Home>diy>Building & Construction>What Is BIM Architecture?

Building & Construction
What Is BIM Architecture?
Modified: December 7, 2023
Learn about BIM architecture and its role in building construction. Understand how this technology enhances efficiency and collaboration in the construction industry.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
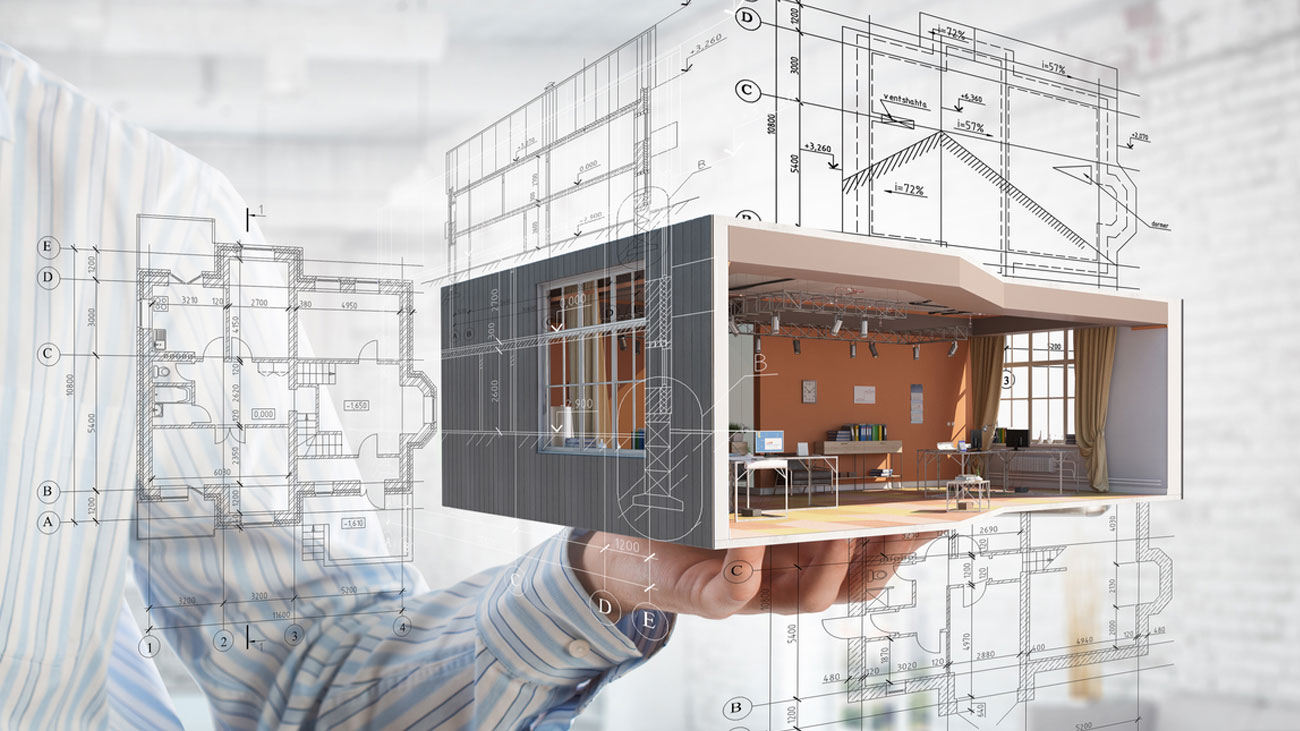
Building Information Modeling, commonly known as BIM, has revolutionized the field of architecture and construction. It is a digital technology that enables architects, engineers, and construction professionals to create, collaborate, and manage building projects in a more efficient and effective manner. By integrating 3D modeling, data visualization, and information management, BIM architecture is transforming the way buildings are designed, constructed, and maintained.
In the traditional approach to construction projects, various professionals worked independently on their respective tasks, leading to a lack of coordination, communication gaps, and cost overruns. BIM architecture overcomes these challenges by providing a centralized platform that facilitates collaboration, streamlines workflows, and enhances project accuracy.
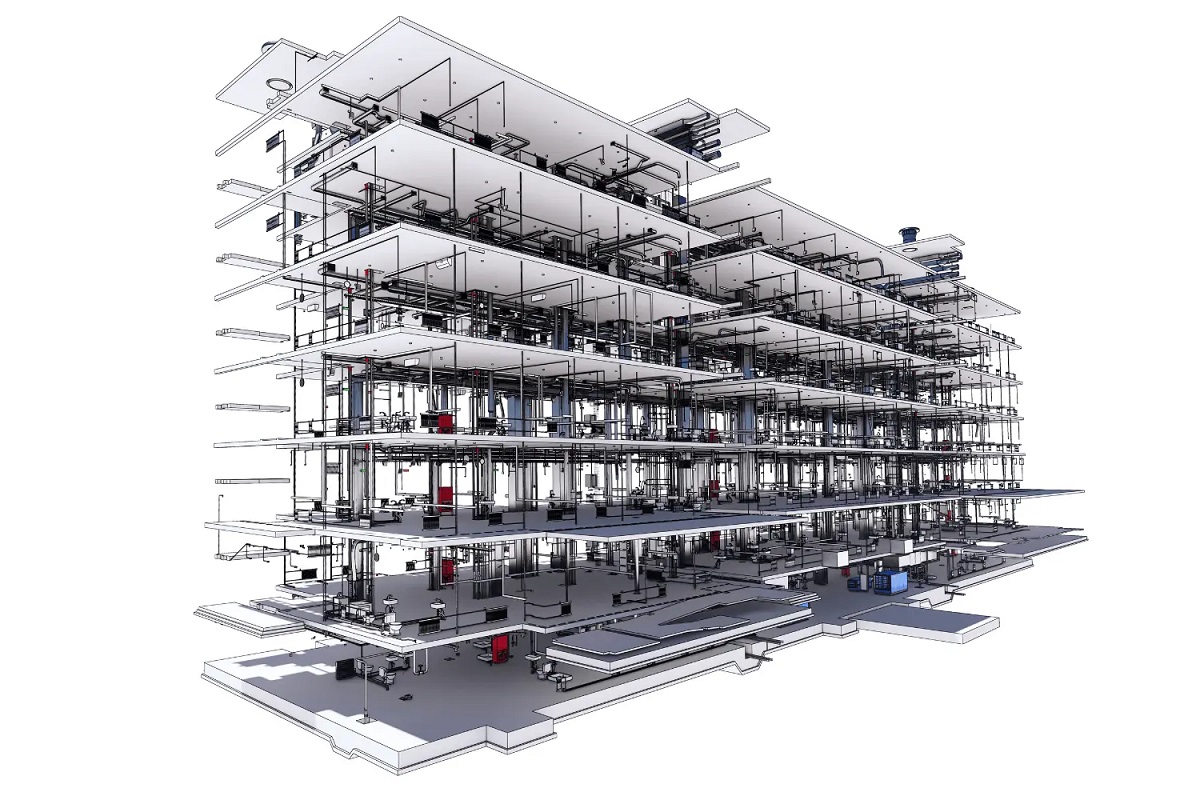
With BIM, architects can create detailed 3D models of buildings, including structural elements, mechanical systems, and interior finishes. These models are not only visually appealing but also contain valuable information about the building components. This information can include material specifications, cost estimations, energy performance data, and maintenance schedules.
BIM architecture offers a range of benefits that address the limitations of traditional construction practices. These benefits extend beyond the design phase and positively impact the entire project lifecycle.
Key Takeaways:
- BIM architecture revolutionizes construction by enabling efficient collaboration, enhanced visualization, and cost savings. Its applications span design, clash detection, facility management, and sustainability analysis.
- Despite challenges, the future of BIM architecture looks promising with increased integration, cloud-based solutions, mobile technologies, big data analytics, digital twin technology, sustainable design, and advanced visualization.
Read more: What Is BIM?
Definition of BIM Architecture
BIM Architecture, as mentioned earlier, stands for Building Information Modeling. It is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a building or infrastructure project. It encompasses the entire lifecycle of a construction project, from its initial design and construction to its operation and maintenance.
At its core, BIM architecture is a collaborative process that uses innovative software tools to create and manage digital models of buildings. These models contain intelligent data and information that enables stakeholders to visualize, simulate, and analyze various aspects of the building project.
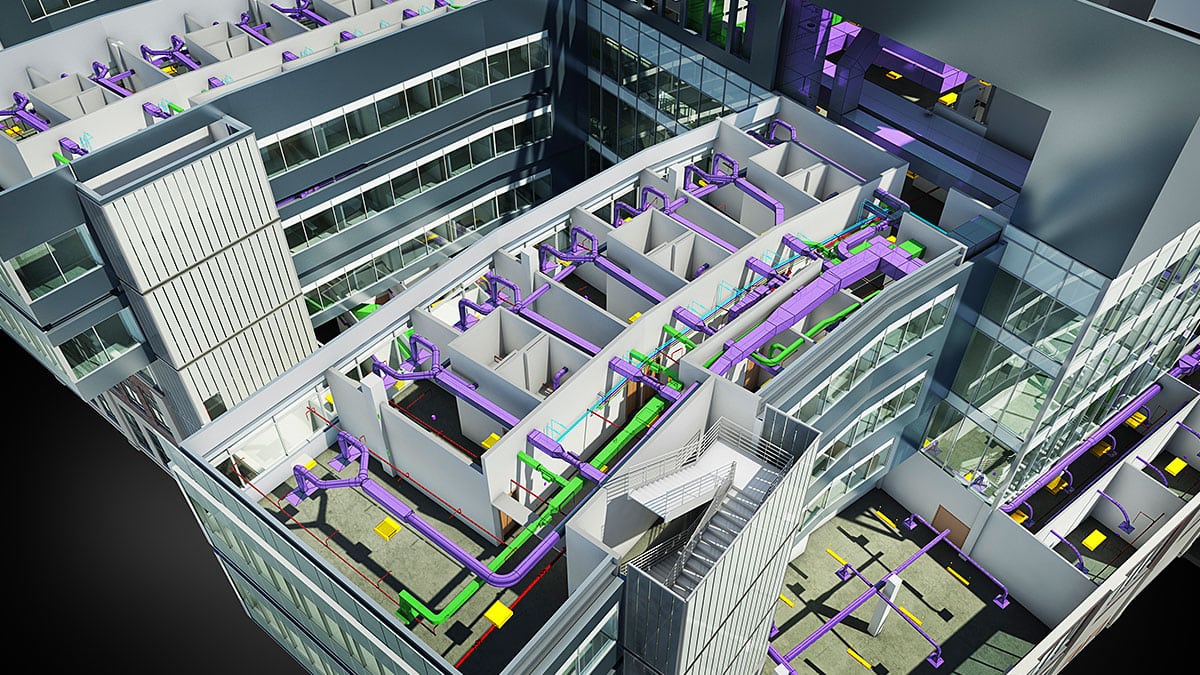
BIM architecture goes beyond traditional 2D drawings by creating accurate and realistic 3D models. These models are built upon a database that stores information about every component of the building, including dimensions, material properties, and connections. This information can range from structural details, such as beams and columns, to mechanical systems, electrical layouts, and even interior finishes.
BIM architecture also enables the integration of other important project data, such as cost estimates, scheduling information, and energy performance analysis. By consolidating all this information into a single digital model, BIM architecture provides a comprehensive view of the project for all stakeholders involved.
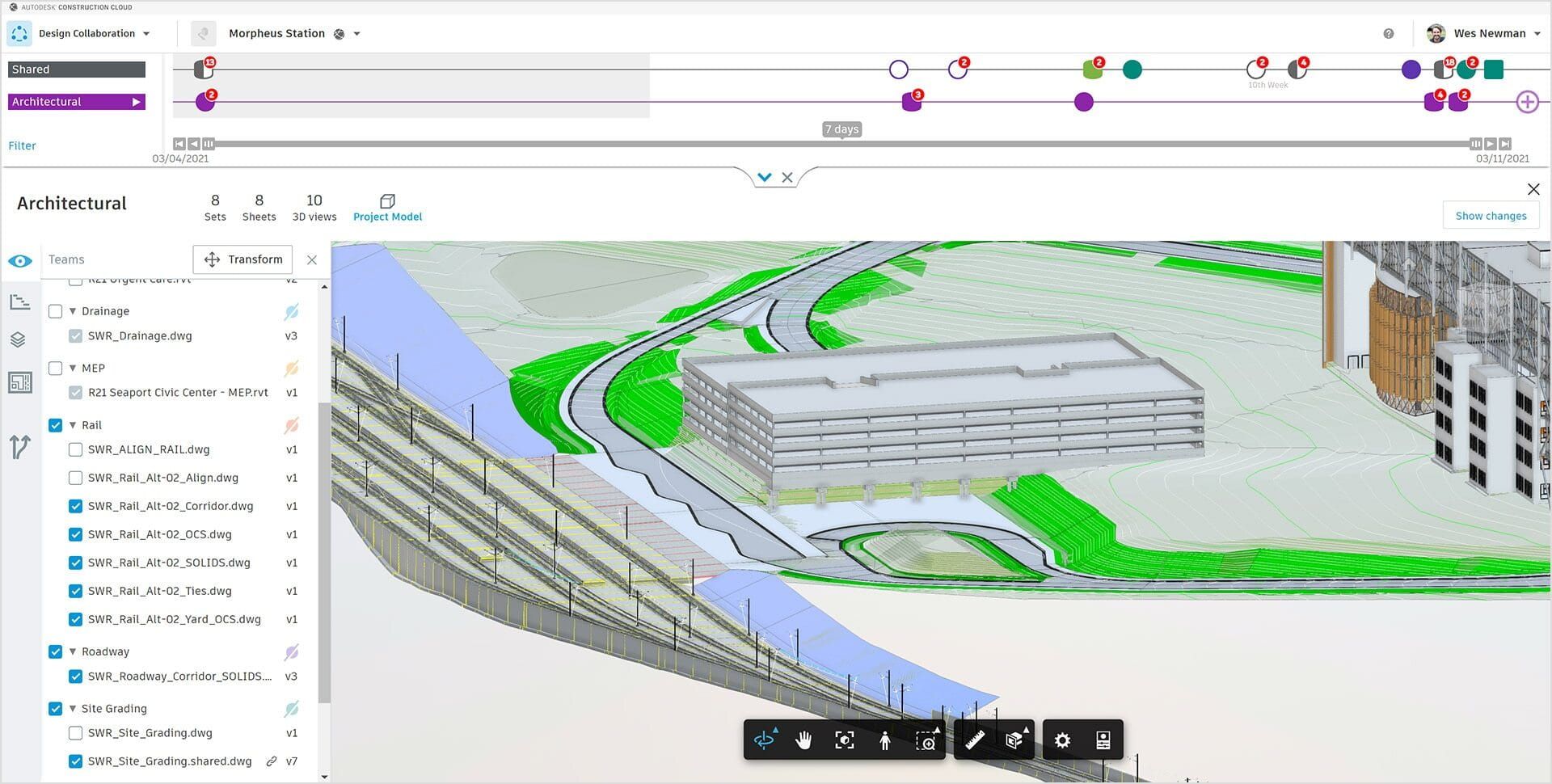
Furthermore, BIM architecture promotes collaboration and coordination among different disciplines involved in the building project. Architects, engineers, contractors, and owners can work together in real-time, sharing information and making more informed decisions. This collaborative approach reduces conflicts, minimizes errors, and improves overall project efficiency.
Overall, BIM architecture is a powerful tool that enables better communication, integration, and visualization throughout the entire lifecycle of a construction project. It facilitates effective decision-making, improves project outcomes, and enhances the overall value delivered to clients.
Benefits of BIM Architecture
BIM architecture offers a multitude of benefits that revolutionize the way construction projects are planned, designed, and executed. These benefits extend to all stakeholders involved, including architects, engineers, contractors, and building owners. Here are some key advantages of implementing BIM architecture:
- Improved Collaboration: BIM architecture provides a centralized platform that promotes collaboration and coordination among project teams. It enables real-time sharing of information and seamless communication, reducing conflicts and enhancing teamwork.
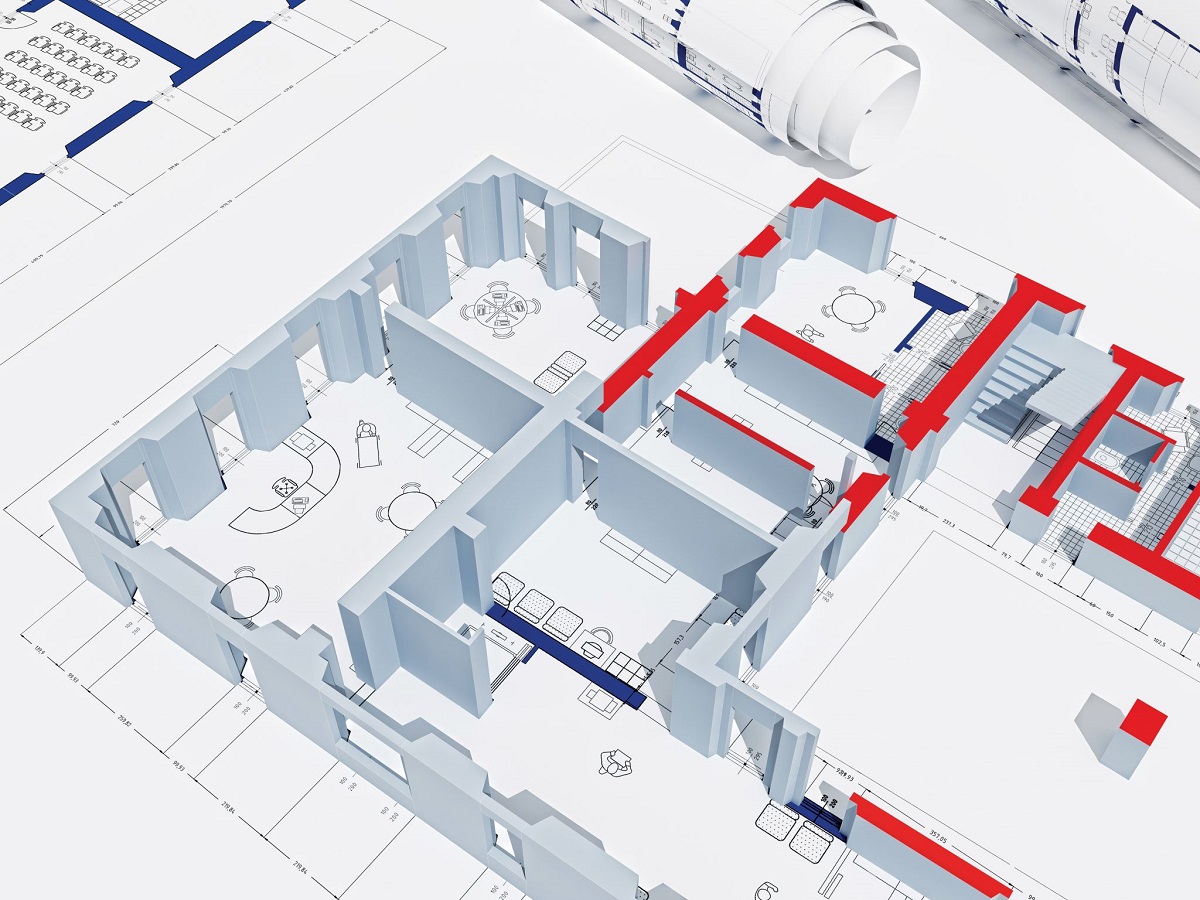
- Enhanced Visualization: With the use of 3D models, BIM architecture allows stakeholders to visualize the building project in a realistic manner. This enables better understanding and decision-making, reducing errors and rework.
- Increased Accuracy: BIM architecture eliminates the reliance on traditional 2D drawings, which are prone to errors and misinterpretation. The digital models created in BIM are accurate and contain detailed information about every component, resulting in improved accuracy throughout the project lifecycle.
- Cost and Time Savings: BIM architecture facilitates more efficient project planning, scheduling, and coordination, resulting in cost and time savings. It helps identify clashes, conflicts, and design issues early on, minimizing the need for costly rework.
- Improved Sustainability: BIM architecture offers powerful tools for energy analysis and performance evaluation. It enables better decision-making regarding building materials, systems, and energy efficiency measures, leading to more sustainable and environmentally-friendly designs.
- Enhanced Facility Management: BIM models can be utilized beyond the construction phase to assist in building maintenance and facility management. The comprehensive information stored in the models helps streamline maintenance processes, asset management, and renovations.
- Increased Client Satisfaction: BIM architecture allows clients to have a clear understanding of the final product before construction even begins. This promotes transparency, improves communication, and increases client satisfaction by aligning expectations with the finished building.
Overall, BIM architecture promotes efficiency, collaboration, and improved project outcomes. It brings significant benefits to the construction industry, leading to cost savings, better decision-making, and ultimately, the delivery of high-quality buildings that meet the needs of clients.
Applications of BIM Architecture
BIM architecture has wide-ranging applications across various stages of a construction project. From initial design to facility management, BIM offers benefits throughout the entire lifecycle of a building. Here are some key applications of BIM architecture:
- Design and Visualization: BIM architecture allows architects and designers to create detailed 3D models of buildings. This helps in visualizing the final product, exploring design alternatives, and making informed decisions regarding aesthetics, functionality, and spatial layout.
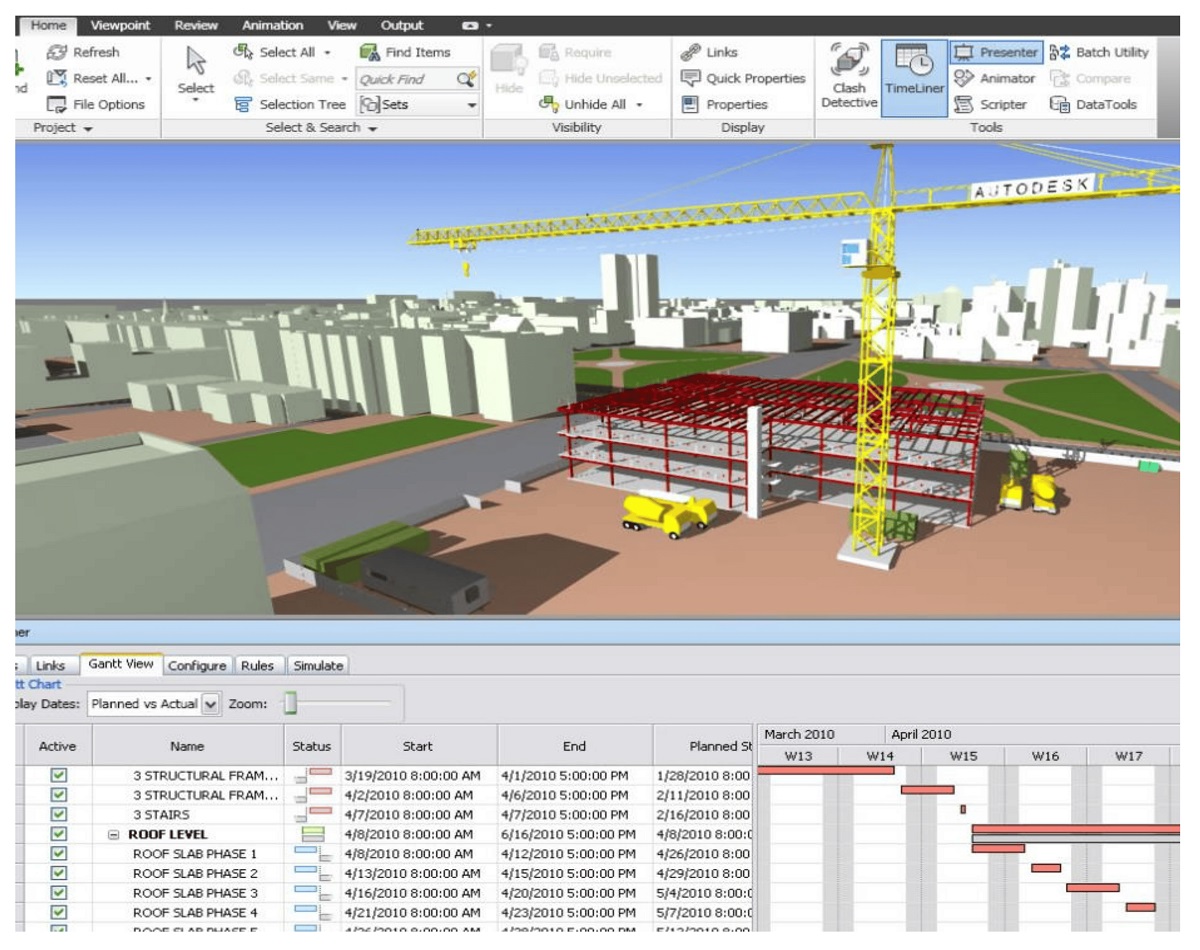
- Clash Detection and Coordination: BIM architecture aids in clash detection by identifying conflicts between different building systems, such as structural, mechanical, electrical, and plumbing. It enables early identification of clashes, minimizing rework, and ensuring smooth coordination between various disciplines.
- Cost Estimation and Quantity Takeoff: BIM architecture integrates cost estimation tools that allow for accurate quantity takeoff and cost estimation. It helps in tracking and managing project costs, providing stakeholders with valuable insights into budgeting and financial planning.
- Construction Planning and Sequencing: BIM architecture assists in creating construction schedules and sequences by visualizing the building process step by step. It enables contractors to identify potential construction issues, optimize sequencing, and streamline workflow, leading to improved efficiency and productivity.
- Maintenance and Facility Management: BIM models contain detailed information about building components, equipment, and systems, making them ideal for facility management. Owners and operators can use BIM architecture to efficiently manage maintenance activities, track assets, and plan renovations or retrofits.
- Sustainability Analysis: BIM architecture offers tools for energy analysis, daylighting simulations, and environmental performance evaluations. These tools enable designers to assess the sustainability and energy efficiency of the building, making informed decisions to reduce environmental impact.
- Asset and Data Management: BIM architecture allows for the integration and management of various types of data related to the building project. This can include documentation, specifications, equipment details, and maintenance schedules. Having all this information in one central location streamlines data management and ensures easy access for stakeholders.
These are just some of the applications of BIM architecture. Its versatility and flexibility allow it to be adapted to specific project requirements, making it an indispensable tool for modern construction practices.
When working with BIM architecture, it’s important to establish clear communication and collaboration processes with all project stakeholders to ensure the successful implementation of BIM throughout the project lifecycle.
Implementation Challenges of BIM Architecture
Although BIM architecture offers numerous advantages, its implementation can come with its fair share of challenges. These challenges can vary depending on the size of the project, the level of technology adoption, and the expertise of the project team. Here are some common implementation challenges of BIM architecture:
- Cost of Technology: Implementing BIM architecture requires investment in software licenses, hardware, training, and infrastructure. The initial cost of technology adoption can be a significant barrier, especially for small to mid-sized firms. However, the long-term benefits often outweigh the initial investment.
- Resistance to Change: The transition from traditional practices to BIM architecture may face resistance from professionals who are accustomed to conventional methods. There can be reluctance towards learning new software tools, processes, and workflows. Overcoming this resistance requires effective change management and continuous training.
- Skill and Knowledge Gap: Proficiency in BIM software and methodologies is essential for successful implementation. However, there is often a skill and knowledge gap within the industry. It can take time and effort to train existing professionals or recruit new talent with BIM expertise.
- Collaboration and Coordination: BIM architecture relies heavily on collaboration and coordination among project team members. Achieving effective collaboration can be challenging, especially when working with multiple stakeholders who may have different levels of technology adoption and communication practices.
- Data Quality and Standardization: BIM architecture relies on accurate and standardized data for optimal results. However, data quality can vary, leading to potential errors and inconsistencies in the models. Establishing data standards and ensuring data accuracy across different sources can be a complex task.
- Interoperability: BIM software tools often come from different vendors, and interoperability between these tools can be a challenge. Efforts to integrate data, workflows, and model exchange between different software platforms require careful planning and coordination.
- Legal and Contractual Issues: Implementing BIM architecture may require updating contract documents and addressing legal issues related to ownership of digital models, intellectual property, and liability for errors or omissions. It is essential to have clear contractual agreements and legal frameworks in place.
Overcoming these implementation challenges requires a proactive approach, commitment from stakeholders, ongoing training and education, and a willingness to adapt to new technologies and processes. With time, experience, and continuous improvement, these challenges can be effectively addressed, ensuring successful implementation of BIM architecture.
Read more: What Is A BIM File?
Future of BIM Architecture
The future of BIM architecture is incredibly promising as advancements in technology continue to shape the construction industry. Here are some key trends that will shape the future of BIM architecture:
- Increased Integration: BIM architecture will become even more integrated with other digital technologies. This includes the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Augmented Reality (AR). These technologies will enhance collaboration, data management, and project visualization.
- Cloud-based Solutions: The adoption of cloud computing in BIM architecture will enable real-time collaboration, improved scalability, and accessibility of project information. Cloud-based solutions will allow stakeholders to access BIM models from anywhere, facilitating remote work and enhancing project efficiency.
- Mobile Technologies: Mobile applications and devices will play a significant role in the future of BIM architecture. Professionals will be able to access and update BIM models on the go, improving communication, data collection, and decision-making processes.
- Big Data and Analytics: BIM architecture will leverage the power of big data and advanced analytics to gain valuable insights from project information. Data-driven analytics will help in optimizing designs, predicting project outcomes, and improving construction and facility management processes.
- Digital Twin Technology: The concept of digital twins, which involves creating a virtual replica of a physical building and its systems, will gain prominence in BIM architecture. Digital twins will facilitate predictive maintenance, performance monitoring, and optimization of building operations.
- Sustainable Design and Green Building: BIM architecture will continue to support sustainable design practices by integrating energy analysis, environmental simulations, and materials selection tools. This will enable architects to create more efficient, environmentally-friendly buildings that reduce energy consumption and carbon footprint.
- Advanced Visualization: The future of BIM architecture will see advancements in visualization technologies, including virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR). These technologies will enable stakeholders to experience and interact with BIM models in immersive and realistic ways, improving design review, construction coordination, and client engagement.
With these advancements, BIM architecture will become even more essential in the construction industry, transforming the way buildings are designed, constructed, and maintained. The future of BIM architecture holds the promise of increased efficiency, collaboration, sustainability, and overall project success.
Conclusion
BIM architecture has revolutionized the construction industry, offering a more efficient and effective approach to building design, construction, and management. By leveraging digital technologies, BIM architecture has transformed the way building projects are planned, visualized, and executed.
Throughout this article, we have explored the definition and benefits of BIM architecture. We have seen how it enables improved collaboration, enhanced visualization, increased accuracy, and cost and time savings. BIM architecture has applications across various stages of a construction project, from design and clash detection to facility management and sustainability analysis.
However, implementing BIM architecture does come with its challenges. These challenges include the cost of technology, resistance to change, skill and knowledge gaps, data quality, and interoperability issues. Overcoming these challenges requires a proactive mindset, commitment from stakeholders, and ongoing training and education.
The future of BIM architecture looks promising, with advancements such as increased integration with other technologies, cloud-based solutions, mobile technologies, big data and analytics, digital twin technology, sustainable design practices, and advanced visualization. These developments will further enhance the efficiency, collaboration, and sustainability of construction projects.
In conclusion, BIM architecture is transforming the way buildings are designed, constructed, and maintained. Its adoption brings numerous benefits and opportunities for the construction industry. By embracing BIM architecture, professionals can enhance collaboration, improve project outcomes, and deliver high-quality buildings that meet the expectations of clients and society as a whole.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is BIM Architecture?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.









0 thoughts on “What Is BIM Architecture?”