Home>diy>Building & Construction>What Is A BIM File?

Building & Construction
What Is A BIM File?
Modified: December 7, 2023
Discover the meaning and purpose of a BIM file in the building construction industry. Learn how this digital format enhances collaboration and streamlines project management.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
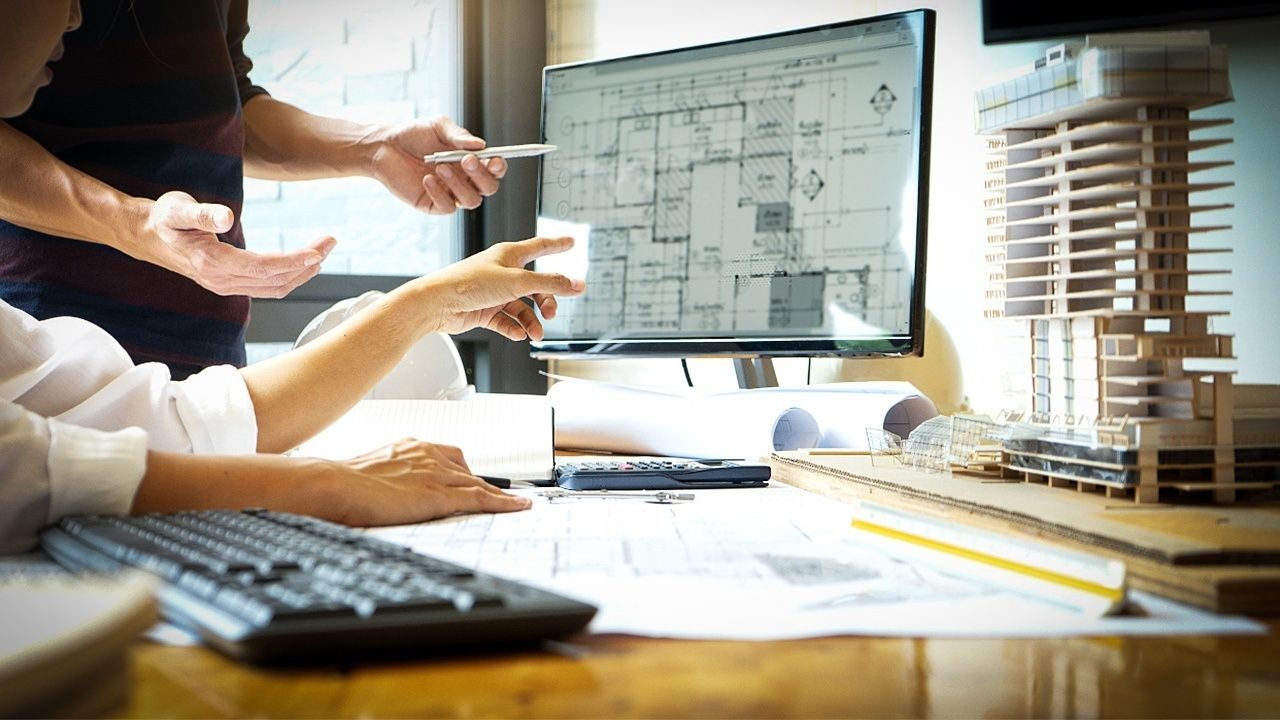
In the world of construction and architecture, technology has revolutionized the way we plan, design, and execute building projects. One such technological advancement is the Building Information Modeling (BIM) system, which has become an integral part of the construction industry. BIM provides a digital representation of a building’s physical and functional characteristics, allowing architects, engineers, and contractors to collaborate and coordinate effectively throughout the construction process.
At the heart of the BIM system lies the BIM file, a digital file that stores all the information related to a building project. This file encompasses a wide range of data, including 3D models, technical specifications, cost estimates, scheduling information, and more. In this article, we will delve into the world of BIM files, exploring their definition, benefits, common file formats, and much more.
Key Takeaways:
- BIM files revolutionize construction by providing comprehensive digital representations, enhancing collaboration, visualization, cost estimation, and sustainability analysis. The future holds even more potential with AI, IoT, and VR/AR integration.
- BIM file compatibility and data exchange continue to improve, driven by open BIM standards and cloud-based collaboration. The future of BIM files looks promising, with advancements in AI, IoT, VR/AR, and expanded data capabilities.
Read more: What Is BIM?
Definition of BIM File
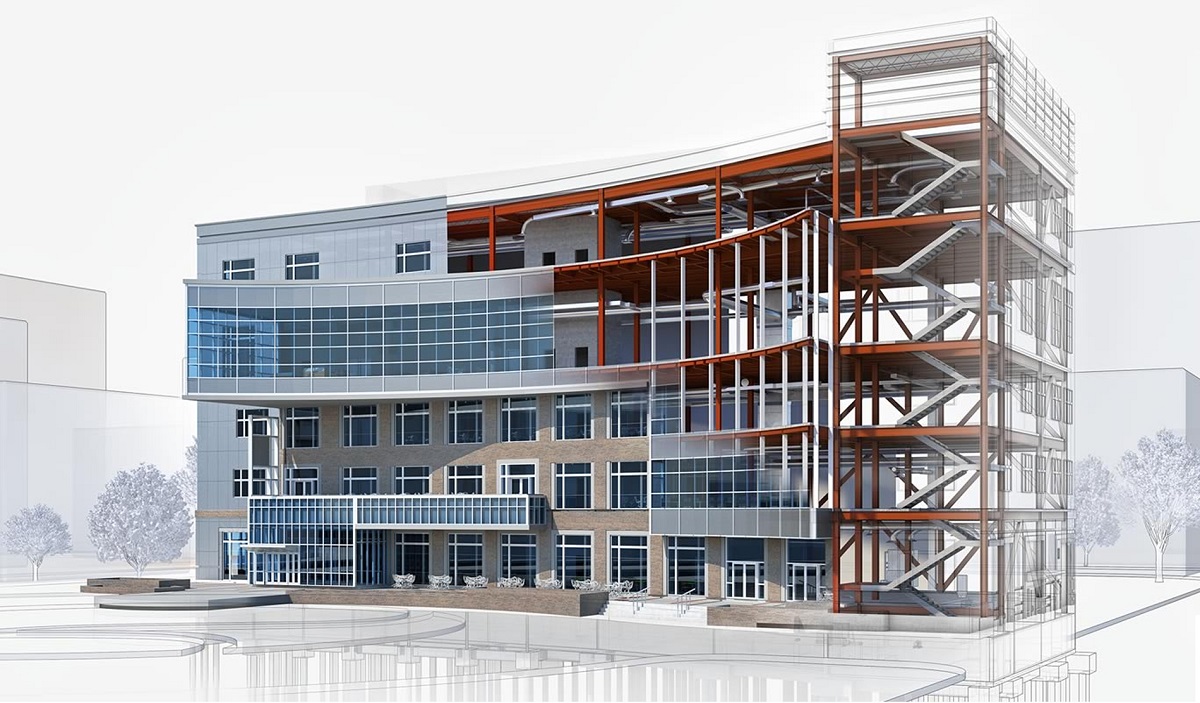
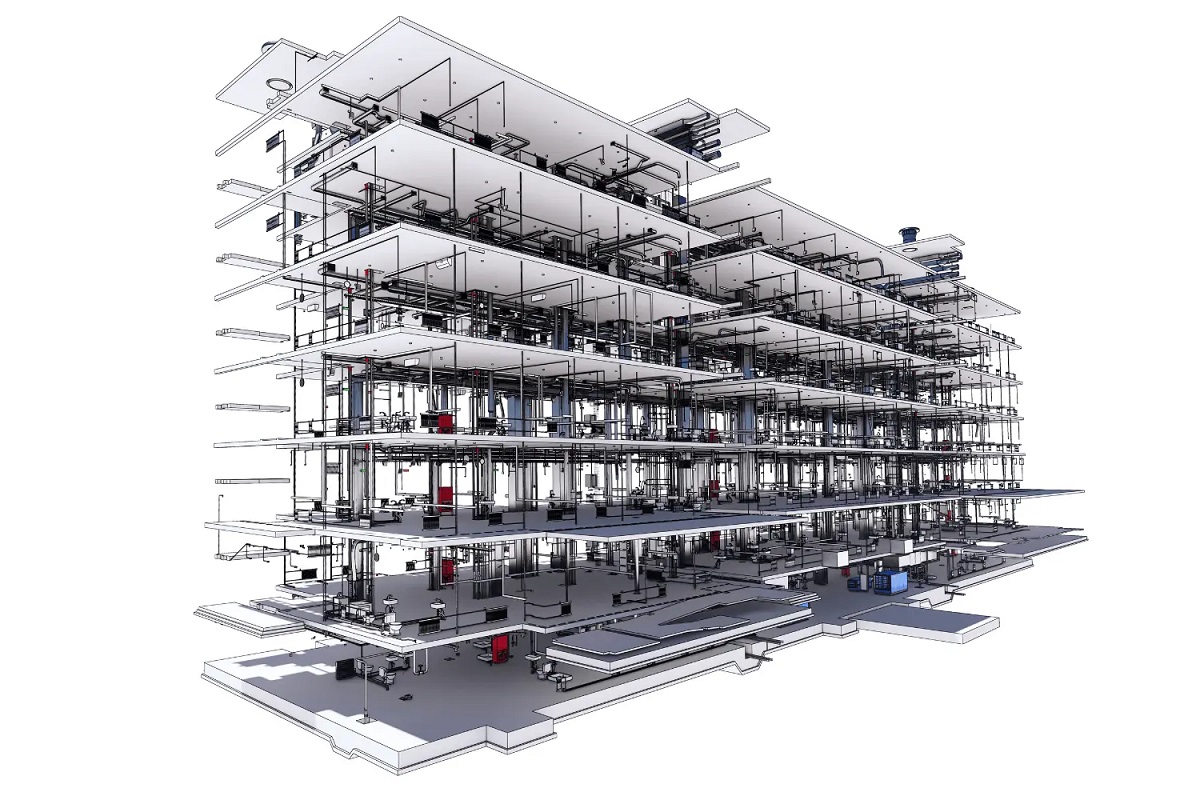
A BIM file, short for Building Information Modeling file, is a digital file that contains comprehensive and detailed information about a building project. It serves as a central repository for all the data related to the design, construction, and operation of a building. A BIM file goes beyond a simple 3D model by incorporating various layers of information, such as structural, mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems.
Unlike traditional 2D drawings or blueprints, a BIM file provides a holistic view of the building, enabling stakeholders to visualize and understand every aspect of the construction project. It acts as a dynamic and intelligent database that stores not only the geometric representation of a building but also its functional and operational details.
BIM files are created and modified using specialized software applications known as BIM authoring tools. These tools allow architects, engineers, and other professionals to collaboratively create and modify the BIM file throughout the different stages of a project’s lifecycle. As changes are made to the design or specifications, the BIM file updates automatically, ensuring that all parties involved have access to the most up-to-date information.
Furthermore, a BIM file is much more than just a visual representation of a building. It serves as a comprehensive database where information about materials, quantities, costs, scheduling, and performance can be stored. This data-rich environment allows for better decision-making, improved coordination, and reduced errors during the construction process.
Overall, a BIM file acts as a digital twin of the physical building, providing a centralized and intelligent source of information that supports efficient project management and collaboration among stakeholders.
Benefits of BIM File
The utilization of BIM files in the construction industry offers various benefits to all stakeholders involved in a building project. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Improved Collaboration and Coordination: BIM files facilitate better collaboration and coordination among architects, engineers, contractors, and other professionals involved in the construction process. All relevant information is stored in a centralized file, allowing for seamless communication and real-time updates. This leads to fewer clashes, better decision-making, and enhanced project outcomes.
- Enhanced Visualization: BIM files provide a realistic 3D representation of the building, enabling stakeholders to visualize the final product before construction begins. This helps to identify potential design flaws, make necessary modifications, and ensure that the client’s vision is accurately translated into reality.
- Improved Cost Estimation: BIM files contain detailed information about materials, quantities, and costs, allowing for more accurate and efficient cost estimation. This helps in budget management, minimizing cost overruns and ensuring financial transparency throughout the project lifecycle.
- Efficient Construction Process: BIM files enable a more streamlined and efficient construction process. The accurate and detailed information in the file helps contractors plan and sequence activities, identify clashes, and optimize resource allocation. This leads to improved productivity, reduced rework, and faster project completion.
- Improved Facilities Management: Beyond the construction phase, BIM files can be utilized for efficient facilities management. The file contains valuable operational and maintenance information, such as equipment specifications, warranty details, maintenance schedules, and more. This enables better maintenance planning, cost-effective operations, and improved building performance over its lifecycle.
- Sustainable Design and Analysis: BIM files support sustainable building design and analysis. They allow architects and engineers to assess environmental impacts, energy efficiency, and sustainability aspects of the building. By simulating different scenarios and analyzing data within the file, professionals can make informed decisions to create more sustainable and energy-efficient buildings.
Overall, the adoption of BIM files promotes better communication, collaboration, and decision-making, resulting in more efficient and successful building projects.
Common BIM File Formats
While there are several BIM file formats available, some of the most common ones used in the construction industry include:
- Industry Foundation Classes (IFC): IFC is an open and neutral file format developed by BuildingSMART. It is widely adopted and allows for interoperability between different BIM software platforms. IFC files can store a wide range of information, including geometry, properties, and relationships, making it a versatile choice for exchanging data between different stakeholders.
- Revit (RVT): Revit, developed by Autodesk, is a popular BIM software application. It uses the .RVT file format to store BIM data, including 3D models, schedules, and annotations. Revit files can contain highly detailed and parametric information, making it an effective format for architectural and engineering teams.
- COBie (Construction Operations Building Information Exchange): COBie is not a file format per se, but rather a data schema used to exchange facility management information. It captures information such as asset details, warranties, maintenance schedules, and more. COBie data can be exported to various file formats, including spreadsheets and XML, for easy integration into facility management systems.
- DWG (Drawing): DWG is a proprietary file format developed by Autodesk and widely used in the construction industry. While primarily associated with 2D drawings, DWG files can also incorporate 3D BIM data. They are commonly used for design collaboration and can be opened in various AutoCAD software applications.
- IFD (Industry Foundation Class for Data): IFD is another file format based on the IFC standard. It focuses on storing and exchanging non-graphical data related to BIM projects, such as schedules, cost data, and assembly details. IFD files can be used to supplement IFC files, enabling better integration between different software systems.
It is important to note that BIM software applications may support multiple file formats, allowing for seamless interoperability and data exchange between different platforms. The choice of file format often depends on the specific software being used and the requirements of the project.
Regardless of the file format, proper file management and version control are essential to ensure smooth collaboration and data integrity throughout the construction process.
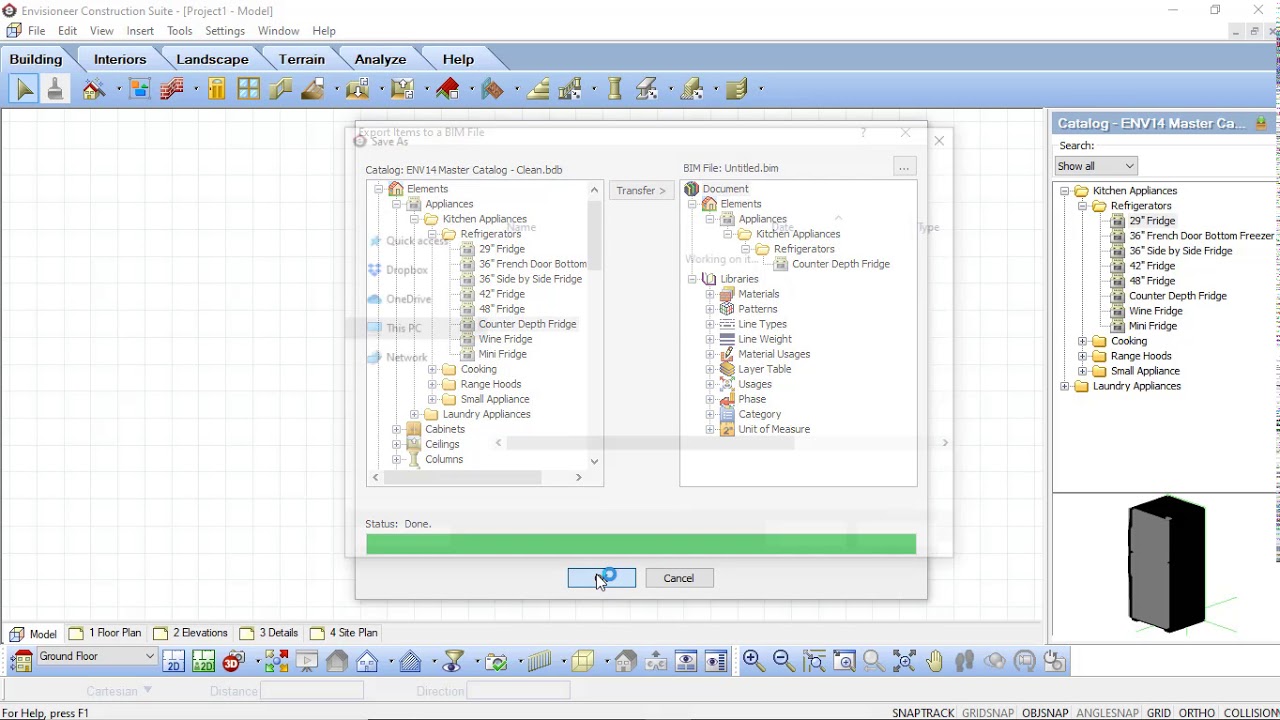
How to Open and View a BIM File
Opening and viewing a BIM file requires specialized BIM software capable of interpreting the file format. Here are the steps to open and view a BIM file:
- Select a BIM Software: First, you need to choose a BIM software application that supports the specific file format of the BIM file you want to open. Popular options include Autodesk Revit, ArchiCAD, Navisworks, Tekla, and Trimble Connect.
- Installation and Setup: Download and install the chosen BIM software on your computer. Ensure that your system meets the software’s minimum requirements. Once installed, follow the setup and configuration instructions provided by the software.
- Open the BIM Software: Launch the software and navigate to the option to open a file. This can usually be found in the application’s main menu or toolbar. Click on the “Open” or “Import” button to proceed.
- Locate the BIM File: In the file browser window, locate the directory where the BIM file is saved. Select the file and click “Open” or “Import” to load it into the BIM software.
- Navigation and Exploration: Once the BIM file is loaded, you can navigate and explore the model in the software’s 3D view. Use navigation tools like pan, zoom, and orbit to move around the virtual building. You can also switch between different views, such as floor plans, elevations, and sections, to analyze specific areas of the building.
- Accessing BIM Data: BIM software allows you to access and query the data within the BIM file. You can click on objects or elements in the model to view their properties, dimensions, and other relevant information. This provides insights into the building’s components and facilitates analysis and coordination.
- Collaboration and Markups: BIM software often includes collaboration features that enable multiple users to work on the same model simultaneously. You can make markups, annotations, and comments on the model to communicate and share information with team members. These collaboration tools enhance communication and coordination among project stakeholders.
It is important to note that BIM files can be large and complex, requiring sufficient computing resources to open and view them smoothly. Additionally, some BIM software applications offer cloud-based solutions, allowing access to BIM files from any device with an internet connection.
By following these steps, you can open and view a BIM file using the appropriate BIM software, enabling you to explore the digital representation of the building project and access valuable data within the file.
When working with BIM files, it’s important to ensure that all project team members are using compatible software versions to avoid compatibility issues.
Read more: What Is BIM 360?
BIM File Conversion
BIM file conversion refers to the process of transforming a BIM file from one format to another. This can be useful when different stakeholders in a construction project use different software applications that support specific file formats. BIM file conversion enables seamless data exchange and collaboration between various software platforms. Here are some key aspects to consider regarding BIM file conversion:
- Understanding File Formats: Familiarize yourself with the different BIM file formats and their specific characteristics. Each format has its own advantages and limitations, so it is important to choose the most appropriate format for your needs.
- Identifying Conversion Requirements: Determine why you need to convert the BIM file. Are you collaborating with stakeholders who use different software? Do you require a specific file format for a particular analysis or application? Understanding your conversion requirements will guide you in selecting the appropriate tools and methods.
- Choose a Conversion Method: There are several methods available for BIM file conversion. Some software applications offer built-in conversion tools, allowing you to export/import different file formats directly. Alternatively, third-party conversion software or plugins can be used to convert BIM files between different formats.
- Consider Compatibility: When converting BIM files between formats, ensure compatibility between the source and target software applications. Verify that the software can properly read and interpret the converted file to avoid any loss of data or information.
- Review Quality and Accuracy: After converting the BIM file, it is crucial to review the converted file for any discrepancies or errors. Pay attention to the geometry, attributes, and other important information to ensure that the converted file accurately represents the original model.
- File Size and Performance: Keep in mind that converting a BIM file may affect its size and performance. Some file formats may have better compression techniques, resulting in smaller file sizes. However, be cautious that too much compression could degrade the quality of the model or cause performance issues in the software.
- Version Control: When working with converted BIM files, it is essential to establish version control and maintain clear documentation of the conversion process. This will help manage changes and ensure that everyone involved is using the most up-to-date file.
By understanding the different file formats, assessing conversion requirements, choosing the right method, ensuring compatibility, reviewing accuracy, and considering file size and performance, BIM file conversion can be a seamless and efficient process. Proper planning and attention to detail will ensure effective collaboration and data exchange among project stakeholders using different software applications.
BIM File Compatibility
BIM file compatibility refers to the ability of different software applications to work together and exchange data seamlessly. In the construction industry, where various stakeholders use different software tools, ensuring compatibility between BIM files is crucial for effective collaboration and project management. Here are some key aspects to consider regarding BIM file compatibility:
- Interoperability: Interoperability is the foundation of BIM file compatibility. It refers to the ability of software applications to exchange and interpret information from different file formats. An interoperable BIM environment allows stakeholders to work together regardless of the software they use.
- Open BIM Standards: Open BIM standards, such as Industry Foundation Classes (IFC), promote file compatibility and interoperability. IFC is an open and neutral file format that allows BIM data to be exchanged between different software applications without loss of information. Using open standards helps minimize barriers and enables seamless collaboration.
- Software Integration: Some software applications offer built-in features or plugins to import/export BIM files in various formats. This integration simplifies compatibility between different file formats and enhances collaboration among stakeholders who use different software applications.
- File Format Support: When selecting BIM software, it is important to consider the range of file formats the software supports. The more file formats a software application can read and write, the more compatible it is with other software tools. This flexibility allows for smoother data exchange between stakeholders using different software applications.
- Metadata and Data Exchange: BIM file compatibility is not just about geometry and visual representation. It also involves the exchange of metadata and non-graphical data, such as properties, attributes, and scheduling information. Ensuring that metadata is preserved and accurately exchanged between software applications is crucial for maintaining data consistency and integrity.
- Version Control: BIM file compatibility may also involve managing different versions of the same file. It is important to establish version control protocols and communicate any updates or changes to all stakeholders. Clear documentation and communication minimize confusion and ensure that everyone is working with the latest version of the file.
- Regular Testing and Validation: As software applications and file formats evolve, it is essential to regularly test and validate BIM file compatibility. Stay updated with the latest software versions and file format standards to ensure that your BIM files remain compatible and can be seamlessly exchanged with other stakeholders.
By prioritizing interoperability, utilizing open BIM standards, leveraging software integration, considering file format support, ensuring accurate metadata exchange, implementing version control, and regularly testing compatibility, BIM file compatibility can be achieved. This enables stakeholders to collaborate effectively, eliminate data silos, and streamline the construction process.
BIM File Applications
BIM files have a wide range of applications across the construction industry, offering numerous benefits to stakeholders involved in the building process. Here are some key areas where BIM files are utilized:
- Design and Visualization: BIM files are extensively used in the design phase of a project. They provide a detailed 3D visualization of the building, enabling architects, engineers, and clients to better understand the design concept. BIM files allow for virtual walkthroughs, lighting analysis, and material selection, aiding in the decision-making process.
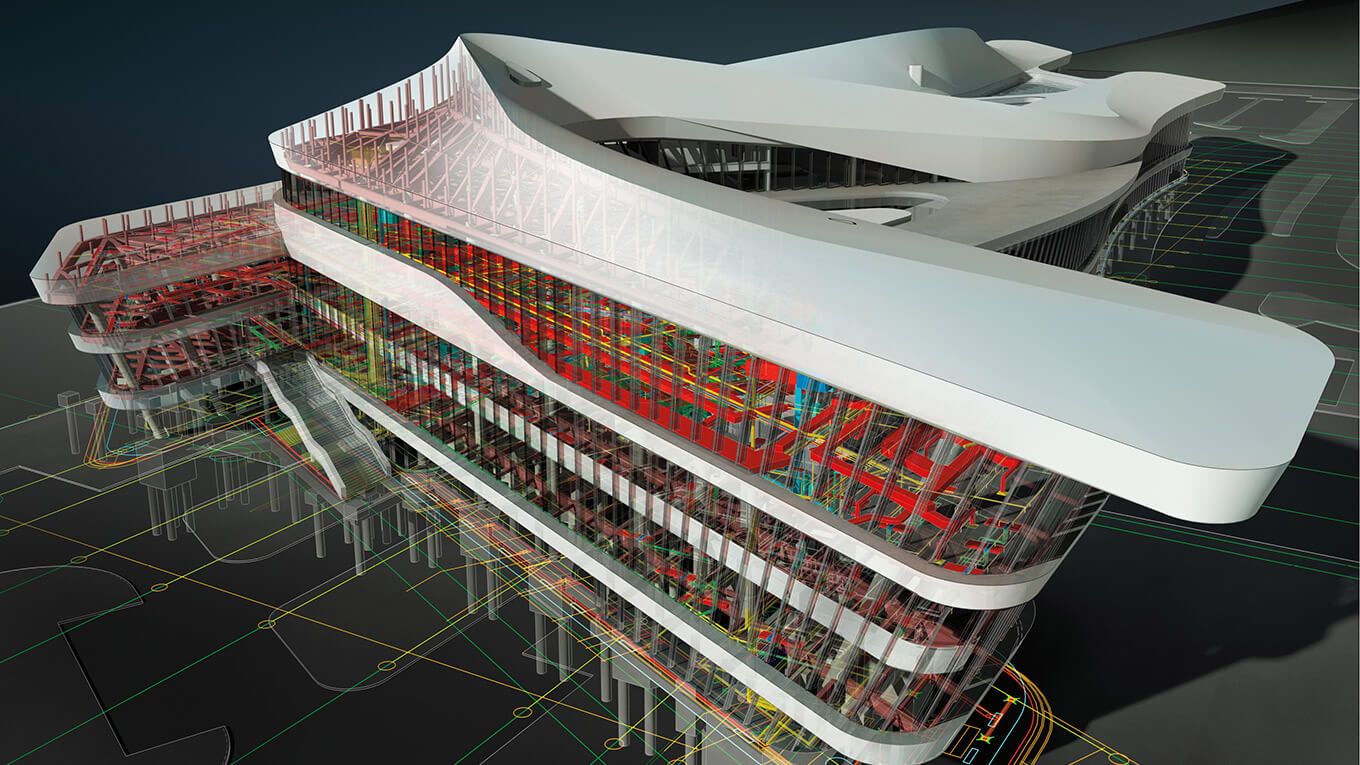
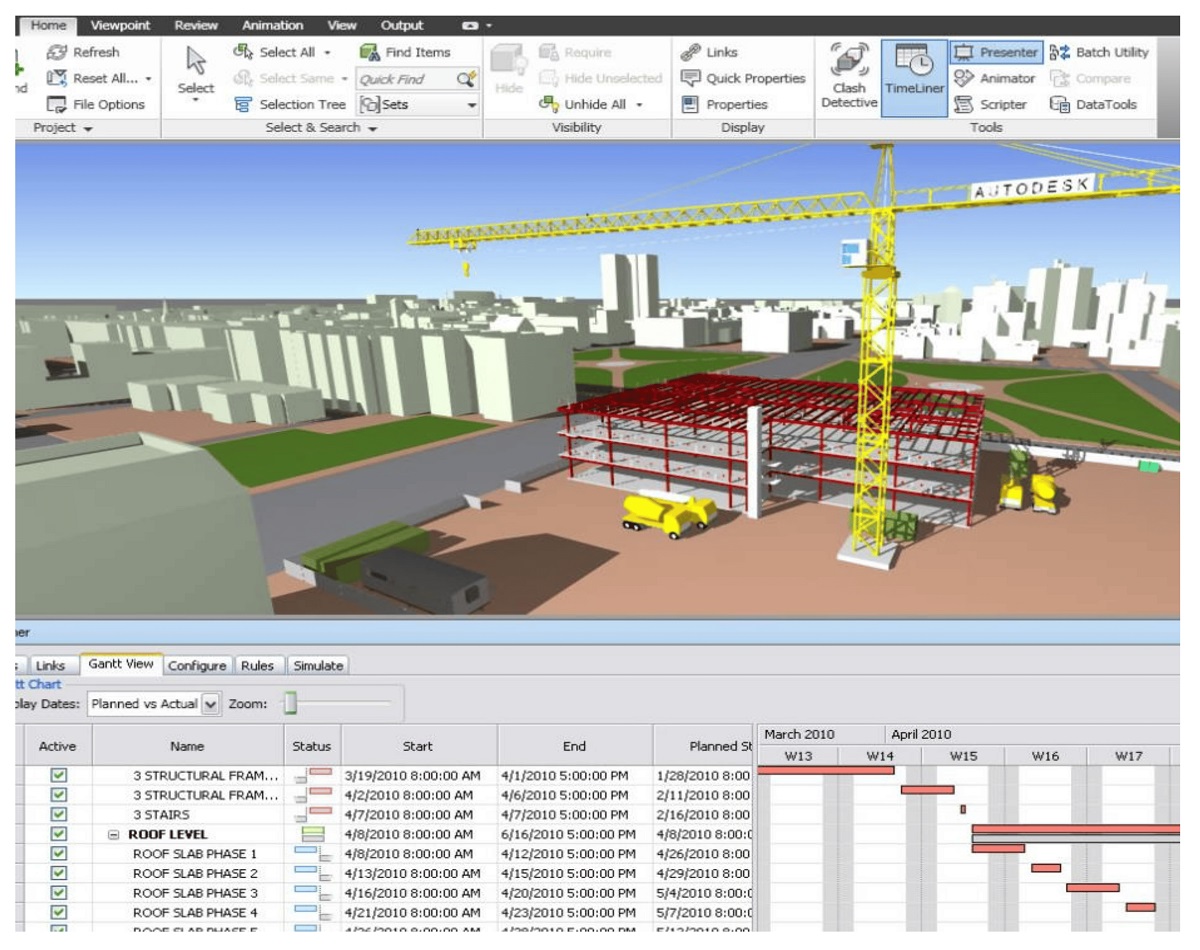
- Construction Planning and Coordination: BIM files play a vital role in construction planning and coordination. They allow contractors to better understand the building’s structure, systems, and logistics, resulting in improved sequencing, clash detection, and resource allocation. BIM files aid in reducing conflicts, optimizing construction schedules, and minimizing cost overruns.
- Cost Estimation and Quantity Takeoff: BIM files contain valuable information about materials, components, and quantities. Construction professionals can leverage this data to generate accurate cost estimates and perform quantity takeoffs. BIM files enable more efficient and precise cost management throughout the project lifecycle.
- Sustainability Analysis: BIM files support sustainability analysis, allowing professionals to evaluate the environmental impact of the building. Through energy analysis, daylighting simulation, and lifecycle assessment, BIM files help optimize resource usage and enhance the overall sustainability of the project.
- Facilities Management: Following the completion of a construction project, BIM files continue to be valuable in the facilities management phase. They serve as a repository of information about the building’s equipment, maintenance schedules, and warranty details. BIM files facilitate efficient maintenance planning, asset management, and facility operations throughout the building’s lifecycle.
- Clash Detection and Risk Mitigation: BIM files enable clash detection by overlaying various building systems and components, such as architectural, structural, mechanical, and electrical. This helps identify and resolve clashes and conflicts before construction begins, reducing errors and rework. BIM files support risk mitigation by improving coordination and reducing potential on-site issues.
- Construction Documentation: BIM files can be leveraged to generate construction documentation, such as detailed drawings, schedules, and specifications. This streamlines the documentation process and ensures consistency and accuracy in the creation of construction deliverables.
- Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality: BIM files can be integrated with virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies to create immersive and interactive experiences. Stakeholders can visualize the building in a virtual environment, enabling real-time interactions and simulations for design validation, user experience, and training purposes.
These are just some of the many applications of BIM files in the construction industry. By leveraging the power of BIM technology, stakeholders can enhance collaboration, improve decision-making, and streamline the entire construction process.
Future of BIM Files
The future of BIM files looks promising, as advancements in technology and industry practices continue to shape the construction industry. Here are some potential developments and trends that will impact the future of BIM files:
- Cloud-based Collaboration: Cloud-based BIM platforms are on the rise, allowing stakeholders to access and collaborate on BIM files from anywhere, using any device. This enables seamless real-time collaboration, eliminates data silos, and enhances communication and coordination among project teams.
- Enhanced Interoperability: As the industry moves toward greater interoperability, BIM software applications will continue to improve their compatibility with different file formats. The adoption of open standards, such as IFC, will enable smoother data exchange and seamless collaboration across diverse software platforms.
- Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML technologies have the potential to revolutionize BIM files. These technologies can analyze massive amounts of data within BIM files, offering insights and predictions for optimizing design, construction, and facility management processes. AI-powered automation can streamline tasks such as clash detection, cost estimation, and scheduling.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: The integration of IoT devices with BIM files will enable the collection of real-time data on building performance, energy usage, and occupant behavior. This data can be used to optimize building operations, enhance maintenance strategies, and improve energy efficiency.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR): VR and AR technologies will continue to enhance the visualization and communication aspects of BIM files. Stakeholders will be able to explore virtual models in a more immersive manner, making design reviews, clash detection, and client presentations more engaging and effective.
- BIM on Mobile Devices: With the increasing power and capabilities of mobile devices, BIM files will become more accessible on smartphones and tablets. This allows on-site personnel to access and interact with BIM data in real-time, improving collaboration, reducing errors, and enhancing efficiency on the construction site.
- Digital Twin Integration: Combining BIM files with the concept of digital twins will enable the creation of a synchronized virtual representation of the physical building throughout its lifecycle. This integration will facilitate better predictive maintenance, monitoring of energy usage, and optimization of building performance.
- Expanded Data Capabilities: BIM files will continue to evolve beyond geometry and visual representation. They will incorporate more robust data, including sensor data, materials information, and manufacturer specifications. This enhanced data-rich environment will provide a more comprehensive understanding of the building and support better decision-making.
The future of BIM files is bright, as technological advancements and industry collaboration push the boundaries of what is possible. As these trends continue to unfold, BIM files will become even more valuable in driving innovation, improving efficiency, and transforming the way buildings are designed, constructed, and managed.
Read more: What Is BIM In Revit?
Conclusion
BIM files have revolutionized the construction industry by providing a comprehensive and intelligent digital representation of building projects. These files serve as a central repository of information, encompassing not only 3D models but also crucial data about the building’s functional, operational, and cost aspects.
The benefits of BIM files are vast and wide-ranging. They enable improved collaboration, coordination, and visualization throughout the construction process. Stakeholders can make informed decisions, minimize errors, optimize resource allocation, and streamline project timelines and costs.
With the widespread adoption of open BIM standards and advancements in cloud-based collaboration, BIM file compatibility and data exchange among diverse software platforms will continue to improve. The integration of AI, ML, IoT, and VR/AR technologies will further enhance the capabilities of BIM files, allowing for predictive analytics, real-time monitoring, and immersive experiences.
The future of BIM files is promising. As technology continues to evolve, BIM files will become even more powerful, providing a holistic view of building projects and facilitating efficient facilities management. The integration of digital twins, expanded data capabilities, and mobile device accessibility will drive innovation and enhance decision-making throughout the lifecycle of a building.
In conclusion, BIM files are a game-changer for the construction industry. They offer a wealth of benefits, including improved collaboration, enhanced visualization, cost estimation accuracy, sustainability analysis, and streamlined facilities management. As the industry embraces new technologies and standards, the potential for BIM files to revolutionize construction processes, drive efficiency, and create sustainable and intelligent buildings is limitless.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A BIM File?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.









0 thoughts on “What Is A BIM File?”