Home>Home Security and Surveillance>What Should I Set For My Wireless Security


Home Security and Surveillance
What Should I Set For My Wireless Security
Modified: March 6, 2024
Gain peace of mind and protect your home with top-notch wireless security. Discover the best strategies to set up effective home-security-and-surveillance measures.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of wireless security! With the increasing popularity of wireless networks in homes, it’s becoming more important than ever to ensure the safety and privacy of your wireless connection.
In today’s digital age, where everything from our smartphones to our thermostats is connected to the internet, securing your wireless network is crucial. Not only does it protect your personal information and sensitive data, but it also prevents unauthorized access to your network.
In this article, we will discuss the essential settings and measures you should consider to optimize the security of your wireless network. By implementing these steps, you can create a robust barrier against potential hackers and keep your home network safe.
So, let’s dive into the world of wireless security and uncover the secrets to setting up an impenetrable fortress for your home network.
Key Takeaways:
- Secure your wireless network by choosing WPA2 encryption, setting a strong password, and changing the default SSID to protect against unauthorized access and potential threats.
- Enhance wireless security with MAC Address Filtering, disabling SSID broadcasting, and regularly updating firmware to create a robust and secure network environment.
Understanding Wireless Security
Before delving into the various settings and measures you can employ to enhance the security of your wireless network, it’s important to have a basic understanding of how wireless security works.
Wireless networks rely on radio signals to transmit data between devices such as laptops, smartphones, and routers. While this wireless connectivity offers convenience and flexibility, it also presents a potential vulnerability. Without proper security measures in place, anyone within range can potentially eavesdrop on your network and gain access to your sensitive information.
Wireless security works by implementing encryption algorithms to protect your data as it is transmitted over the airwaves. Encryption converts your data into an unreadable format, known as ciphertext, making it virtually impossible for unauthorized individuals to decipher the information without the encryption key.
There are several types of encryption methods used in wireless networks, with the most common being WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy), WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access), and WPA2. Each of these encryption methods offers different levels of security, with WEP being the least secure and WPA2 being the most secure. It’s important to choose the appropriate encryption method when setting up your wireless network.
In addition to encryption, there are other settings and measures you can employ to bolster the security of your wireless network. These include setting a strong password, changing the default network SSID (Service Set Identifier), enabling MAC Address filtering, disabling SSID broadcasting, and regularly updating firmware for your network devices.
By understanding these basic concepts of wireless security and implementing the right settings and measures, you can create a robust and secure environment for your wireless network. In the following sections, we will dive deeper into each of these topics and provide step-by-step guidance on how to optimize the security of your wireless network.
Factors to Consider for Wireless Security Settings
When it comes to securing your wireless network, there are several factors to consider. These factors determine the overall strength and effectiveness of your security measures. Let’s dive into each of these factors and explore how they can contribute to a secure wireless network environment.
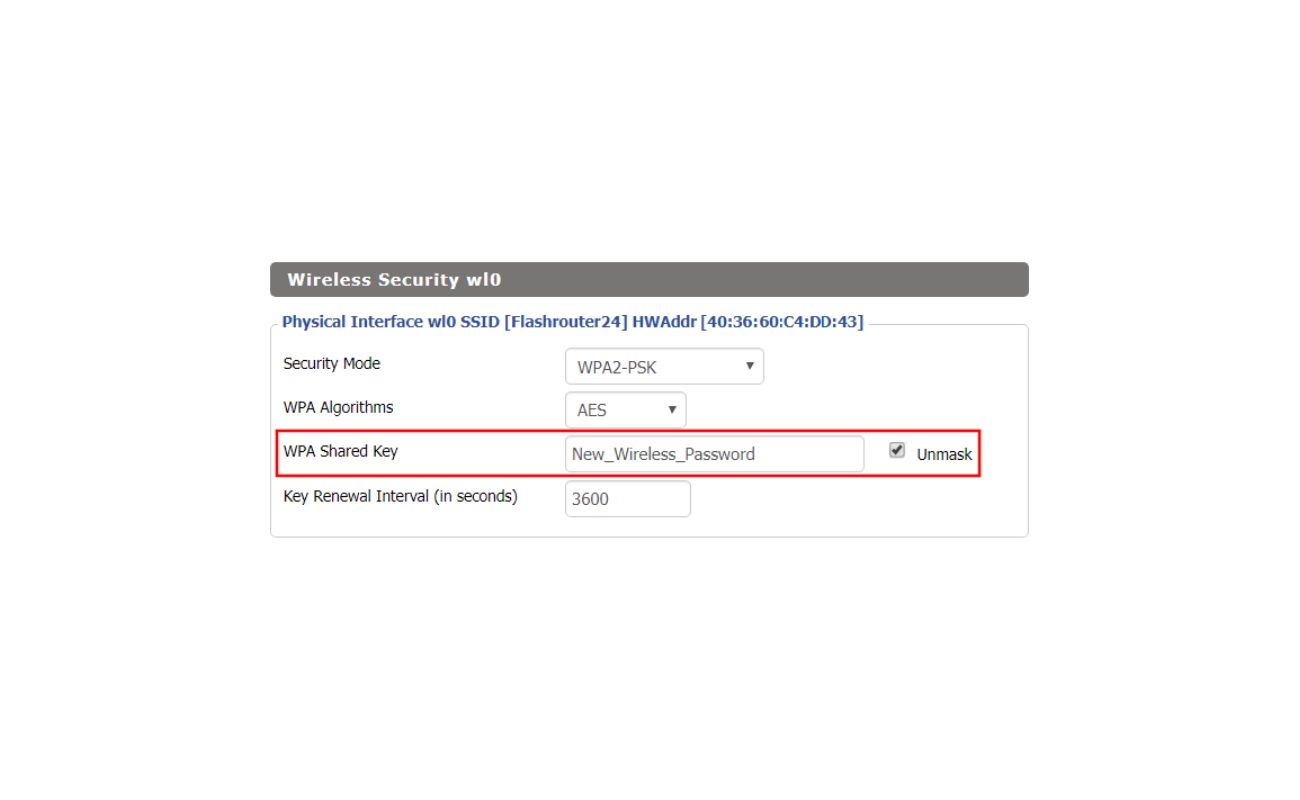
- Encryption Method: The encryption method you choose for your wireless network plays a crucial role in protecting your data. It is recommended to use WPA2, as it is the most secure encryption method currently available. WEP and WPA are outdated and vulnerable to attacks. Ensure that your wireless router supports WPA2 encryption and enable it in your network settings.
- Password Strength: Setting a strong password for your wireless network is essential. Avoid using easily guessable passwords such as “password” or “123456”. Instead, create a unique and complex password that includes a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters. It is also advisable to change your password regularly.
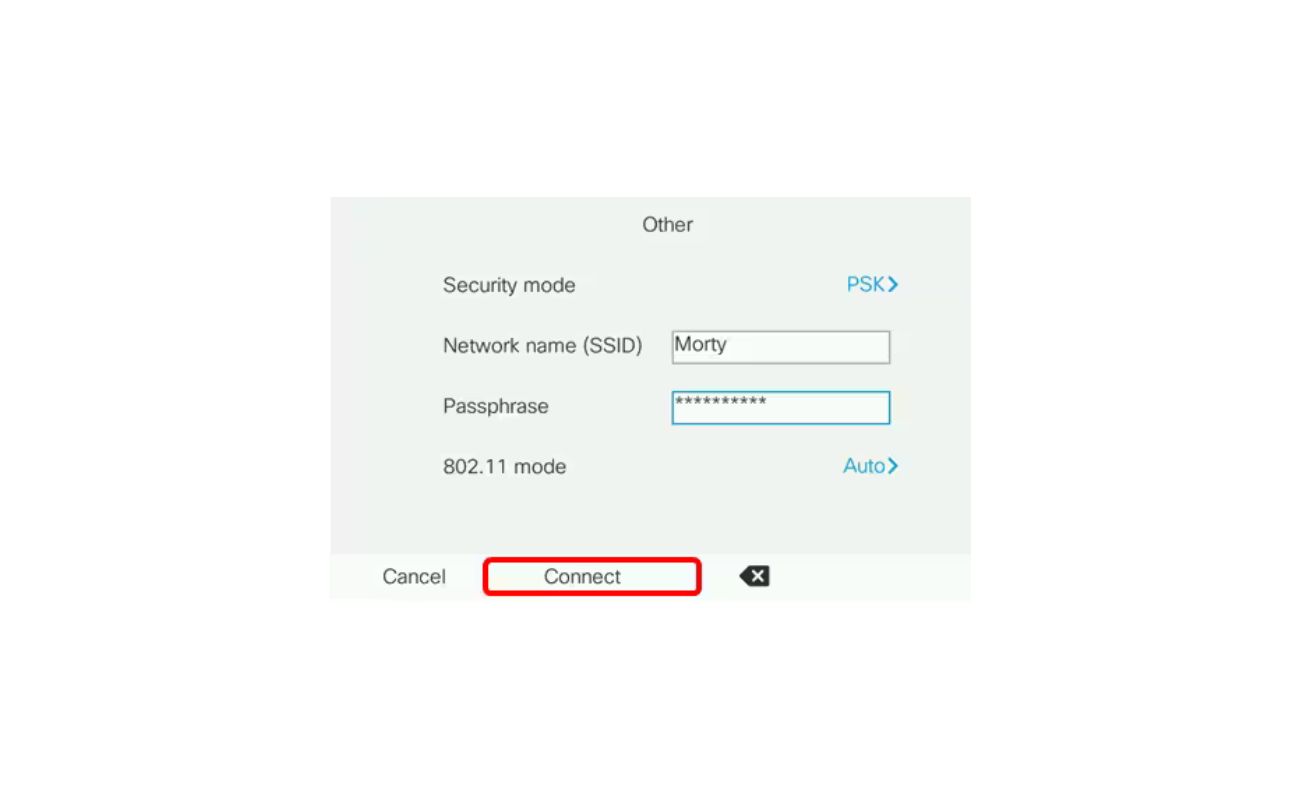
- Default SSID: The SSID is the name of your wireless network. It is important to change the default SSID that comes with your router. Using the default SSID makes it easier for attackers to identify the type of router you are using, which may provide them with valuable information for launching an attack. Choose a unique name that doesn’t reveal any personal information.
- MAC Address Filtering: Every network device has a unique MAC (Media Access Control) address. By enabling MAC address filtering, you can specify which devices are allowed to connect to your wireless network. Simply add the MAC addresses of your trusted devices to the filter list, and any device with an unrecognized MAC address will be denied access.
- SSID Broadcasting: By default, wireless routers broadcast their SSID, making it visible to anyone in range. Disabling SSID broadcasting can add an extra layer of security. While it won’t prevent determined attackers from finding your network, it will make it less visible to casual passersby and discourage potential intruders.
Considering these factors when configuring your wireless security settings will significantly enhance the overall security of your network. In the next sections, we will provide step-by-step instructions on how to implement these settings on your wireless router, ensuring a robust and secure wireless environment.
Choosing the Right Encryption Method
When it comes to securing your wireless network, choosing the right encryption method is crucial. Encryption converts your data into an unreadable format, preventing unauthorized individuals from accessing and deciphering your sensitive information. Let’s explore the various encryption methods available and guide you in selecting the most secure option for your wireless network.
There are three main encryption methods used in wireless networks: WEP, WPA, and WPA2. These methods differ in terms of their security levels, with WEP being the least secure and WPA2 being the most secure.
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy): WEP was the first encryption method introduced for wireless networks. However, it has been widely deemed insecure due to significant vulnerabilities. Attackers can easily crack WEP encryption and gain access to your network within minutes using readily available tools. It is strongly recommended to avoid using WEP and opt for more secure alternatives.
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access): WPA was introduced as a replacement for WEP and addressed some of the security flaws. While it is more secure than WEP, it is still vulnerable to certain attacks. WPA uses TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) for encryption, which provides improved security compared to WEP. However, due to known vulnerabilities, it is not considered as secure as WPA2.
WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access II): WPA2 is currently the most secure encryption method for wireless networks. It utilizes AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) encryption, which is considered highly secure. WPA2 provides robust protection against various attacks, making it the preferred choice for securing your wireless network. It is highly recommended to use WPA2 encryption if your wireless router and devices support it.
To check which encryption method your wireless router supports, log in to your router’s administration interface and navigate to the wireless settings. Look for the security or encryption options and select WPA2 if available. If your router only supports WEP or WPA, consider upgrading your router to a model that supports WPA2 for enhanced security.
Remember, selecting the right encryption method is a crucial step in securing your wireless network. By opting for WPA2 encryption, you can ensure the highest level of security and protect your sensitive data from potential attackers.
Setting a Strong Password for Your Wireless Network
One of the most important steps in securing your wireless network is setting a strong password. A strong password adds an extra layer of defense against unauthorized access and keeps your network and data safe. Here are some tips to help you create a strong password for your wireless network:
1. Length and Complexity: Your password should be at least 12 characters long and include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid using easily guessable phrases or personal information related to you, such as your name, address, or birthdate.
2. Avoid Common Passwords: Steer clear of common or easily guessable passwords like “password,” “123456,” or “qwerty.” These passwords are commonly used and make your network an easy target for hackers.
3. Unique Passwords: Each wireless network should have a unique password. Avoid using the same password for multiple networks or devices. If one network gets compromised, the rest remain secure.
4. Regularly Change Your Password: It’s essential to change your wireless network password regularly to maintain security. Set a reminder to update your password every 3-6 months or whenever there’s a significant security breach.
5. Use a Password Manager: If you’re concerned about remembering multiple complex passwords, consider using a password manager. Password managers securely store and generate unique passwords for all your networks and devices.
6. Keep Password Confidential: Do not share your wireless network password with unauthorized individuals. Only provide the password to trusted individuals who need access to your network.
Once you’ve created a strong password, configure it in your router’s wireless security settings. Log in to your router’s administration interface, navigate to the wireless settings, and look for the option to set a password or passphrase. Enter your strong password in the designated field and save the changes.
Remember, a strong password is your first line of defense against unauthorized access to your wireless network. By following these guidelines and setting a secure password, you can significantly enhance the security of your network and protect your valuable data.
Tip: Set up WPA2 or WPA3 encryption for your wireless network to ensure strong security. Use a complex password with a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols to protect your network from unauthorized access.
Changing Default Network SSID
When setting up a wireless network, it’s important to change the default SSID (Service Set Identifier) that comes with your router. The SSID is the name of your network, and leaving it as the default can make your network more vulnerable to attacks. Here’s why changing the default SSID is crucial for your network’s security:
Avoids Identification: Using the default SSID provided by your router makes it easier for attackers to identify the type of router you are using. This information can be valuable to hackers, as it helps them identify vulnerabilities specific to that router model and launch targeted attacks.
Protects Against Default Password Exploitation: Some routers come with default login credentials, including a default password. If your network’s default SSID reveals the manufacturer of your router, hackers can quickly find the default login credentials associated with that router model. Changing the default SSID makes it harder for attackers to determine the specific router model and exploit default login credentials.
Prevents Social Engineering Attacks: Attackers may attempt social engineering attacks by spoofing your network’s default SSID. For example, they might set up a network with the same SSID as a popular router brand to trick unsuspecting users into connecting to their network. By changing the default SSID to something unique, you can protect your devices and users from falling victim to such attacks.
Changing the default SSID is a relatively simple process. Here’s how you can do it:
- Access your router’s administration interface by typing the router’s IP address into your web browser. The IP address is usually printed on the back or bottom of your router or mentioned in the router’s manual.
- Log in using the administrator username and password. If you haven’t changed these credentials before, consult your router’s documentation for the default login details.
- Navigate to the wireless settings section in your router’s administration interface.
- Look for the SSID field or network name and replace the default SSID with a unique name of your choice. Avoid using personal information or easily identifiable information in the SSID.
- Save the changes and restart your router for the new SSID to take effect.
By changing the default SSID to a unique name, you enhance your network’s security by making it more difficult for attackers to identify your router model and exploit default settings. This simple step goes a long way in protecting your wireless network from potential threats.
Enabling MAC Address Filtering
MAC Address Filtering is an additional security measure that can be enabled on your wireless network to enhance its protection. MAC addresses are unique identifiers assigned to network devices, such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets. By enabling MAC Address Filtering, you can restrict access to your network to only those devices whose MAC addresses you have allowed. This can help prevent unauthorized devices from connecting to your network. Here’s how you can enable MAC Address Filtering:
- Access your router’s administration interface by entering the router’s IP address in your web browser.
- Login using the administrator credentials. If you haven’t modified these credentials before, refer to your router’s documentation for the default login details.
- Navigate to the wireless settings section in the router’s administration interface.
- Look for the MAC Address Filtering or Access Control feature. The location and naming may vary depending on your router’s model and firmware.
- Enable MAC Address Filtering and select the desired filtering mode. The two common modes are “Allow” and “Deny”. In the “Allow” mode, only devices with MAC addresses added to the filter list will be allowed to connect. In the “Deny” mode, devices with MAC addresses added to the filter list will be blocked from connecting.
- Obtain the MAC addresses of the devices you want to grant access to your network. You can find the MAC address in the settings of the device or by using the command “ipconfig /all” (for Windows) or “ifconfig” (for macOS and Linux) in the command prompt/terminal.
- Add the MAC addresses to the filter list in your router’s administration interface. Some routers allow you to manually enter MAC addresses, while others provide a list where you can add and remove addresses.
- Save the changes and restart your router for the new settings to take effect.
Enabling MAC Address Filtering provides an extra layer of security by allowing you to specify which devices can connect to your wireless network. However, keep in mind that MAC addresses can be spoofed, meaning attackers can imitate trusted devices’ MAC addresses. Therefore, it is recommended to combine MAC Address Filtering with other security measures, such as strong encryption and passwords, for effective protection against unauthorized access.
By enabling MAC Address Filtering, you can strengthen the security of your wireless network by allowing only trusted devices to connect, thus minimizing the risk of unauthorized access to your network and data.
Disabling SSID Broadcasting
Disabling SSID (Service Set Identifier) broadcasting is a security measure that can be applied to your wireless network to reduce its visibility to potential attackers. The SSID is the name of your network that appears when nearby devices search for available networks. By default, routers broadcast the SSID, making it visible to anyone in range. However, disabling SSID broadcasting can add an extra layer of security to your network. Here’s how you can disable SSID broadcasting:
- Access your router’s administration interface by typing the router’s IP address into your web browser.
- Login using the administrator username and password. If you haven’t changed these credentials before, refer to your router’s documentation for the default login details.
- Navigate to the wireless settings section in your router’s administration interface.
- Look for the SSID broadcasting option.
- Select the option to disable SSID broadcasting. The exact wording may vary depending on your router’s model and firmware.
- Save the changes and restart your router for the new settings to take effect.
Disabling SSID broadcasting has both advantages and considerations:
Advantages of Disabling SSID Broadcasting:
- Reduced Visibility: By disabling SSID broadcasting, your network becomes invisible to casual passersby and reduces the chances of potential attackers easily identifying and targeting your network.
- Discourages Unauthorized Connections: While disabling SSID broadcasting won’t prevent determined attackers from finding your network, it can discourage casual users from attempting to connect to your network.
Considerations of Disabling SSID Broadcasting:
- Inconvenience: After disabling SSID broadcasting, you will need to manually enter the network name (SSID) on each device that you want to connect to your network. This can be cumbersome, especially if you have multiple devices or frequently have guests who need to connect to your network.
- Compatibility: Some older devices or network adapters may have difficulty connecting to a network with disabled SSID broadcasting. Consider the compatibility of your devices before disabling SSID broadcasting.
Keep in mind that disabling SSID broadcasting alone is not sufficient for securing your wireless network. It should be combined with other security measures such as strong encryption, passwords, and MAC address filtering for optimal network security.
By disabling SSID broadcasting, you can reduce the visibility of your network and add an extra layer of security. Although there are some considerations, when combined with other security measures, this can help protect your wireless network from potential threats.
Regularly Updating Firmware for Network Devices
Regularly updating the firmware for your network devices is a critical aspect of maintaining the security and functionality of your network. Firmware is the software that runs on your devices, such as your wireless router or access points, and updating it ensures that you have the latest bug fixes, security patches, and feature enhancements. Here’s why firmware updates are important and how you can perform them:
Security Enhancements: Network device manufacturers regularly release firmware updates to address security vulnerabilities and protect against emerging threats. Hackers are constantly finding new ways to exploit weaknesses in firmware, and keeping your devices up to date is essential to stay one step ahead of potential attackers.
Bug Fixes and Stability: Firmware updates also include bug fixes and stability improvements, resolving issues that may cause performance degradation, connectivity problems, or other network-related issues. Keeping your devices up to date ensures optimal functionality and a better user experience.
Feature Enhancements: In addition to security and stability, firmware updates often introduce new features and functionalities. These updates can improve the performance and capabilities of your network devices, providing you with a better overall networking experience.
To perform firmware updates on your network devices, follow these general steps:
- Identify the manufacturer and model of your network device. This information is typically found on the device itself or in its documentation.
- Visit the manufacturer’s website and navigate to the support or downloads section.
- Search for firmware updates specific to your device model. Manufacturers usually provide firmware files and instructions for updating.
- Download the latest firmware file for your device.
- Access your device’s administration interface through a web browser. Enter the device’s IP address in the browser and log in using the administrator credentials.
- Navigate to the firmware update section or similar settings in the administration interface.
- Locate the firmware update file you downloaded and follow the on-screen instructions to upload and install the update.
- Once the update is complete, restart your device to ensure the new firmware takes effect.
It’s important to note that firmware updates can vary depending on the manufacturer and device model. Always follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer to ensure a successful update.
Regularly checking for and performing firmware updates is crucial for maintaining the security and performance of your network devices. Set a reminder to check for updates periodically or enable automatic firmware updates if supported by your devices. By keeping your network devices’ firmware up to date, you can ensure a more secure and reliable network environment.
Read more: What Is My Wireless Security Type
Conclusion
Securing your wireless network is essential to protect your personal information, sensitive data, and maintain the privacy of your online activities. By implementing the appropriate security settings, you can create a robust barrier against potential threats and ensure the safety of your network and devices.
In this article, we discussed several important factors to consider for wireless security. We explored the significance of choosing the right encryption method, such as WPA2, and the importance of setting a strong password for your network to prevent unauthorized access. Changing the default network SSID helps reduce the visibility of your network, while MAC Address Filtering adds an extra layer of protection by allowing only trusted devices to connect.
Additionally, we covered the benefits of disabling SSID broadcasting to make your network less visible to potential attackers. Lastly, we emphasized the importance of regularly updating the firmware for your network devices to ensure they have the latest security patches, bug fixes, and feature enhancements.
Remember, a comprehensive approach to wireless security involves incorporating multiple layers of defense. It is recommended to implement a combination of these security measures to create a robust and secure network environment.
By proactively implementing these measures and staying informed about the latest security best practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security threats.
Take the time to evaluate the security settings of your wireless network and make the necessary adjustments. Your efforts in securing your network will go a long way in safeguarding your sensitive information, providing peace of mind, and ensuring a secure online experience for you and your family.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Should I Set For My Wireless Security
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.