

Articles
What Is A Neutral Electrical Wire
Modified: January 4, 2024
Learn about the importance and function of neutral electrical wires in our informative articles. Gain insights on their role in electrical circuits and safety measures.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
The electrical system is a fundamental component of modern human life. It powers our homes, businesses, and industries, providing us with the energy needed to carry out countless tasks and activities. Within this complex network of circuits, wires, and connections, one component plays a crucial role in ensuring the safe and efficient distribution of electricity – the neutral electrical wire.
In this article, we will explore the concept of the neutral electrical wire, its functions, color coding, and its significance in both residential and commercial wiring systems. We will also touch upon common issues that may arise with the neutral wire and offer troubleshooting tips to address them. Whether you are a homeowner, a business owner, or simply someone interested in understanding the basics of electrical systems, this article will provide you with valuable insights into the world of neutral electrical wires.
Key Takeaways:
- The neutral electrical wire is a crucial component in electrical systems, providing a safe return path for current, balancing loads, and ensuring voltage regulation. Proper installation and color coding are essential for its effective functionality.
- Understanding common issues with the neutral wire, such as loose connections and open neutrals, is crucial for troubleshooting and maintaining electrical safety. Always consult qualified professionals for electrical work to ensure compliance and safety.
Read more: What Is 4 Wire Electrical Wire
Definition of Neutral Electrical Wire
The neutral electrical wire, often referred to simply as the “neutral wire,” is a crucial component of an electrical circuit. It is one of the three main wires used in electrical systems, alongside the hot wire and the ground wire. While the hot wire carries the electrical current from the power source to the outlets and appliances, and the ground wire provides a safe path for excess electricity to disperse, the neutral wire serves as a return path for the current back to the source.
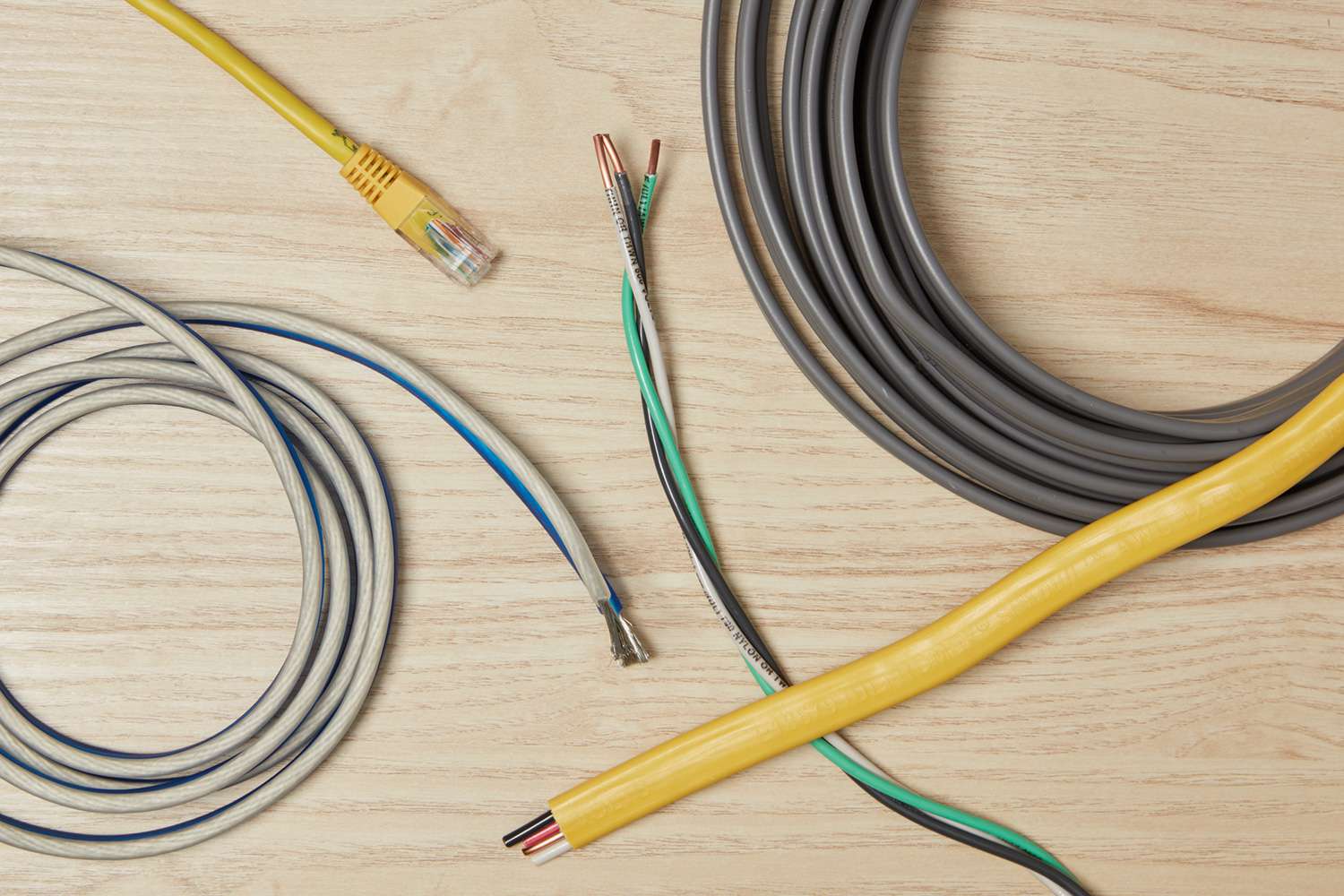
The neutral wire is typically color-coded in white or gray to differentiate it from the hot wire, which is usually black or red. It is connected to the grounding system at the main electrical panel, providing a complete pathway for the flow of electricity. The neutral wire has a voltage potential close to zero, ensuring that any imbalance in the electrical circuit is corrected and the current is distributed evenly across all components.
It is important to note that the presence of a neutral wire is not always required in electrical systems. Some appliances, such as certain types of light fixtures and small electronic devices, may operate on a two-wire system that does not include a neutral wire. However, in most residential and commercial wiring, the neutral wire is an essential component to ensure the safe and efficient functioning of the electrical system.
Functions of Neutral Electrical Wire
The neutral electrical wire performs several crucial functions in an electrical system. Let’s take a closer look at some of its main functions:
- Completes the Electrical Circuit: The neutral wire acts as a return path for the electrical current, completing the circuit between the power source and the connected devices or appliances. Without a neutral wire, the circuit would be incomplete, and electricity would not flow.
- Carries Current Under Normal Operating Conditions: In a properly functioning electrical circuit, the neutral wire carries the same amount of current as the hot wire. This balance ensures that the electrical load is evenly distributed and prevents the occurrence of electrical shocks or other hazards.
- Provides a Reference Point for Voltage: The neutral wire has a voltage potential close to zero. This allows it to serve as a reference point against which the voltage of the hot wire and other electrical components can be measured. It helps maintain a stable electrical system and prevents voltage fluctuations.
- Facilitates Proper Ground Fault Detection: In the event of a ground fault or an unintended electrical connection between a hot wire and a conductive surface, the neutral wire plays a crucial role. It helps detect the imbalance in the electrical current, allowing protective devices, such as circuit breakers or ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs), to detect and interrupt the circuit, preventing potential electrical hazards.
- Allows the Use of Single-Pole Breakers: The neutral wire enables the use of single-pole circuit breakers in residential and commercial wiring. Single-pole breakers are commonly used to protect individual branch circuits. They rely on the presence of a separate neutral wire for safe and efficient operation.
Overall, the neutral electrical wire plays a vital role in creating a reliable and safe electrical system. Without it, the electrical circuit would be incomplete, leading to potential hazards and inefficiencies. Its functions extend beyond simply providing a return path for the current, contributing to the proper functioning of the entire electrical infrastructure.
Neutral Electrical Wire in Residential Wiring
In residential wiring systems, the neutral electrical wire is an essential component that ensures the safe and efficient distribution of electricity throughout the home. Here are some important points to understand about the role of the neutral wire in residential wiring:
- Power Distribution: The neutral wire acts as a pathway for the return of electrical current back to the utility transformer or the main electrical panel. It completes the circuit and facilitates the distribution of energy from the power source to the various outlets, lights, and appliances in the home.
- Balancing the Load: The neutral wire plays a vital role in balancing the electrical load in a residential wiring system. In a properly functioning circuit, the current flow in the neutral wire should be equal to the current flow in the hot wires. By ensuring load balance, the neutral wire helps prevent voltage fluctuations and overloading of circuits, which can lead to electrical fires or equipment damage.
- Safety Grounding: While the ground wire is primarily responsible for safety grounding in residential wiring, the neutral wire also contributes to the safe operation of electrical systems. It helps provide a low-impedance path for any errant electrical current that may occur due to a fault or short circuit. This helps protect people and equipment from potential electrical shocks and reduces the risk of electrical damage.
- Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs): GFCIs are commonly used in residential wiring to provide an added layer of protection against electrical shocks. GFCIs monitor the imbalance in the electrical current between the hot and neutral wires. If a ground fault is detected, GFCIs quickly interrupt the circuit, preventing potential harm. The presence of the neutral wire is crucial for the proper functioning of GFCIs.
- Branch Circuit Wiring: In residential wiring, the neutral wire is connected to the neutral bus bar in the main electrical panel. From there, it branches out to various circuit breakers and is connected to the neutral terminals of outlets, switches, and appliances throughout the home. This allows the flow of current to be safely distributed and ensures that each branch circuit has a complete circuit path.
Overall, the neutral electrical wire is a critical component of residential wiring systems. Its presence and proper installation are essential for the safe and effective functioning of electrical circuits in homes, providing electricity for lighting, heating, cooling, and powering various appliances and devices we use everyday.
Neutral Electrical Wire in Commercial Wiring
In commercial wiring systems, the neutral electrical wire plays a crucial role in ensuring the safe and efficient distribution of electricity to various commercial buildings, offices, and facilities. Here are some key points to understand about the role of the neutral wire in commercial wiring:
- Powering Commercial Equipment: The neutral wire is responsible for providing a return path for the electrical current from commercial equipment to the utility transformer or the main electrical panel. This allows for the smooth operation of electrical devices, machinery, and appliances within commercial settings.
- Load Balancing: The neutral wire helps maintain load balance within commercial electrical systems. Balancing the electrical load across all phases helps prevent voltage fluctuations, reduces the risk of circuit overloading, and ensures the proper functioning of commercial equipment. It is especially important in commercial settings where a significant amount of power is consumed.
- Ground Fault Protection: The presence of the neutral wire is crucial for the functionality of ground fault protection devices in commercial wiring systems. Ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) play a critical role in quickly detecting and interrupting electrical circuits when a ground fault occurs. The neutral wire is an integral part of the GFCI’s operation, as it is used in monitoring the balance between the electrical current flowing through the hot and neutral wires. If an imbalance is detected, the GFCI shuts off the circuit to prevent electrical shocks or other hazards.
- Three-Phase Power Systems: Many commercial buildings and industrial facilities use three-phase power systems, which consist of three hot wires and one neutral wire. In these systems, the neutral wire helps balance the load and provides a reference point for voltage measurements. It ensures that the electrical power is evenly distributed across all three phases, preventing power quality issues and optimizing the performance of commercial machinery and equipment.
- Branch Circuit Wiring: In commercial wiring, the neutral wire is connected to the neutral bar in the main electrical panel. From there, it branches out to various circuit breakers and is connected to the neutral terminals of outlets, switches, and equipment throughout the commercial space. This allows for the proper distribution of current and ensures that each branch circuit has a complete circuit path.
The neutral wire is an essential component of commercial wiring systems, providing reliable and safe electrical power to run businesses and commercial operations smoothly. Proper installation, maintenance, and adherence to electrical codes and standards are crucial to ensuring the effective and safe use of the neutral wire in commercial settings.
A neutral electrical wire is typically colored white or gray and carries the return current from the electrical device back to the power source. It is essential for completing the electrical circuit and should always be handled with care to avoid electrical hazards.
Neutral Electrical Wire Color Coding
Color coding is an important aspect of electrical wiring, as it helps identify the different wires and their respective functions. In the case of the neutral electrical wire, it is typically color-coded to distinguish it from other wires in the electrical system. The standard color used for the neutral wire is white or gray. Here are some key points to understand about the color coding of the neutral wire:
- White or Gray: In most residential and commercial wiring systems, the neutral wire is colored white or gray. This color coding helps differentiate it from the hot wires, which are typically black or red. The use of a consistent color scheme throughout the electrical system ensures uniformity and allows for easy identification of the neutral wire.
- International Standards: The color coding for electrical wires may vary in different regions or countries. It’s important to consult local electrical codes and regulations to ensure compliance with the specific color coding requirements. For example, in some countries, the neutral wire may be colored blue instead of white or gray.
- Visual Identification: The color coding of the neutral wire provides a visual indicator to electricians and other professionals working on the electrical system. It helps prevent confusion and ensures that the neutral wire is correctly identified during installation, maintenance, or troubleshooting.
- Importance of Accuracy: Properly identifying the neutral wire is crucial to ensure the safe and efficient functioning of the electrical system. Connecting a wire incorrectly or misidentifying the neutral wire can lead to electrical hazards, including potential electrical shocks or fires. Therefore, it is essential to accurately follow the color coding standards and guidelines for identifying the neutral wire.
- Color Coding Exceptions: It is important to note that there may be situations where exceptions to the neutral wire color coding exist. For example, in older homes or buildings with outdated wiring systems, the neutral wire may not be color-coded consistently, or unconventional color coding may be used. In such cases, it is prudent to consult a qualified electrician to identify and correctly work with the neutral wire.
Understanding the color coding of the neutral wire is essential for anyone working with electrical systems. It helps ensure proper identification, installation, and maintenance of the neutral wire, contributing to the overall safety and functionality of the electrical system. Proper adherence to color coding standards is a best practice that every electrician and homeowner should follow for a reliable and well-organized electrical infrastructure.
Importance of Properly Installed Neutral Electrical Wire
The proper installation of the neutral electrical wire is of utmost importance in any electrical system. A correctly installed neutral wire ensures the safe and efficient functioning of the electrical circuits and appliances. Here are some key reasons why proper installation is crucial:
- Electrical Safety: The neutral wire plays a critical role in maintaining electrical safety. A properly installed neutral wire helps balance the electrical load in a circuit, preventing overloading and reducing the risk of electrical shocks, fires, or damage to equipment. It provides a safe return path for the electrical current and ensures that the voltage between the hot wire and the ground wire remains within safe limits.
- Voltage Regulation: The neutral wire is essential for regulating voltage in an electrical system. It helps maintain a stable electrical potential and ensures that the voltage is evenly distributed across the circuit. Without a properly installed neutral wire, voltage fluctuations and irregularities may occur, which can cause damage to sensitive electronic devices and lead to inconsistent performance of electrical equipment.
- Ground Fault Protection: The presence of a properly installed neutral wire is vital for the effectiveness of ground fault protection devices, such as circuit breakers and ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs). These devices rely on the neutral wire to detect any imbalances in the electrical current and quickly interrupt the circuit in case of a ground fault. Without a properly installed neutral wire, the ground fault protection may be compromised, increasing the risk of electrical hazards.
- Proper Circuit Functionality: The neutral wire completes the electrical circuit and is essential for the proper functioning of electrical devices. Without a properly installed neutral wire, circuits may become incomplete, leading to interruptions in power supply, malfunctioning of appliances, and potential damage to electrical wiring and components.
- Compliance with Electrical Codes: Properly installing the neutral wire is necessary to comply with electrical codes and regulations. Electrical codes exist to ensure the safety and reliability of electrical systems. Failure to install the neutral wire correctly can result in violations of these codes, potentially leading to legal issues and jeopardizing the safety of occupants in residential, commercial, or industrial settings.
When it comes to electrical installations, including the installation of the neutral wire, it is best to rely on the expertise of qualified electricians. They have the knowledge and experience to ensure that the neutral wire is properly installed, connected, and grounded according to electrical codes and industry best practices. This guarantees the safe and efficient operation of the electrical system and provides peace of mind for the occupants or users of the space.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting with Neutral Electrical Wire
While the neutral electrical wire is a crucial component of an electrical system, issues can arise that may affect its functionality. Here are some common issues that can occur with the neutral wire and troubleshooting tips to address them:
- Loose or Damaged Connections: Over time, connections between the neutral wire and other components may become loose or damaged. This can result in intermittent power or disruptions in the electrical circuit. Inspect the connections, tighten any loose screws or connections, and replace damaged or corroded wires or connectors as necessary.
- Open Neutral: An open neutral occurs when there is a break or interruption in the neutral wire. This can result in unbalanced voltage and potential hazards. Use a multimeter to test for continuity along the neutral wire and identify any breaks. Repair or replace the damaged section of the wire to restore proper continuity.
- Neutral Wire Overloaded: If the neutral wire is carrying excessive current due to an overload, it can result in overheating and potential damage to the wires and electrical components. Identify the cause of the overload, which may be due to multiple devices drawing excessive power, and redistribute the load across multiple circuits. Consider upgrading the circuit or consulting an electrician for a more comprehensive solution.
- Grounding Issues: The neutral wire is connected to the grounding system to ensure the safe dissipation of excess electrical current. If there are grounding issues, such as a faulty ground wire or improper grounding connections, it can affect the performance of the neutral wire. Inspect the grounding system, repair or replace any faulty grounding components, and ensure proper grounding connections are made.
- Neutral Wire Misidentified: In some cases, the neutral wire may be misidentified or incorrectly connected. This can lead to improper functioning of the electrical system and potential hazards. Make sure to follow the appropriate color coding standards for neutral wire identification. If needed, consult an electrician to verify and correct any misidentifications or incorrect connections.
It is important to remember that electrical work should be performed by qualified professionals. If you encounter any issues or are unsure about how to troubleshoot problems with the neutral wire, consult a licensed electrician. They have the expertise and knowledge to diagnose and address any electrical issues safely and effectively.
Conclusion
The neutral electrical wire is a vital component of any electrical system, playing a critical role in ensuring the safe and efficient distribution of electricity. It serves as a return pathway for the current and helps balance the electrical load, regulate voltage, and provide ground fault protection. The proper installation of the neutral wire is essential for maintaining electrical safety, preventing electrical hazards, and ensuring the reliable functioning of electrical circuits and equipment.
In residential wiring, the neutral wire enables the distribution of power throughout the home, while in commercial wiring, it powers various equipment and devices in commercial settings. The correct color coding of the neutral wire, typically white or gray, helps electricians identify and work with it effectively. However, it’s important to consult local electrical codes and regulations, as color coding standards may vary.
Understanding common issues that can occur with the neutral wire is crucial for troubleshooting and ensuring the proper functioning of the electrical system. Whether it’s loose connections, open neutrals, overloaded wires, grounding issues, or incorrect identification, addressing these issues promptly and accurately is essential for maintaining electrical safety.
It is important to note that electrical work should always be performed by qualified professionals to ensure compliance with electrical codes, regulations, and safety standards. Electricians have the expertise and knowledge to handle the installation, troubleshooting, and maintenance of the neutral wire and other electrical components.
In conclusion, the neutral electrical wire is a vital element in electrical systems, allowing for safe and efficient power distribution. By understanding its definition, functions, color coding, and importance of proper installation, we can appreciate its role in creating a reliable and secure electrical infrastructure. Regular inspections, maintenance, and adherence to electrical standards and guidelines will help ensure the optimal performance and safety of the neutral wire, promoting the overall functionality and longevity of electrical systems.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is A Neutral Electrical Wire
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.









0 thoughts on “What Is A Neutral Electrical Wire”