
Articles
What Does High Head Pressure Mean In HVAC
Modified: January 19, 2024
Learn about high head pressure in HVAC systems and what it means in our informative articles. Understand the causes and solutions to keep your HVAC running smoothly.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
When it comes to maintaining an efficient and effective HVAC system, understanding the various components and their functions is crucial. One important aspect to consider is the head pressure in an HVAC system.
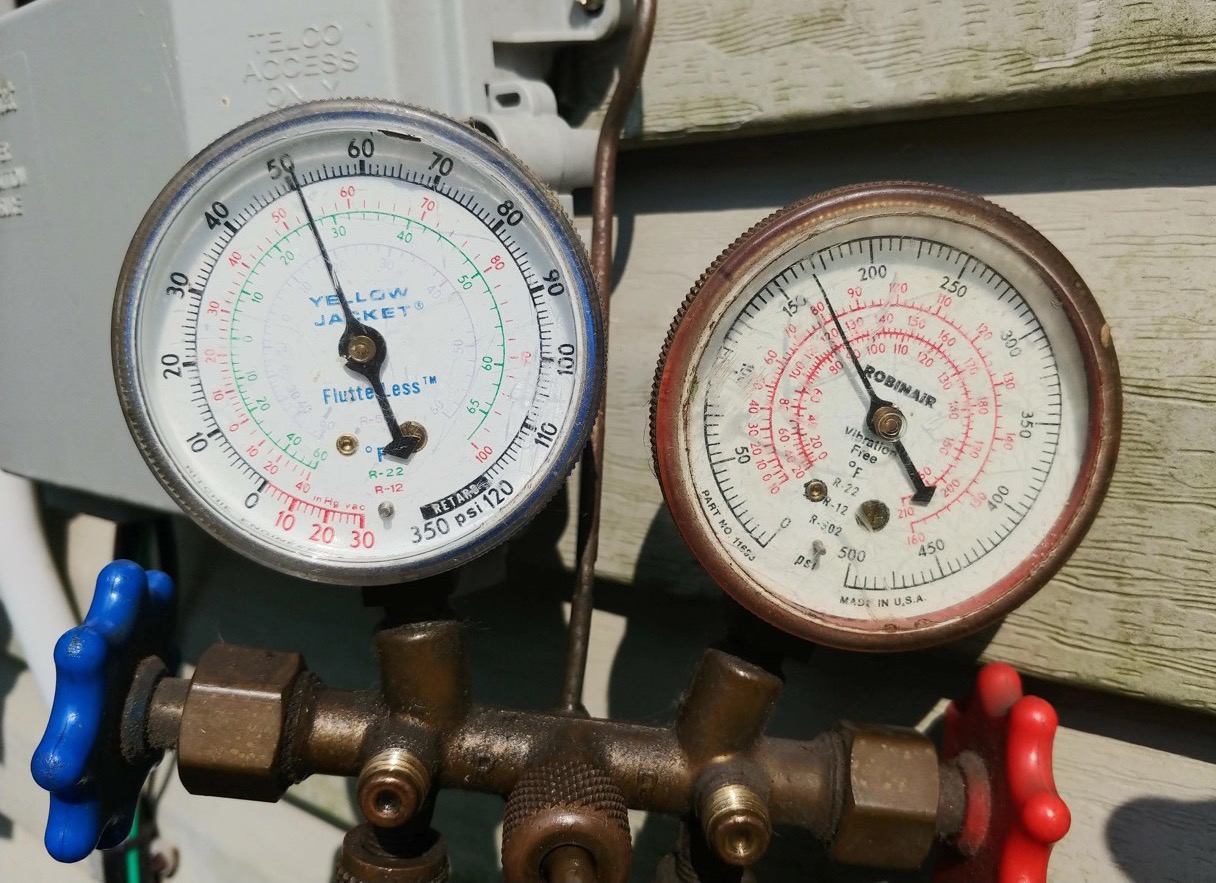
Head pressure, also known as discharge pressure, refers to the pressure exerted by the refrigerant in the condenser of an HVAC system. It plays a vital role in the overall performance and efficiency of the system.
In this article, we will delve into the concept of head pressure in HVAC systems, its causes, symptoms, effects, troubleshooting, and preventive measures to mitigate high head pressure. By understanding these key points, you will be better equipped to identify, diagnose, and address any issues related to high head pressure in your HVAC system.
Key Takeaways:
- High head pressure in HVAC systems can lead to reduced cooling capacity, increased energy consumption, and potential damage to system components. Regular maintenance and preventive measures are crucial in preventing and addressing this issue.
- Symptoms of high head pressure include reduced cooling efficiency, increased energy consumption, frequent cycling, and unusual noises. Prompt troubleshooting and professional assistance from an HVAC technician are essential for addressing high head pressure effectively.
Read more: What Does Ecm Mean In HVAC
Definition of Head Pressure in HVAC
Head pressure, also referred to as discharge pressure, is a vital component of the refrigeration cycle in an HVAC system. It is the pressure exerted by the refrigerant in the condenser as it transforms from a high-pressure gas to a high-pressure liquid, following compression in the compressor.
The head pressure is measured in PSI (pounds per square inch) and is crucial for the proper operation of the HVAC system. It helps ensure efficient heat transfer and cooling by facilitating the release of heat absorbed by the refrigerant in the evaporator coils.
The head pressure is influenced by several factors, including the ambient temperature, the amount of heat being absorbed by the evaporator coils, and the efficiency of the airflow across the condenser coils.
Proper head pressure is essential for the efficient operation of the HVAC system and maintaining optimal performance. If the head pressure is too low or too high, it can lead to various issues, including reduced cooling capacity, increased energy consumption, and potential damage to the compressor and other components of the system.
Causes of High Head Pressure
High head pressure in an HVAC system can be caused by various factors. Understanding these causes can help identify and address the issue effectively. Here are some common causes of high head pressure:
- Dirty Condenser Coils: Accumulation of dirt, debris, and other contaminants on the condenser coils restricts airflow, reducing heat dissipation and resulting in higher head pressure.
- Restricted Airflow: Insufficient airflow across the condenser coils due to a clogged air filter, blocked vents or registers, or a malfunctioning fan motor can lead to high head pressure.
- Overcharged Refrigerant: Excess refrigerant in the system can cause the head pressure to rise. This can occur during installation or due to improper servicing.
- Faulty Condenser Fan Motor: A malfunctioning condenser fan motor will hinder the airflow across the condenser coils, leading to a rise in head pressure.
- Malfunctioning Expansion Valve: A faulty expansion valve can cause the refrigerant to flow into the evaporator coils at a higher rate than it should, resulting in increased head pressure.
- External Heat Sources: Excessive heat from external sources, such as direct sunlight, nearby equipment, or inadequate spacing around the HVAC unit, can cause the head pressure to rise.
- Compression Ratio: If the compression ratio in the system is too high, it can contribute to high head pressure. This can occur if the compressor is oversized or if the expansion valve is not functioning correctly.
Identifying the specific cause of high head pressure is vital in order to implement the appropriate troubleshooting and corrective measures. It is recommended to consult with a qualified HVAC technician to accurately diagnose and address the issue.
Symptoms of High Head Pressure
High head pressure in an HVAC system can manifest through various symptoms. Identifying these symptoms can help you detect and address the issue promptly. Here are some common symptoms of high head pressure:
- Reduced Cooling Capacity: One of the primary symptoms of high head pressure is reduced cooling capacity. You may notice that your HVAC system is no longer effectively cooling your space or maintaining the desired temperature.
- Increased Energy Consumption: High head pressure forces the HVAC system to work harder to achieve the desired cooling effect. As a result, it consumes more energy, leading to higher utility bills.
- Frequent Cycling: If your HVAC system cycles on and off more frequently than usual, it could be an indication of high head pressure. This rapid cycling occurs as the system tries to cope with the excessive pressure.
- Tripped Safety Switches: High head pressure can trigger various safety switches in the HVAC system. These switches are designed to protect the components from potential damage. If you notice that safety switches are frequently tripping, it could be a sign of high head pressure.
- Unusual Noises: Excessive pressure in the system can cause components to strain or malfunction, leading to unusual noises. You might hear grinding, hissing, or banging sounds coming from the HVAC unit.
- Reduced Lifespan of Components: High head pressure puts extra stress on the compressor, condenser, and other components of the HVAC system. Over time, this can lead to premature wear and tear, reducing the lifespan of these components.
If you observe any of these symptoms, it is important to address the issue promptly to prevent further damage to the HVAC system. Seeking professional help from a qualified HVAC technician is recommended to accurately diagnose and fix the problem.
High head pressure in HVAC can be caused by issues such as dirty condenser coils, overcharged refrigerant, or a malfunctioning condenser fan. Regular maintenance and troubleshooting can help identify and resolve the issue.
Effects of High Head Pressure on HVAC Systems
High head pressure in an HVAC system can have detrimental effects on its overall performance and efficiency. Understanding these effects is crucial in order to mitigate the issue and prevent further damage. Here are some common effects of high head pressure:
- Reduced Cooling Efficiency: High head pressure hinders the heat transfer process in the condenser coils, leading to reduced cooling efficiency. This means that the HVAC system may struggle to cool the space adequately, resulting in discomfort for occupants.
- Increased Energy Consumption: As the HVAC system struggles to maintain proper cooling with high head pressure, it requires more energy to operate efficiently. This increased energy consumption can result in higher utility bills and unnecessary expenses.
- Potential Compressor Damage: High head pressure puts excessive strain on the compressor, the heart of the HVAC system. The extra pressure can cause the compressor to work harder and potentially lead to overheating, compressor failure, and costly repairs.
- Refrigerant Leaks: The increased pressure and strain on the HVAC system can lead to leaks in the refrigerant lines. These leaks not only contribute to further performance issues but also require immediate attention to prevent further damage.
- Reduced Lifespan of Components: Components such as the compressor, condenser fan motor, and other parts of the HVAC system are subjected to increased stress and wear with high head pressure. This can result in a shorter lifespan for these components, necessitating more frequent repairs or replacements.
- Overall System Inefficiency: High head pressure affects the overall performance and efficiency of the HVAC system. The reduced cooling capacity and increased energy consumption can cause the system to operate below optimal levels, leading to discomfort and dissatisfaction for occupants.
Addressing high head pressure promptly is crucial to mitigate these effects and ensure the longevity and efficiency of the HVAC system. Consulting with a qualified HVAC technician is recommended to accurately diagnose the problem and implement the necessary repairs or adjustments.
Read more: What Does Seer Mean For HVAC
Troubleshooting and Fixing High Head Pressure
When encountering high head pressure in an HVAC system, it is important to promptly troubleshoot and address the issue to prevent further damage and ensure optimal performance. Here are some troubleshooting steps and potential fixes for high head pressure:
- Clean Condenser Coils: Start by inspecting the condenser coils and clean them thoroughly. Removing any dirt, debris, or obstructions that block airflow across the coils can significantly improve heat dissipation and reduce head pressure.
- Check Airflow: Verify that the airflow across the condenser coils is not restricted. Ensure that the air filters are clean and not clogged, and check for any blocked vents or registers. If needed, replace the air filters and clear any obstructions to improve airflow.
- Verify Refrigerant Charge: Check the refrigerant charge level in the system. If it is overcharged, remove the excess refrigerant to bring it to the recommended level. If it is undercharged, add refrigerant as per manufacturer guidelines. It is crucial to follow proper procedures and consult a qualified technician for refrigerant handling.
- Inspect Condenser Fan Motor: Check the condenser fan motor for proper operation. Ensure that it is running smoothly and that the blades are not damaged or obstructed. If the fan motor is malfunctioning, consider repairing or replacing it to restore proper airflow.
- Inspect Expansion Valve: Inspect the expansion valve for proper functioning. If it is faulty or sticking, causing an improper flow of refrigerant, it may contribute to high head pressure. Consider repairing or replacing the expansion valve as needed.
- Reduce External Heat Sources: Identify and minimize any external heat sources affecting the HVAC system. Provide adequate spacing around the unit and shield it from direct sunlight or nearby equipment that generates heat.
- Check Compression Ratio: If the high head pressure persists, it may be necessary to evaluate the compression ratio of the system. This requires specialized knowledge and equipment to ensure the proper functioning of the compressor and expansion valve. Consult a qualified HVAC technician for this evaluation.
Remember, troubleshooting and fixing high head pressure can be complex and require expertise. It is advisable to seek the assistance of a qualified HVAC technician who can accurately diagnose the issue and implement the necessary repairs or adjustments. Regular maintenance and professional servicing of the HVAC system can also help prevent high head pressure and ensure its optimal performance.
Preventing High Head Pressure in HVAC Systems
Preventing high head pressure in an HVAC system is essential to maintain its efficiency, prolong the lifespan of components, and avoid costly repairs. Here are some preventive measures you can take to minimize the risk of high head pressure:
- Regular Maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance for your HVAC system to ensure it operates optimally. This includes cleaning the condenser coils, replacing air filters, lubricating fan motors, and checking refrigerant levels. Regular maintenance helps identify and address potential issues before they lead to high head pressure.
- Clean Condenser Coils: Keep the condenser coils clean and free from dirt, debris, and obstructions. Regularly inspect and clean the coils to maintain proper airflow and heat dissipation.
- Maintain Proper Airflow: Ensure good airflow across the condenser coils by keeping vents and registers unobstructed. Regularly check and change air filters to prevent clogging and reduce strain on the system.
- Monitor Refrigerant Charge: Regularly monitor and maintain the proper refrigerant charge in your HVAC system. Avoid overcharging or undercharging, as both can lead to high head pressure. Consult a qualified technician for accurate refrigerant handling.
- Inspect Fan Motors: Regularly inspect and maintain the condenser fan motor. Ensure that the motor is functioning properly, with clean blades, and no obstructions. Lubricate the motor as per manufacturer guidelines to keep it running smoothly.
- Control External Heat Sources: Minimize the impact of external heat sources on your HVAC system. Provide sufficient spacing around the unit and use shading devices to reduce exposure to direct sunlight. Avoid placing heat-generating equipment near the HVAC system.
- Optimize System Design: Ensure that the HVAC system is properly sized and designed for the space it serves. An oversized or undersized system can lead to inefficiencies and potentially high head pressure. Consult with a professional HVAC designer to ensure an optimal system design.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines for installation, servicing, and maintenance of your HVAC system. This includes using recommended refrigerant types, following proper charging procedures, and adhering to maintenance schedules.
By implementing these preventive measures, you can minimize the risk of high head pressure in your HVAC system. Regular maintenance, proper airflow, and adherence to manufacturer guidelines are key to keeping your HVAC system running efficiently and reducing the likelihood of costly repairs associated with high head pressure.
Conclusion
Understanding head pressure in HVAC systems is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and efficiency. High head pressure can lead to reduced cooling capacity, increased energy consumption, and potential damage to system components. By familiarizing yourself with the causes, symptoms, effects, troubleshooting steps, and preventive measures for high head pressure, you can better identify and address the issue in a timely manner.
Regular maintenance, such as cleaning condenser coils, checking airflow, monitoring refrigerant charge, and inspecting fan motors, is essential in preventing high head pressure. Additionally, controlling external heat sources, optimizing system design, and following manufacturer guidelines for installation and maintenance can help maintain proper head pressure levels and ensure the longevity of your HVAC system.
If you suspect high head pressure in your HVAC system and are unable to resolve the issue yourself, it is recommended to consult with a qualified HVAC technician. They have the knowledge, experience, and tools to accurately diagnose the problem and implement the necessary repairs or adjustments.
By taking proactive measures to prevent high head pressure and promptly addressing any issues that arise, you can ensure that your HVAC system operates efficiently, providing optimal comfort and energy efficiency for your space.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Does High Head Pressure Mean In HVAC
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Does High Head Pressure Mean In HVAC”