Home>diy>Building & Construction>How To Become A BIM Manager


Building & Construction
How To Become A BIM Manager
Modified: January 23, 2024
Learn the essential steps and skills to transition into a successful BIM Manager role in the building construction industry. Gain valuable insights and expertise in this in-demand field.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Building Information Modeling, commonly known as BIM, has revolutionized the construction industry. It has transformed the way professionals plan, design, build, and manage projects. With the increasing adoption of BIM technology, there is a growing demand for skilled professionals who can effectively manage and implement BIM processes in construction projects.
A BIM Manager plays a crucial role in overseeing the implementation of BIM throughout the project lifecycle. They are responsible for ensuring the successful integration of BIM technology, coordinating with multidisciplinary teams, and driving efficient collaboration among stakeholders.
In this article, we will explore the responsibilities of a BIM Manager, the education and skills required to pursue this career path, and the steps involved in becoming a BIM Manager. We will also discuss the job opportunities available in this field and the potential salary prospects. Additionally, we will touch upon the future trends and challenges that BIM Managers may face.
Whether you are a recent graduate looking to kickstart your career in the construction industry or a seasoned professional seeking to transition into a new role, this article will provide you with valuable insights into the world of BIM management.
Key Takeaways:
- Becoming a successful BIM Manager requires a combination of relevant education, technical skills, and continuous learning. Networking and staying updated with industry trends are vital for career growth in this dynamic field.
- BIM Managers play a crucial role in driving collaboration, efficiency, and successful project outcomes in the construction industry. As the demand for skilled BIM professionals grows, aspiring managers should focus on acquiring the necessary skills and staying adaptable to industry advancements.
Read more: How To Become A BIM Technician
Overview of BIM
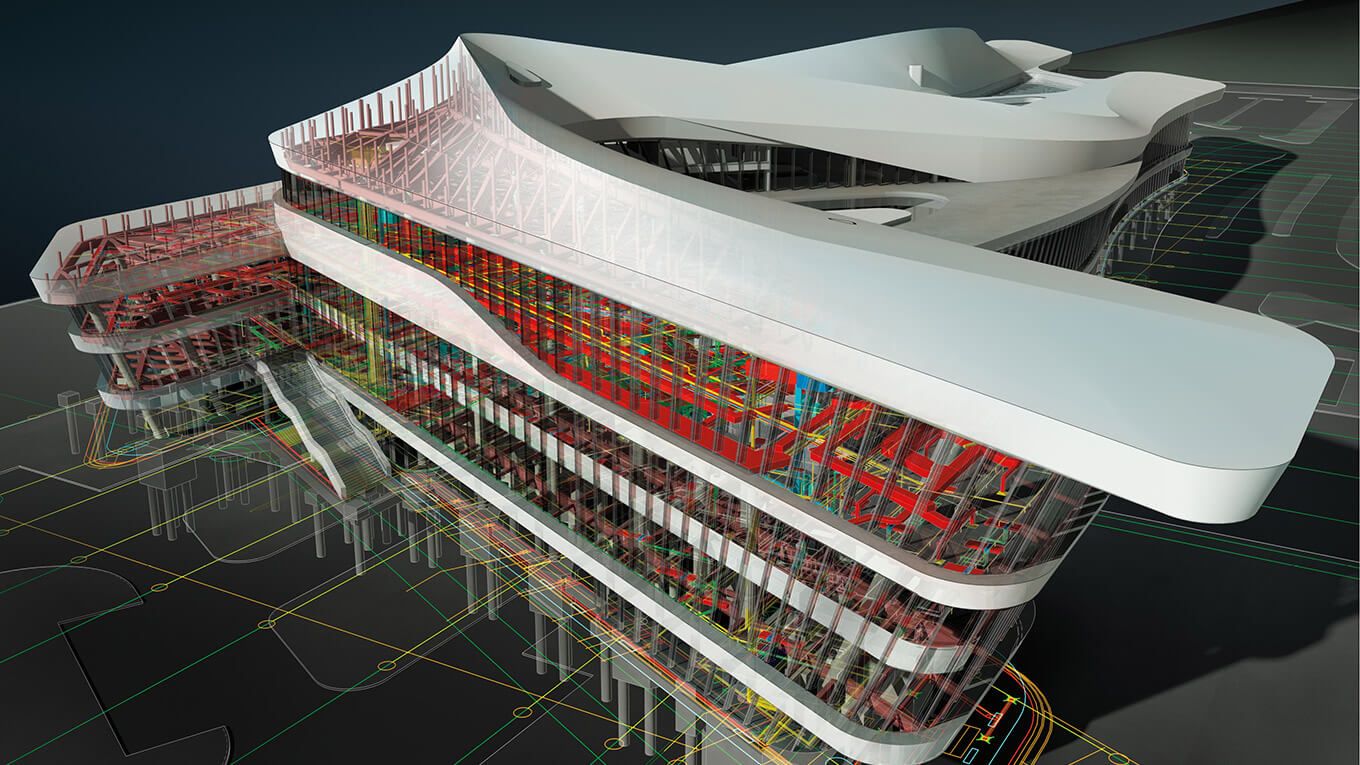
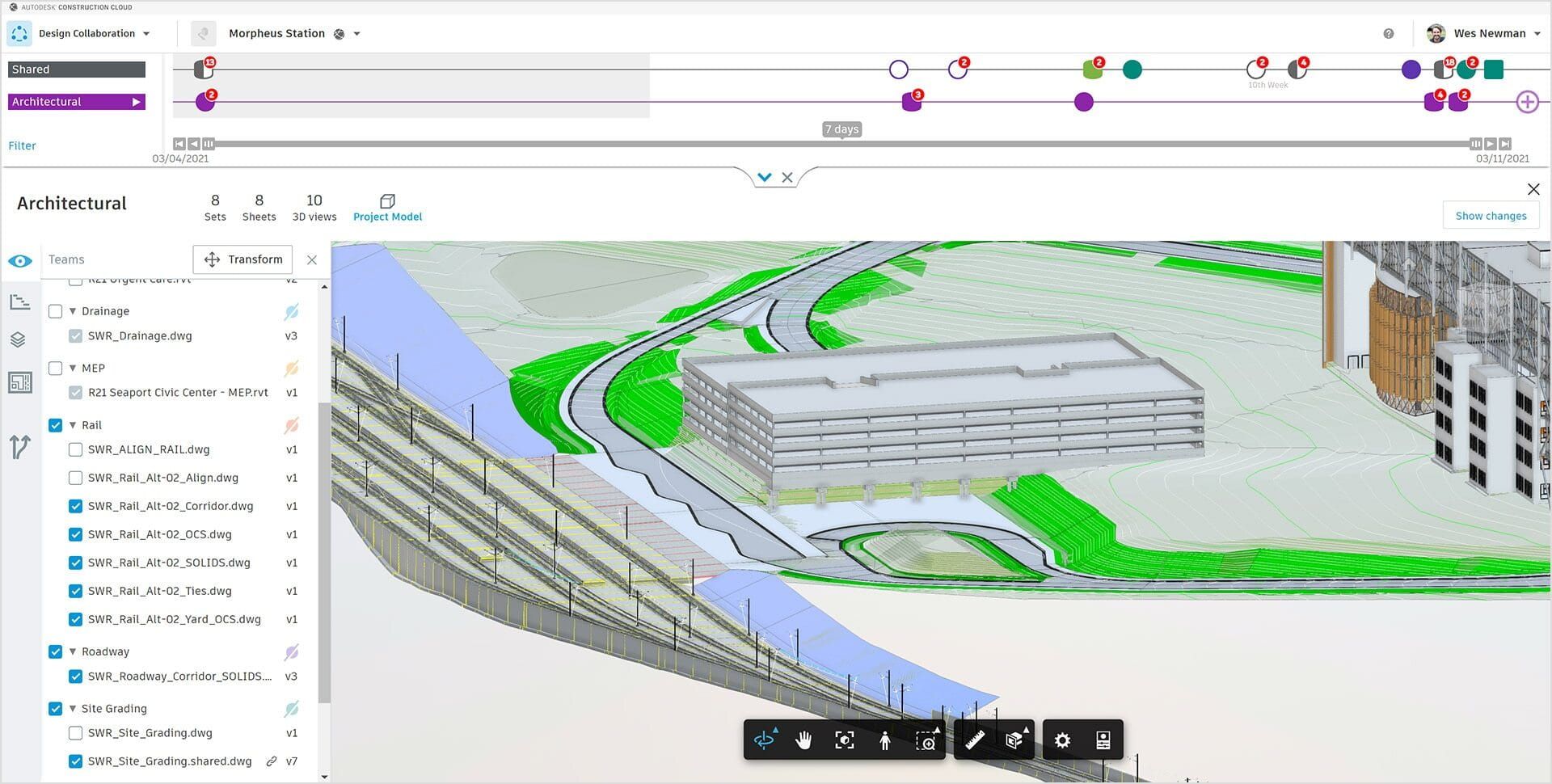
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a building or infrastructure project. It integrates both 3D geometric models and non-geometric data to facilitate collaboration, communication, and decision-making throughout the project lifecycle. BIM allows stakeholders to visualize and simulate the construction process, identify clashes or design conflicts, and make informed decisions to improve project efficiency and mitigate risks.
BIM encompasses a wide range of tools, technologies, and processes that enable the creation and management of a virtual model of the project. This model serves as a shared knowledge resource for all project participants, including architects, engineers, contractors, and facility managers. It enables seamless collaboration, effective communication, and improved project outcomes.
One of the key benefits of BIM is its ability to eliminate information silos. Traditionally, each discipline involved in the construction process would work with their own sets of drawings and specifications. This often led to discrepancies and coordination issues. With BIM, all stakeholders work on a single, shared model, ensuring that everyone has access to the latest information and can coordinate their work effectively.
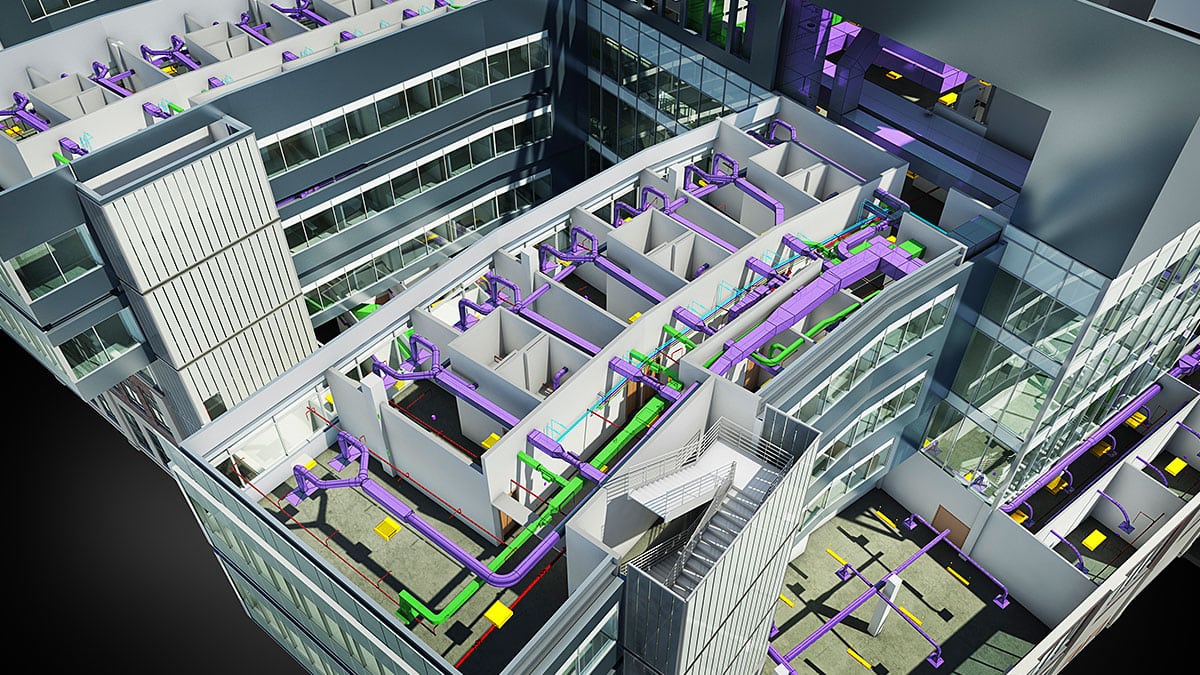
BIM enables multidisciplinary coordination and clash detection. It allows architects, structural engineers, mechanical engineers, and other professionals to simulate and analyze their design within the virtual model, identifying clashes or conflicts early on. This reduces the likelihood of rework and delays during the construction phase.
Beyond design coordination, BIM also facilitates better cost estimation, scheduling, and facility management. By integrating cost data and construction schedules with the virtual model, BIM enables more accurate cost estimates and improved project planning. Additionally, the model can be used by facility managers to efficiently operate and maintain the building or infrastructure after construction.
As technology continues to advance, BIM is evolving to incorporate more advanced features such as augmented reality and virtual reality, allowing stakeholders to experience and interact with the virtual model in a more immersive way.
In summary, BIM is a sophisticated and powerful tool that enhances collaboration, improves project outcomes, and streamlines the construction process. With its widespread adoption, the demand for skilled BIM professionals, such as BIM Managers, is on the rise.
Responsibilities of a BIM Manager
A BIM Manager plays a crucial role in implementing and managing BIM processes within a construction project. Their primary responsibility is to ensure the successful integration and utilization of BIM technology across all project stages. Here are some of the key responsibilities of a BIM Manager:
- BIM Implementation: The BIM Manager is responsible for defining and implementing BIM protocols, standards, and workflows for the project. They ensure that all project participants adhere to these standards and use the appropriate BIM tools and software.
- Coordination and Collaboration: A BIM Manager facilitates effective communication and collaboration among the multidisciplinary teams involved in the project. They coordinate clashes or conflicts among different design disciplines and ensure that the project progresses smoothly.
- BIM Modeling and Documentation: BIM Managers are responsible for overseeing the creation and maintenance of the BIM model. They ensure the accuracy and completeness of the model and the associated documentation, such as drawings, schedules, and specifications.
- Quality Control: The BIM Manager performs regular quality checks on the BIM model to ensure that it meets the project requirements and standards. They identify and resolve any issues or discrepancies, ensuring the model’s accuracy and reliability.
- BIM Training and Support: BIM Managers provide training and support to project team members who are less familiar with BIM technology. They help to bridge the gap between traditional processes and BIM methodologies, ensuring the successful adoption and implementation of BIM within the project.
- Project Performance Analysis: BIM Managers analyze the performance of the BIM model throughout the project lifecycle. They assess the effectiveness of the BIM processes and identify areas for improvement, leading to increased efficiency and productivity.
- Stay Updated with BIM Technology Trends: BIM Managers continuously update their knowledge and stay abreast of the latest trends and advancements in BIM technology. They explore new tools, methodologies, and industry best practices to enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of BIM processes within the organization.
In summary, a BIM Manager plays a critical role in ensuring the successful implementation of BIM processes, standards, and technology within a construction project. They are responsible for coordination, documentation, quality control, training, and performance analysis. By fulfilling these responsibilities effectively, they contribute to improved project outcomes, reduced risks, and increased overall project efficiency.
Education and Skills Required
To pursue a career as a BIM Manager, certain education and skills are necessary to effectively fulfill the role. While there is no specific degree or certification required to become a BIM Manager, having a combination of relevant education and skills can greatly enhance your prospects in this field. Here are some of the key requirements:
- Education: A bachelor’s degree in Architecture, Engineering, Construction Management, or a related field is typically preferred for a BIM Manager role. This educational background provides a solid foundation in construction principles and processes, as well as an understanding of design and project management.
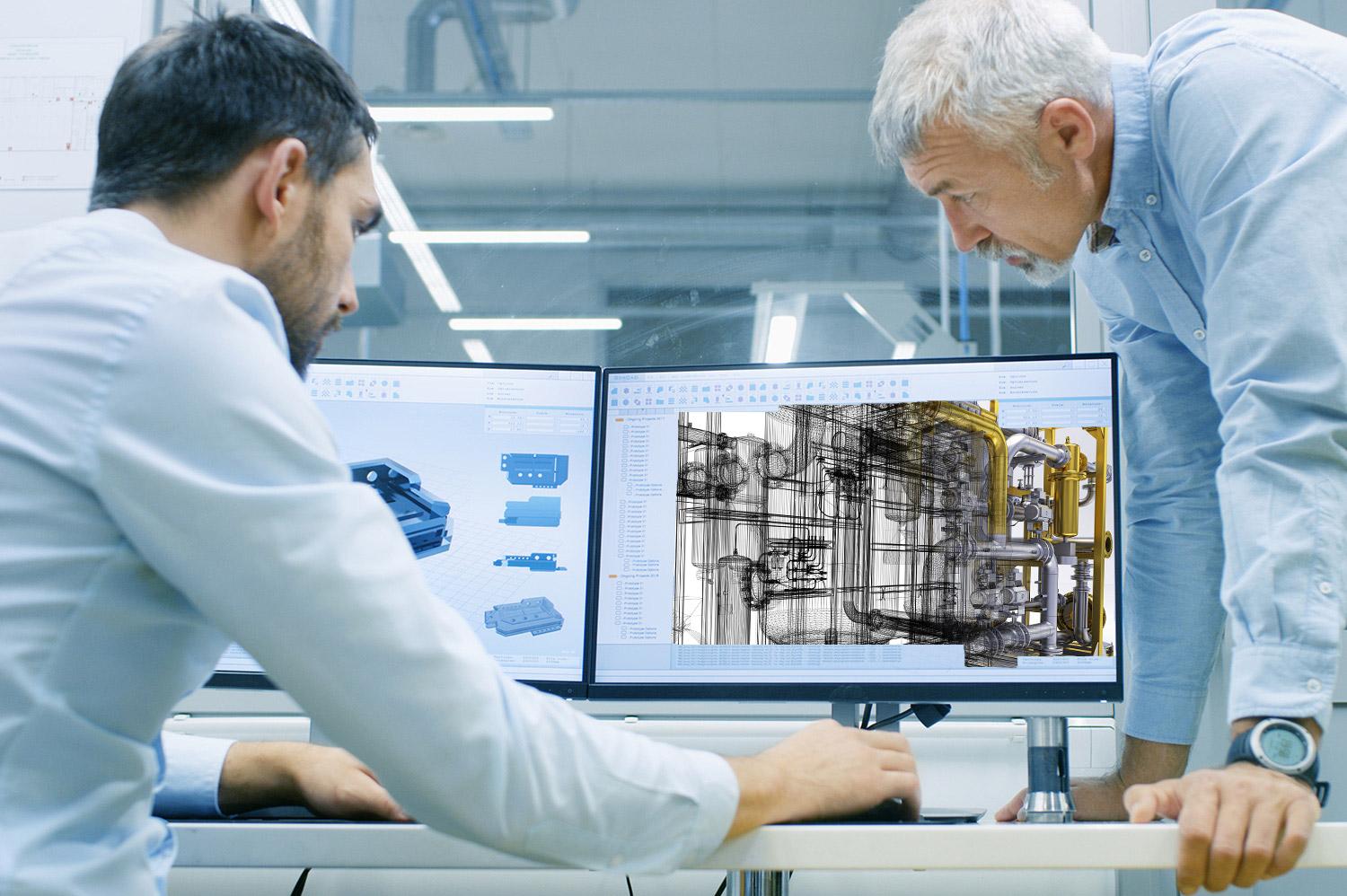
- BIM Knowledge: A strong understanding of BIM principles, processes, and technologies is essential for a BIM Manager. This includes knowledge of BIM software platforms such as Autodesk Revit, Navisworks, or Bentley MicroStation. Familiarity with other BIM-related tools and technologies, such as clash detection software and collaborative platforms, is also beneficial.
- Technical Skills: Proficiency in using BIM software and technologies is crucial for a BIM Manager. This includes the ability to create and modify 3D models, coordinate and manage clashes, generate construction documentation, and perform analysis and simulations within the BIM environment. Knowledge of scripting languages, such as Python or Dynamo, can also be advantageous.
- Project Management Skills: BIM Managers need to have a solid understanding of project management principles and methodologies. They should be able to plan, organize, and coordinate BIM processes effectively, ensuring that projects are completed on time and within budget. Strong communication, problem-solving, and decision-making skills are also essential in this role.
- Collaboration and Leadership: BIM Managers work with multidisciplinary teams and need to possess excellent collaboration and leadership skills. They must be able to facilitate effective communication, mediate conflicts, and motivate team members to work towards common project goals.
- Continuous Learning: The field of BIM is continuously evolving, with new technologies and methodologies emerging. A BIM Manager should have a passion for learning and be committed to staying updated with the latest trends and advancements in BIM technology. Attending conferences, workshops, and pursuing relevant certifications can contribute to professional development in this field.
In summary, a combination of a relevant educational background, strong BIM knowledge, technical skills, project management skills, collaboration abilities, and a commitment to continuous learning are essential for a successful career as a BIM Manager. By acquiring these education and skills, you can position yourself for exciting opportunities in the field of BIM management.
Steps to Becoming a BIM Manager
If you are interested in pursuing a career as a BIM Manager, there are several steps you can take to build the necessary skills and experience. While the exact path may vary depending on your individual circumstances, here are some general steps to help you on your journey to becoming a BIM Manager:
- Obtain a relevant degree or certification: Consider pursuing a bachelor’s degree in Architecture, Engineering, Construction Management, or a related field. This will provide you with a solid foundation in construction principles and processes. Alternatively, you can also explore certifications specific to BIM, such as Autodesk Certified Professional or Certified Revit Professional, to demonstrate your proficiency in BIM software.
- Gain experience in the AEC industry: Seek opportunities to gain practical experience in the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) industry. This can be done through internships, entry-level positions, or volunteering. This experience will help you understand the dynamics of the industry, familiarize yourself with construction processes, and gain exposure to BIM practices.
- Develop strong technical skills in BIM software: Invest time in learning and mastering BIM software platforms such as Autodesk Revit, Navisworks, or Bentley MicroStation. Take advantage of online tutorials, courses, and hands-on projects to develop your proficiency. Practice creating and modifying 3D models, coordinating clashes, and generating construction documentation within the BIM environment.
- Expand knowledge in other related areas: While BIM is a key aspect of the role, acquiring knowledge in other related areas can make you a well-rounded BIM Manager. Familiarize yourself with project management principles and methodologies, as well as construction documentation standards and protocols. Additionally, explore topics such as sustainable design, energy efficiency, and emerging BIM technologies.
- Networking and professional development: Attend industry events, join professional organizations, and connect with other professionals in the field. Networking can provide valuable opportunities to learn, share experiences, and stay updated with the latest trends and practices in BIM. Consider pursuing ongoing professional development through conferences, workshops, and online courses to enhance your knowledge and skills.
It is important to note that the path to becoming a BIM Manager is not linear and may require patience and perseverance. Continuously seek opportunities to apply your skills and gain practical experience. Proactively look for projects or roles that allow you to take on BIM-related responsibilities and showcase your abilities.
By following these steps and continually expanding your knowledge and experience in BIM, you can position yourself for a successful career as a BIM Manager.
Obtain a Relevant Degree or Certification
If you aspire to become a BIM Manager, obtaining a relevant degree or certification is an important first step. While there is no specific educational requirement to become a BIM Manager, having a solid foundation in a related field can greatly enhance your knowledge and prospects in this role.
Consider pursuing a bachelor’s degree in Architecture, Engineering, Construction Management, or a related field. These disciplines provide a comprehensive understanding of the construction industry and the principles behind building design and construction. You will learn about architectural concepts, structural systems, construction techniques, and project management methodologies, which are essential for managing BIM processes effectively.
In addition to a degree, it can be beneficial to acquire certifications specific to BIM. Certifications demonstrate your expertise and proficiency in BIM software and processes, making you a more competitive candidate in the job market. Some popular certifications in the BIM field include Autodesk Certified Professional, Certified Revit Professional, and BIM Certified Professional. These certifications validate your knowledge and skills in using industry-standard BIM tools.
When choosing a degree program or certification, ensure that it covers the relevant aspects of BIM technology, processes, and standards. Look for programs that include courses in BIM modeling, clash detection, virtual design and construction, and BIM management. It is also useful to explore courses or certifications that provide hands-on training with popular BIM software platforms such as Autodesk Revit, Navisworks, or Bentley MicroStation.
Remember, obtaining a degree or certification is not just about the qualification itself. It is an opportunity to gain knowledge, skills, and practical experience. Take advantage of internships, cooperative education programs, or research projects to apply classroom learning in real-world scenarios. This hands-on experience will not only cement your understanding of BIM but also provide valuable insights into the complexities and challenges of working in the construction industry.
Additionally, stay informed about the latest advancements and trends in BIM. Attend webinars, industry conferences, and workshops to stay updated with new technologies, processes, and industry best practices. Building a strong foundation through education and certifications, combined with practical experience, will pave the way for a successful career as a BIM Manager.
Gain Experience in the AEC Industry
To become a BIM Manager, it is crucial to gain practical experience in the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) industry. This experience will provide you with valuable insights into the industry’s dynamics, construction processes, and BIM practices. Here are some steps you can take to gain experience in the AEC industry:
Internships and Entry-level Positions: Seek out internships or entry-level positions in architectural firms, engineering firms, construction companies, or BIM consulting firms. These opportunities will expose you to real-world construction projects, allowing you to learn about project workflows, coordination processes, and the role of BIM in the industry. Work closely with experienced professionals and seek mentorship to enhance your understanding and hone your skills.
Volunteering and Freelancing: Consider volunteering your services or taking on freelance projects in the AEC industry. This can be an excellent way to gain hands-on experience and expand your network. Offer your BIM services to local nonprofits, community organizations, or small construction firms. These opportunities will allow you to apply your BIM skills, work on actual projects, and build a portfolio that showcases your capabilities.
Collaboration and Teamwork: Collaborate with professionals from different disciplines within the AEC industry. Engage in multidisciplinary projects where you can interact with architects, engineers, contractors, and other stakeholders. This collaboration will broaden your perspective and help you understand the challenges and requirements of each discipline. It will also develop your communication and teamwork skills, which are essential for a BIM Manager.
Professional Networking: Attend industry events, conferences, and seminars to network with professionals in the AEC industry. Join professional organizations and participate in online forums or LinkedIn groups focused on BIM and construction. Building relationships with industry experts can lead to job opportunities and provide valuable insights into industry trends and advancements. Actively participate in discussions, share your ideas, and seek advice from experienced professionals.
Continual Learning: Stay updated with the latest developments in the AEC industry and BIM by investing time in continuous learning. Embrace online courses, tutorials, and webinars that focus on BIM technologies, software updates, and industry best practices. This commitment to lifelong learning will not only enhance your skills but also demonstrate your dedication to staying current in a rapidly evolving field.
Remember, gaining experience in the AEC industry is a gradual process. Seize opportunities to work on diverse projects that involve BIM implementation, coordination, and collaboration. Embrace any chance to enhance your skills, showcase your expertise, and contribute to the successful delivery of projects. Over time, your experience and expertise will grow, paving the way for a rewarding career as a BIM Manager.
Stay updated with the latest BIM software and technology, pursue relevant certifications, and gain experience in project management and coordination. Networking with industry professionals can also help in advancing your career as a BIM manager.
Develop Strong Technical Skills in BIM Software
In order to become a successful BIM Manager, it is essential to develop proficiency in BIM software tools. These software platforms are the backbone of BIM processes and play a crucial role in managing and coordinating construction projects. Here are some steps you can take to enhance your technical skills in BIM software:
Choose the Right BIM Software: Familiarize yourself with popular BIM software platforms such as Autodesk Revit, Navisworks, Bentley MicroStation, or ArchiCAD. Research the features, capabilities, and market prevalence of each software to determine which one aligns best with your career goals and industry requirements. It is advantageous to have expertise in multiple software platforms as it broadens your opportunities and allows you to adapt to different project requirements.
Take Online Tutorials and Courses: Many online platforms offer tutorials and courses specifically designed to teach BIM software. Take advantage of these resources to learn the fundamentals and advanced techniques of each software platform. Work your way through step-by-step tutorials, complete exercises, and engage in hands-on projects to gain practical experience. This self-paced learning approach allows for flexibility and enables you to customize your learning journey according to your schedule and pace.
Utilize Software Documentation and Help Resources: BIM software vendors provide extensive documentation and help resources for their products. Explore the official documentation, user forums, and knowledge bases to deepen your understanding of the software functionalities. These resources often provide valuable tips, tricks, and best practices that can enhance your efficiency and productivity when working with BIM software.
Participate in Hands-On Projects: Apply your knowledge by engaging in hands-on projects that require the use of BIM software. This could involve volunteering for BIM implementation projects or collaborating with other professionals on real-world construction projects. By actively using the software in practical scenarios, you will gain firsthand experience and encounter challenges that will further develop your technical skills.
Stay Updated with Software Developments: BIM software tools are constantly evolving with new features, updates, and enhancements. Stay up to date with the latest developments by attending webinars, participating in user groups, and following industry publications. By staying informed, you can take advantage of new functionalities and workflows that can streamline your work and improve project outcomes.
Explore Scripting and Automation: BIM software’s scripting capabilities, such as Python or Dynamo, can further enhance your efficiency and automate repetitive tasks. Invest time in learning scripting languages relevant to the software you are using. Scripting skills can enable you to create custom workflows, develop specialized tools, and optimize your work processes.
Remember, developing technical skills in BIM software is an ongoing process. Continuously practice and explore new features and tools. Engage with other professionals in online communities or user groups to exchange knowledge and learn from their experiences. By becoming proficient in BIM software, you will be equipped to handle complex design and coordination challenges, making you a valuable asset as a BIM Manager.
Expand Knowledge in Other Related Areas
To excel as a BIM Manager, it is important to have a broad understanding of various aspects related to the construction industry. While having strong technical skills in BIM software is crucial, expanding your knowledge in other related areas will make you a well-rounded and versatile professional. Here are some ways to expand your knowledge in these areas:
Project Management: Familiarize yourself with project management principles and methodologies. Understand concepts such as scope management, cost management, and schedule management. Acquire knowledge in planning and executing construction projects efficiently. This will enable you to effectively coordinate BIM processes within the project context, ensuring that projects are delivered on time and within budget.
Construction Documentation: Gain proficiency in creating and interpreting construction documentation. Familiarize yourself with industry standards and protocols such as Building Codes, National CAD Standards, and International Association of Plumbing and Mechanical Officials (IAPMO) codes. Understand the components of construction documentation, including drawings, specifications, and schedules. This knowledge will enable you to effectively communicate project requirements and coordinate with various stakeholders.
Sustainable Design and Energy Efficiency: Develop an understanding of sustainable design principles and energy-efficient construction practices. Learn about green building rating systems such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design). Gain knowledge of strategies for reducing energy consumption, water usage, and environmental impact in construction projects. An awareness of sustainable design practices will help you integrate sustainability considerations into BIM workflows and contribute to more sustainable built environments.
Emerging Technologies: Stay updated with emerging technologies and trends in the construction industry. Explore topics such as augmented reality, virtual reality, laser scanning, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). Understand how these technologies can be integrated with BIM to enhance project visualization, data capture, and communication. Having knowledge of these emerging technologies will keep you at the forefront of industry advancements and allow you to adapt to changing project requirements.
Regulatory Compliance: Gain an understanding of regulatory compliance requirements that impact the construction industry. This includes codes and regulations related to fire safety, accessibility, environmental impact, and building certifications. Familiarize yourself with local building codes and regulations to ensure that projects meet legal requirements. This knowledge will enable you to effectively incorporate compliance considerations into BIM workflows and collaborate with regulatory officials.
Industry Research and Best Practices: Engage in research and keep yourself informed about industry best practices. Stay up to date with research publications, industry journals, and case studies. This will expose you to innovative ideas, proven methodologies, and successful project implementations. Actively seeking out new insights and staying informed about the latest developments will equip you with the knowledge to overcome challenges and drive continuous improvement in your role as a BIM Manager.
By expanding your knowledge in these related areas, you will be able to collaborate effectively with multidisciplinary teams, understand the complexities of construction projects, and drive efficient and sustainable outcomes. This holistic approach will make you a valuable asset in the construction industry as a BIM Manager.
Read more: What Is BIM?
Networking and Professional Development
Networking and professional development are vital aspects of becoming a successful BIM Manager. Building a strong professional network and continuously expanding your knowledge and skills will open doors to new opportunities and keep you at the forefront of the industry. Here are some steps you can take to enhance your networking and professional development:
Attend Industry Events: Participate in industry events such as conferences, trade shows, and seminars focused on BIM, construction, and related fields. These events provide excellent opportunities to network with industry professionals, learn from experts, and stay updated with the latest trends and advancements in BIM technology and practices. Engage in discussions, ask questions, and exchange ideas with peers and industry leaders.
Join Professional Organizations: Become a member of professional organizations that focus on BIM, architecture, engineering, or construction management. Examples include the BuildingSMART International, the American Institute of Architects (AIA), or the Construction Management Association of America (CMAA). Being part of these organizations will give you access to valuable resources, industry publications, training programs, and networking opportunities.
Participate in Online Forums and Groups: Engage in online forums, LinkedIn groups, and social media communities dedicated to BIM and construction. These platforms provide a virtual space to connect with professionals from around the world, share insights, and ask questions. Contribute to discussions, showcase your knowledge, and learn from the experiences of others in the field.
Connect with Peers and Mentors: Seek out professionals who are already established in the field of BIM management and connect with them. Attend local meetups or industry events to meet knowledgeable individuals who can mentor and guide you. Establishing relationships with experienced BIM Managers can provide you with valuable insights, career advice, and potential job opportunities.
Continuous Learning: Commit to lifelong learning and actively seek out professional development opportunities. Take advantage of online courses, webinars, and workshops that focus on BIM software updates, emerging technologies, and industry best practices. Enhancing your skill set and staying updated with the latest developments will make you a valuable asset as a BIM Manager and enhance your career prospects.
Seek Certifications: Consider pursuing certifications that validate your skills and expertise in BIM management. Certifications such as the BIM Management Professional Certification (BMPC) or the Certified Construction Manager (CCM) can demonstrate your commitment to professional growth and improve your credibility in the industry. These certifications may require a certain level of experience and passing an examination.
Be Active Online: Establish an online presence through platforms such as LinkedIn or professional blogs. Share your knowledge, insights, and projects to showcase your expertise in BIM and construction management. Engage with industry influencers and thought leaders on social media platforms to expand your network and stay up to date with industry trends.
By actively networking and investing in professional development, you will not only expand your knowledge and skills but also create valuable connections and opportunities in the field of BIM management. Building a strong professional network and continually seeking professional growth will position you for a rewarding and successful career as a BIM Manager.
Job Opportunities and Salary Potential
As the adoption of Building Information Modeling (BIM) continues to grow in the construction industry, the demand for skilled BIM Managers is increasing. BIM Managers play a critical role in implementing BIM processes, facilitating collaboration, and ensuring the successful integration of BIM technology within construction projects. Here are some insights into job opportunities and salary potential in the field of BIM management:
Job Opportunities: Job opportunities for BIM Managers can be found in architectural firms, engineering companies, construction management firms, and general contractors. BIM Managers are also in demand in government agencies, consulting firms, and BIM service providers. Additionally, large construction projects, such as infrastructure or commercial developments, often require dedicated BIM Managers to oversee and manage BIM processes.
Roles and Titles: BIM Managers may also be known by various other titles, including BIM Coordinator, BIM Specialist, Virtual Design and Construction (VDC) Manager, or BIM Consultant. The actual title may vary depending on the company or organization, but the core responsibilities and skill sets remain similar.
Salary Potential: The salary potential for BIM Managers can vary depending on factors such as experience, location, industry sector, and the scale of projects. According to industry reports, the average salary for BIM Managers ranges from $65,000 to $110,000 per year, with the potential for higher earnings as you gain more experience and expertise in the field. Salary can also be influenced by additional factors such as educational qualifications, certifications, and demonstrated leadership abilities.
Career Growth: The field of BIM management offers significant opportunities for career growth. As you gain experience and demonstrate proficiency in managing BIM processes, you may have the potential to advance into higher-level roles such as BIM Director, BIM Strategist, or BIM Program Manager. These positions involve overseeing multiple BIM projects, developing BIM strategies, and guiding organizations to leverage BIM technology for improved project outcomes.
Industry Trends: It is worth noting that the field of BIM management continues to evolve rapidly. As technology advancements continue and new practices are adopted, BIM Managers need to stay updated with the latest trends and tools. This includes exploring emerging technologies such as augmented reality, virtual reality, and cloud-based collaboration platforms. BIM Managers who are knowledgeable and adaptable to these advancements will be better positioned for long-term career growth and success.
In summary, the demand for skilled BIM Managers is on the rise as the industry recognizes the value of efficient collaboration and data-driven decision-making. BIM Managers have diverse job opportunities across various sectors and the potential for career growth. As the industry continues to embrace BIM technology, the role of BIM Managers will become increasingly important, making it an exciting and rewarding career choice for those passionate about construction and technology.
Challenges and Future Trends in BIM Management
While Building Information Modeling (BIM) brings numerous benefits to the construction industry, there are also challenges that BIM Managers need to navigate. Understanding these challenges and being aware of future trends can help BIM Managers stay ahead in the field and effectively manage BIM processes. Here are some of the major challenges and future trends in BIM Management:
Data Management and Integration: Managing and integrating large amounts of data from various stakeholders can be a significant challenge. BIM Managers must ensure data accuracy, consistency, and accessibility throughout the project lifecycle. As project teams increasingly adopt cloud-based collaboration platforms and utilize real-time data, BIM Managers will need to develop expertise in data management and integration to effectively handle these complexities.
Standardization and Interoperability: The construction industry lacks consistent standards for BIM implementation, resulting in interoperability issues between different software platforms. BIM Managers must navigate these challenges by understanding industry standards, protocols, and file formats. With future trends focusing on openBIM and the adoption of industry-wide standards, BIM Managers will need to stay updated and actively participate in standardization efforts to ensure smooth collaboration across projects.
Skills Gap and Training: As BIM technology continues to evolve, there is a growing demand for skilled BIM professionals. BIM Managers must address the skills gap in the industry by investing in training programs, mentorship, and professional development. The ability to acquire new skills and adapt to emerging technologies will be crucial for BIM Managers to remain competitive in the field.
Change Management and Collaboration: The successful implementation of BIM requires strong change management skills and effective collaboration among multidisciplinary teams. BIM Managers must navigate resistance to change, foster collaboration, and bridge the gap between traditional processes and BIM methodologies. Future trends indicate greater emphasis on collaborative platforms, virtual design coordination, and integrated project delivery methods, making effective change management and collaboration even more critical.
Data Security and Privacy: With the increasing reliance on cloud-based platforms and sharing sensitive project data, BIM Managers must address concerns related to data security and privacy. They need to ensure that appropriate security measures are in place to protect intellectual property and maintain client confidentiality. As the industry continues to address these issues, BIM Managers will play a vital role in implementing robust data security protocols and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations.
Emerging Trends: Looking ahead, BIM Managers should stay informed about emerging trends that will shape the future of BIM. Some of these trends include incorporating artificial intelligence and machine learning into BIM processes, utilizing virtual and augmented reality for enhanced project visualization and stakeholder engagement, and leveraging big data analytics for data-driven decision-making. BIM Managers who embrace these trends and continuously update their skills and knowledge will stay at the forefront of the industry.
As BIM becomes increasingly standardized and adopted across the construction industry, BIM Managers will navigate challenges related to data management, interoperability, skills development, change management, and data security. By staying informed about future trends and proactively addressing these challenges, BIM Managers can successfully lead the way in implementing BIM technology and optimizing project outcomes.
Conclusion
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has transformed the construction industry, revolutionizing the way professionals plan, design, construct, and manage projects. As the role of BIM Managers becomes increasingly important in ensuring the successful implementation of BIM processes, it is crucial to be equipped with the necessary education, skills, and experience.
In this article, we explored the responsibilities of a BIM Manager, which include overseeing BIM implementation, coordinating multidisciplinary teams, and ensuring the accuracy and completeness of the BIM model. We discussed the importance of obtaining a relevant degree or certification in fields such as architecture, engineering, or construction management.
We also highlighted the need to develop strong technical skills in BIM software, such as Autodesk Revit, Navisworks, or Bentley MicroStation, and expand knowledge in related areas such as project management, construction documentation, and sustainable design.
The steps to becoming a successful BIM Manager involve gaining experience in the AEC industry, expanding technical skills, networking, and continuously pursuing professional development opportunities. We discussed the potential job opportunities and salary prospects for BIM Managers, as well as the challenges and future trends in the field.
In conclusion, the role of a BIM Manager is critical in driving collaboration, efficiency, and successful project outcomes. By obtaining the relevant education, developing technical skills, and staying updated with industry trends, aspiring BIM Managers can position themselves for rewarding and fulfilling careers.
As the construction industry continues to embrace BIM technology, the demand for skilled BIM Managers will only grow. By staying adaptable, continuously learning, and addressing challenges such as data management, interoperability, and change management, BIM Managers can excel in their roles and drive innovation within the industry.
Whether you are just starting your journey in the AEC industry or looking to advance your career as a BIM professional, the path to becoming a BIM Manager requires dedication, continual learning, and a passion for integrating technology to shape the future of construction. Embrace the opportunities that arise, stay connected with industry professionals, and continue to refine your skills to excel in this fast-evolving field.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Become A BIM Manager
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.










0 thoughts on “How To Become A BIM Manager”