Home>Home Maintenance>How Does A Car Air Conditioner Compressor Work


Home Maintenance
How Does A Car Air Conditioner Compressor Work
Modified: August 17, 2024
Learn how a car air conditioner compressor works and the importance of home maintenance for optimal performance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on how a car air conditioner compressor works. A functioning air conditioner is a vital component of any vehicle, especially during those sweltering summer months. The compressor plays a crucial role in the cooling process, as it is responsible for pressurizing the refrigerant and circulating it throughout the system.
In this article, we will delve into the inner workings of a car air conditioner compressor, discussing its various components and the principles behind its operation. We will also explore the compression cycle and the importance of the lubrication system in maintaining optimal performance. Additionally, we will touch upon common problems that may arise with car air conditioner compressors and provide troubleshooting and maintenance tips to keep your system running smoothly.
So, let’s dive in and unravel the mysteries of the car air conditioner compressor.
Key Takeaways:
- The car air conditioner compressor works by compressing refrigerant gas to cool the vehicle’s interior. Understanding its components and working principles can help troubleshoot issues and ensure a comfortable driving experience.
- Regular maintenance, such as checking for leaks, cleaning the compressor, and monitoring coolant levels, is crucial for extending the lifespan of the car air conditioner compressor. Seeking professional help for complex issues is advisable.
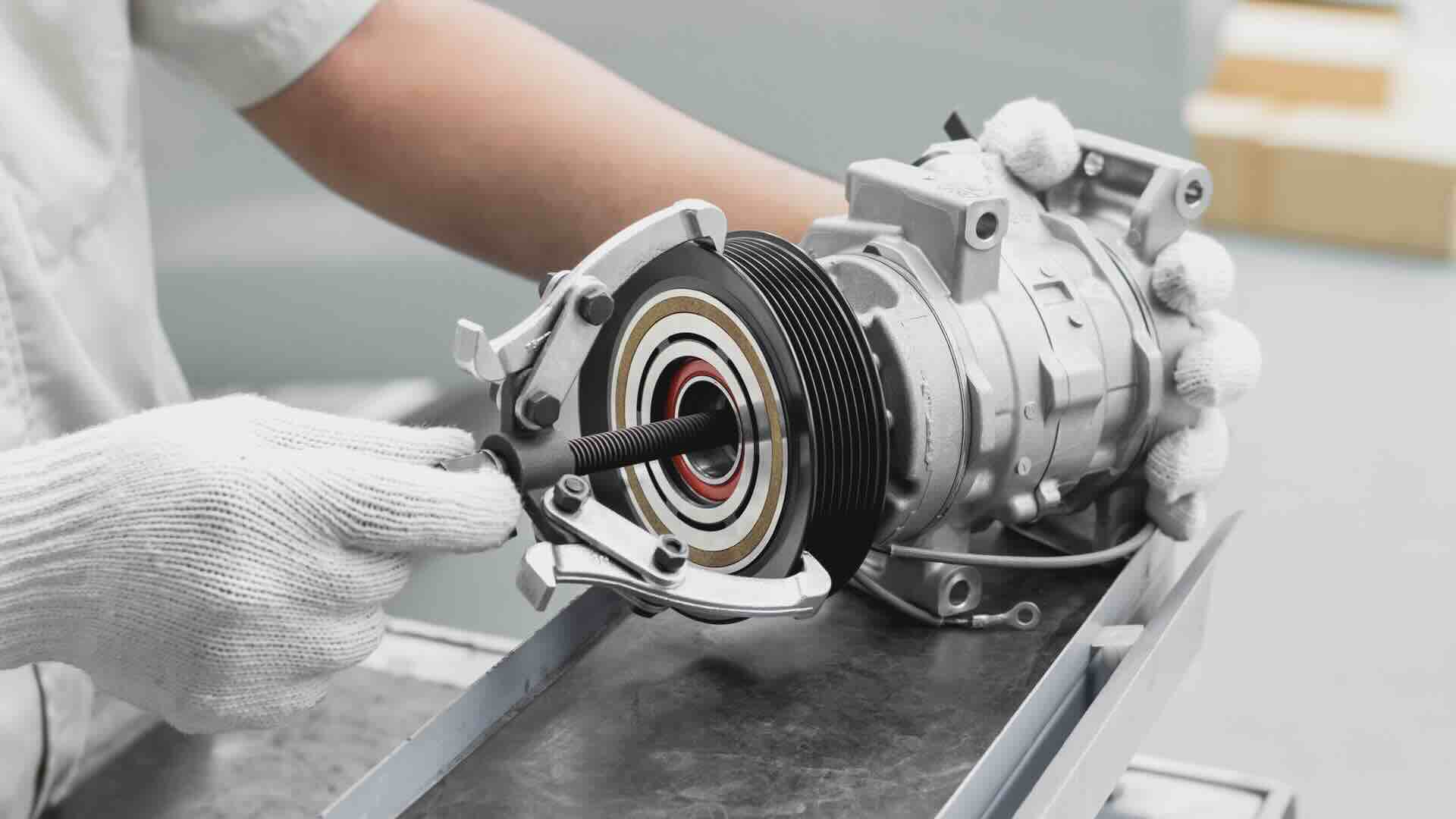
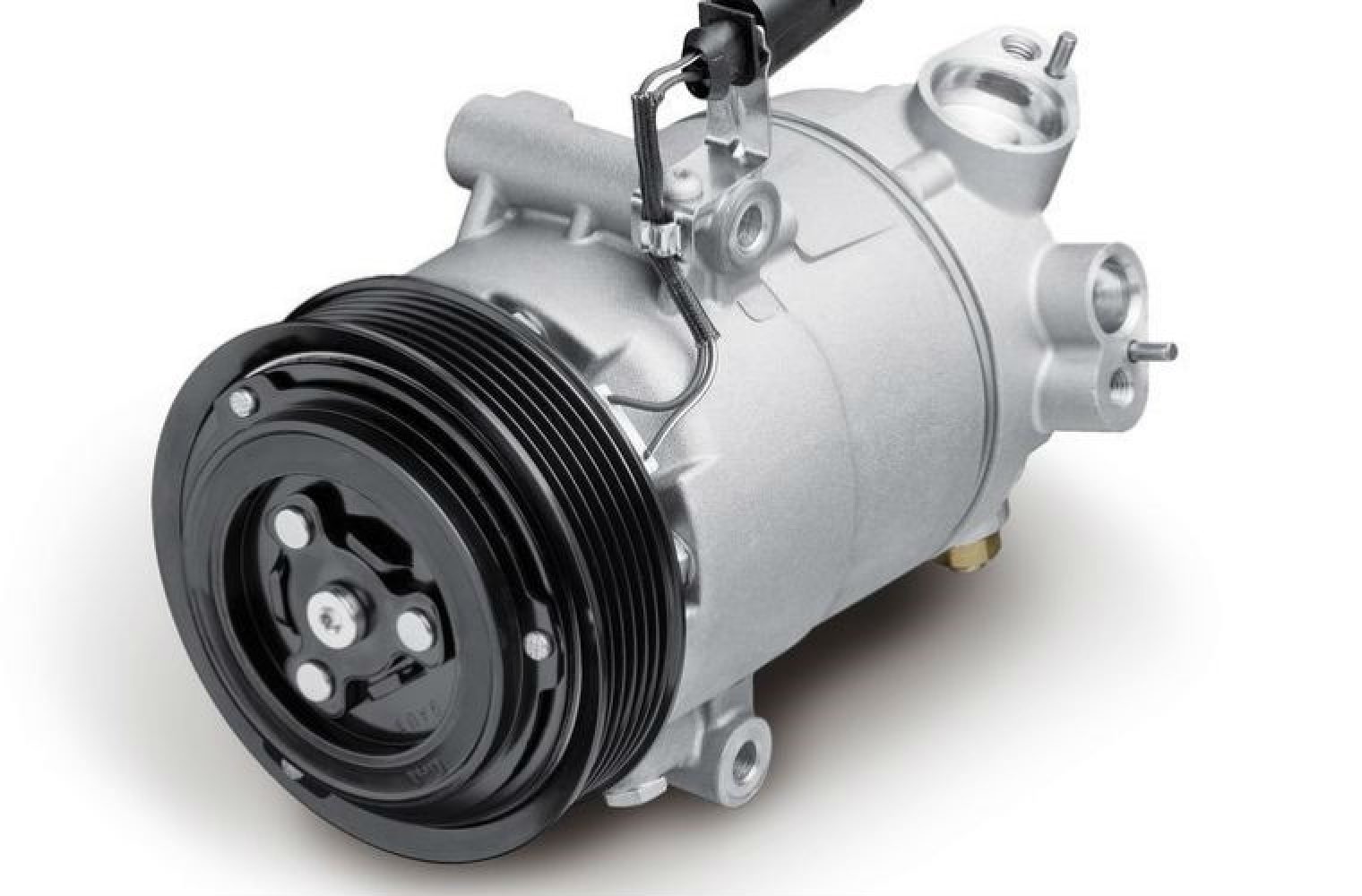
Components of a Car Air Conditioner Compressor
A car air conditioner compressor is a complex mechanical device composed of several key components that work together to facilitate the cooling process. Understanding these components is crucial to grasp how the compressor functions. Let’s take a closer look at each one:
- Compressor Housing: The compressor housing serves as the outer casing that encloses the internal components. It is typically made of high-strength materials to withstand the pressure created during operation.
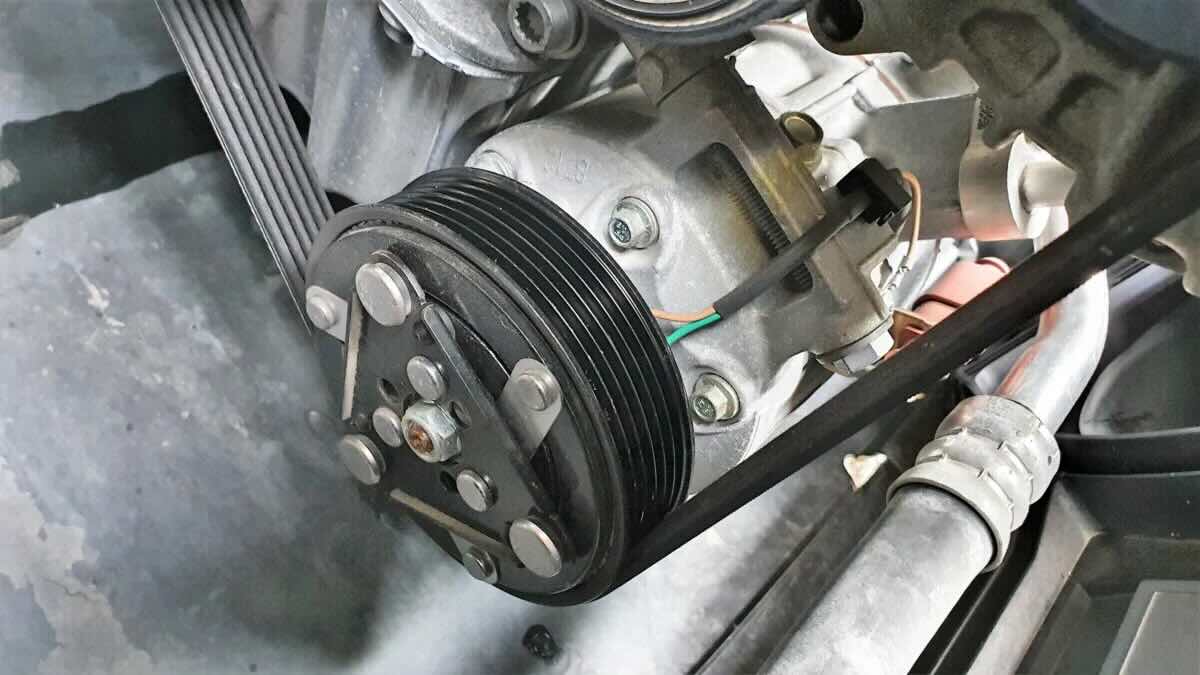
- Drive Pulley: The drive pulley is connected to the vehicle’s engine by a belt. It is responsible for transmitting power from the engine to the compressor.
- Swash Plate: The swash plate is a disc-shaped component that rotates along with the drive pulley. Its angle of inclination determines the compression capacity of the compressor.
- Connecting Rods: These rods connect the swash plate to the pistons. They convert the rotational motion of the swash plate into reciprocating motion.
- Pistons: The pistons move back and forth within the compressor cylinder to compress the refrigerant. They are connected to the connecting rods and are responsible for creating the pressure required for the cooling process.
- Reed Valves: Reed valves, also known as check valves, are responsible for regulating the flow of refrigerant through the compressor. They open and close to allow refrigerant to enter and exit the compression chamber.
- Oil Separator: The oil separator is a component that separates the oil from the refrigerant. It ensures that only the refrigerant circulates through the system while preventing oil from causing any disruptions.
- Pressure Relief Valve: The pressure relief valve is a safety mechanism that prevents excessive pressure buildup within the compressor. If the pressure exceeds the specified limit, the valve opens to release the extra pressure and protect the compressor from damage.
These components work together harmoniously to ensure the efficient operation of the car air conditioner compressor. The drive pulley transfers power from the engine to the compressor, while the swash plate, connecting rods, and pistons generate the compression necessary for the cooling process. The reed valves regulate the flow of refrigerant, and the oil separator and pressure relief valve further aid in maintaining optimal performance and safety.
Working Principles of a Car Air Conditioner Compressor
The car air conditioner compressor operates on a principle known as the vapor compression cycle, which involves the transformation of refrigerant from a low-pressure gas to a high-pressure, high-temperature gas. This transformation is facilitated by the compressor and is essential for the cooling process to occur. Let’s explore the working principles of a car air conditioner compressor in more detail:
1. Suction: The process starts with the suction phase. The compressor draws in low-pressure refrigerant gas from the evaporator through the suction line. As the gas enters the compressor cylinder, the reed valves open to allow the refrigerant to flow in.
2. Compression: Once inside the compressor cylinder, the refrigerant gas encounters the pistons and the swash plate. The rotating motion of the swash plate causes the pistons to move back and forth, compressing the refrigerant gas. This compression raises the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant.
3. Discharge: After being compressed, the high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant gas is discharged from the compressor through the discharge line. The reed valves on the output side of the compressor close to prevent any backflow of refrigerant.
4. Condensation: The hot, high-pressure refrigerant gas then enters the condenser, where it releases heat and undergoes a phase change into a high-pressure liquid. The condenser, usually located in front of the vehicle’s radiator, facilitates the transfer of heat from the refrigerant to the surrounding air.
5. Expansion: The high-pressure liquid refrigerant passes through the expansion valve, which is a small orifice. The expansion valve acts as a metering device, controlling the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator while reducing its pressure. This pressure drop allows the refrigerant to evaporate and absorb heat from the cabin air.
6. Evaporation: As the refrigerant evaporates in the evaporator, it absorbs heat from the surrounding air, cooling it. The now low-pressure, low-temperature refrigerant gas returns to the compressor, and the cycle repeats.
This continuous cycle of compression, condensation, expansion, and evaporation ensures a constant flow of cooled air into the vehicle’s cabin, creating a comfortable and pleasant driving experience.
Understanding the working principles of a car air conditioner compressor is crucial for troubleshooting and maintaining the system. By familiarizing yourself with these principles, you can better identify any potential issues and ensure optimal performance of your car’s air conditioning system.
Compression Cycle Explained
The compression cycle is a fundamental process in a car air conditioner compressor that plays a vital role in cooling the vehicle’s interior. This cycle involves the transformation of refrigerant gas from a low-pressure state to a high-pressure state, which is necessary for effective cooling. Let’s delve into the compression cycle and understand its stages:
Stage 1: Suction
At the beginning of the compression cycle, the compressor draws in low-pressure refrigerant gas from the evaporator. This gas enters the compressor cylinder through the suction line, facilitated by the opening of the reed valves. The purpose of this stage is to prepare the refrigerant for compression.
Stage 2: Compression
Once inside the compressor cylinder, the refrigerant gas encounters the swash plate and the pistons. The rotating motion of the swash plate causes the pistons to move back and forth. As the pistons move, they compress the refrigerant gas, raising its pressure and temperature. The compression stage is crucial because it increases the energy of the refrigerant, preparing it for the subsequent stages of the cycle.
Stage 3: Discharge
After compression, the high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant gas is discharged from the compressor into the discharge line. The reed valves on the output side of the compressor close to prevent any backflow of refrigerant. The purpose of this stage is to transport the compressed gas to the next component in the air conditioning system, which is typically the condenser.
Stage 4: Condensation
In the condenser, the hot, high-pressure refrigerant gas releases heat and undergoes a phase change into a high-pressure liquid. This transformation occurs as the condenser facilitates the transfer of heat from the refrigerant to the surrounding air. The condensation stage is essential because it allows for the dissipation of heat and the conversion of the refrigerant into a high-pressure liquid state.
Stage 5: Expansion
The high-pressure liquid refrigerant then flows through the expansion valve, which acts as a metering device. The expansion valve carefully regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator while reducing its pressure. This pressure drop enables the refrigerant to expand and evaporate, setting the stage for the next stage of the compression cycle.
Stage 6: Evaporation
As the refrigerant evaporates in the evaporator, it absorbs heat from the surrounding air, cooling it in the process. The cooled air is then circulated back into the vehicle’s cabin. Meanwhile, the low-pressure, low-temperature refrigerant gas returns to the compressor to begin the compression cycle again.
This compression cycle is a continuous process that ensures a constant flow of cooled air into the vehicle’s interior, providing comfort during hot weather. Understanding the stages of the compression cycle is essential for troubleshooting any issues that may arise with a car’s air conditioner compressor and maintaining optimal performance of the system.
Regular maintenance of your car’s air conditioner compressor, such as cleaning the condenser and checking for leaks, can help ensure its efficient operation and prevent costly repairs.
Lubrication System in a Car Air Conditioner Compressor
The lubrication system plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of a car air conditioner compressor. Just like any other mechanical device, the compressor requires proper lubrication to minimize friction, reduce wear and tear, and extend its lifespan. Let’s explore how the lubrication system works in a car air conditioner compressor:
Compressor Oil:
Compressor oil is specifically designed to withstand the harsh operating conditions within the compressor. It is formulated to provide lubrication, reduce friction, and dissipate heat. The oil is typically stored in the compressor housing or in a separate oil reservoir.
Oil Pump:
The oil pump is responsible for circulating the compressor oil throughout the system. It is usually driven by the compressor itself or by the engine. The pump draws oil from the oil reservoir or compressor housing and distributes it to various components of the compressor, including the bearings, pistons, and swash plate.
Bearing Lubrication:
The compressor contains bearings that support and facilitate the rotation of various components, such as the swash plate and pistons. These bearings are subjected to high-speed rotation and friction, making proper lubrication critical. The lubrication system ensures that an adequate amount of oil reaches the bearings to reduce friction and prevent excessive wear.
Piston Lubrication:
The pistons within the compressor cylinder also require lubrication to glide smoothly within the cylinder walls. The oil from the lubrication system coats the pistons, creating a thin protective film that minimizes friction and facilitates efficient movement. This lubrication is essential for the pistons to compress the refrigerant effectively.
Swash Plate Lubrication:
The swash plate, which is responsible for the reciprocating motion of the pistons, also requires lubrication. As the swash plate rotates, it may generate friction against the adjacent components. The lubrication system ensures that the swash plate remains properly lubricated, reducing friction and promoting smooth operation.
Oil Separator:
As the compressor circulates the refrigerant, a small amount of compressor oil may mix with the refrigerant. The oil separator, located within the system, helps separate the oil from the refrigerant. This ensures that only the refrigerant circulates through the system and prevents the oil from interfering with the cooling process.
Regular maintenance of the lubrication system is crucial for the longevity and optimal performance of the car air conditioner compressor. It involves checking oil levels, inspecting for leaks, and ensuring proper oil circulation. Consult your vehicle’s manual or seek professional assistance to determine the recommended oil type and maintenance schedule for your specific compressor.
By maintaining a well-functioning lubrication system, you can minimize friction-related issues, reduce wear and tear, and prolong the life of your car air conditioner compressor.
Common Problems with Car Air Conditioner Compressors
While car air conditioner compressors are designed to be reliable, they can encounter problems over time. Understanding common issues that can arise will help you identify and address them promptly. Let’s explore some of the most common problems that occur with car air conditioner compressors:
1. Compressor Failure:
Compressor failure is one of the most significant problems that car owners may encounter. It can be caused by various factors, including wear and tear, electrical issues, refrigerant leaks, or overheating. Signs of a failing compressor include a lack of cold air, unusual noises, or reduced airflow from the vents.
2. Refrigerant Leaks:
Refrigerant leaks can occur in the compressor or other parts of the air conditioning system. Leaks can result from damaged hoses, worn seals, or other components. A refrigerant leak can lead to insufficient cooling or a complete loss of cold air from the system.
3. Clutch Issues:
The compressor clutch is responsible for engaging and disengaging the compressor from the engine. Over time, the clutch or its magnetic coil can wear out, causing problems with compressor operation. Symptoms of clutch issues include unusual noises when the air conditioner is turned on or a failure to engage the compressor.
4. Electrical Problems:
Electrical issues can prevent the compressor from functioning properly. Faulty wiring, blown fuses, or malfunctioning relays can disrupt the flow of electricity to the compressor, resulting in a lack of cold air. Diagnosing and resolving electrical problems may require the expertise of a qualified technician.
5. Excessive Noise:
If your air conditioner compressor is producing unusual or excessive noise, it may indicate a problem. Noises such as grinding, squealing, or rattling could be a sign of a failing compressor, worn-out bearings, or loose components. It’s important to address these noises promptly to prevent further damage.
6. Poor Performance:
If the air conditioning system is not cooling the vehicle as effectively as it used to, it could be a sign of compressor issues. This could be due to a worn-out compressor, improper refrigerant levels, a faulty expansion valve, or other related problems. It’s recommended to have the system inspected and serviced to restore optimal performance.
When experiencing any of these problems, it is important to consult a professional technician who specializes in automotive air conditioning systems. They have the expertise and tools necessary to accurately diagnose and repair compressor issues, ensuring that your car’s air conditioning system is functioning efficiently.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting can help prevent or address issues with your car air conditioner compressor. By taking proper care of your system, you can extend its lifespan and ensure optimal performance. Here are some troubleshooting and maintenance tips to keep in mind:
1. Regularly Inspect for Leaks:
Check for signs of refrigerant leaks, such as oil stains or a decrease in cooling performance. If you suspect a leak, have it repaired by a professional technician. Addressing leaks promptly will prevent further damage to the compressor and the air conditioning system as a whole.
2. Keep the System Clean:
Regularly clean the exterior of the compressor to remove dirt, debris, and dust that can accumulate and hinder airflow. Use a soft cloth or brush to gently clean the surface. Ensure that the surrounding areas, such as the condenser and hoses, are also kept clean for optimal cooling performance.
3. Monitor Coolant Levels:
Check the coolant levels in your air conditioning system. If the levels are low, it may indicate a leak or an issue with the compressor. Consult a professional technician to identify and rectify the problem, and to recharge the coolant to the appropriate levels.
4. Pay Attention to Unusual Noises:
If you notice any strange noises coming from the air conditioner, such as grinding, squealing, or rattling, it is important to have the compressor inspected by a professional. Unusual noises can be a sign of a failing compressor or other mechanical issues that need to be addressed to prevent further damage.
5. Have Regular Maintenance Checks:
Schedule regular inspections and maintenance checks with a qualified technician who specializes in automotive air conditioning systems. They will ensure that all components are functioning properly, perform necessary cleaning and lubrication, and identify any potential issues before they escalate.
6. Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines:
Refer to your vehicle’s manual and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for regular maintenance and recommended service intervals. Adhering to these guidelines will help keep your air conditioning system in top shape and minimize the risk of compressor issues.
7. Seek Professional Help:
If you encounter any significant issues with your car air conditioner compressor or are unsure about any troubleshooting steps, it is best to consult a professional technician. They have the expertise and knowledge to diagnose and address complex problems to ensure the proper functioning of your compressor and air conditioning system.
By following these troubleshooting and maintenance tips, you can prevent common issues, identify potential problems early on, and maintain the longevity and efficiency of your car air conditioner compressor.
Conclusion
Understanding how a car air conditioner compressor works is essential for maintaining the comfort and functionality of your vehicle’s cooling system. The compressor, with its various components and working principles, plays a vital role in the cooling process. By familiarizing yourself with its inner workings and common issues, you can troubleshoot problems more effectively and ensure the compressor’s optimal performance.
Regular maintenance and attention to the lubrication system are key to prolonging the lifespan of your compressor. Checking for refrigerant leaks, cleaning the compressor and surrounding areas, monitoring coolant levels, and addressing unusual noises are all important steps to keep your compressor in good condition.
When encountering issues with your car air conditioner compressor, it is advisable to seek the assistance of a professional technician. They have the expertise and tools necessary to diagnose and repair problems, ensuring that your air conditioning system functions efficiently.
By following the troubleshooting and maintenance tips provided in this article, you can prevent common problems, address issues promptly, and extend the lifespan of your car air conditioner compressor. Remember to consult your vehicle’s manual for specific maintenance guidelines and recommended service intervals.
Investing time and effort in proper maintenance will not only keep you cool during hot summer drives but also contribute to a comfortable and enjoyable journey for you and your passengers.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Does A Car Air Conditioner Compressor Work
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.