
Articles
What Causes An Electric Motor To Lose Power
Modified: March 1, 2024
Discover the reasons behind the loss of power in electric motors with our informative articles. Learn how to troubleshoot and fix motor power issues.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Electric motors play a crucial role in a wide range of applications, from powering industrial machinery to propelling vehicles. However, there are instances when an electric motor may experience a loss of power, leading to reduced efficiency and performance. Understanding the factors that can cause an electric motor to lose power is essential for troubleshooting and ensuring optimal functioning.
In this article, we will explore the common reasons behind a loss of power in electric motors. By identifying these causes, you can take appropriate measures to diagnose and resolve motor performance issues.
Now, let’s dive into the factors that can contribute to the loss of power in electric motors.
Key Takeaways:
- Regular maintenance, proper lubrication, and load management are crucial in preventing power loss in electric motors. Understanding and addressing common issues can ensure optimal performance and longevity.
- Insufficient voltage supply, overheating, worn brushes, faulty bearings, and damaged windings are common factors contributing to power loss in electric motors. Addressing these issues promptly is essential for maintaining optimal performance.
Read more: What Causes An Electric Motor To Overheat
Insufficient Voltage Supply
One of the primary factors that can cause an electric motor to lose power is insufficient voltage supply. Electric motors require a specific voltage to operate efficiently, and any deviation from the recommended voltage can result in reduced performance.
If the voltage supply to the motor is lower than the required amount, it can lead to a decrease in the motor’s power output. This can occur due to various reasons, such as inadequate electrical infrastructure, voltage drops in long power lines, or overloaded circuits.
To address this issue, it is essential to ensure that the voltage supply to the motor meets the manufacturer’s specifications. If the voltage is below the recommended level, you may need to investigate the electrical system and make necessary adjustments, such as upgrading the power supply or redistributing the load.
In some cases, power fluctuations or voltage spikes can also affect the motor’s performance. These sudden changes in voltage can cause the motor to experience power loss or even damage its components. Installing voltage stabilization devices or surge protectors can help mitigate the impact of voltage fluctuations and protect the motor from potential damage.
Regularly monitoring the voltage supply and addressing any issues promptly can help prevent power loss in electric motors and ensure their optimal performance.
Overheating
Another common factor that can cause an electric motor to lose power is overheating. When a motor operates at higher temperatures than its designed limits, it can experience a drop in performance, leading to power loss.
Overheating can occur due to a variety of reasons, including inadequate cooling mechanisms, insufficient ventilation, excessive mechanical load, or extended periods of continuous operation. It can also be caused by a buildup of dirt or debris on the motor’s cooling fins or vents, hindering the dissipation of heat.
When a motor overheats, its internal components expand, which can result in increased resistance and decreased efficiency. This can cause a decrease in power output and even lead to motor failure if not addressed promptly.
To prevent overheating, it is crucial to ensure proper cooling and ventilation of the motor. This can be achieved by regularly cleaning the cooling fins and vents to remove any accumulated dirt or debris. Additionally, ensuring adequate airflow around the motor, avoiding overloading the motor beyond its capacity, and allowing sufficient rest periods during extended operation can all help prevent overheating.
If overheating persists despite these preventive measures, it may be necessary to consult a qualified technician to inspect the motor for any underlying issues, such as faulty cooling fans, damaged insulation, or worn-out bearings.
Regular maintenance and monitoring of the motor’s temperature can help mitigate the risk of overheating and maintain optimal power output.
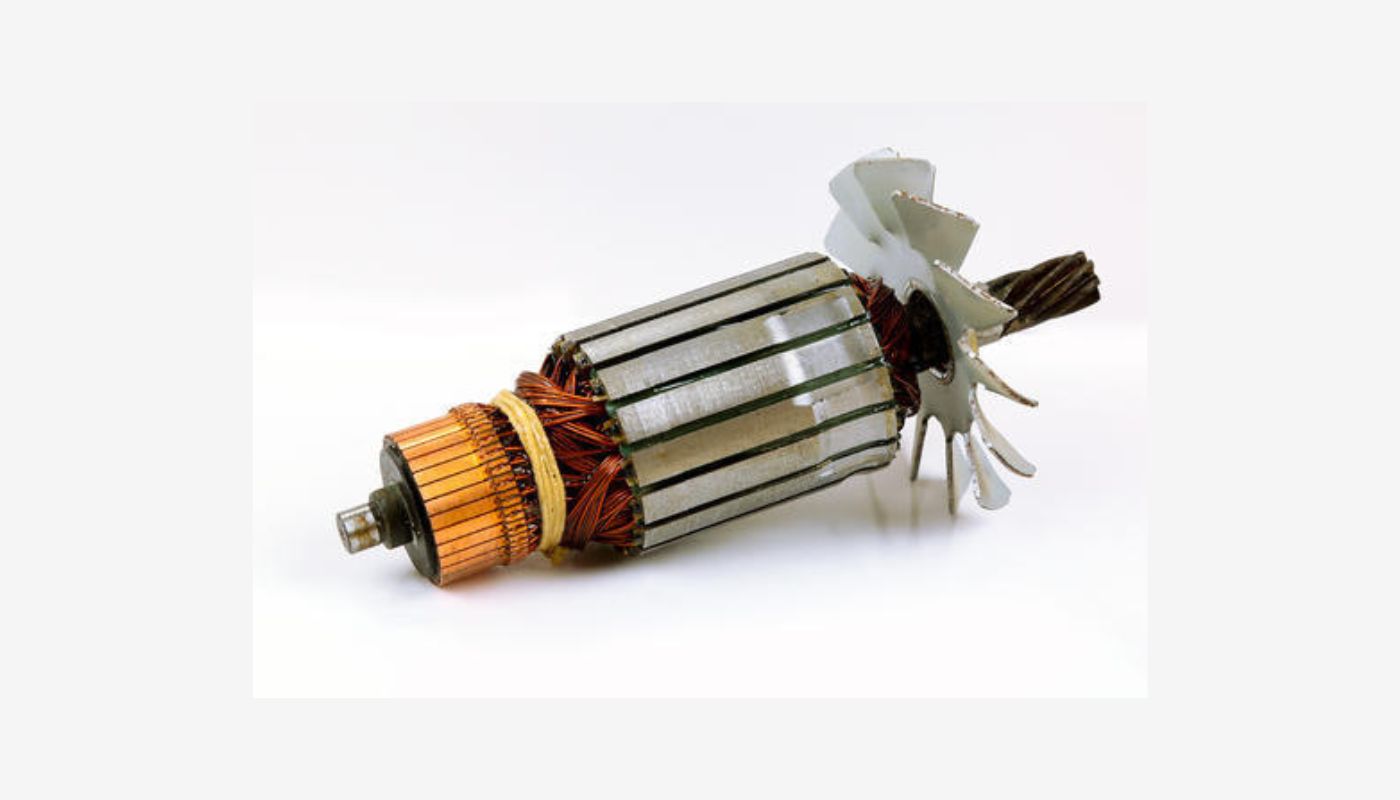
Worn Brushes
Worn-out brushes can also contribute to a loss of power in electric motors. Brushes are crucial components that facilitate the transfer of electrical current from the power source to the motor’s rotating armature.
Over time, the brushes can wear down due to friction and normal usage. As the brushes become worn, their contact with the armature weakens, leading to increased resistance and reduced electrical current flow. This can result in a drop in power output and overall motor performance.
To address this issue, regular inspection and maintenance of the brushes are essential. If the brushes are worn down or damaged, they should be replaced promptly to restore optimal contact and electrical conductivity.
In some cases, the brush holder or commutator may also require cleaning or adjustment. Any buildup of carbon deposits or debris on the surfaces can impair the brush-armature contact, leading to power loss. Cleaning the brush holder and commutator, and ensuring proper alignment, can help maintain efficient power transfer.
It is important to note that brushes have a limited lifespan and will eventually require replacement. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines for brush replacement intervals and using high-quality brushes can help prolong the motor’s performance and prevent power loss.
Regular maintenance of the brushes, along with routine inspections and timely replacements, can help ensure optimal power output and extend the lifespan of the electric motor.
Faulty Bearings
Faulty bearings can contribute to power loss in electric motors. Bearings are essential components that support the motor’s rotating shaft and enable smooth operation. Over time, bearings can wear down due to factors such as friction, inadequate lubrication, or contaminants entering the bearing housing.
When bearings become faulty or worn, they can create excessive friction and resistance, causing a decrease in the motor’s efficiency and power output.
Symptoms of faulty bearings include unusual noises, excessive vibration, or increased operating temperature. If these signs are detected, it is crucial to address the issue promptly to prevent further damage and power loss.
Replacing faulty bearings is the most effective solution to restore the motor’s performance. This process typically involves disassembling the motor and replacing the damaged bearings with new ones that are properly sized and lubricated.
Regular maintenance and inspection of the motor’s bearings can help identify early signs of wear or damage. This can be done by checking for any abnormal noise or vibration during operation. Additionally, ensuring proper lubrication and cleanliness of the bearing housing can extend the lifespan of the bearings and prevent premature failures.
By maintaining the motor’s bearings in good condition, you can minimize power loss and ensure optimum performance of the electric motor.
Regular maintenance, such as cleaning and lubricating the motor, can help prevent power loss. Check for loose connections and worn out parts, and ensure proper ventilation for the motor to prevent overheating.
Faulty Windings
Faulty windings are another potential cause of power loss in electric motors. The windings, also known as coils, are responsible for producing the magnetic fields that drive the motor’s rotation.
If the motor’s windings become damaged or develop faults, it can lead to a decrease in power output. This can occur due to factors such as insulation breakdown, overheating, excessive vibration, or electrical overload.
When the winding insulation breaks down, it can result in short circuits or open circuits within the motor. This disrupts the flow of electricity and causes a loss of power. Similarly, overheating or excessive vibration can cause the windings to deteriorate over time, leading to decreased efficiency and power output.
Identifying faulty windings typically requires a thorough inspection of the motor by a qualified technician. Specialized testing equipment, such as insulation resistance testers or winding resistance analyzers, may be used to assess the condition of the windings.
If faulty windings are detected, repairs or rewinding of the motor may be necessary. This involves removing the damaged windings and replacing them with new ones, ensuring proper insulation and connections are in place.
To prevent winding failures, it is important to maintain the motor within its operating temperature limits, avoid electrical overloads, and ensure adequate ventilation and cooling. Regular maintenance, including cleaning and inspection of the motor, can also help identify and address winding issues before they lead to significant power loss.
By addressing faulty windings promptly and ensuring proper maintenance, you can maintain optimal power output and extend the lifespan of the electric motor.
Contaminated or Damaged Commutator
The commutator is a critical component of electric motors that helps to maintain the flow of electrical current to the motor’s armature. It consists of a series of copper segments that are insulated from each other but make contact with the brushes.
If the commutator becomes contaminated or damaged, it can lead to a loss of power in the motor. Contamination can occur due to the buildup of dust, debris, or carbon deposits, while damage can result from factors such as wear, arcing, or excessive vibration.
Contamination on the commutator surface can create an insulating barrier that hinders the flow of current to the armature. This reduces the power output and efficiency of the motor. Similarly, damaged segments or rough surface texture can result in increased friction and resistance, causing further power loss.
To address contamination on the commutator, it is necessary to clean the surface thoroughly using a commutator cleaning brush or a soft, lint-free cloth. Care should be taken to avoid scratching or damaging the surface during cleaning. In some cases, mild solvents or cleaning solutions may be used to remove stubborn debris or deposits.
If the commutator is damaged or worn, it may be necessary to repair or replace it. This involves re-machining the surface or replacing the entire commutator assembly, depending on the extent of the damage.
Regular inspection and cleaning of the commutator, along with proper maintenance of the brushes, can help prevent contamination and minimize the risk of power loss. It is also important to address any underlying issues that may contribute to commutator damage, such as excessive vibration or inadequate lubrication.
By ensuring the cleanliness and integrity of the commutator, you can maintain optimal power output and prolong the lifespan of the electric motor.
High Friction
High friction is another factor that can contribute to power loss in electric motors. Friction occurs when there is resistance to the motor’s rotational movement, resulting in energy loss and decreased power output.
There are several potential causes of high friction in electric motors. One common issue is inadequate lubrication of moving parts, such as bearings or gears. Insufficient lubrication can lead to increased friction, causing the motor to work harder and consume more energy.
Excessive load or mechanical resistance on the motor can also result in high friction. If the motor is working beyond its rated capacity or if there is an obstruction in the system, such as a misaligned belt or a seized mechanical component, it can lead to increased friction and consequently reduce power output.
To address high friction, it is important to implement proper lubrication practices. Regularly checking and replenishing lubricants for the motor’s bearings, gears, and other moving parts can help reduce friction and improve overall efficiency.
Additionally, ensuring that the motor operates within its specified load and capacity limits is crucial. Avoiding overloading the motor and addressing any mechanical issues or obstructions promptly can help minimize friction and prevent power loss.
Regular maintenance and inspection of the motor’s components, such as bearings and belts, can also help identify and address any sources of high friction before they lead to significant power loss.
By reducing friction and implementing proper maintenance practices, you can optimize the power output and efficiency of the electric motor.
Mechanical Load
The mechanical load placed upon an electric motor can significantly impact its power output. The mechanical load refers to the amount of work or force that the motor needs to exert to perform its intended function.
When an electric motor is subjected to a heavy or excessive mechanical load, it can experience a decrease in power output. This occurs because the motor has to work harder to overcome the resistance caused by the load, resulting in reduced efficiency and potential power loss.
Several factors can contribute to a high mechanical load on an electric motor. One common issue is overloading the motor beyond its specified capacity. This can occur when the motor is subjected to a higher torque requirement than it is designed to handle, leading to diminished power output and potential damage to the motor.
Misalignment of belts or pulleys can also contribute to an increased mechanical load. When the mechanical components are not properly aligned, it can cause excessive friction and resistance, reducing the motor’s efficiency and performance.
To address the issue of mechanical load, it is important to ensure that the motor is operating within its specified load limits. Understanding the motor’s capacity and torque requirements is essential in order to avoid overloading it.
Regular maintenance and inspection of mechanical components, such as belts, pulleys, or gear systems, can help identify and correct any misalignments or issues that may be placing an excessive load on the motor.
By operating the motor within its designated load limits and addressing any mechanical issues promptly, you can optimize power output and prolong the life of the electric motor.
Read more: What Causes A Toilet Bowl To Lose Water
Conclusion
Electric motors are essential for a wide range of applications, and it is crucial to ensure that they operate at their optimal performance levels. A loss of power in electric motors can be detrimental to their efficiency and functionality.
In this article, we have explored some of the common reasons behind a loss of power in electric motors. Insufficient voltage supply can lead to decreased power output, while overheating can result from various factors such as inadequate cooling or excessive mechanical load.
Worn brushes can also contribute to power loss, as they hinder the proper transfer of current to the motor’s armature. Faulty bearings, damaged windings, and contaminated or damaged commutators are additional factors that can impact power output.
High friction and excessive mechanical load can also lead to decreased power output in electric motors. Proper lubrication, maintenance, and load management practices are crucial in mitigating these issues.
In conclusion, maintaining and troubleshooting electric motors for power loss requires regular inspection, proper maintenance, and prompt action to address any underlying issues. By understanding and addressing the factors that can contribute to power loss, you can ensure that your electric motors perform at their best and maintain their longevity.
Remember to consult a qualified technician or follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for specific motor-related issues to ensure the best outcomes in diagnosing and resolving power loss in electric motors.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Causes An Electric Motor To Lose Power
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “What Causes An Electric Motor To Lose Power”