Home>Technology>Smart Home Devices>What Is A MICR Printer


Smart Home Devices
What Is A MICR Printer
Modified: February 18, 2024
Learn how MICR printers can enhance security and efficiency for smart home devices. Find out how MICR technology works and its benefits.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of printing technology, MICR (Magnetic Ink Character Recognition) printers have emerged as a crucial tool for businesses and financial institutions. The unique capabilities of MICR printing make it an essential component in the processing of secure and efficient financial documents. Understanding the intricacies of MICR printing is vital for businesses seeking to streamline their financial operations and ensure compliance with industry standards.
In this article, we will delve into the fundamentals of MICR printing, exploring its underlying technology, applications, advantages, and limitations. By gaining insight into the inner workings of MICR printers, readers will develop a comprehensive understanding of this specialized printing method and its significance in the realm of financial document processing.
Join us on a journey through the world of MICR printing, where precision, security, and reliability converge to meet the demands of modern financial systems. Let's unravel the mysteries of MICR technology and uncover the myriad ways it shapes the financial landscape.
Key Takeaways:
- MICR printing uses special magnetic ink to create characters that can be read by machines, making it crucial for accurate and secure processing of financial documents in banks and businesses.
- While MICR printing offers high accuracy and security, it also comes with challenges like specialized consumables and complex printing processes, which businesses need to consider for efficient adoption.
Read more: What Is Printer Duplexing
What is MICR?
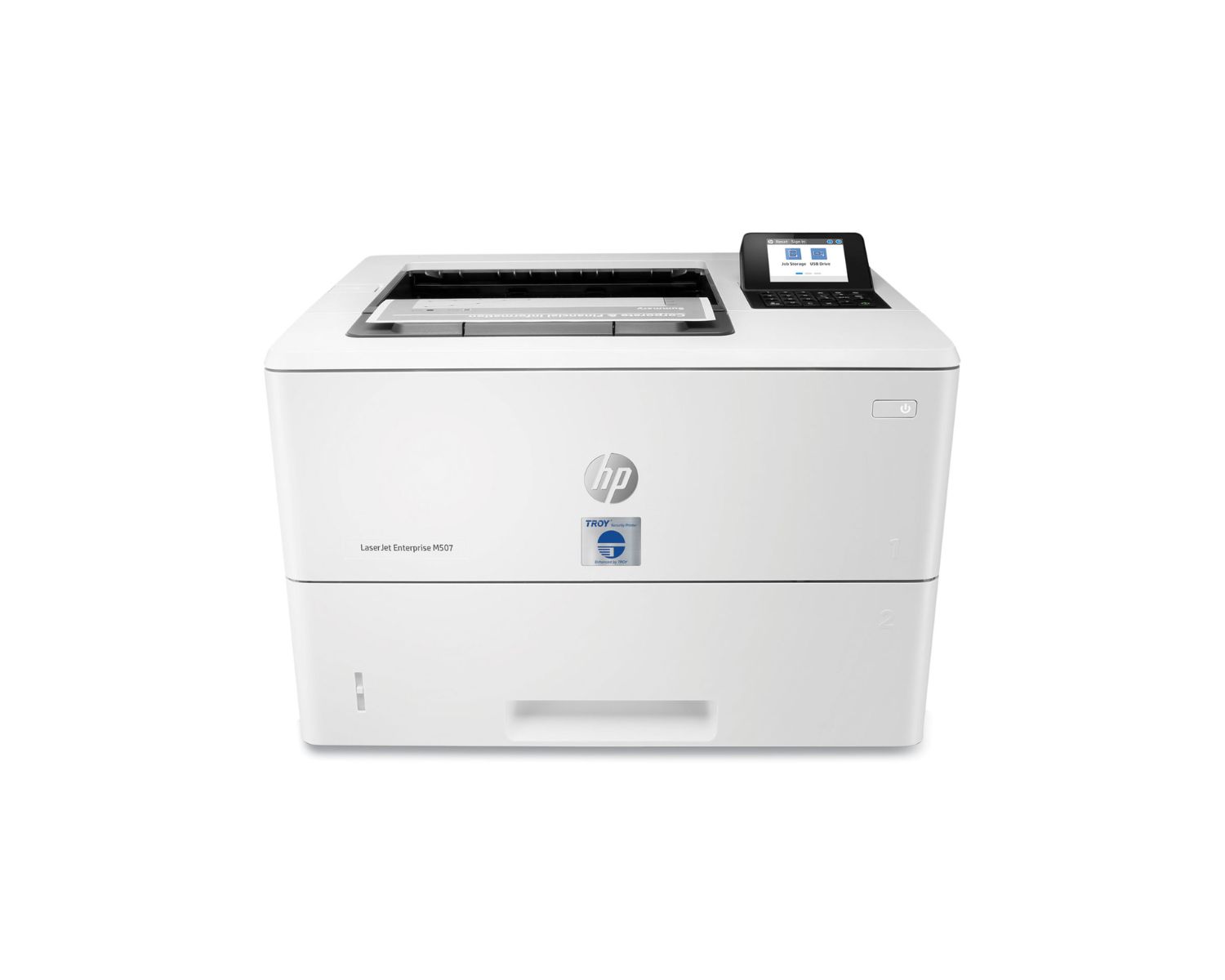
MICR, which stands for Magnetic Ink Character Recognition, is a specialized printing technology used primarily in the banking industry for processing checks and other financial documents. Unlike traditional inkjet or laser printing, MICR printing involves the use of magnetic ink or toner to create machine-readable characters. These characters, typically in the form of numbers and symbols, are printed with a unique font known as E-13B or CMC-7, which is specifically designed for MICR encoding.
The primary purpose of MICR printing is to facilitate the automated processing of financial documents, enabling high-speed and accurate data capture. The magnetic properties of the ink allow MICR characters to be easily recognized and interpreted by magnetic ink character recognition devices, such as check-reading machines and automated sorting equipment.
One of the defining features of MICR printing is the precision and consistency with which characters are produced. This level of accuracy is essential for ensuring that financial institutions can reliably process and validate checks, deposit slips, and other critical documents. Additionally, the use of magnetic ink enhances security by deterring fraudulent alterations and counterfeiting attempts, as the magnetic properties are not easily replicated using standard printing methods.
Overall, MICR technology serves as a cornerstone of efficient check processing and secure financial transactions, playing a vital role in maintaining the integrity and reliability of banking operations. Its widespread adoption within the financial sector underscores its significance in upholding the standards of accuracy, security, and automation that are essential for modern financial systems.
How does a MICR printer work?
A MICR printer operates on a fundamentally different principle compared to conventional inkjet or laser printers. The key to its functionality lies in the use of magnetic ink or toner, which enables the creation of characters with magnetic properties. The process of MICR printing involves several distinct stages, each contributing to the production of machine-readable characters with unparalleled accuracy and reliability.
1. Magnetic Ink: The first step in MICR printing is the utilization of magnetic ink or toner, which contains iron oxide particles. These particles impart magnetic properties to the printed characters, allowing them to be easily detected and interpreted by MICR reading devices.
2. Specialized Fonts: MICR characters are printed using specialized fonts, such as E-13B or CMC-7, which are designed to meet the precise standards of magnetic ink character recognition. These fonts feature unique shapes and encoding patterns that are optimized for machine readability, ensuring consistent and accurate data capture.
3. Precision Printing: MICR printers are engineered to achieve exceptional precision in character placement and ink deposition. This level of precision is critical for meeting the strict requirements of MICR encoding, where even minor deviations can compromise the readability and integrity of the printed characters.
4. Quality Control: Throughout the printing process, MICR printers incorporate rigorous quality control measures to verify the accuracy and conformity of the printed characters. This includes monitoring ink density, alignment, and overall print quality to uphold the standards of MICR encoding.
5. Verification and Testing: Once the characters are printed, they undergo thorough verification and testing to ensure compliance with MICR standards. This often involves the use of specialized testing equipment to assess the magnetic signal strength and readability of the printed characters.
By meticulously following these steps, MICR printers are able to produce financial documents with machine-readable characters that meet the stringent requirements of magnetic ink character recognition. The combination of magnetic ink, specialized fonts, and precision printing techniques culminates in the creation of documents that are optimized for high-speed processing and reliable data capture, making MICR printing an indispensable component of modern financial operations.
Uses of MICR Printers
The specialized capabilities of MICR printers make them indispensable in various industries, with a primary focus on financial institutions and businesses that handle a high volume of secure document processing. Here are some key applications of MICR printers:
- Check Printing: MICR printers are extensively used for printing checks, incorporating machine-readable MICR encoding at the bottom of each check. This encoding contains essential information, including the bank’s routing number, the customer’s account number, and the check number, enabling automated processing and validation.
- Document Processing: Beyond check printing, MICR printers are employed in the production of various financial documents, such as deposit slips, money orders, and official bank forms. By incorporating MICR encoding, these documents can be efficiently processed and sorted using automated equipment.
- Banking Operations: Financial institutions rely on MICR printers to streamline their banking operations, facilitating the rapid processing and validation of checks and related documents. This enhances operational efficiency and accuracy while maintaining the security of financial transactions.
- Secure Transactions: MICR printing plays a crucial role in ensuring the security and integrity of financial transactions. The use of magnetic ink and machine-readable encoding helps prevent unauthorized alterations and counterfeiting, safeguarding the authenticity of financial documents.
- Compliance Requirements: Many regulatory standards and industry guidelines mandate the use of MICR printing for specific financial documents, particularly in the banking and payment processing sectors. Compliance with these requirements is essential for maintaining the credibility and legality of financial transactions.
Overall, the versatility and reliability of MICR printers make them an essential tool for businesses and financial institutions that prioritize secure and efficient document processing. By leveraging the unique capabilities of MICR technology, organizations can uphold the standards of accuracy, security, and compliance that are paramount in the realm of financial operations.
A MICR printer is a specialized printer that uses magnetic ink character recognition technology to print numbers and symbols that can be easily read by bank processing systems. These printers are commonly used for printing checks and other financial documents.
Advantages of MICR Printing
The adoption of MICR printing offers a multitude of advantages, particularly in the context of financial document processing and secure transactions. Here are the key benefits associated with MICR printing:
- High Accuracy: MICR printing ensures unparalleled accuracy in the reproduction of machine-readable characters, enabling reliable data capture and processing. This level of precision is essential for minimizing errors and streamlining financial document validation.
- Efficient Automation: MICR-encoded documents can be rapidly processed and sorted using automated equipment, facilitating efficient check processing and document handling within financial institutions. This automation reduces manual intervention and expedites transaction processing.
- Enhanced Security: The use of magnetic ink and machine-readable encoding enhances the security of financial documents, deterring counterfeiting and unauthorized alterations. MICR printing contributes to the integrity and authenticity of checks and related financial instruments.
- Compliance Adherence: MICR printing aligns with industry standards and regulatory requirements, ensuring that financial documents meet the necessary compliance criteria. This adherence to established standards is crucial for maintaining the legality and credibility of financial transactions.
- Reliability in Processing: MICR-encoded documents are optimized for high-speed processing and readability, minimizing the risk of errors and delays in check clearance and transaction validation. This reliability is fundamental to the seamless functioning of financial systems.
Overall, the advantages of MICR printing converge to establish it as a cornerstone of efficient, secure, and compliant financial document processing. By harnessing the precision, automation, and security offered by MICR technology, businesses and financial institutions can uphold the standards of accuracy and reliability that are paramount in the realm of financial transactions.
Read more: What Is Scanning On A Printer
Disadvantages of MICR Printing
While MICR printing offers numerous advantages, it is important to acknowledge the potential limitations and challenges associated with this specialized printing technology. Understanding the disadvantages of MICR printing provides valuable insight into its practical considerations and areas for improvement. Here are some notable drawbacks of MICR printing:
- Specialized Consumables: MICR printing requires the use of magnetic ink or toner, which can be more expensive than standard printing consumables. This specialized requirement adds to the overall operational costs of MICR printing equipment and maintenance.
- Complex Printing Process: The precision and quality control measures involved in MICR printing contribute to a more intricate printing process compared to conventional printing methods. This complexity may necessitate additional training and expertise for operating and maintaining MICR printers.
- Limited Color Options: Due to the focus on magnetic ink and machine-readable encoding, MICR printing is primarily monochromatic, offering limited color options for printed characters and designs. This constraint may impact the visual aesthetics of printed documents.
- Equipment Investment: Implementing MICR printing technology requires investment in specialized printers and related hardware, which can represent a significant upfront cost for businesses and financial institutions. The initial capital outlay for MICR-compatible equipment may pose a financial barrier for some organizations.
- Maintenance Requirements: MICR printers demand meticulous maintenance to ensure consistent print quality and adherence to MICR standards. Regular upkeep and monitoring of printing equipment are essential to sustain the reliability and accuracy of MICR-encoded documents.
While these disadvantages underscore the nuanced considerations associated with MICR printing, they also present opportunities for innovation and optimization in the realm of secure document processing. By addressing these challenges, the ongoing evolution of MICR technology can further enhance its efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and versatility in meeting the diverse needs of businesses and financial institutions.
Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of MICR printing, it becomes evident that this specialized technology plays a pivotal role in the realm of financial document processing, offering a unique blend of precision, security, and efficiency. The magnetic ink character recognition capabilities of MICR printing have positioned it as a cornerstone of modern banking operations, enabling the rapid and reliable processing of checks, deposit slips, and other critical financial documents.
While MICR printing presents distinct advantages, such as high accuracy, efficient automation, and enhanced security, it is essential to acknowledge the associated challenges, including specialized consumables, complex printing processes, and equipment investment. By recognizing these considerations, businesses and financial institutions can make informed decisions regarding the adoption and optimization of MICR printing technology.
Looking ahead, the ongoing advancements in printing technology and materials hold the promise of addressing some of the limitations of MICR printing, paving the way for enhanced cost-effectiveness, color options, and streamlined maintenance. As the demands of secure document processing continue to evolve, MICR printing stands poised to adapt and innovate, ensuring its relevance in an increasingly digital and interconnected financial landscape.
In essence, the enduring significance of MICR printing lies in its ability to uphold the standards of accuracy, security, and compliance that are essential for the integrity of financial transactions. By embracing the precision and reliability offered by MICR technology, businesses and financial institutions can navigate the intricate demands of financial document processing with confidence, knowing that the legacy of MICR printing continues to shape the future of secure and efficient financial operations.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A MICR Printer
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Is A MICR Printer”