Home>diy>Architecture & Design>What Does CAD Mean?

Architecture & Design
What Does CAD Mean?
Modified: January 24, 2024
Discover the meaning of CAD in the context of architecture design. Learn how Computer-Aided Design revolutionizes the way professionals create and visualize structures.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of CAD! Have you ever wondered what CAD means or how it revolutionized the design and architecture industry? CAD, short for Computer-Aided Design, has become an integral part of modern architecture and design work. It has transformed the way architects, engineers, and designers conceptualize, develop, and communicate their ideas.
In this article, we will dive into the world of CAD, exploring its definition, history, applications, advantages, and disadvantages. So, whether you’re a design enthusiast or a professional in the field, join us on this journey to discover what CAD really means.
Key Takeaways:
- CAD, or Computer-Aided Design, has revolutionized the design industry by enabling precise visualization, enhanced collaboration, and efficient workflows, empowering professionals to bring innovative solutions to life.
- While CAD offers numerous advantages such as increased efficiency and accurate visualization, designers need to be mindful of potential drawbacks including cost, complexity, and limitations in conceptualization.
Read more: What Does CAD Mean In TinkerCAD
Definition of CAD
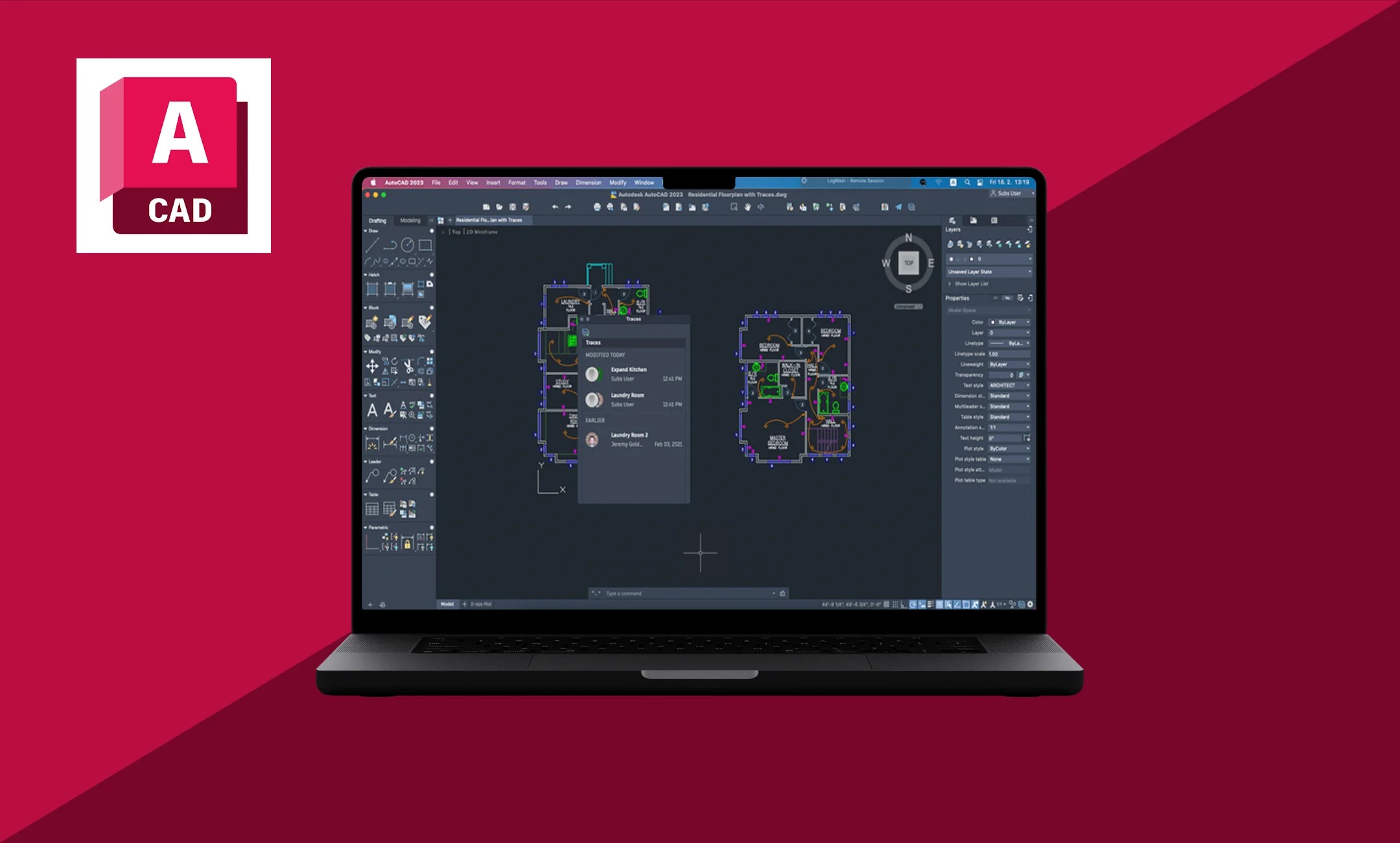
CAD, or Computer-Aided Design, refers to the use of computer software to create, modify, analyze, and optimize designs. It allows designers to create precise, detailed, and complex 2D and 3D models of objects, structures, and spaces.
CAD software provides a digital platform where architects, engineers, and designers can visualize their ideas, make modifications, and simulate real-world scenarios before the actual construction or manufacturing process begins. It offers a range of tools and features that facilitate the design process, including drawing tools, modeling capabilities, rendering options, and virtual reality integration.
With CAD, designers can create accurate representations of their concepts and ideas, enabling them to communicate effectively with clients, stakeholders, and construction teams. It provides a common visual language that bridges the gap between creativity and technical feasibility.
CAD systems utilize a combination of geometric modeling and drafting techniques to generate precise and detailed drawings. These drawings include dimensions, annotations, and other essential information required for construction, fabrication, or production.
Over the years, CAD software has evolved to encompass various industries, including architecture, engineering, industrial design, automotive design, and aerospace. It has become an indispensable tool for professionals in these fields, enabling them to streamline their workflows, reduce errors, and enhance overall efficiency.
Now that we understand the definition of CAD let’s take a closer look at its fascinating history.
History of CAD
The history of CAD dates back to the 1960s, when computers started to become more accessible and powerful. Early pioneers recognized the potential of using computers for design and began developing software to assist with the drafting process.
One of the earliest CAD systems was Sketchpad, developed by Ivan Sutherland in 1963. It allowed designers to interact with the computer using a light pen and create digital sketches. This groundbreaking technology laid the foundation for future CAD advancements.
In the 1970s, CAD software began to gain traction and become more widely adopted. The development of graphics displays and the introduction of computer-aided drafting systems facilitated more accurate and efficient design processes.
Throughout the 1980s and 1990s, CAD software continued to evolve rapidly. The introduction of 3D modeling capabilities revolutionized the industry, allowing designers to create more realistic and intricate models. The ability to rotate, zoom, and manipulate 3D objects on a screen revolutionized the design process, enabling designers to visualize concepts from different angles and perspectives.
In the early 2000s, the advent of Building Information Modeling (BIM) took CAD to a whole new level. BIM integrated CAD with additional information, such as cost estimation, scheduling, and facility management. This allowed for more comprehensive and collaborative design processes, leading to improved project outcomes.
Today, CAD software continues to advance at a rapid pace. With the introduction of cloud computing and virtual reality, designers can now access their CAD projects from anywhere in the world and experience immersive simulations of their designs.
The history of CAD showcases the remarkable journey from basic drafting tools to sophisticated software that has transformed the design and architecture industry. As we move forward, let’s explore the myriad applications of CAD in diverse fields.
CAD Applications
CAD has revolutionized numerous industries, enabling professionals to create precise designs, streamline workflows, and visualize projects before they become a reality. Here are some of the key applications of CAD:
- Architecture: CAD is extensively used in the architectural field for creating detailed building designs, floor plans, and construction documentation. It allows architects to visualize designs in 2D and 3D, make changes efficiently, and communicate their ideas effectively with clients and construction teams.
- Engineering: CAD plays a crucial role in engineering disciplines such as civil, mechanical, electrical, and structural engineering. It facilitates the creation of engineering designs, prototypes, and detailed engineering drawings. CAD software enables engineers to analyze stress, strain, and other physical properties, improving the efficiency and safety of structures and systems.
- Product Design and Manufacturing: CAD is utilized extensively in product design and manufacturing industries. Industrial designers and engineers use CAD software to develop prototypes, refine designs, simulate product behavior, and create manufacturing specifications. The ability to create digital models assists in reducing errors and speeding up the production process.
- Automotive and Aerospace: CAD is widely employed in the automotive and aerospace industries for designing vehicles, aircraft, and spacecraft. It allows designers to optimize aerodynamics, perform stress analysis, and simulate crash tests. CAD software aids in improving fuel efficiency, reducing weight, and enhancing safety features.
- Interior Design: CAD software is commonly used in the interior design industry to create detailed layouts, furniture placement, and visualizations. Designers can experiment with different materials, colors, and textures, providing clients with realistic representations of their envisioned spaces.
- Virtual Reality and Gaming: CAD is instrumental in the creation of virtual reality experiences and video game design. It enables the development of realistic 3D environments, character modeling, and animation.
- Urban Planning: CAD software plays a vital role in urban planning and development. It helps city planners to create detailed plans, analyze traffic flow, and simulate the impact of proposed developments on the existing environment.
These are just a few examples of the wide-ranging applications of CAD. Its versatility and power make it an invaluable tool in countless design-related fields.
CAD stands for Computer-Aided Design. It is the use of computer software to create, modify, analyze, and optimize designs for various industries such as architecture, engineering, and manufacturing.
Advantages of CAD
CAD has revolutionized the design and architecture industry, providing numerous advantages over traditional manual drafting methods. Here are some of the key advantages of CAD:
- Increased Efficiency: CAD software allows for faster and more efficient design creation compared to manual drafting. Designers can easily make changes, copy and reuse elements, and automate repetitive tasks, saving both time and effort.
- Accurate and Precise: CAD ensures a high level of accuracy and precision in design creation. Measurements, dimensions, and annotations can be easily added and modified, reducing errors and ensuring consistency throughout the design process.
- Visualization and Realism: CAD enables designers to visualize their designs in 2D and 3D, providing a more realistic representation. This allows for better understanding and communication of the design intent with clients, stakeholders, and construction teams.
- Enhanced Collaboration: CAD software facilitates collaboration among team members, whether they are in the same office or located across the globe. Design files can be easily shared, and multiple designers can work on the same project simultaneously, improving productivity and coordination.
- Simulations and Analysis: CAD software allows for simulations and analysis of designs before they are constructed or manufactured. The ability to perform stress analysis, fluid dynamics simulations, and virtual testing helps in identifying potential issues, improving performance, and reducing costly errors.
- Documentation and Data Management: CAD systems provide efficient documentation and data management capabilities. Design revisions, construction documentation, and other project-related information can be easily stored, accessed, and managed, ensuring better project organization and traceability.
- Cost and Time Savings: CAD helps in reducing costs and time associated with the design and construction process. By accurately visualizing and analyzing designs early on, potential issues can be identified and resolved, resulting in fewer construction delays and change orders.
- Sustainability: CAD software can aid in implementing sustainable design practices. It allows for energy analysis, material optimization, and the evaluation of alternative design options, contributing to environmentally conscious decision-making.
These advantages highlight the significant impact that CAD has on the design industry, enhancing productivity, accuracy, collaboration, and sustainability.
Read more: What Does CAD Mean In Technology
Disadvantages of CAD
While CAD offers numerous advantages, it also comes with a few disadvantages that designers and professionals need to be aware of. Here are some of the key disadvantages of CAD:
- Cost: CAD software can be expensive, especially for specialized industry-specific applications. Additionally, the cost of hardware upgrades and training for CAD software can add to the overall expenses.
- Complexity: CAD software can have a steep learning curve, requiring significant time and effort to master. Designers need to invest time in training and ongoing learning to fully utilize the software’s capabilities.
- Dependency on Technology: CAD systems rely heavily on technology, and any disruption or technical issues can cause delays in the design process. Power outages, software crashes, or hardware failures can lead to loss of work and productivity.
- Lack of Tangibility: Unlike manual drafting, CAD lacks the tangibility of hand-drawn sketches and designs. Some designers may feel disconnected from the physical aspect of design, missing the tactile experience of pen and paper.
- Over-reliance on Software: CAD software can sometimes lead designers to rely too heavily on the software’s capabilities rather than utilizing their design skills and creativity. This can result in designs that lack originality and innovation.
- Compatibility Issues: CAD files created in one software may not be fully compatible with other software, leading to potential issues when sharing or collaborating on projects with different CAD systems.
- Security Risks: CAD files often contain sensitive and proprietary designs that need to be protected. However, there is a risk of unauthorized access, intellectual property theft, and the potential for design leaks.
- Limitations in Conceptualization: While CAD excels in detailed design and technical drawings, it may have limitations when it comes to free-flowing and conceptual sketching. Some designers may find it challenging to capture initial ideas and concepts using CAD software.
Despite these disadvantages, CAD’s benefits and advancements in technology continue to outweigh the downsides, making it an indispensable tool in the design and architecture industry.
Conclusion
CAD, or Computer-Aided Design, has transformed the design and architecture industry, revolutionizing the way professionals create, modify, and communicate their ideas. With its powerful software, CAD allows for precise and detailed design creation, facilitating efficient workflows and enhancing collaboration among team members.
Throughout this article, we explored the definition of CAD and its fascinating history. We delved into the wide-ranging applications of CAD in industries such as architecture, engineering, product design, and more. We also discussed the advantages of CAD, including increased efficiency, accurate visualization, enhanced collaboration, and simulations for analysis.
However, it is important to note that CAD does come with a few drawbacks, including the cost of software and hardware, complexity, potential dependency on technology, and limitations in conceptualization. It’s crucial for designers and professionals to be aware of these disadvantages and address them accordingly.
In conclusion, CAD has revolutionized the design industry and continues to empower architects, engineers, and designers to create innovative and sustainable solutions. By leveraging CAD’s capabilities, professionals can streamline their workflows, reduce errors, enhance collaboration, and bring their design visions to life.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect CAD to evolve further, incorporating new features and capabilities to meet the ever-changing needs of the design and architecture community. So, embrace the power of CAD and explore the endless possibilities it offers in shaping the future of design.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Does CAD Mean?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Does CAD Mean?”