

Articles
What Is a DC Fan
Modified: January 18, 2024
Discover everything you need to know about DC fans in our informative articles. Gain insights, tips, and guidance on choosing the right fan for your needs.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
A DC fan, also known as a direct current fan, is an essential component of various electronic devices and cooling systems. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the optimal temperature and preventing overheating by providing efficient airflow. With advancements in technology, DC fans have become increasingly popular due to their energy efficiency, compact design, and ability to operate at various speeds.
In this article, we will delve into the world of DC fans, explore their functions, components, types, advantages, and applications. So, let’s dive in and discover what makes DC fans an indispensable part of modern electronic devices!
Key Takeaways:
- DC fans are essential for maintaining optimal temperatures in electronic devices, preventing overheating and ensuring longevity and reliability. Their energy efficiency, compact design, and advanced features make them indispensable in various industries.
- With precise airflow control, quiet operation, and diverse applications, DC fans offer superior cooling solutions. Their ability to dissipate heat effectively and prevent damage makes them a crucial component in modern electronic devices.
Read also: 12 Amazing Dc Fan for 2024
Definition of DC Fan
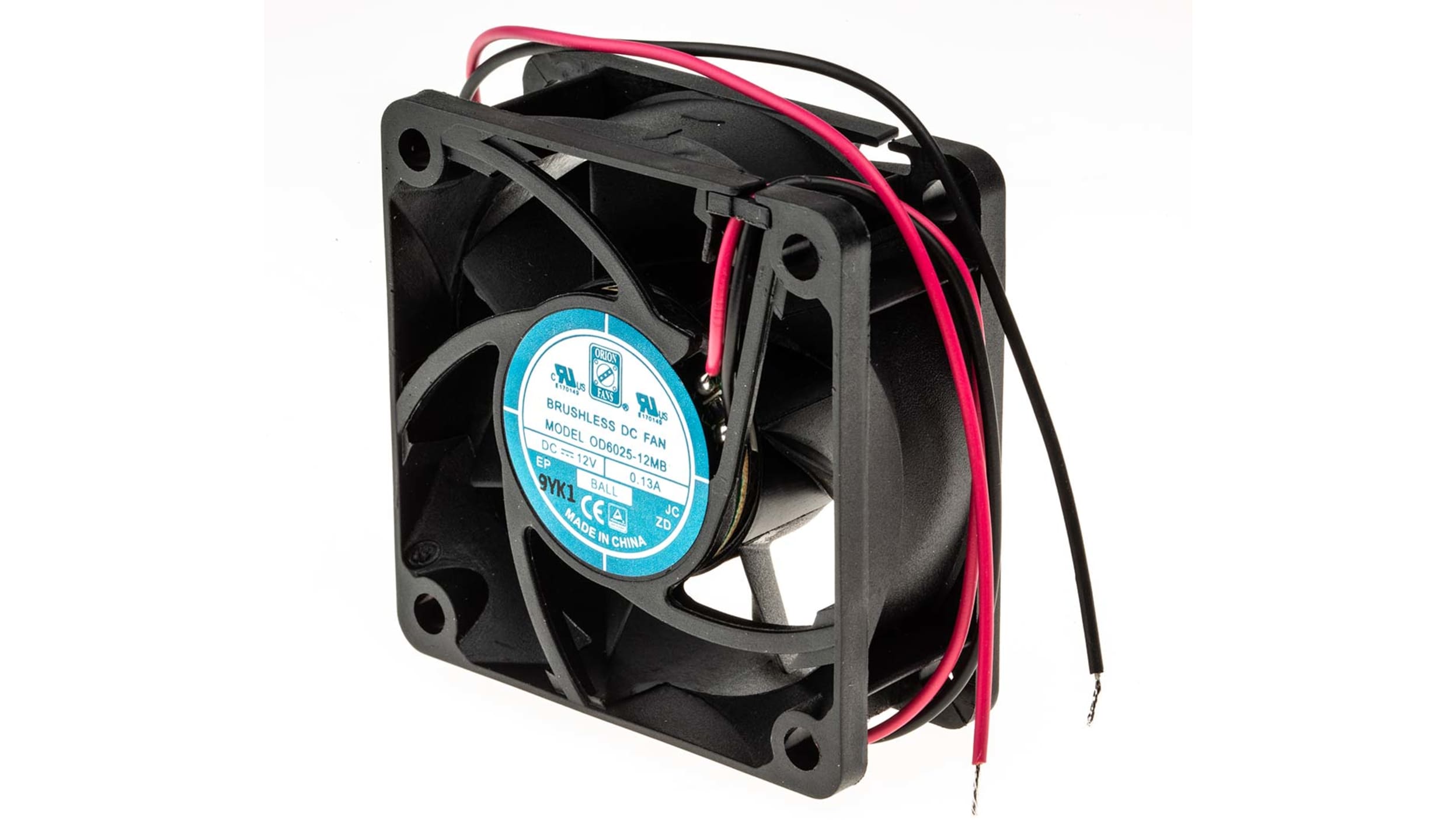
A DC fan is an electronically powered cooling device that utilizes direct current (DC) to generate airflow and regulate the temperature of electronic components, machinery, and systems. It is specifically designed to dissipate heat by promoting the circulation of air, thereby preventing the accumulation of hot air and maintaining optimal operating conditions.
The primary function of a DC fan is to cool electronic equipment and prevent thermal damage caused by excessive heat, which can lead to reduced performance, system failures, and even permanent damage in some cases. By implementing a DC fan, heat is efficiently expelled from various components, such as computer processors, power supplies, amplifiers, and other electronic devices, ensuring their proper functionality and prolonging their lifespan.
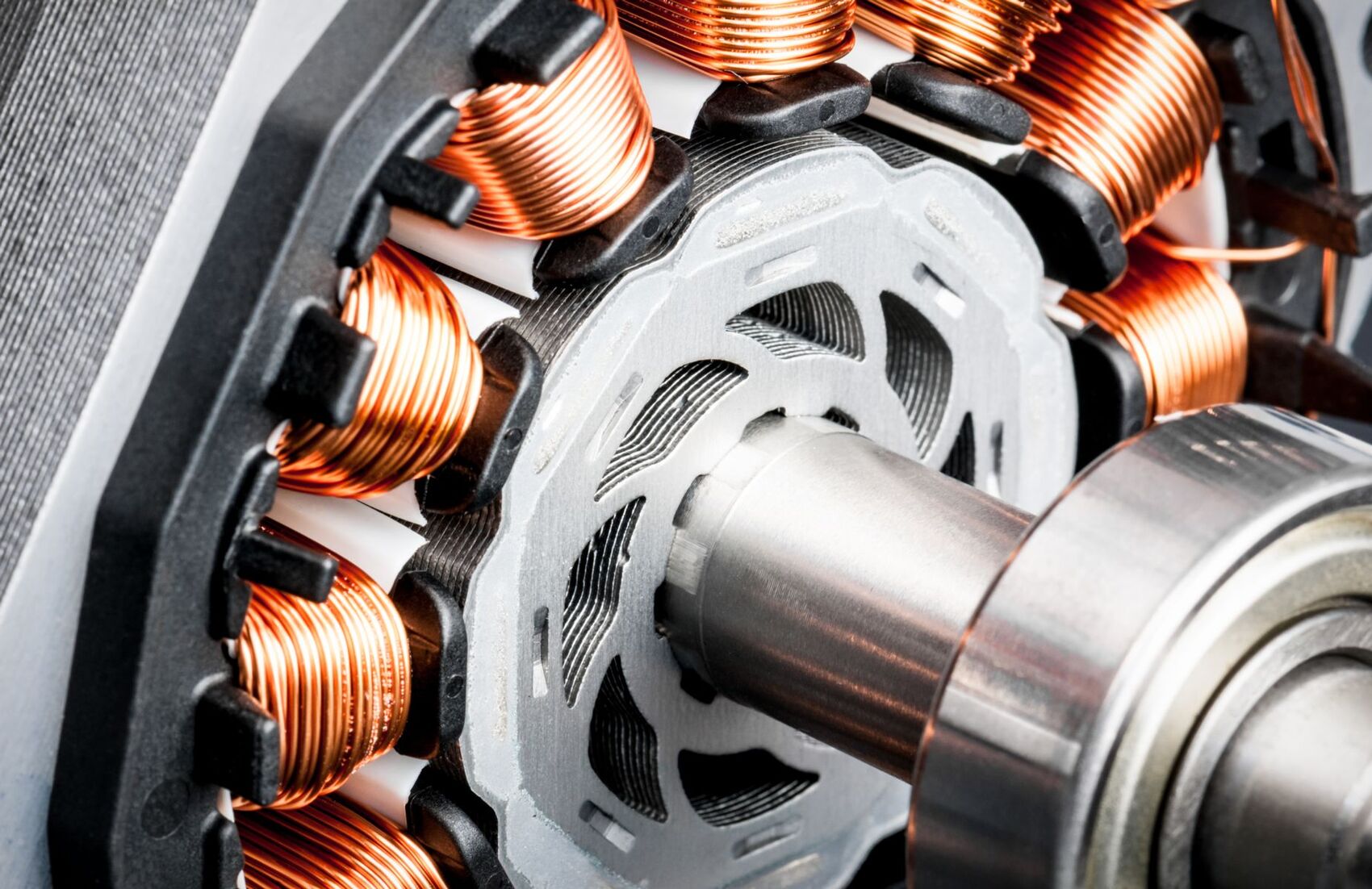
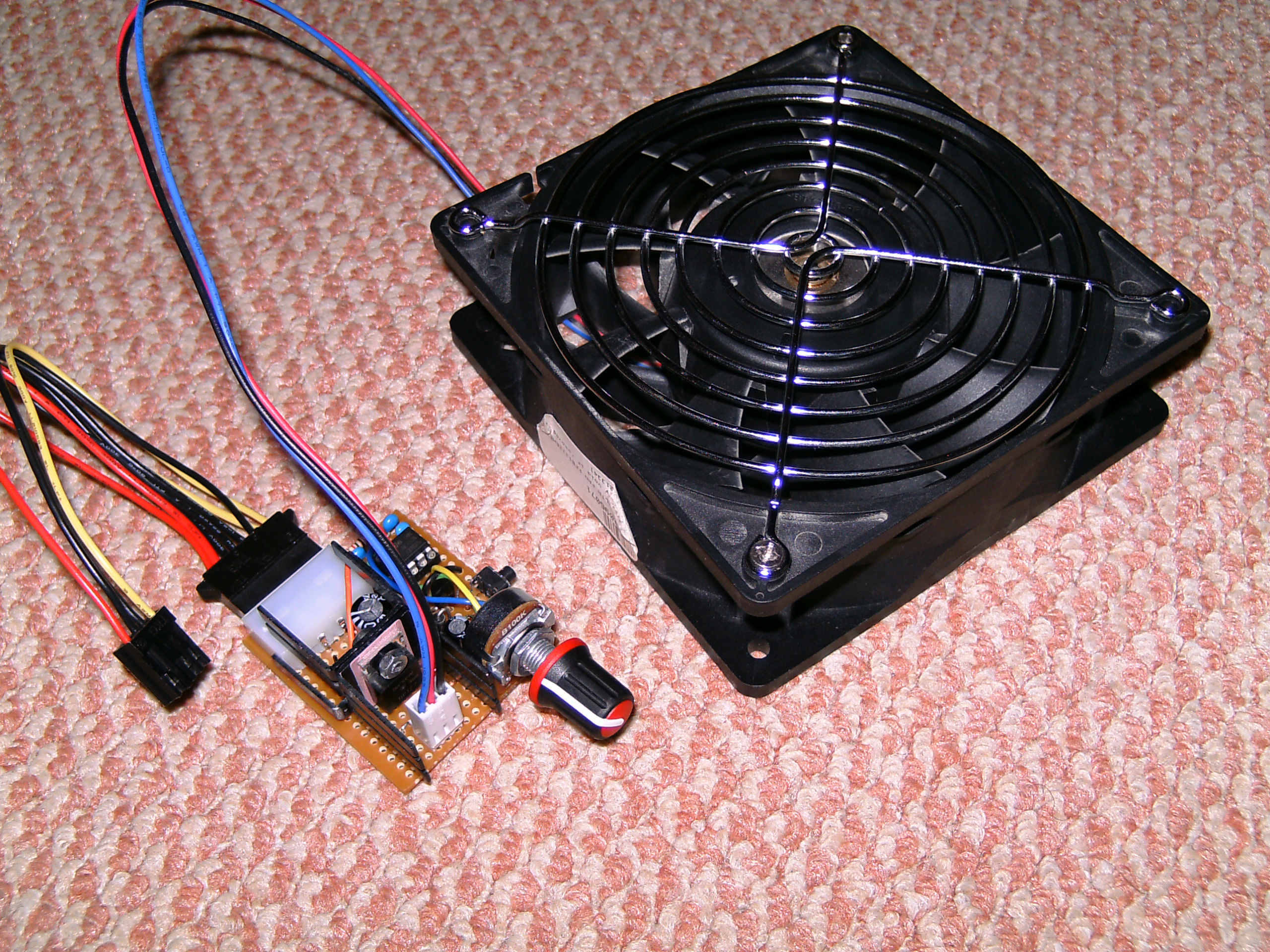
DC fans consist of a motor, impeller blades, and a housing. The motor is powered by a direct current power source, typically using a DC power supply or a battery. The impeller blades are responsible for producing a flow of air, which is generated as the motor rotates. The housing encloses the motor and impeller and provides stability and protection to the fan.
With advancements in technology, DC fans have evolved to incorporate advanced features such as speed control, temperature sensors, and PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) circuitry. These features allow for precise airflow adjustment, automated temperature regulation, and quieter operation.
In summary, a DC fan is a vital component that ensures the safe and efficient operation of electronic devices by effectively dissipating heat and maintaining equilibrium in the system’s temperature. Its versatility, reliability, and energy efficiency make it an indispensable cooling solution in various industries, including electronics, automotive, telecommunications, and more.
Function of DC Fan
The primary function of a DC fan is to regulate and maintain the temperature of electronic devices and systems by efficiently circulating air and dissipating heat. It achieves this through the following key processes:
- Airflow Generation: The impeller blades of the DC fan generate a flow of air when the motor rotates. As the blades spin, they create a pressure difference, sucking air from one side and pushing it out on the other side. This airflow helps to remove stagnant, hot air from the vicinity of electronic components and replace it with cooler air.
- Heat Dissipation: When electronic devices are in operation, they generate heat. If this heat is not effectively dissipated, it can lead to overheating and potential damage. The DC fan works by directing the airflow towards the heat-generating components, such as CPUs, GPUs, or power transistors, and carries away the heat, keeping the temperature within safe limits.
- Cooling Efficiency: DC fans are designed to provide efficient cooling by utilizing different factors such as fan size, blade design, and speed control. The size of the fan determines the amount of air it can move, while the blade design affects the direction and intensity of the airflow. Speed control mechanisms, such as pulse width modulation (PWM), allow for precise control over the fan speed, enabling a balance between cooling performance and noise level.
- Temperature Monitoring: Many DC fans are equipped with built-in temperature sensors. These sensors monitor the temperature of the system or the surrounding environment and adjust the fan speed accordingly. When the temperature increases, the fan speed increases as well, ensuring that an adequate amount of airflow is provided to maintain the temperature within the desired range.
Overall, the function of a DC fan is to prevent overheating and maintain a stable temperature in electronic devices and systems. By effectively circulating air and dissipating heat, DC fans play a crucial role in ensuring the longevity, reliability, and optimal performance of various electronic equipment, ranging from computer processors and graphics cards to industrial machinery and automotive components.
Components of DC Fan
A DC fan consists of several key components that work together to generate airflow and provide efficient cooling. These components include:
- Motor: The motor is the driving force of the DC fan. It converts electrical energy from the power source into mechanical energy to rotate the fan blades. DC fans usually utilize brushless DC motors (BLDC) as they offer higher efficiency, quieter operation, and longer lifespan compared to traditional brushed motors.
- Impeller Blades: The impeller blades are attached to the motor shaft and are responsible for generating the airflow. The number, size, and shape of the blades affect the amount of air moved by the fan. Different blade configurations, such as axial or centrifugal, are used based on the specific cooling requirements of the device or system.
- Housing: The housing of the DC fan encloses and protects the motor and impeller assembly. It is typically made of plastic or metal and is designed to maximize airflow efficiency while providing structural stability. The housing also includes openings or vents that allow the intake and exhaust of air.
- Bearings: The bearings provide smooth and frictionless rotation of the fan blades. Two common types of bearings used in DC fans are sleeve bearings and ball bearings. Sleeve bearings are cost-effective and suitable for low to medium-speed applications, while ball bearings offer higher durability and are ideal for high-speed and continuous operation.
- Connector/Cable: DC fans are equipped with a connector or cable that allows for easy connection to a power source. The most common connector types used in DC fans include 2-pin or 3-pin connectors. Some fans may also feature additional wires for PWM (pulse width modulation) control or temperature sensors.
- Control Circuitry: Advanced DC fans incorporate control circuitry to enhance their performance and functionality. This may include speed control mechanisms, temperature sensors, and PWM circuitry. Speed control allows for adjusting the fan speed according to the cooling requirements, while temperature sensors monitor the system temperature and adjust the fan speed accordingly for optimal cooling.
These components work together harmoniously to provide efficient airflow, dissipate heat, and maintain the desired temperature within electronic devices and systems. Each component’s design and characteristics contribute to the overall performance, reliability, and longevity of the DC fan.
When choosing a DC fan, consider the airflow requirements, noise level, and power consumption to ensure it meets your needs. Look for a reputable manufacturer for quality and reliability.
Types of DC Fans
DC fans come in various types, each designed to meet specific cooling requirements and fit diverse applications. The common types of DC fans include:
- Axial Fans: Axial fans are the most common type of DC fans. They are characterized by the flow of air parallel to the fan’s axis. These fans create airflow by pulling air through the fan blades and expelling it in the same direction. Axial fans are compact, lightweight, and provide high airflow. They are commonly found in desktop computers, electronic enclosures, and small appliances where space is limited.
- Radial Fans: Also known as centrifugal fans, radial fans generate airflow by drawing air into the inlet and forcing it out at a perpendicular angle to the fan’s rotational axis. This radial direction of airflow allows for higher pressure and is ideal for applications that require greater air pressure, such as cooling high-density electronic components or ventilation systems.
- Blower Fans: Blower fans are a type of centrifugal fan characterized by their compact design and high-pressure capabilities. They have a small diameter and are commonly used in tight spaces or in applications that require focused airflow, such as cooling CPU heatsinks, graphics cards, and automotive cooling systems.
- DC Motor Fans: DC motor fans are specifically designed for applications where both cooling and motor operation are required simultaneously. The fan is integrated with the DC motor, allowing for efficient cooling of the motor components during its operation. These fans are commonly used in robotics, electric vehicles, and industrial machinery.
- Multi-speed Fans: Multi-speed fans offer the flexibility to adjust the fan speed according to the cooling needs. They have multiple speed settings, allowing users to choose between high-speed cooling for intensive tasks or low-speed operation for quieter and energy-efficient cooling. These fans are commonly used in computers, laptops, and household appliances.
- Smart Fans: Smart fans are equipped with advanced control features, such as temperature sensors and PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) control. These fans can dynamically adjust the fan speed based on temperature changes, ensuring optimal cooling efficiency and noise reduction. They are commonly used in high-performance gaming PCs, servers, and other demanding applications.
The choice of the DC fan type depends on the specific cooling requirements, available space, airflow capacity, pressure requirements, and noise considerations of the application. By selecting the appropriate type of DC fan, optimal cooling performance can be achieved for various electronic devices and systems.
Read more: What Is An Ac Dc Adapter
Advantages of DC Fans
DC fans offer several advantages over traditional cooling solutions, making them a popular choice in various industries. The key advantages of DC fans include:
- Energy Efficiency: DC fans are highly energy-efficient compared to their AC counterparts. They consume less power, resulting in lower electricity costs and reduced energy waste. This makes them environmentally friendly and ideal for applications where energy efficiency is a priority.
- Variable Speed Control: DC fans allow for precise control over the fan speed. With features like pulse width modulation (PWM) control, users can adjust the speed of the fan to meet specific cooling requirements. This flexibility in speed control enables efficient cooling without compromising on noise levels.
- Quiet Operation: The advanced design and motor technology of DC fans contribute to their quiet operation. They produce minimal noise or vibration, making them suitable for noise-sensitive environments such as offices, bedrooms, and recording studios.
- Compact Size: DC fans are compact and lightweight, occupying minimal space within electronic devices or cooling systems. This makes them suitable for applications where space is limited or where the size and weight of the cooling solution need to be minimized.
- Long Lifespan: DC fans are designed to be durable and long-lasting. The use of brushless DC motors eliminates the need for brushes, reducing wear and tear over time. This results in an extended lifespan compared to fans with traditional brushed motors.
- Better Cooling Performance: DC fans are designed to provide efficient cooling performance. Their optimized blade design and airflow generation mechanisms ensure effective heat dissipation, preventing overheating and maintaining optimal operating temperatures in electronic devices and systems.
- Advanced Features: Many DC fans come with advanced features such as temperature sensors, built-in controllers, and smart fan technology. These features allow for automated temperature regulation, self-adjustment of fan speed based on temperature variations, and enhanced cooling efficiency.
These advantages make DC fans the preferred choice in various applications, including computers, servers, telecommunications equipment, automotive cooling systems, and industrial machinery. With their energy efficiency, compact size, and excellent cooling capabilities, DC fans are an essential component in maintaining the performance, reliability, and longevity of electronic devices and systems.
Applications of DC Fans
DC fans find a wide range of applications across various industries, thanks to their efficient cooling capabilities and versatility. Some of the common applications of DC fans include:
- Computers and Laptops: DC fans are extensively used in computer systems and laptops to cool down the central processing unit (CPU), graphics processing unit (GPU), and other internal components. They help maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevent performance issues caused by overheating.
- Telecommunications Equipment: DC fans are essential in cooling telecommunications equipment such as routers, switches, and modems. They ensure reliable and uninterrupted operation by dissipating heat generated by these devices during high data transmission or extended usage periods.
- Server Rooms and Data Centers: Data centers and server rooms house crucial computing infrastructure that generates substantial heat. DC fans are employed to cool server racks, cabinets, and equipment to maintain a stable temperature and prevent hardware malfunctions or failures.
- Automotive Cooling Systems: In automobiles, DC fans are used in cooling systems to regulate the temperature of the engine, radiator, and other components. They help dissipate excess heat and prevent engine overheating, ensuring efficient and reliable vehicle operation.
- Home Appliances: DC fans are found in various home appliances like air conditioners, refrigerators, and ventilation systems. They assist in cooling the compressor, condenser, and other critical components, improving the overall efficiency and lifespan of these appliances.
- Industrial Machinery: DC fans are utilized in industrial machinery and equipment for cooling purposes. They help cool power electronics, motor drives, control panels, and other critical components, ensuring optimal performance and preventing damage from excessive heat.
- Medical Equipment: Medical equipment, such as MRI machines, X-ray systems, and ultrasound devices, generates substantial heat during operation. DC fans are employed to maintain ideal operating temperatures, ensuring accurate and reliable performance of these vital medical devices.
- Greenhouses and Indoor Gardens: DC fans are used in greenhouse and indoor garden setups to facilitate proper air circulation and temperature control. They help regulate humidity, prevent hotspots, and provide the necessary airflow for healthy plant growth.
These are just a few examples of the diverse applications of DC fans. Their ability to efficiently dissipate heat, compact size, and energy-efficiency make them an essential component in a wide range of electronic devices, cooling systems, and industrial processes.
Conclusion
DC fans play a vital role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures for electronic devices and cooling systems in various industries. With their energy efficiency, compact design, and efficient airflow generation, DC fans have become the preferred choice for cooling applications.
Throughout this article, we have explored the definition, function, components, types, advantages, and applications of DC fans. These cooling devices offer several benefits, including energy efficiency, variable speed control, quiet operation, compact size, and long lifespan. They are widely used in computers, telecommunications equipment, automotive cooling systems, home appliances, industrial machinery, and more.
The advancements in DC fan technology, such as PWM control, temperature sensors, and smart features, have further enhanced their cooling capabilities. These features allow for precise cooling adjustments, automated temperature regulation, and improved overall cooling efficiency.
As the demand for electronic devices and the need for efficient cooling continue to grow, DC fans will remain in high demand. Their reliable cooling performance and ability to prevent overheating are crucial for maintaining the longevity, reliability, and optimal functioning of electronic equipment.
In conclusion, DC fans have become an indispensable component in various industries, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of electronic devices. With their numerous advantages and wide-ranging applications, DC fans will continue to be an essential element in the world of cooling technology.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A DC Fan
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Is a DC Fan”