, simulation, and analysis. Creo Parametric also integrates well with other PTC solutions.
These are just a few examples of the commonly used CAD software programs. The choice of software depends on the specific needs of the industry, the complexity of the design, and the desired features and capabilities.
Future Trends in CAD Technology
The ever-evolving field of CAD technology continues to bring new advancements and innovations. Here are some future trends that are shaping the future of CAD:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: The integration of AI and machine learning is expected to revolutionize CAD software. AI algorithms can automate repetitive tasks, enhance design optimization, and enable intelligent decision-making. Machine learning can analyze vast amounts of design data to identify patterns and generate optimized designs.
- Generative Design: Generative design is a cutting-edge technology that uses algorithms to generate design options based on user-defined constraints and objectives. By exploring numerous design possibilities and iterating quickly, generative design can help designers find innovative and efficient solutions that were previously unexplored.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR): VR/AR technologies are expected to play a significant role in the future of CAD. Designers will be able to immerse themselves in virtual environments, visualize designs in real-world contexts, and experience designs in interactive ways. This will enhance the design review process and facilitate better stakeholder communication and decision-making.
- Cloud-Based CAD: Cloud-based CAD software offers numerous benefits, such as increased accessibility, flexibility, and collaboration. As cloud infrastructure and connectivity continue to improve, CAD software will be increasingly hosted on the cloud, allowing for real-time collaboration, automatic software updates, and seamless integration with other cloud-based applications.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: The integration of CAD with IoT technologies will enable designers to create smart and connected products. CAD software will facilitate the design of IoT devices, where physical components and digital systems work together seamlessly. This integration will open up new possibilities for product innovation and automation.
- Mobile CAD: With the increasing power and capabilities of mobile devices, CAD software is becoming more mobile-friendly. Designers will have the flexibility to work on their projects using smartphones or tablets, allowing for on-the-go design and collaboration. Mobile CAD apps will continue to improve, offering a range of design and editing tools.
- Simulation-Driven Design: Simulation capabilities will become more integrated within CAD software, enabling designers to simulate and analyze designs in real-time. This will allow for iterative design improvements and faster decision-making, without the need to switch between software applications.
- Human-Centered Design: CAD software will increasingly focus on human-centered design principles, taking into account user experience, ergonomics, and accessibility. Features such as human body modeling, haptic feedback, and virtual reality testing will ensure that designs are optimized for end-users’ comfort and usability.
- Green Design and Sustainability: CAD software will incorporate tools and analysis capabilities to support sustainable design practices. Designers will be able to assess the environmental impact of their designs, optimize energy efficiency, and utilize sustainable materials. This will contribute to a more environmentally conscious approach to design and construction.
- Advanced Multidisciplinary Collaboration: CAD software will continue to improve collaboration among multidisciplinary teams. Cross-disciplinary design reviews, real-time collaboration, and integrated data management systems will facilitate seamless communication and information exchange, enhancing productivity and synergy among team members.
These future trends in CAD technology hold the potential to reshape the design process and revolutionize multiple industries. As technology continues to advance, CAD software will empower designers and engineers with powerful tools, automation, and intelligent capabilities to bring their ideas to life.
Conclusion
CAD technology has undoubtedly transformed the way architecture, engineering, and design are approached. From its early beginnings in the 1960s to the present day, CAD has revolutionized the design process, increasing productivity, accuracy, and collaboration.
CAD software offers a wide range of features and tools that enable designers and engineers to create precise and detailed designs. Whether it’s 2D drafting, 3D modeling, simulation, or analysis, CAD software empowers professionals to bring their ideas to life with greater ease and efficiency.
As CAD technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see exciting advancements that will shape the future of design. The integration of artificial intelligence, generative design, and virtual reality will unlock new possibilities for innovation and creativity.
Cloud computing and mobile CAD will provide increased accessibility and flexibility, allowing designers to work seamlessly from anywhere and collaborate in real-time. The integration of IoT will enable the creation of smart and connected products, enhancing functionality and user experience.
Additionally, CAD software will continue to prioritize sustainability and green design, helping designers create environmentally-friendly designs that minimize impact and promote sustainable practices.
In conclusion, CAD software has become an indispensable tool in the fields of architecture, engineering, and design. Its numerous benefits, including increased productivity, improved accuracy, and enhanced collaboration, make it a vital technology for professionals in a wide range of industries.
As we look to the future, CAD technology will undoubtedly continue to shape the design landscape, empowering designers and engineers with intelligent and innovative tools that push the boundaries of what is possible.
Curious about diving deeper into the world of CAD software? Our next read is just right for you. If you found our discussion on CAD intriguing, you'll certainly want to learn more about AutoCAD, one of the most widely used CAD programs. This detailed guide offers a closer look at its functionalities, uses, and why professionals prefer it for various design challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions about In Terms Of Engineering Software, What Does CAD Stand For
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.










0 thoughts on “In Terms Of Engineering Software, What Does CAD Stand For”