Home>diy>Architecture & Design>What Is CAD Rendering


Architecture & Design
What Is CAD Rendering
Modified: October 20, 2024
Learn about CAD rendering and its importance in architecture design. Enhance your architectural projects with realistic and immersive visualizations.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of CAD rendering, where imagination meets reality. In the realm of architectural and industrial design, CAD rendering plays a crucial role in bringing ideas to life. Whether it’s creating stunning visualizations of skyscrapers or designing intricate product prototypes, CAD rendering has revolutionized the way we conceptualize and present our designs.
CAD rendering, short for Computer-Aided Design rendering, is the process of using computer software to generate realistic and lifelike images of objects or environments. It allows designers, architects, and engineers to visualize their concepts, analyze their functionality, and communicate their ideas effectively.
With the advancements in technology, CAD rendering has become an indispensable tool in the design industry. It enables designers to create photorealistic images, interactive 3D models, and virtual walkthroughs, thereby providing clients and stakeholders with a realistic preview of the final product.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the world of CAD rendering, discussing its importance in design, the various types of rendering techniques, the benefits it offers, its application in different industries, and the challenges it may present. So, let’s embark on this journey and explore the fascinating world of CAD rendering.
Key Takeaways:
- CAD rendering revolutionizes design by enhancing visualization, improving communication, and saving time and costs. It empowers designers to bring their ideas to life in a visually stunning and realistic manner.
- The future of CAD rendering holds immense potential, with advancements in real-time ray tracing, AI-powered rendering, and integration with VR and AR. It will continue to transform industries and enhance the design process.
Read more: What Is Rendering In Construction
Definition of CAD Rendering
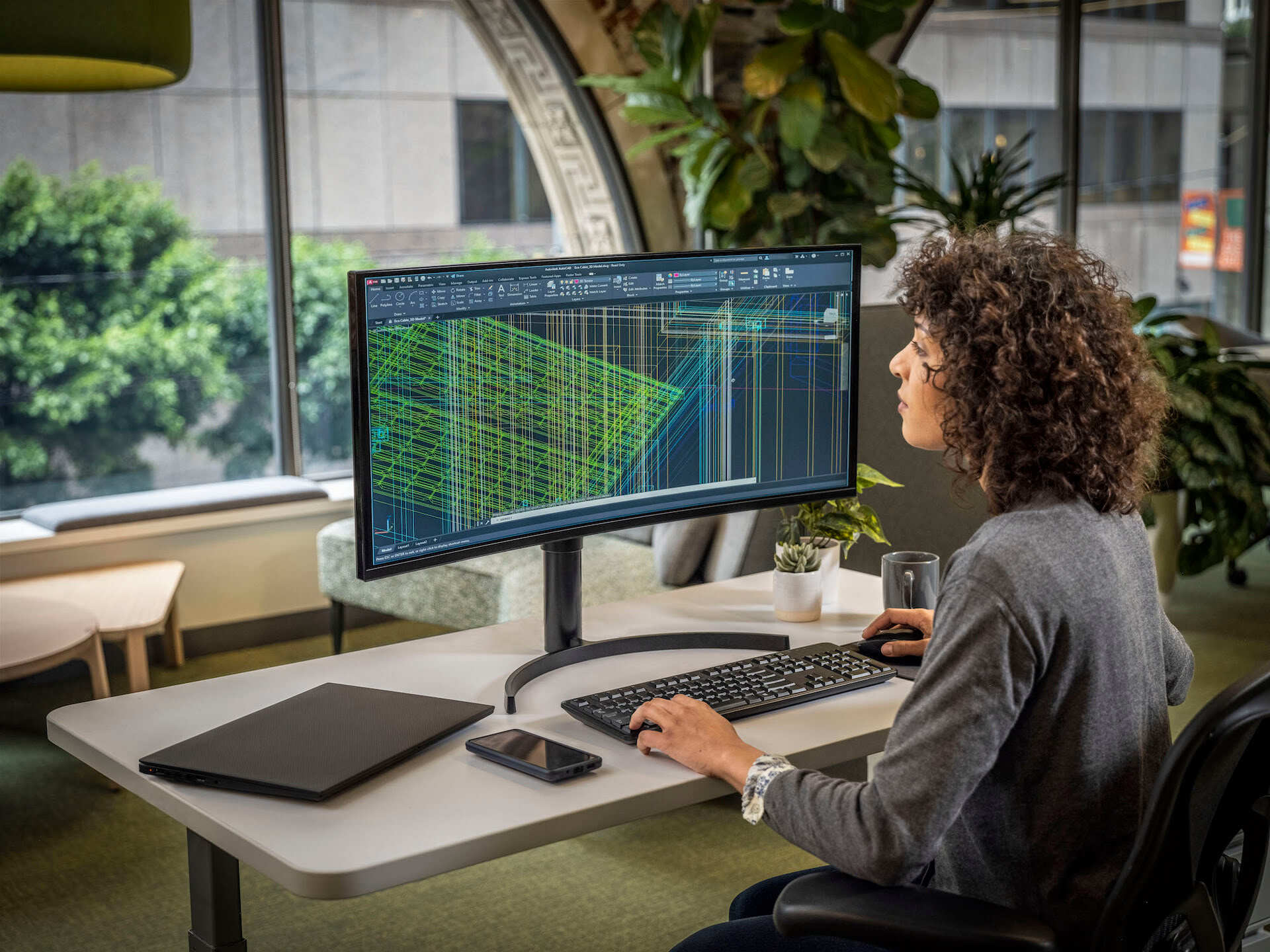
CAD rendering, also known as computer-generated rendering or 3D rendering, refers to the process of using computer software to transform three-dimensional digital models into two-dimensional images or animations with realistic lighting, textures, and materials. It is a vital part of the design process, allowing designers to visualize their ideas and communicate them effectively to clients, stakeholders, and collaborators.
Through CAD rendering, designers can create highly detailed and lifelike representations of objects, spaces, and environments. The process involves adding realistic lighting, shadows, reflections, and textures to the 3D model to achieve a visually compelling result. This helps in conveying the aesthetics, functionality, and overall concept of the design to the audience.
There are various rendering techniques used in CAD rendering, such as ray tracing, radiosity, and rasterization. These methods simulate the behavior of light in different ways, resulting in varying levels of realism and computational complexity. Each technique has its own strengths and limitations, and the choice of rendering technique depends on the specific requirements and constraints of the project.
CAD rendering is widely used in industries like architecture, interior design, product design, automotive design, and entertainment. It enables designers to showcase their ideas in a visually stunning and realistic manner, helping clients and stakeholders to make informed decisions about the design. It also plays a crucial role in marketing and advertising, as rendered images and animations can be used to create captivating visual content for websites, brochures, and presentations.
Importance of CAD Rendering in Design
CAD rendering is an essential tool in the design industry, offering a multitude of benefits for designers, architects, and engineers. It enhances the design process, improves communication, and enables better decision-making. Let’s explore the importance of CAD rendering in more detail:
1. Visualizing Design Concepts: CAD rendering allows designers to transform their abstract ideas and concepts into realistic visual representations. It brings designs to life by adding textures, materials, colors, and lighting to 3D models. This visualization aid helps clients and stakeholders understand and evaluate the design, ensuring that everyone is on the same page from the start.
2. Realistic Presentations: With CAD rendering, presentations become more compelling and persuasive. Instead of relying on traditional 2D drawings or blueprints, designers can showcase their designs through high-quality renderings, providing a realistic preview of the final product. This helps clients visualize the end result and make informed decisions.
3. Design Analysis and Iteration: CAD rendering enables designers to analyze various design factors, such as lighting, materials, and proportions, before the actual construction or production begins. By making virtual modifications and iterations, designers can evaluate different design options and identify potential issues, saving time and resources in the long run.
4. Improved Communication: CAD renderings bridge the communication gap between designers, clients, and other stakeholders. Rendered images and animations effectively convey design intent, eliminating the need for lengthy explanations or technical jargon. This improves collaboration, fosters better understanding, and ensures that all parties are aligned with the design vision.
5. Marketing and Advertising: CAD renderings are a powerful marketing tool. They can be used to create visually captivating images and animations for websites, brochures, and presentations. These marketing materials can generate excitement, attract potential clients, and set the design apart from competitors.
6. Cost and Time Savings: CAD rendering can help optimize the design process by identifying and rectifying design flaws digitally, rather than during the physical construction or manufacturing stages. This reduces costly mistakes, rework, and delays. Additionally, CAD rendering allows for faster design iterations, enabling designers to explore multiple options efficiently.
Overall, CAD rendering is a game-changer in the design industry. It empowers designers to showcase their creativity, improve communication, analyze designs effectively, and save costs and time. With its realistic visualizations and immersive experiences, CAD rendering is revolutionizing the way designs are conceptualized, presented, and implemented.
Different Types of CAD Rendering
CAD rendering encompasses a range of techniques and approaches to create realistic visual representations of designs. Each type of rendering has its own unique features and advantages. Let’s explore some of the different types of CAD rendering:
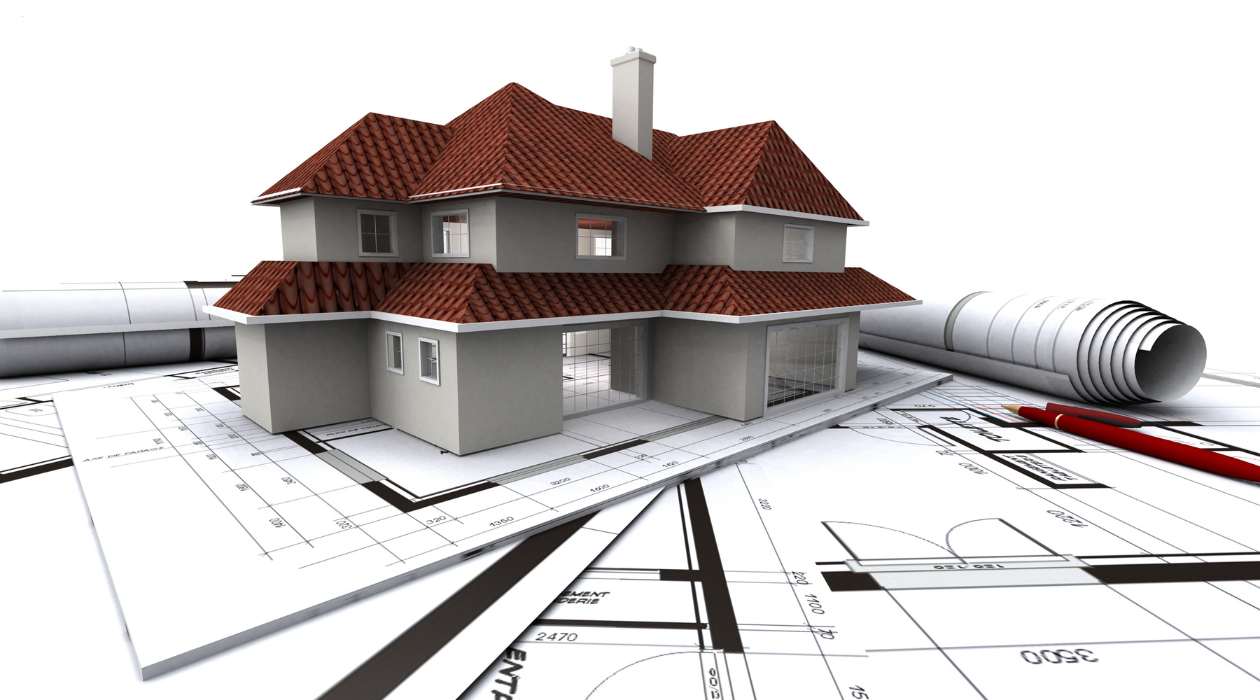
1. Photorealistic Rendering: This type of rendering aims to create images that closely resemble real-life photographs. It focuses on achieving accurate lighting, reflection, and material properties to produce highly realistic visuals. Photorealistic rendering is commonly used in architecture, interior design, and product visualization to provide clients with an immersive representation of the final design.
2. Non-Photorealistic Rendering: Unlike photorealistic rendering, non-photorealistic rendering (NPR) aims to create stylized and artistic visuals that don’t necessarily mimic real-world appearance. NPR techniques can include cartoon-style rendering, line drawings, or watercolor-like effects. It is often used in animation, gaming, and conceptual design to convey a specific mood or artistic vision.
3. Interactive Rendering: Interactive rendering allows for real-time manipulation and exploration of 3D models. It provides designers and clients with the ability to navigate through the virtual environment, change materials, adjust lighting, and observe the impact of modifications instantaneously. This type of rendering is commonly used in architectural walkthroughs, virtual reality (VR) experiences, and gaming.
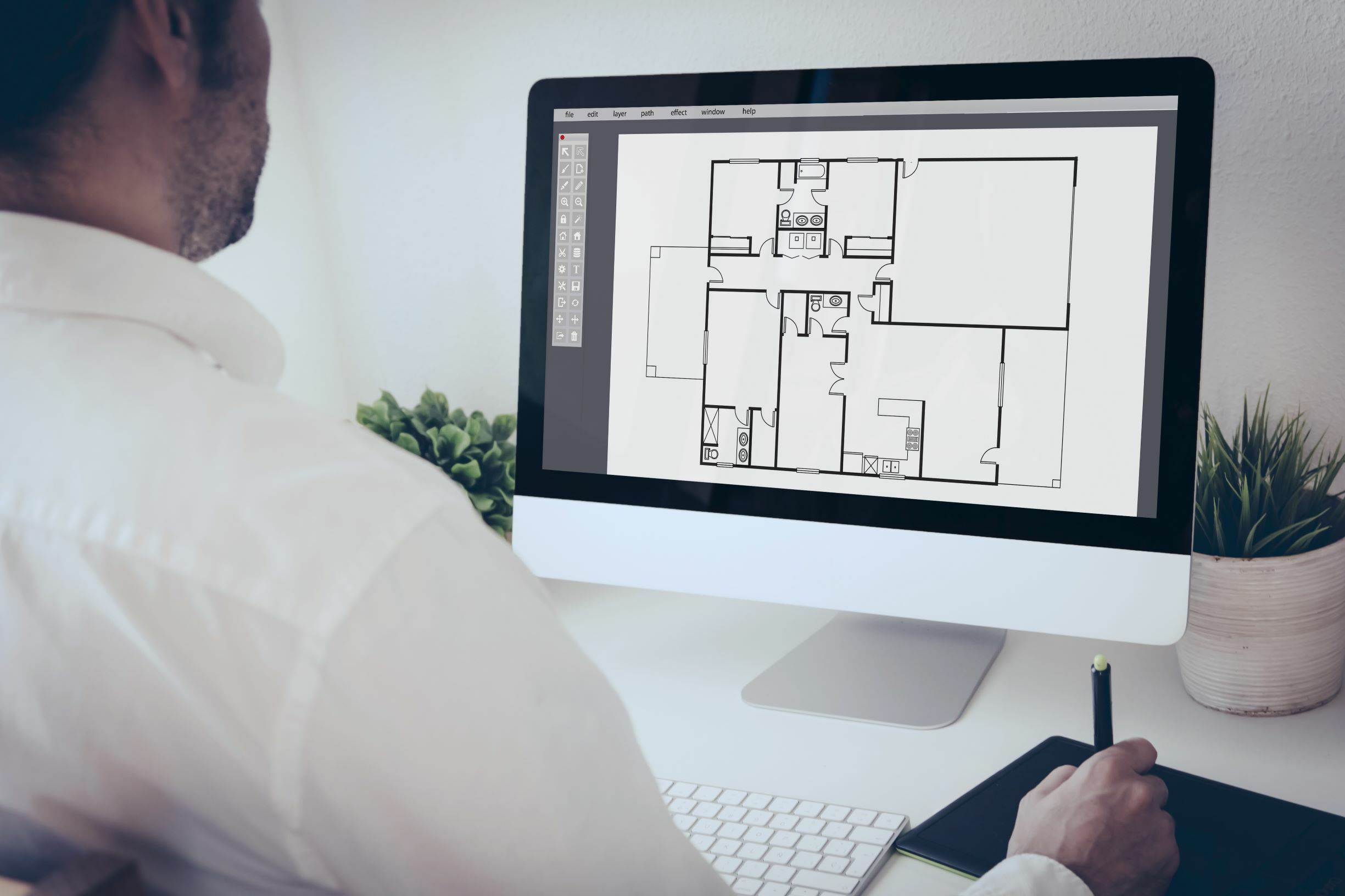
4. Wireframe Rendering: Wireframe rendering focuses on displaying the underlying structure of a 3D model by emphasizing the edges and contours. It is commonly used in the early stages of design to analyze the form and geometry of objects without distractions. Wireframe rendering is particularly useful for architects and industrial designers to evaluate proportions and overall aesthetics.
5. Shadow Rendering: Shadow rendering is dedicated to accurately depicting shadows and their effects on objects and environments. It takes into account the position of the light source, as well as the materials and geometry of the objects, to produce realistic and visually appealing shadows. Shadow rendering is crucial in architectural and interior design for evaluating the impact of natural or artificial lighting.
6. Product Visualization Rendering: Product visualization rendering focuses on showcasing and highlighting the features of a specific product. It often involves displaying the product from various angles and perspectives, with close attention to textures, materials, and details. This type of rendering is commonly used in product design, marketing, and e-commerce.
The choice of rendering technique depends on the specific project requirements, the desired visual style, and the intended audience. Many designers utilize a combination of rendering methods to achieve the desired outcome. As technology advances, new rendering techniques and approaches continue to emerge, providing designers with more tools and possibilities to bring their designs to life.
Benefits of CAD Rendering
CAD rendering offers a multitude of benefits for design professionals and clients alike. From better visualization to improved decision-making, CAD rendering has transformed the design industry. Let’s explore some of the key benefits of CAD rendering:
1. Enhanced Visualization: CAD rendering provides designers with a realistic representation of their designs, enabling them to visualize concepts in detail. By adding lighting, textures, and materials to 3D models, CAD rendering brings designs to life and allows for a better understanding of the final product’s aesthetics and functionality.
2. Improved Communication: CAD renderings bridge the communication gap between designers, clients, and stakeholders. With photorealistic images or interactive 3D models, designers can effectively convey their ideas, concepts, and design intent to others. This clear and visual communication helps in avoiding misunderstandings and facilitates better collaboration.
3. Cost and Time Savings: CAD rendering allows for virtual design iterations and analysis before the physical construction or production stages. This helps identify and rectify design flaws and issues early on, leading to cost savings and avoiding expensive rework. Additionally, CAD rendering speeds up the design process by enabling faster iterations and modifications.
4. Realistic Prototyping: With CAD rendering, designers can create realistic virtual prototypes that closely resemble the final product. This allows for a comprehensive evaluation of the design’s form, function, and overall appeal. It also provides clients and stakeholders with a clear understanding of the final product, reducing the need for physical prototypes and minimizing waste.
5. Marketing and Sales: CAD renderings are powerful marketing tools. They can be used to create visually stunning images and animations that effectively showcase the design to potential clients. CAD renderings help in generating enthusiasm, attracting leads, and increasing sales in industries such as real estate, product design, and automotive design.
6. Flexibility and Customization: CAD rendering allows for easy modifications and customization of designs. Designers can experiment with different materials, colors, lighting setups, and architectural elements to achieve the desired outcome. This flexibility enables designers to meet various client requirements and preferences.
7. Design Analysis: CAD rendering facilitates detailed analysis of designs. With the ability to visualize lighting effects, shadows, and material interactions, designers can better assess the visual impact of their designs. This analysis helps in refining the design, optimizing functionality, and aligning it with the intended design goals.
Overall, CAD rendering offers significant advantages in terms of visualization, communication, cost savings, marketing, and design analysis. It has revolutionized the design industry by enabling designers to present their ideas effectively, make informed decisions, and create visually stunning and realistic designs.
When creating CAD renderings, use high-quality textures and lighting to enhance the realism of the final image. This can make your designs more visually appealing and easier to understand for clients and stakeholders.
Read more: What Is CAD?
Process of CAD Rendering
The process of CAD rendering involves several steps to transform a 3D model into a visually compelling and realistic image or animation. Though the specific details may vary depending on the software and techniques used, here is a general overview of the process:
1. Creating the 3D Model: The first step in CAD rendering is to create a 3D model of the object or environment. This can be done using CAD software, 3D modeling software, or even through scanning real-world objects using 3D scanners. The 3D model will serve as the foundation for the rendering process.
2. Defining Materials and Textures: Once the 3D model is created, the next step involves assigning materials and textures to the various surfaces of the model. This includes determining the properties of materials such as wood, metal, glass, or fabric and applying textures to achieve the desired look and feel.
3. Lighting Setup: Lighting plays a crucial role in CAD rendering as it affects the overall appearance and realism of the final image. In this step, the lighting setup is defined, including the position, type, and intensity of light sources. This helps in creating realistic shadows, reflections, and highlights in the rendering.
4. Adjusting Camera and Viewpoint: The camera position and viewpoint are adjusted to frame the scene or object to be rendered. This involves setting the correct angles, distances, and focal lengths to capture the most aesthetically pleasing and informative view. Multiple viewpoints can be defined for different renderings or animation sequences.
5. Rendering Settings and Parameters: The rendering settings are defined to determine the level of detail, quality, and complexity of the final rendering. This includes specifying parameters such as image resolution, rendering algorithm, raytracing settings, global illumination, and anti-aliasing options. These settings have a significant impact on the realism and computational requirements of the rendering.
6. Render Process: Once all the necessary parameters and settings are defined, the actual render process begins. This process involves the computer software performing complex calculations to simulate the behavior of light rays and their interaction with materials and surfaces. The render process can take from a few seconds to several hours, depending on the complexity of the scene and the computational power of the hardware.
7. Post-Processing and Final Touches: After the initial render is complete, post-processing techniques can be applied to enhance the final rendering. This includes image adjustments, color correction, depth of field effects, and adding visual effects to achieve the desired look. These final touches ensure the rendering is visually appealing and aligns with the intended design vision.
8. Output and Delivery: Once the rendering is finalized, it is saved in the desired file format, such as JPEG, PNG, or TIFF, and can be delivered digitally or in print. The final rendering can be used for client presentations, marketing materials, or further post-production editing.
It is important to note that the CAD rendering process is iterative, and multiple iterations may be required to achieve the desired result. Designers often experiment with different settings, materials, and lighting setups to refine the rendering and meet specific design goals.
Applications of CAD Rendering
CAD rendering finds application in various industries where visualizing and communicating designs is crucial. Let’s explore some of the key applications of CAD rendering:
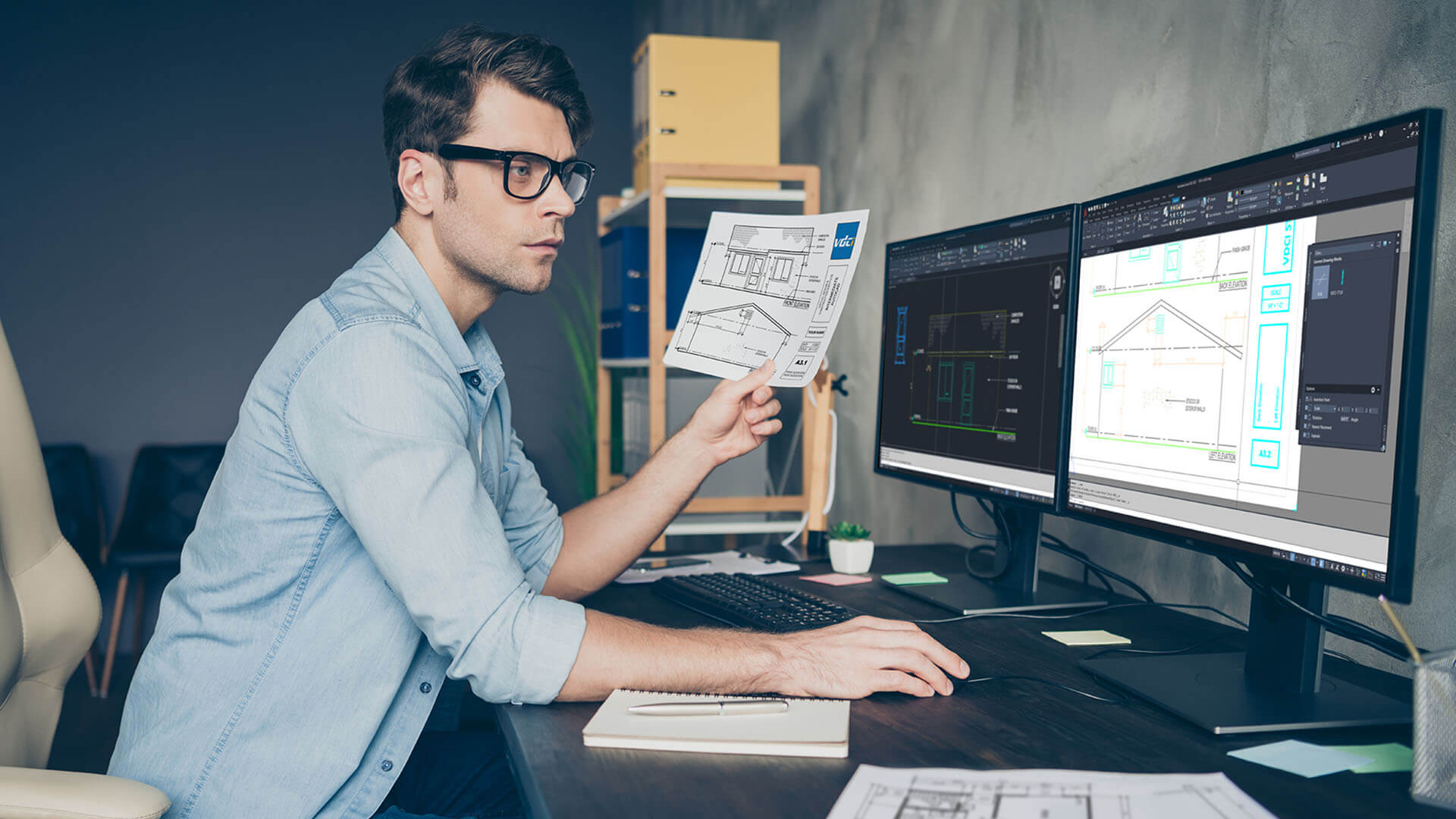
1. Architecture and Interior Design: CAD rendering is extensively used in architecture and interior design to create realistic visualizations of buildings, homes, and interior spaces. It helps architects and designers showcase their designs to clients, allowing them to visualize the aesthetics, lighting, materials, and spatial layout of the final structure.
2. Product Design and Manufacturing: CAD rendering plays a vital role in product design and manufacturing. It allows designers to visualize and refine their product designs, test ergonomics, and evaluate the overall aesthetics and functionality before manufacturing. Detailed renderings help communicate design intent to manufacturers, marketing teams, and potential customers.
3. Automotive and Industrial Design: CAD rendering is a valuable tool in the automotive and industrial design industries. It enables designers to create highly detailed renderings of vehicles, machinery, and industrial equipment, providing a realistic preview of the final product. This aids in design evaluation, marketing, and prototyping.
4. Real Estate and Property Development: CAD renderings are extensively used in real estate and property development to showcase properties, both residential and commercial. High-quality renderings allow potential buyers and investors to visualize the properties before they are constructed, aiding in marketing and sales efforts.
5. Gaming and Animation: CAD rendering is a crucial component in the gaming and animation industries. It helps create visually stunning and immersive environments, characters, and objects. Realistic rendering techniques are employed to ensure that the virtual world is visually appealing and engaging for the players or viewers.
6. Advertising and Marketing: CAD rendering serves as a powerful marketing tool by helping create captivating visuals for brochures, advertisements, websites, and promotional videos. High-quality renderings help companies showcase their products or designs in a visually appealing manner, attracting potential customers and clients.
7. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): CAD rendering plays a significant role in creating immersive virtual reality experiences and augmented reality applications. Rendered 3D models are used as the basis for creating interactive and realistic virtual environments, allowing users to explore and interact with the virtual world in a more engaging and realistic manner.
8. Film and Visual Effects: CAD rendering is extensively used in the film and visual effects industry to create realistic and visually stunning scenes and special effects. It helps in generating computer-generated imagery (CGI) elements that seamlessly integrate with live-action footage, creating awe-inspiring visuals.
These are just a few examples of the wide-ranging applications of CAD rendering. As technology continues to advance, CAD rendering will continue to evolve and find new applications in various industries, revolutionizing the way designs are visualized, presented, and experienced.
Challenges and Limitations of CAD Rendering
While CAD rendering offers numerous benefits, it also comes with its own set of challenges and limitations. These factors should be considered when utilizing CAD rendering in design projects. Let’s explore some of the key challenges and limitations:
1. Computational Requirements: CAD rendering can be computationally intensive, requiring significant processing power and memory to handle complex scenes and realistic lighting calculations. Large-scale projects or scenes with intricate details may require high-performance hardware or rendering farms to achieve acceptable rendering times.
2. Time and Cost Constraints: Rendering high-quality and realistic images or animations can be time-consuming. The rendering process can sometimes take several hours or even days to complete, depending on the complexity of the scene and the desired level of detail. This can create time constraints, especially in projects with tight deadlines.
3. Learning Curve and Technical Skills: CAD rendering software often has a steep learning curve, and mastering the tools and techniques requires expertise and technical skills. Designers may need to invest time and effort in learning and staying updated with the software and rendering techniques to achieve desired results.
4. Realism vs. Speed Trade-off: Achieving high levels of realism in CAD rendering can require longer rendering times. Designers and artists often face the challenge of balancing the desired level of realism with project deadlines. Finding the right trade-off between quality and efficiency is crucial to optimize rendering processes.
5. Complexity of Materials: Rendering realistic materials, such as glass, metals, or fabrics, can be challenging. Simulating the behavior of light and accurately capturing the nuances of material properties can require advanced rendering techniques and specialized material libraries. Achieving accurate and visually appealing materials can be time-consuming and may require significant adjustments.
6. Limitations of Hardware: The capabilities of hardware, such as graphics cards and processors, can impose limitations on the complexity and level of realism achievable in CAD rendering. Older or less powerful hardware may struggle to handle rendering tasks efficiently or may not support certain rendering techniques, leading to limitations in the quality and complexity of the final output.
7. Uncanny Valley: CAD renderings that strive for hyper-realism can sometimes fall into the uncanny valley, where the image appears almost but not quite realistic, leading to a sense of unease or discomfort. Striking the right balance between realism and stylization is crucial to avoid this uncanny valley effect.
Despite these challenges and limitations, CAD rendering continues to evolve and improve, offering more advanced tools, rendering algorithms, and hardware capabilities. Designers and artists can overcome these challenges by staying updated with the latest advancements, optimizing workflows, and utilizing the available resources to achieve the desired results.
Future of CAD Rendering
The future of CAD rendering looks promising as advancements in technology continue to push the boundaries of what is possible. From enhanced realism to real-time rendering, several trends are shaping the future of CAD rendering. Let’s explore some of the key developments that we can expect:
1. Real-Time Ray Tracing: Real-time ray tracing is becoming more accessible with the advancements in graphics processing units (GPUs) and rendering algorithms. This technology allows for interactive rendering with accurate global illumination, shadows, and reflections in real-time, enabling designers to make instantaneous design decisions and visualize the final result in a more immersive way.
2. AI-powered Rendering: Artificial intelligence (AI) is set to revolutionize CAD rendering. Machine learning algorithms can automate various aspects of the rendering process, such as optimizing material properties, lighting setups, or camera angles. AI-powered rendering can significantly improve the efficiency, realism, and quality of CAD renderings.
3. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): The integration of CAD rendering with virtual reality and augmented reality technologies is transforming the way designs are experienced. Realistic renderings can be viewed in immersive VR environments or superimposed onto the real world using AR devices. This advancement opens up new possibilities for design evaluation, visualization, and collaboration.
4. Improved Realism and Interactivity: As hardware capabilities continue to improve, CAD rendering will achieve even higher levels of realism with accurate physics simulations, advanced material models, and lifelike textures. The use of advanced rendering techniques like subsurface scattering and volumetric rendering will further enhance the visual appeal and believability of renderings.
5. Cloud Rendering: Cloud-based rendering services are becoming more prevalent, allowing designers to offload rendering tasks to remote servers. Cloud rendering offers scalability and eliminates the need for expensive hardware investments, enabling designers to access high-quality rendering capabilities on-demand.
6. Collaborative Rendering and Design: CAD rendering will continue to facilitate collaborative design processes by allowing multiple users to simultaneously work on and visualize a project. Real-time collaboration tools will enable designers, clients, and stakeholders to provide feedback, make design decisions, and assess visualizations in a collaborative environment.
7. Integration of Rendering with BIM: Building Information Modeling (BIM) is already revolutionizing the architecture and construction industry. In the future, CAD rendering will be seamlessly integrated with BIM workflows, allowing for the visualization of design changes in real-time and facilitating better communication and coordination between different stakeholders.
These advancements in CAD rendering will pave the way for new possibilities and transformative applications. Designers will have more tools at their disposal to create photorealistic and immersive visualizations, improving design evaluation, communication, and decision-making processes.
As technology continues to evolve, the future of CAD rendering holds immense potential for creating breathtaking visual experiences, enhancing the design process, and revolutionizing industries such as architecture, product design, and entertainment.
Read more: What Are CAD Software
Conclusion
CAD rendering has emerged as a powerful tool in the design industry, revolutionizing the way designers conceptualize, communicate, and present their ideas. It facilitates the visualization of designs in realistic and immersive ways, improving collaboration, decision-making, and client engagement. From architecture to product design, CAD rendering has found applications in various industries, enabling designers to bring their imagination to life.
The benefits of CAD rendering are undeniable. It enhances visualization by transforming abstract concepts into realistic visual representations. CAD rendering improves communication by providing clients and stakeholders with a clear understanding of the design intent. It also saves time and costs by allowing for virtual design iterations and analysis before the physical construction or manufacturing stages.
As with any technology, CAD rendering does come with its own set of challenges and limitations. Computational requirements, time constraints, and the need for technical skills can pose hurdles in the rendering process. Designers must also carefully balance the level of realism with the constraints of time and hardware limitations. However, with advancements in hardware capabilities, AI-powered rendering, and real-time ray tracing, these challenges are being addressed, opening up new possibilities for the future of CAD rendering.
In the future, CAD rendering will continue to evolve and transform the design industry. Real-time rendering, AI-powered automation, and integration with virtual reality and augmented reality will further enhance the realism, interactivity, and immersive experiences of CAD renderings. Cloud rendering and collaborative rendering will facilitate remote collaboration and design reviews, improving communication and team efficiency.
CAD rendering will play an instrumental role in shaping the future of design, whether it’s in architecture, interior design, product design, or other industries. It will empower designers to create visually stunning, highly detailed, and accurate visualizations, enabling them to truly capture the essence of their designs and communicate their ideas effectively.
As we move forward, let us embrace the possibilities that CAD rendering brings and leverage its capabilities to push the boundaries of design, innovation, and creativity.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is CAD Rendering
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Is CAD Rendering”