Home>Furniture & Design>Interior Design Trends>What Is Laminated Glass

Interior Design Trends
What Is Laminated Glass
Modified: March 23, 2024
Discover the benefits of laminated glass for interior design trends. Learn how laminated glass enhances safety, aesthetics, and functionality in modern spaces.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Laminated glass is a versatile and innovative material that has revolutionized the way we think about safety, security, and design in the realm of architecture and interior design. This advanced type of glass is engineered to provide exceptional strength and protection, making it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications. From residential homes to commercial skyscrapers, laminated glass has become an indispensable element in modern construction and design.
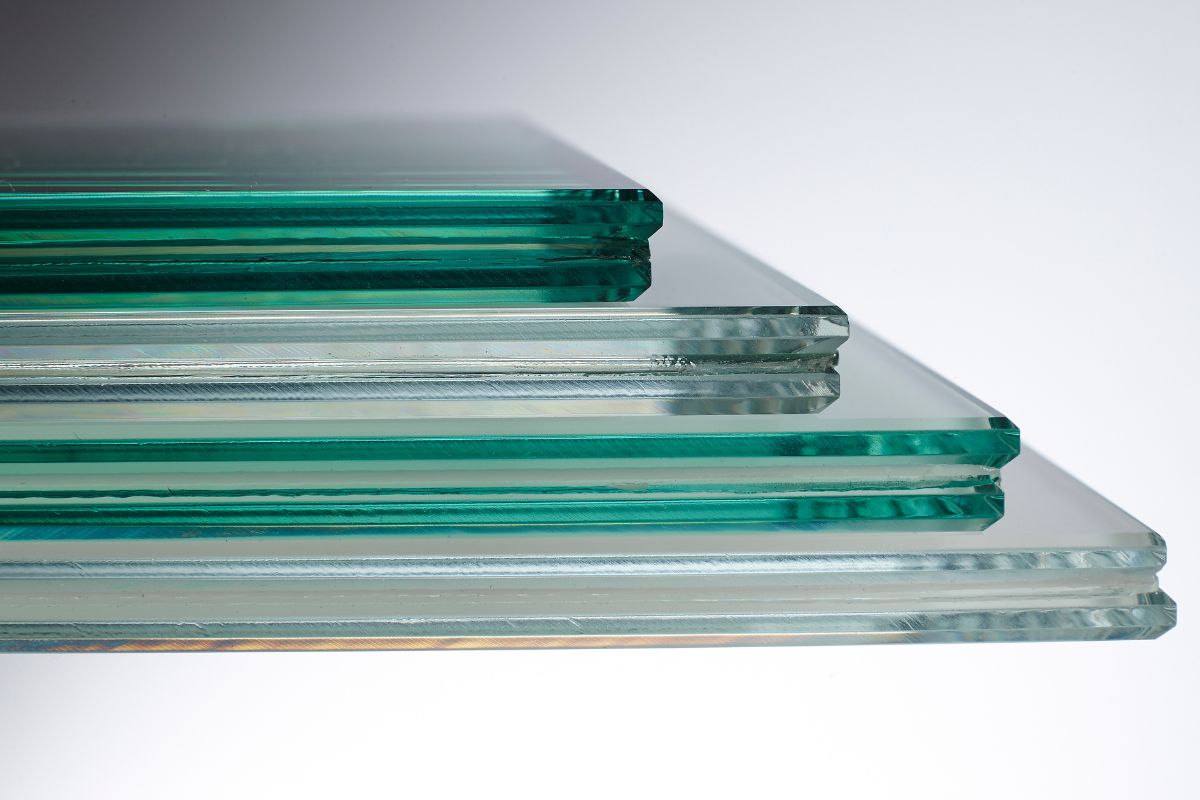
The unique composition and manufacturing process of laminated glass set it apart from traditional glass materials. By combining multiple layers of glass with an interlayer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), laminated glass achieves remarkable durability and resilience. This construction enables the glass to remain intact even when shattered, reducing the risk of injury from sharp shards and maintaining the structural integrity of the installation.
In addition to its exceptional strength, laminated glass offers a myriad of benefits that cater to both practical and aesthetic considerations. Its ability to mitigate noise transmission and filter out harmful UV rays makes it an attractive choice for enhancing comfort and sustainability within interior spaces. Furthermore, the versatility of laminated glass allows for creative applications in architectural design, enabling the incorporation of natural light and panoramic views while ensuring the safety and security of occupants.
As the demand for sustainable and resilient building materials continues to grow, laminated glass has emerged as a frontrunner in meeting these evolving needs. Its ability to withstand extreme weather conditions, resist forced entry, and provide sound insulation positions it as a cornerstone of modern architectural solutions. Whether used in skylights, balustrades, or curtain walls, laminated glass embodies a harmonious blend of functionality and elegance, elevating the overall aesthetic appeal of any space.
In the subsequent sections, we will delve deeper into the composition, manufacturing process, benefits, applications, and safety features of laminated glass, shedding light on its multifaceted nature and the pivotal role it plays in shaping the future of interior design and architecture.
Key Takeaways:
- Laminated glass is a super strong and safe material made by bonding layers of glass with a special interlayer. It keeps people safe, reduces noise, and looks really cool in buildings!
- Laminated glass is like a superhero for buildings, protecting them from bad weather and keeping people safe. It’s also great for letting in natural light and making spaces look amazing.
Read more: How To Tell If Glass Is Laminated
Composition of Laminated Glass
Laminated glass is engineered using a meticulous composition that imbues it with exceptional strength and safety features. This innovative material typically consists of two or more layers of glass, which are bonded together by an interlayer made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA). The layers of glass can vary in thickness and may include different types of glass, such as annealed, tempered, or even coated glass, depending on the specific requirements of the application.
The interlayer, often referred to as the "sandwiched" layer, plays a crucial role in enhancing the structural integrity of laminated glass. In the event of breakage, the interlayer effectively holds the shattered glass in place, preventing it from dispersing into sharp, hazardous fragments. This unique characteristic significantly reduces the risk of injury, making laminated glass an ideal choice for applications where safety is paramount.
The interlayer also contributes to the remarkable resilience of laminated glass, enabling it to withstand impact and external forces. This feature is particularly valuable in areas prone to severe weather conditions or potential security threats. Additionally, the interlayer acts as a sound insulator, dampening external noise and enhancing the acoustic comfort of interior spaces.
Furthermore, the interlayer can be customized to incorporate various interlayer colors, patterns, or even embedded materials, offering designers and architects a wide range of creative possibilities. This flexibility allows for the integration of laminated glass into diverse design concepts, adding a touch of sophistication and individuality to architectural projects.
The combination of glass and interlayer in laminated glass results in a composite material that exhibits superior optical clarity and transparency. This clarity makes it an excellent choice for applications where unobstructed views and natural light transmission are desired, such as glass facades, skylights, and interior partitions.
In essence, the composition of laminated glass epitomizes a harmonious fusion of strength, safety, and design versatility. Its multi-layered structure, coupled with the interlayer's protective and aesthetic properties, positions laminated glass as a cornerstone of modern architectural and interior design solutions.
Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of laminated glass involves a series of precise steps that culminate in the creation of a resilient and versatile material. The process begins with the careful selection of high-quality glass sheets, which are thoroughly inspected for any imperfections or defects. These glass sheets can vary in thickness and type, depending on the specific requirements of the intended application.
Once the glass sheets are approved for use, they undergo a meticulous cleaning process to ensure that they are free from any contaminants or residues. This step is crucial in guaranteeing the optimal adhesion of the interlayer to the glass surfaces, thereby enhancing the overall strength and integrity of the laminated glass.
Subsequently, the cleaned glass sheets are assembled with the interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA). The interlayer is precisely cut to match the dimensions of the glass sheets, ensuring a seamless fit and uniform distribution of the interlayer material.
The assembled layers of glass and interlayer are then subjected to a combination of heat and pressure within a specialized autoclave. This process, known as lamination, facilitates the bonding of the glass and interlayer at a molecular level, resulting in a robust composite structure. The application of heat and pressure causes the interlayer to flow and adhere to the glass surfaces, creating a strong and durable bond.
During lamination, any air bubbles or impurities trapped between the layers are effectively removed, further enhancing the optical clarity and integrity of the laminated glass. This meticulous process ensures that the final product meets stringent quality standards and exhibits exceptional transparency and strength.
Following lamination, the edges of the laminated glass may undergo additional processing, such as polishing or edge sealing, to enhance the overall aesthetics and safety of the material. These finishing touches contribute to the seamless integration of laminated glass into architectural and interior design applications, providing a polished and refined appearance.
In essence, the manufacturing process of laminated glass embodies a fusion of precision engineering and advanced technology, resulting in a material that offers unparalleled strength, safety, and design versatility. This process underscores the commitment to quality and innovation, making laminated glass a cornerstone of modern architectural and interior design solutions.
Benefits of Laminated Glass
Laminated glass offers a myriad of compelling benefits that cater to both practical and aesthetic considerations, making it a preferred choice for a wide range of architectural and interior design applications. The unique properties of laminated glass contribute to its versatility and desirability in modern construction and design solutions.
1. Safety and Security:
One of the most prominent benefits of laminated glass is its exceptional safety features. In the event of breakage, the interlayer holds the shattered glass in place, preventing it from dispersing into sharp, hazardous fragments. This significantly reduces the risk of injury, making laminated glass an ideal choice for applications where safety is paramount. Additionally, the robust construction of laminated glass enables it to withstand impact and external forces, enhancing the security of buildings and occupants.
Read more: What Are Laminate Countertops
2. Durability and Resilience:
Laminated glass exhibits remarkable durability and resilience, making it suitable for use in areas prone to severe weather conditions or potential security threats. Its ability to withstand impact, extreme temperatures, and forced entry enhances the longevity and reliability of architectural installations. This durability contributes to the overall sustainability of buildings, reducing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance.
3. Sound Insulation:
The interlayer in laminated glass acts as a sound insulator, effectively dampening external noise and enhancing the acoustic comfort of interior spaces. This feature is particularly valuable in urban environments or areas with high noise levels, where maintaining a peaceful and comfortable indoor environment is essential. Laminated glass contributes to creating a tranquil and serene atmosphere within buildings, promoting occupant well-being.
4. UV Protection:
Laminated glass can be engineered to provide effective UV protection, safeguarding interior spaces and occupants from harmful ultraviolet radiation. This feature helps mitigate the fading of furnishings, artwork, and interior finishes, preserving the aesthetic appeal and value of the space. By filtering out UV rays, laminated glass contributes to creating a healthy and sustainable indoor environment.
5. Design Versatility:
The versatility of laminated glass allows for creative applications in architectural design, enabling the incorporation of natural light and panoramic views while ensuring the safety and security of occupants. Designers and architects can leverage the optical clarity and transparency of laminated glass to create visually stunning and inviting spaces, seamlessly integrating safety and aesthetics.
In essence, the benefits of laminated glass encompass a harmonious blend of safety, durability, sustainability, and design versatility, making it an indispensable element in modern architectural and interior design solutions. Its ability to enhance safety, security, and comfort while offering creative design possibilities positions laminated glass as a cornerstone of innovative and resilient construction practices.
Read more: What Is A Laminate Floor
Applications of Laminated Glass
Laminated glass finds diverse and impactful applications across various architectural and interior design contexts, owing to its exceptional safety features, durability, and design versatility. The unique properties of laminated glass make it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications, contributing to the safety, aesthetics, and functionality of modern built environments.
1. Glass Facades and Curtain Walls:
Laminated glass is extensively used in the construction of glass facades and curtain walls, where it serves as a protective barrier while allowing natural light to permeate interior spaces. The safety features of laminated glass make it well-suited for high-rise buildings and commercial structures, providing occupants with unobstructed views and ample daylight while ensuring their security.
2. Skylights and Roof Glazing:
Incorporating laminated glass in skylights and roof glazing systems allows for the creation of well-lit and visually engaging interior spaces. The durability and resilience of laminated glass make it an ideal choice for overhead applications, offering protection against impact and extreme weather conditions while enhancing the aesthetic appeal of architectural designs.
3. Glass Balustrades and Railings:
Laminated glass is a popular choice for balustrades and railings in both residential and commercial settings. Its safety features, including resistance to breakage and the ability to hold shattered glass in place, make it a preferred material for ensuring the security of elevated walkways, balconies, and staircases, without compromising on transparency and design flexibility.
4. Interior Partitions and Dividers:
Within interior spaces, laminated glass is utilized for creating partitions and dividers that promote an open and airy ambiance while maintaining safety and privacy. Its sound insulation properties contribute to a peaceful indoor environment, while the optical clarity of laminated glass allows for the seamless integration of natural light, enhancing the overall comfort and visual appeal of the space.
5. Glass Floors and Staircases:
Laminated glass is employed in the construction of glass floors and staircases, adding a touch of modernity and sophistication to architectural designs. Its ability to withstand heavy loads and provide a secure walking surface makes it an attractive choice for applications that require transparency and structural integrity, such as mezzanine floors and feature staircases.
6. Automotive and Transportation:
In the automotive industry, laminated glass is utilized for windshields and side windows, offering enhanced safety and protection for vehicle occupants. Its ability to resist impact and maintain structural integrity in the event of breakage contributes to the overall safety standards in automotive design, ensuring the well-being of passengers.
In essence, the applications of laminated glass span a wide spectrum of architectural and interior design contexts, where its safety, durability, and design versatility play a pivotal role in shaping modern built environments. From iconic skyscrapers to residential dwellings, laminated glass continues to redefine the boundaries of safety, aesthetics, and functionality in architectural and interior design practices.
Safety and Security Features
Laminated glass is renowned for its exceptional safety and security features, making it a preferred choice for applications where protection and resilience are paramount. The unique composition of laminated glass, comprising multiple layers of glass bonded with an interlayer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), imbues it with remarkable strength and protective properties.
In the event of breakage, the interlayer plays a pivotal role in holding the shattered glass in place, preventing it from dispersing into sharp, hazardous fragments. This characteristic significantly reduces the risk of injury, making laminated glass an ideal choice for architectural elements such as windows, doors, and glass partitions. The ability of laminated glass to remain intact even when shattered enhances the safety of occupants and minimizes the potential for accidents, particularly in high-traffic areas or locations prone to impact.
Moreover, the robust construction of laminated glass enables it to withstand impact and external forces, making it resistant to forced entry and vandalism. This feature is particularly valuable in applications where security is a primary concern, such as storefronts, display cases, and public facilities. The enhanced security provided by laminated glass contributes to the overall protection of buildings and occupants, instilling a sense of confidence and well-being.
Additionally, laminated glass offers sound insulation properties, effectively dampening external noise and promoting a peaceful indoor environment. This feature is especially beneficial in urban settings or areas with high noise levels, where maintaining a tranquil and comfortable space is essential. The acoustic comfort provided by laminated glass enhances the overall well-being of occupants, creating a conducive environment for work, relaxation, or social interaction.
In essence, the safety and security features of laminated glass underscore its role as a resilient and protective material in modern architectural and interior design. Its ability to mitigate the risk of injury, resist forced entry, and enhance acoustic comfort positions laminated glass as a cornerstone of safety and security in built environments, contributing to the creation of secure, inviting, and sustainable spaces.
Read more: What Is Cheaper: Carpet Or Laminate?
Conclusion
In conclusion, laminated glass stands as a testament to the seamless integration of safety, resilience, and design versatility in modern architectural and interior design practices. Its unique composition, comprising multiple layers of glass bonded with an interlayer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), embodies a harmonious fusion of strength, transparency, and protective properties. The manufacturing process of laminated glass, characterized by precision engineering and advanced technology, underscores a commitment to quality and innovation, resulting in a material that offers unparalleled durability and optical clarity.
The benefits of laminated glass extend beyond its safety features, encompassing its ability to provide sound insulation, UV protection, and design flexibility. From glass facades and skylights to interior partitions and balustrades, laminated glass finds diverse and impactful applications across various architectural contexts, contributing to the creation of inviting, well-lit, and secure spaces. Its role in enhancing safety, security, and comfort while offering creative design possibilities positions laminated glass as a cornerstone of innovative and resilient construction practices.
As the demand for sustainable and resilient building materials continues to grow, laminated glass has emerged as a frontrunner in meeting these evolving needs. Its ability to withstand extreme weather conditions, resist forced entry, and provide sound insulation makes it an indispensable element in modern architectural and interior design solutions. Whether used in iconic skyscrapers or residential dwellings, laminated glass continues to redefine the boundaries of safety, aesthetics, and functionality in architectural and interior design practices.
In essence, laminated glass represents a harmonious blend of form and function, embodying the ethos of safety, sustainability, and design innovation. Its enduring presence in the built environment serves as a testament to its enduring value and the pivotal role it plays in shaping the future of interior design and architecture. With its multifaceted benefits and applications, laminated glass remains a symbol of resilience and elegance, enriching the built environment and elevating the human experience within architectural spaces.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is Laminated Glass
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.












0 thoughts on “What Is Laminated Glass”