
Articles
How Does Radiant Floor Heating Work
Modified: January 8, 2024
Learn how radiant floor heating works and the benefits it offers in our informative articles. Discover how this energy-efficient heating system can keep your home warm and cozy.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the fascinating world of radiant floor heating! When it comes to creating a cozy and comfortable living environment, nothing quite compares to the warm embrace of radiant heat beneath your feet. Whether you’re building a new home or looking to upgrade your heating system, radiant floor heating offers numerous benefits that will transform the way you experience warmth in your space.
But how does radiant floor heating actually work? In this article, we’ll delve into the principles, components, installation process, and maintenance of radiant floor heating systems. We’ll also explore the various types of systems available and compare them to other heating methods. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of how radiant floor heating can elevate your home’s comfort and energy efficiency.
Radiant floor heating operates on the principle of radiative heat transfer, where heat energy is emitted by a warm surface and absorbed by cooler objects in its vicinity. Unlike traditional heating methods that rely on convection to warm the air, radiant floor heating warms the objects in the room directly, resulting in a more even, gentle, and efficient heat distribution.
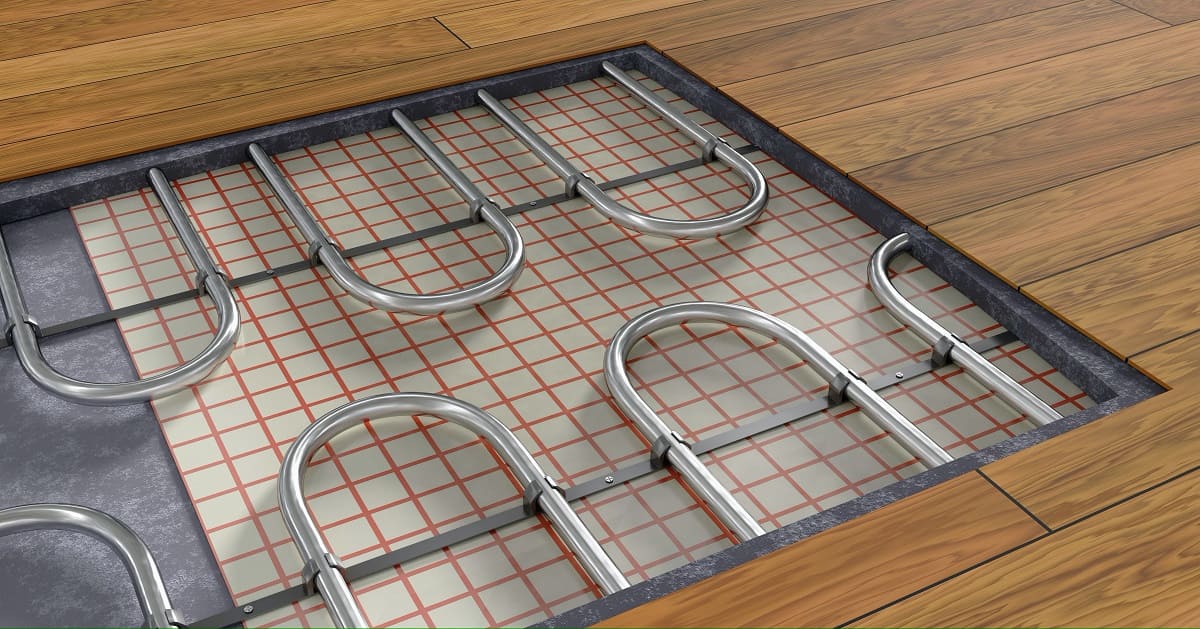
The key components of a radiant floor heating system include a heat source, hydronic tubing or electric heating elements, and a thermostat. The heat source is typically a boiler or a water heater that circulates hot water or a heat transfer fluid through the tubing, which is installed within the floor structure. Alternatively, electric radiant systems use heating cables or mats directly beneath the flooring material.
There are two main types of radiant floor heating systems: hydronic systems and electric systems. Hydronic systems are the most popular choice, utilizing hot water or a heat transfer fluid to carry and distribute heat. Electric systems, on the other hand, use electric resistance to generate heat.
The installation process for radiant floor heating can vary depending on the type of system, the construction of your home, and the flooring materials in place. In general, installation involves placing the tubing or heating elements, connecting them to the heat source, and installing the control and thermostat systems.
Key Takeaways:
- Radiant floor heating operates on the principle of thermal radiation, providing even warmth and eliminating cold spots. It offers energy efficiency, improved indoor air quality, and design flexibility, making it a top choice for comfortable and sustainable heating.
- With its direct heat transfer, radiant floor heating outshines traditional systems, offering energy savings, silent operation, and zone control. Its compatibility with renewable energy and low maintenance make it a smart investment for long-term comfort and efficiency.
Read more: How Much Does Radiant Floor Heating Cost
Principles of Radiant Floor Heating
Radiant floor heating operates on a simple yet effective principle: heat transfer through thermal radiation. Instead of relying on forced air circulation like traditional heating systems, radiant floor heating uses the floor itself as a large radiant surface to evenly distribute heat throughout a space.
When a radiant floor heating system is activated, the warm water or electric heating element heats up the flooring material directly. This warmth then radiates upwards, heating objects and people in the room, rather than just the air. As a result, you experience a comfortable and consistent warmth from the ground up.
The key advantage of radiant floor heating lies in its ability to eliminate cold spots and drafts typically associated with forced-air systems. With radiant heating, the entire floor surface acts as a heat source, ensuring a more consistent and comfortable temperature across the room.
Another principle behind radiant floor heating is thermal mass. Objects with high thermal mass, such as concrete or stone floors, have the ability to absorb and store heat. This heat is gradually released into the room, even after the heating system has been turned off. As a result, the room stays warm for a longer period, improving energy efficiency.
Radiant floor heating not only provides a more comfortable and consistent heat, but it also offers better indoor air quality. Since there is no need for air circulation, there is less dust, allergens, and pollutants being blown around the room, making it an ideal option for those with allergies or respiratory issues.
Overall, the principles of radiant floor heating revolve around efficient heat transfer through thermal radiation, consistent and comfortable warmth, and improved indoor air quality. By harnessing these principles, radiant floor heating delivers the perfect heating solution for any space.
Components of Radiant Floor Heating Systems
Radiant floor heating systems consist of several key components that work together to provide efficient and comfortable heat distribution. Understanding these components is essential for the proper design, installation, and functioning of your radiant floor heating system.
1. Heat Source: The heat source is responsible for generating the heat used in the system. It can be a boiler, water heater, heat pump, or even a solar thermal system. The heat source heats up the water or heat transfer fluid that will flow through the tubing or electric heating elements.
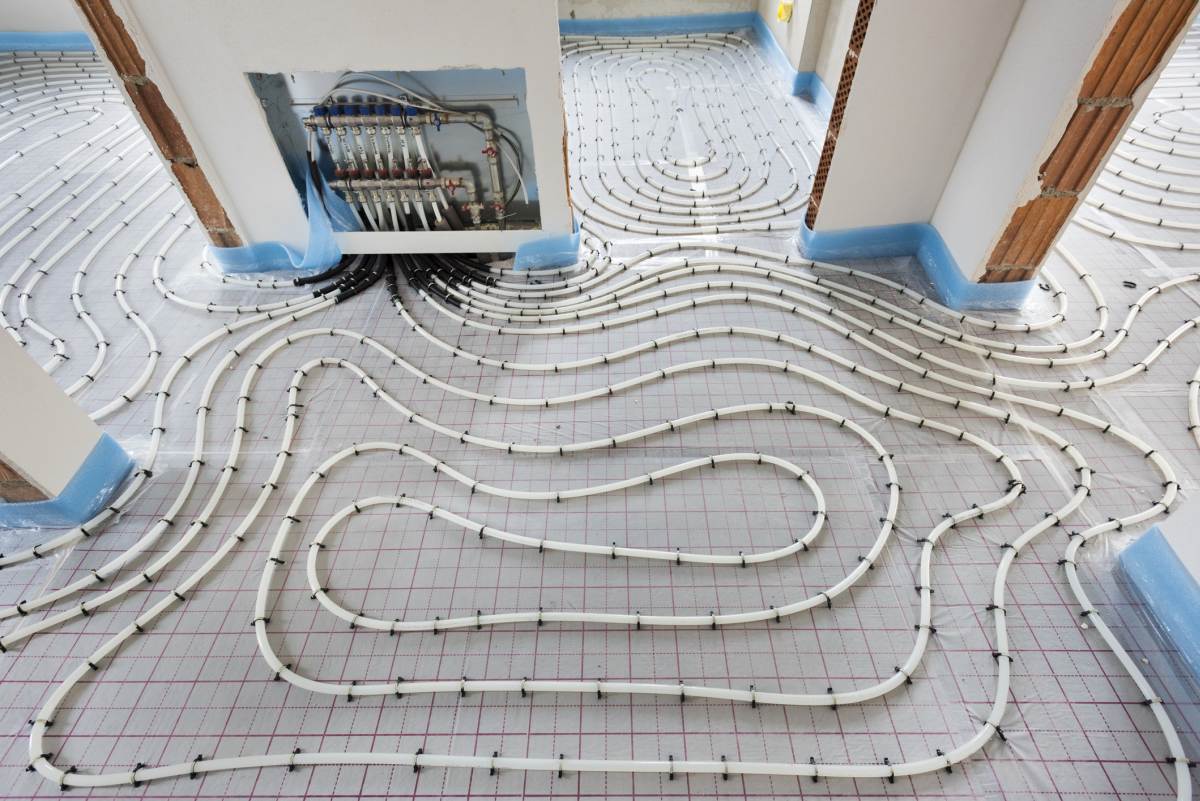
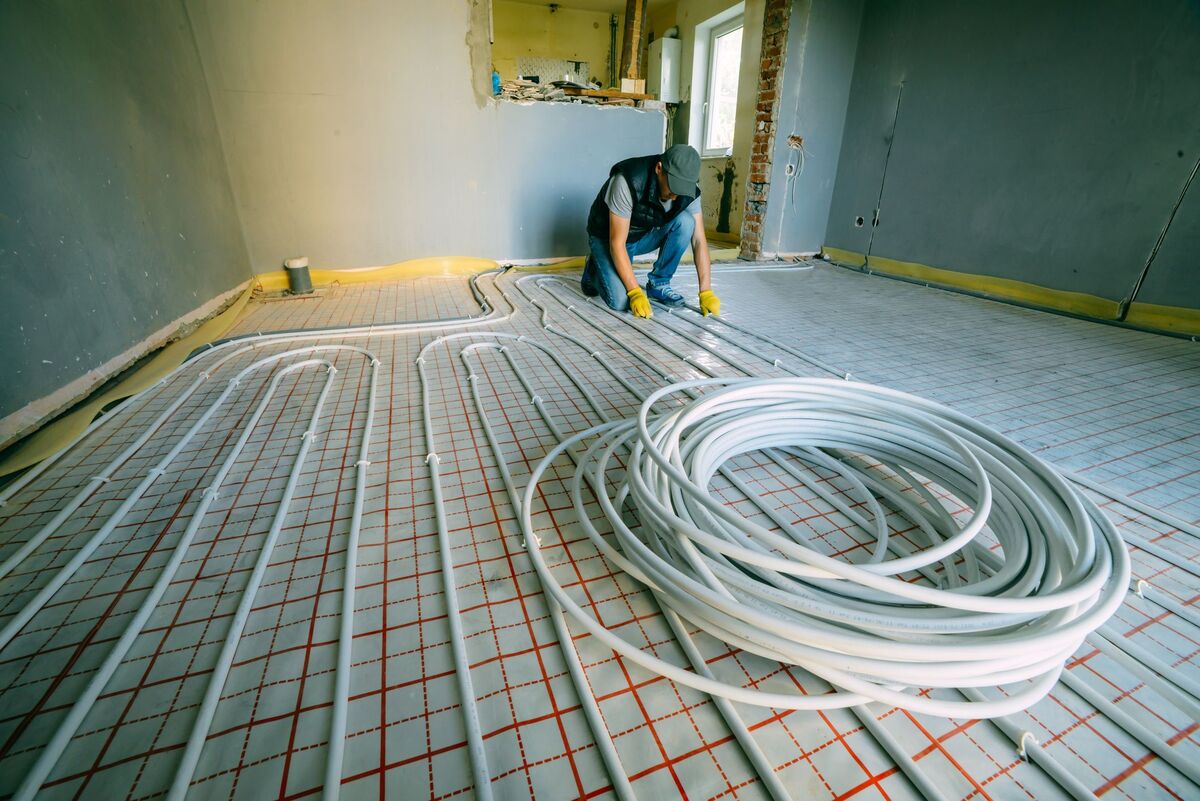
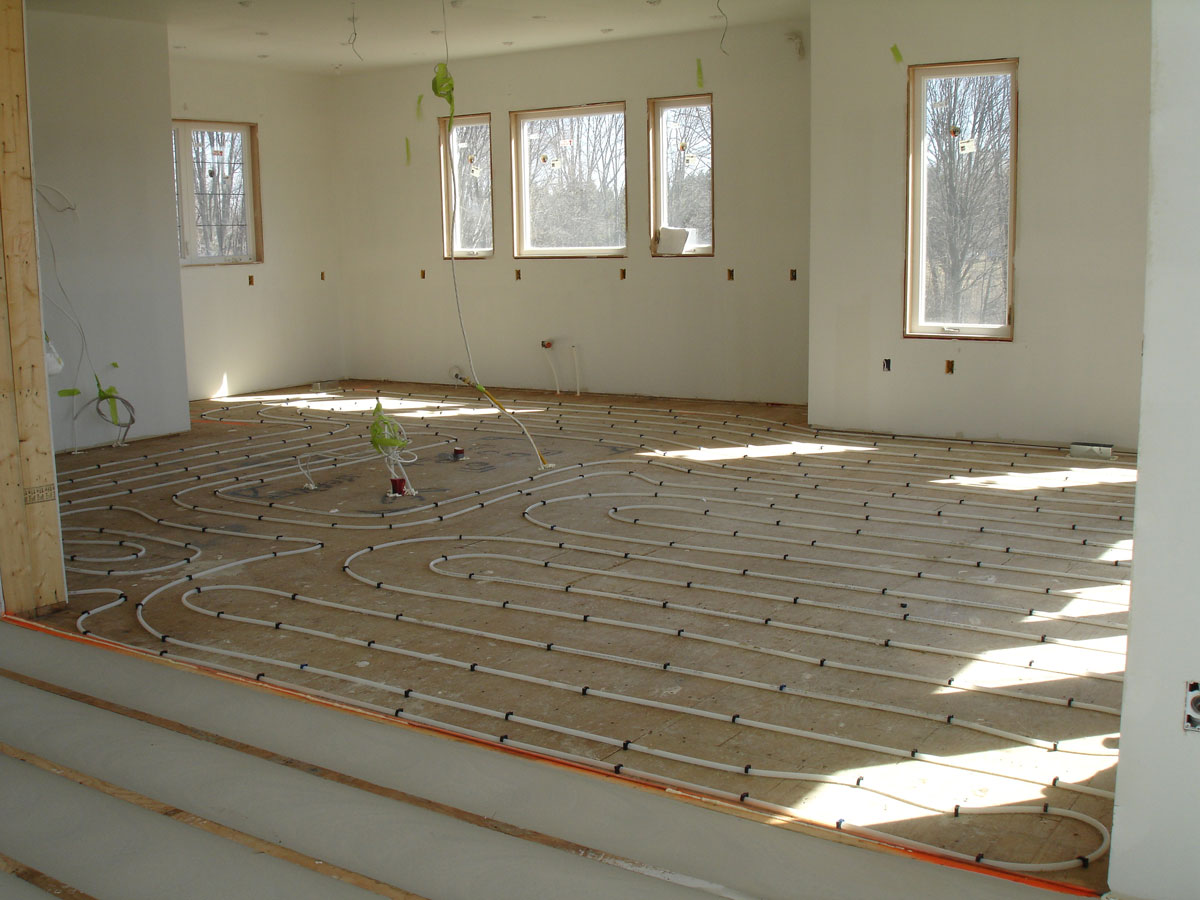
2. Tubing or Heating Element: The tubing or heating element is the heart of the radiant floor heating system. In hydronic systems, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) tubing is commonly used. It is installed within the floor structure, and hot water or a heat transfer fluid flows through it, transferring heat to the floor and radiating it upwards. Electric systems use heating cables or mats that are installed directly beneath the flooring material to generate heat.
3. Manifold: The manifold is where the primary supply and return pipes connect to the individual circuits of tubing or heating cables. It distributes the heated water or heat transfer fluid evenly to each zone or room in the system. The manifold also serves as a control point, allowing you to adjust the flow and temperature of the water.
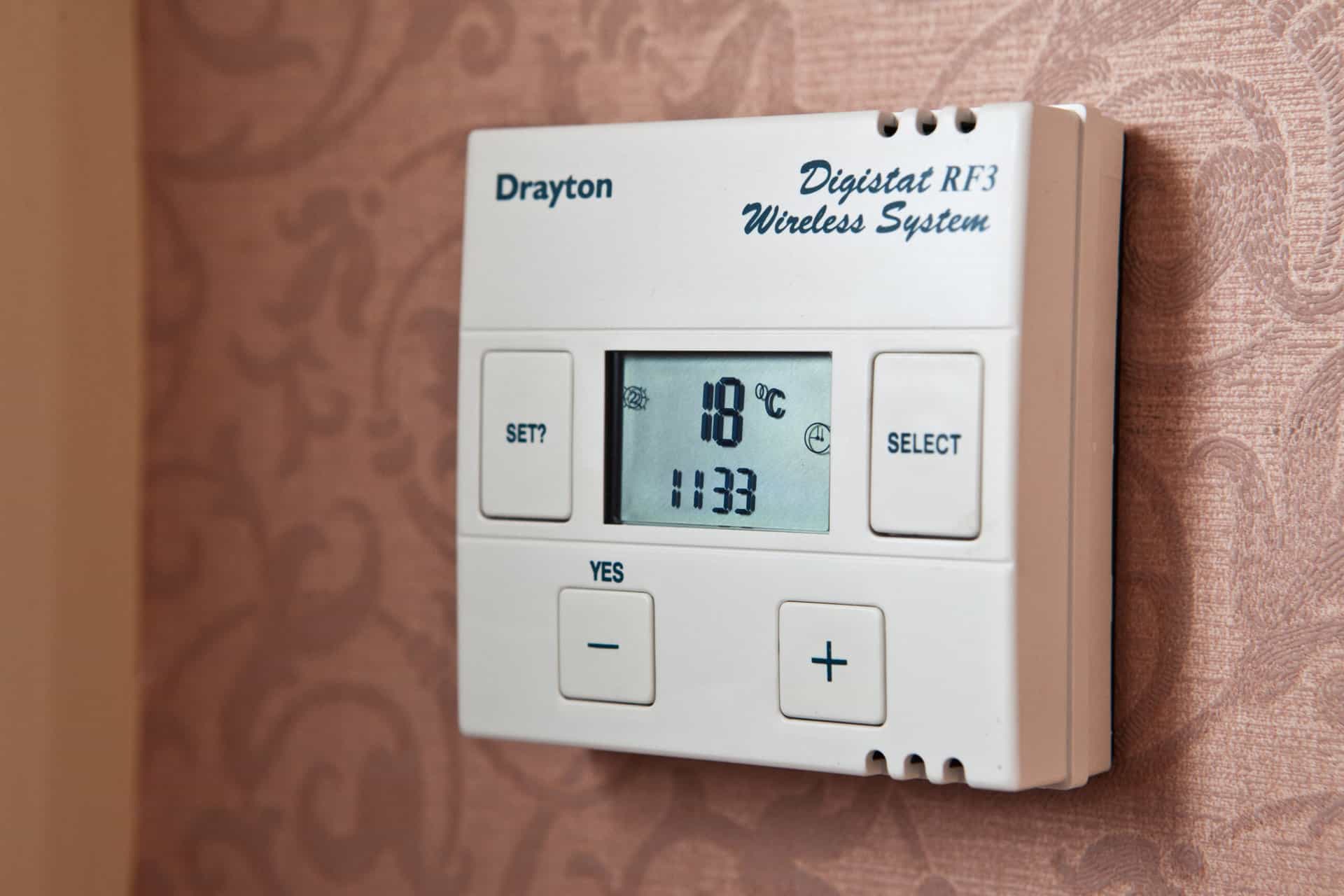
4. Control Systems: A control system is crucial for maintaining the desired temperature and comfort level in each zone. It consists of a thermostat, which allows you to set the temperature and control the system, as well as sensors that measure the floor and room temperature. Advanced control systems may include programmable thermostats, remote-access functionality, and zoning options for independent temperature control in different areas of your home.
5. Insulation: Insulation is an essential component of radiant floor heating systems. It helps to prevent heat loss to the ground or other areas where it is not needed. Insulating materials are typically installed below the tubing or heating element and can include rigid foam insulation boards or reflective insulation films.
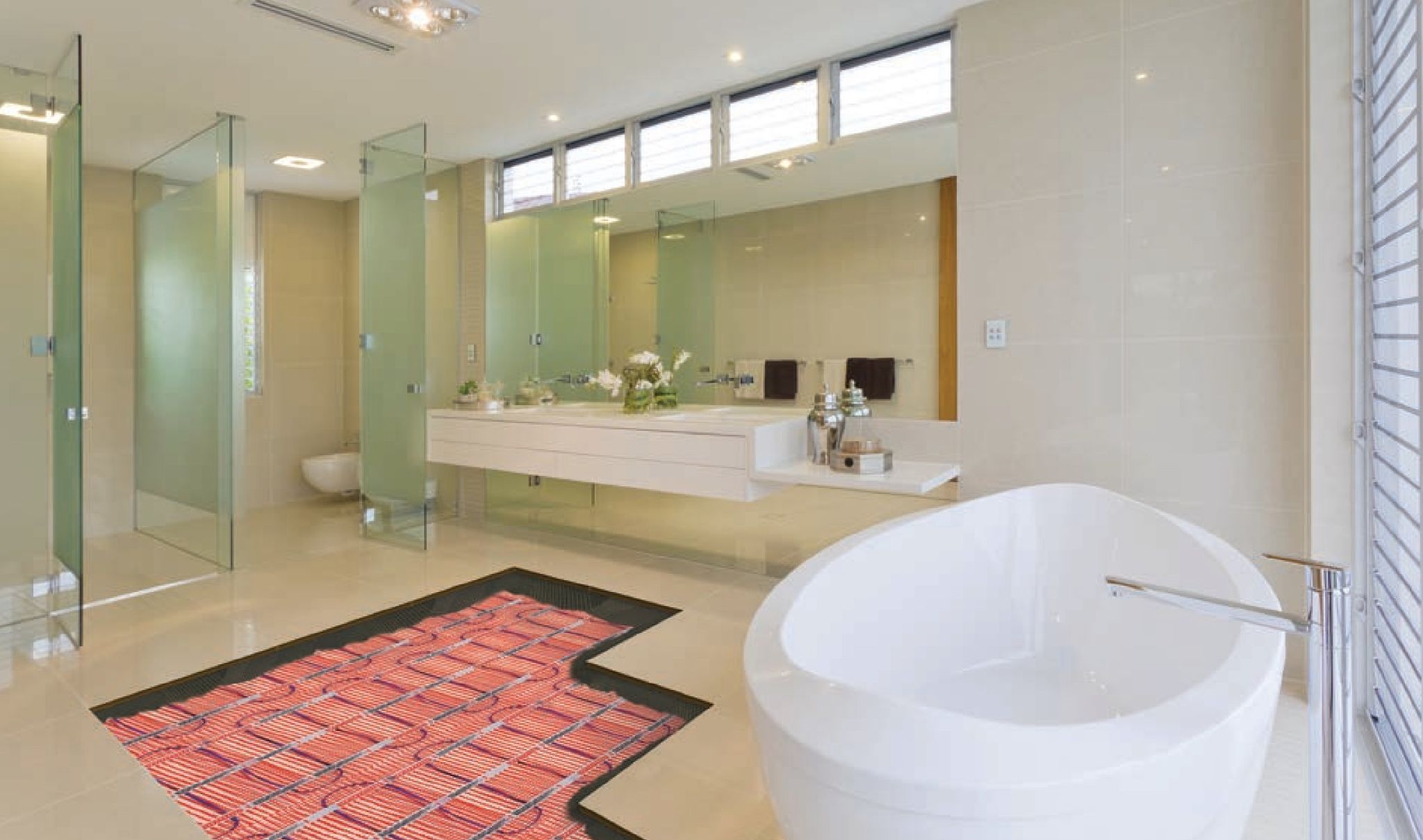
6. Flooring Material: The choice of flooring material is crucial, as it affects the heat transfer efficiency and overall performance of your radiant floor heating system. Materials with high thermal conductivity, such as tile, stone, or concrete, are ideal options as they allow for maximum heat transfer. However, other materials like wood or carpet can still work effectively with proper insulation.
By understanding and ensuring the proper installation and functioning of these components, you can ensure the optimal performance and longevity of your radiant floor heating system. A well-designed and properly installed system will provide you with years of comfort and energy efficiency.
Types of Radiant Floor Heating Systems
Radiant floor heating systems offer different options to cater to various needs and preferences. The two main types of radiant floor heating systems are hydronic systems and electric systems. Each type has its own benefits, considerations, and suitability for different situations.
1. Hydronic Systems: Hydronic radiant floor heating systems are the most common and widely used type. These systems rely on hot water or a heat transfer fluid to distribute heat through a network of tubing installed beneath the floor. The hot water is typically heated by a boiler or a water heater. Hydronic systems offer excellent energy efficiency, especially when paired with condensing boilers or solar thermal systems. They also provide a consistent and comfortable heat output, making them suitable for large spaces or whole-house heating. However, the installation of hydronic systems can be more complex and require professional expertise.
2. Electric Systems: Electric radiant floor heating systems use electric heating cables or mats installed directly beneath the flooring material. These systems are easier and less expensive to install compared to hydronic systems, making them a popular choice for smaller areas or retrofitting projects. Electric systems provide quick heat-up times and precise temperature control, allowing for energy-efficient operation. However, they may have higher operating costs due to electricity consumption. Electric systems are commonly used in bathrooms, kitchens, or specific rooms where supplemental heating is desired.
3. Radiant Panels: Radiant panel systems are another type of radiant floor heating system, but instead of being installed in the floor, they are mounted on the walls or ceilings. These panels are designed to radiate heat directly into the room, creating a comfortable and even heat distribution. Radiant panels are often used in commercial buildings or areas with limited floor space.
4. Air-Heated Systems: Air-heated radiant floor heating systems, as the name suggests, use heated air to provide warmth. These systems blow warm air through a network of ducts installed beneath the floor surface. While these systems can be easier to install and retrofit compared to hydronic systems, they are generally less efficient and may result in uneven heat distribution.
When choosing the type of radiant floor heating system, consider factors such as the size of the area, the availability of a heat source, budget constraints, and personal preferences. Consulting with a professional contractor or installer can help determine the most suitable system for your specific needs.
Installation Process of Radiant Floor Heating
The installation of a radiant floor heating system can vary depending on factors such as the type of system, the construction of your home, and the flooring materials in place. While it is recommended to hire a professional installer for complex installations, understanding the general process can help you make informed decisions and effectively communicate with the installer. Here is a step-by-step overview of the installation process:
1. Planning and Design: Begin by determining the scope of your project and developing a radiant floor heating plan. Consider factors such as the size of the space, the type of system you wish to install, the heat source, and any specific requirements or preferences you may have. It’s crucial to ensure that your heat source is adequate for the system you’ve chosen.
2. Subfloor Preparation: Before installing the radiant floor heating system, ensure that the subfloor is clean, level, and free from any debris, nails, or uneven surfaces. The subfloor material will depend on your home’s construction, but commonly used materials include plywood, concrete, or cement backer boards.
3. Insulation: Install insulation beneath the subfloor to prevent heat from being conducted downward. Insulation helps direct the heat upward, improving the overall efficiency of the system. The type and thickness of insulation will depend on factors such as climate, flooring type, and the specific requirements of your radiant floor heating system.
4. Tubing or Heating Element Installation: If you’re installing a hydronic system, position the tubing within the channels or grooves secured to the subfloor. Pay attention to the layout and spacing guidelines provided by the manufacturer to ensure optimal heat distribution. For electric systems, lay out the heating cables or mats evenly across the subfloor. Be sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions, particularly regarding installation spacing and electrical connections.
5. Manifold and Controls: Install the manifold, which serves as the central point for connecting the supply and return piping to the individual tubing or heating cables. The manifold allows for control over the flow and temperature of the heating fluid. Install the control systems, thermostat, and any zone valves according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
6. Flooring Installation: Once the tubing or heating elements are in place and the system is tested for leaks, you can proceed with installing the flooring material of your choice. The type of flooring material will depend on your preferences, budget, and the compatibility with radiant floor heating. Make sure to choose materials with good thermal conductivity for better heat transfer.
7. System Testing and Balancing: After the flooring installation is complete, test the radiant floor heating system to ensure it is functioning properly. Activate the system and monitor for any leaks, uneven heat distribution, or other issues. It may be necessary to adjust the flow rates or temperatures at the manifold to achieve the desired comfort levels in different areas of your home.
It’s important to note that the complexity of the installation process may vary depending on the specific requirements of your radiant floor heating system and the expertise of the installer. Consulting with a professional contractor is advisable to ensure a successful and efficient installation.
Radiant floor heating works by circulating warm water through pipes installed under the floor, providing even and efficient heat distribution. It’s a great option for heating your home, especially in colder climates.
Read more: How Does Ceiling Heat Work
Benefits of Radiant Floor Heating
Radiant floor heating offers a wide range of benefits that contribute to enhanced comfort, energy efficiency, and overall well-being in your home. Let’s explore some of the key advantages of radiant floor heating:
1. Comfort and Even Heat Distribution: Radiant floor heating provides a superior level of comfort compared to traditional heating systems. The heat radiates from the floor, creating a gentle, even warmth that is distributed throughout the room. Unlike forced-air systems, there are no drafts, cold spots, or noisy fans disrupting your comfort.
2. Energy Efficiency: Radiant floor heating is highly energy efficient due to the direct heat transfer and the ability to set lower thermostat temperatures. The radiant heat warms the objects and surfaces in the room, retaining heat for longer periods even after the system is turned off. This results in reduced energy consumption, lower heating bills, and a smaller carbon footprint.
3. Improved Indoor Air Quality: Unlike forced-air systems that distribute heated air and allergens through ducts, radiant floor heating does not rely on air circulation. This helps to prevent the circulation of dust, allergens, and pollutants, leading to improved indoor air quality and a healthier living environment, especially for those with allergies or respiratory issues.
4. Versatile Installation Options: Radiant floor heating can be installed in new construction or retrofitted into existing homes. With various installation methods and flooring materials available, such as tile, hardwood, or carpet, radiant floor heating seamlessly integrates with different architectural designs and interior styles.
5. Design Freedom: Radiant floor heating eliminates the need for bulky radiators or visible heating vents, allowing you more freedom in furniture placement and interior design. With no radiators taking up wall space, you can enjoy a more aesthetically pleasing and functional living environment.
6. Silent Operation: Radiant floor heating operates silently, creating a peaceful and tranquil atmosphere in your home. Say goodbye to the noise of clanging radiators or blowing air from forced-air systems, and enjoy a quiet and serene environment.
7. Zone Control: Radiant floor heating systems can be divided into different zones, allowing for individual temperature control in various rooms or areas of your home. This ensures personalized comfort and energy efficiency, as you can heat only the spaces you need, reducing energy waste.
8. Increased Home Value: Radiant floor heating is considered a desirable feature in homes. Its energy efficiency, comfort, and modern appeal can increase the value and marketability of your property, making it an attractive investment for potential buyers.
By embracing the benefits of radiant floor heating, you can create a warm, comfortable, and energy-efficient living environment that enhances your well-being and enjoyment in your home. Whether you’re building a new home or considering an upgrade, radiant floor heating offers a truly transformative heating solution.
Efficiency and Energy Savings of Radiant Floor Heating
Radiant floor heating systems offer significant energy efficiency and cost savings compared to traditional heating methods. By harnessing the principles of thermal radiation and eliminating the need for forced air circulation, radiant floor heating systems provide a more efficient and sustainable way to heat your home. Let’s explore the key factors that contribute to the efficiency and energy savings of radiant floor heating:
1. Direct Heat Transfer: Unlike forced-air systems that heat the air and rely on convection to warm the space, radiant floor heating directly heats the objects and surfaces in the room. This method of heat transfer minimizes heat loss and ensures that the heat is distributed evenly throughout the space, resulting in higher comfort levels and reduced energy consumption.
2. Lower Thermostat Settings: Radiant floor heating allows you to set lower thermostat temperatures while still maintaining the desired comfort level. The heat radiating from the floor ensures that you feel warm and cozy without the need for higher temperature settings. Lower thermostat settings translate into energy savings and reduced heating costs.
3. Energy Efficiency of Hydronic Systems: Hydronic radiant floor heating systems, which utilize a boiler or a water heater to heat the water circulating through the tubing, can be highly energy-efficient. Pairing the system with a high-efficiency condensing boiler or a solar thermal system further enhances the energy savings. By utilizing renewable energy sources or condensing technology, you can significantly reduce your carbon footprint and energy consumption.
4. Thermal Mass and Heat Retention: Radiant floor heating systems that incorporate materials with high thermal mass, such as concrete or stone flooring, have the ability to absorb and store heat. As a result, heat is slowly released into the room even after the heating system is turned off. This thermal mass effect helps to maintain a stable and comfortable temperature, reducing the need for frequent cycling of the heating system and optimizing energy efficiency.
5. Zoning and Individual Temperature Control: Radiant floor heating systems can be divided into different zones, allowing for individual temperature control in various rooms or areas of your home. This enables you to heat only the spaces you need, avoiding unnecessary energy consumption in unoccupied areas. Zoning also allows for customized comfort levels, ensuring that each occupant can set their preferred temperature for different zones.
6. Compatibility with Renewable Energy: Radiant floor heating systems can easily be integrated with renewable energy sources, such as solar thermal systems or geothermal heat pumps. By harnessing the power of renewable energy to heat the water or heat transfer fluid in the system, you can further enhance the energy efficiency and sustainability of your radiant floor heating setup.
7. Longevity and Durability: Radiant floor heating systems are known for their longevity and durability. With proper installation and maintenance, these systems can last for decades. This not only reduces the cost of replacement over time but also ensures that you’re maximizing the energy efficiency of your home for the long term.
8. Elimination of Duct Losses: Unlike forced-air systems, radiant floor heating eliminates the energy losses associated with ductwork. Duct losses can account for a significant portion of energy waste in traditional heating systems. By eliminating the need for ducts, radiant floor heating minimizes heat loss and increases energy efficiency.
By considering the efficiency and energy savings offered by radiant floor heating, you can make a smart investment that not only reduces your energy bills but also helps to promote a more sustainable and comfortable living environment.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Radiant Floor Heating Systems
Radiant floor heating systems are known for their reliability and low maintenance requirements. However, like any home heating system, regular maintenance and occasional troubleshooting are necessary to ensure optimal performance and address any issues that may arise. Here are some key maintenance tips and troubleshooting guidelines for radiant floor heating systems:
Maintenance:
- Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect the components of your radiant floor heating system, including the tubing or heating elements, manifold, control systems, and insulation. Look for any signs of leaks, damage, or wear and tear.
- Cleanliness: Keep the flooring surface clean and clear of debris, especially if you have an electric radiant floor heating system. Avoid placing heavy furniture or objects that could obstruct the heat transfer.
- Testing the Thermostat: Test the thermostat periodically to ensure it is functioning properly. Check the temperature readings and verify that the system responds accordingly when adjusting the settings.
- Check for Leaks: If you have a hydronic system, inspect the tubing, connections, and manifold for any signs of leakage. Leaks can lead to inefficient operation and potential damage to the surrounding areas.
- Flushing the System: If you notice reduced heat output or uneven heating, it may be necessary to flush the system to remove any sediment or mineral deposits that can accumulate over time. Consult with a professional technician for proper flushing procedures.
Troubleshooting:
- No Heat: If your radiant floor heating system is not producing any heat, check the thermostat settings and ensure that the system is turned on. Verify that the thermostatic valves or zone controls are functioning correctly. If there are still issues, consult a professional technician to investigate the source of the problem.
- Uneven Heating: If you experience uneven heating, first check the flow rates and temperatures at the manifold. Balancing the flow of water or adjusting the thermostat settings for each zone can help achieve more consistent heat distribution. If the problem persists, it may indicate issues with the tubing layout or insulation, and professional assistance may be required.
- Cold Spots or Cold Floors: If you notice cold spots or cold floors in certain areas, it could indicate a problem with the tubing or heating cables beneath the flooring surface. Inspect for damage or disconnection in the affected areas. If necessary, consult a professional technician to ensure proper repair or replacement.
- Thermostat Malfunction: If the thermostat is not functioning correctly, check the power source, batteries (if applicable), and wiring connections. Make sure the thermostat is properly calibrated and programmed. If the issue persists, consider replacing the thermostat or consult a professional technician for further troubleshooting.
- Noisy Operation: Unusual noises, such as gurgling or banging sounds, can indicate air in the system or improper water flow. Bleeding the air from the system or adjusting the flow rates at the manifold may resolve the issue. If the problem persists, seek professional assistance to identify and rectify the underlying cause.
Remember, if you encounter any issues with your radiant floor heating system that you are not comfortable troubleshooting or repairing yourself, it is always best to seek professional assistance. Regular maintenance and addressing any problems promptly will help ensure the longevity, efficiency, and continued comfort provided by your radiant floor heating system.
Comparison with Other Heating Systems
When considering the heating options for your home, it’s important to evaluate the pros and cons of different heating systems. Let’s compare radiant floor heating with other common heating systems to help you make an informed decision:
1. Forced-Air Heating: Forced-air heating systems, such as furnaces or heat pumps, rely on heating the air and distributing it through ducts in the walls or floors. While forced-air systems are common and relatively affordable to install, they can result in uneven heating, drafts, and a dry indoor environment due to air circulation. In comparison, radiant floor heating offers more even heat distribution, greater comfort, and improved indoor air quality as there is no air blowing around the room.
2. Baseboard Heating: Baseboard heating systems use electric or hydronic heating elements installed along the baseboard. These systems are relatively affordable and can be individually controlled for zoned heating. However, baseboard heating can lead to temperature stratification, with heat concentrating near the floor and cooler air higher in the room. Radiant floor heating, on the other hand, provides more consistent and uniform heat distribution from the ground up.
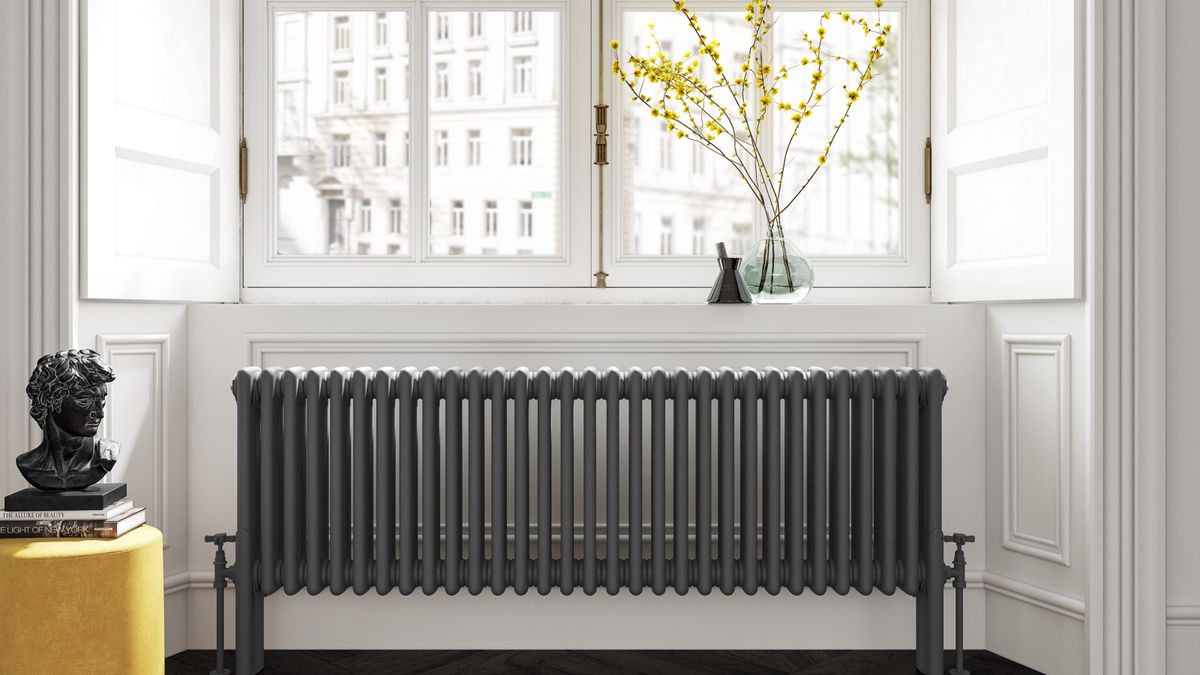
3. Radiator Heating: Radiator heating systems, most commonly seen in older homes, use hot water or steam-filled radiators to heat the space. While radiators can provide localized warmth, they are bulky, take up wall space, and can be noisy. In contrast, radiant floor heating eliminates the need for visible radiators, allowing for greater flexibility in furniture placement and a more aesthetically pleasing living environment.
4. Geothermal Heating: Geothermal heat pumps utilize the stable temperature of the earth to heat or cool a building. They can be highly efficient and environmentally friendly. Geothermal systems can work in conjunction with radiant floor heating, providing sustainable and energy-efficient heating and cooling. However, geothermal systems generally have higher upfront costs and require proper site conditions for ground loop installation.
5. Electric Heating: Electric heating systems, such as electric baseboards or electric furnaces, are relatively simple and cost-effective to install. However, they tend to have higher operating costs and can result in dry air. Radiant floor heating systems that utilize electric heating elements provide greater comfort and energy efficiency compared to traditional electric heating methods due to the even heat distribution and lower thermostat settings.
6. Solar Heating: Solar heating systems harness the power of the sun to heat water or air for space heating. When combined with radiant floor heating, solar energy can significantly reduce energy consumption and carbon footprint. Radiant floor heating systems are compatible with solar thermal systems, making it an excellent option for those seeking sustainable and renewable energy solutions.
Ultimately, the choice of heating system depends on factors such as budget, energy efficiency, comfort, and specific requirements of your home. Radiant floor heating stands out for its even heat distribution, enhanced comfort, energy efficiency, and compatibility with various energy sources. Consulting with a heating professional can help you determine the best heating system for your specific needs and preferences.
Read more: How Are Heated Floors Heated?
Conclusion
Radiant floor heating offers a remarkable heating solution that combines comfort, efficiency, and versatility. This article has provided you with an in-depth understanding of how radiant floor heating works, its principles, components, installation process, and maintenance requirements. We have also explored the benefits of radiant floor heating and compared it to other heating systems.
By utilizing thermal radiation and direct heat transfer, radiant floor heating provides superior comfort, with even heat distribution and the absence of drafts. It offers energy efficiency by allowing lower thermostat settings, utilizing renewable energy sources, and minimizing heat loss. Additionally, radiant floor heating improves indoor air quality and provides flexibility in design and furniture placement.
From hydronic systems to electric systems, radiant floor heating can be tailored to suit your home’s specific needs, whether it’s a new construction or a retrofit project. The installation process may require professional expertise, but the long-term benefits are worth the investment.
Maintenance and troubleshooting are vital for ensuring the continued functionality and efficiency of radiant floor heating systems. Regular inspections, cleanliness, and attention to components like the tubing, manifold, and controls will help maintain optimal performance. Troubleshooting common issues, such as uneven heating or thermostat malfunctions, will ensure that any problems are promptly addressed.
When comparing radiant floor heating to other heating systems, it becomes clear that its superior comfort, energy efficiency, and design flexibility set it apart. Unlike forced-air systems, baseboard heating, or radiators, radiant floor heating provides consistent warmth without noisy operation or air circulation issues. It also outperforms electric heating methods in terms of comfort and energy efficiency.
In conclusion, radiant floor heating is a smart choice for any homeowner seeking ultimate comfort, energy savings, and a sustainable heating solution. Its benefits extend beyond cozy warm floors, providing a healthier indoor environment and increasing the overall value of your home. Consider consulting with a professional heating contractor to explore the feasibility and advantages of radiant floor heating for your specific needs, and transform your living spaces into true havens of comfort and efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Does Radiant Floor Heating Work
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How Does Radiant Floor Heating Work”