

Articles
What Is Electrical Wire Made Of
Modified: December 7, 2023
Learn about the composition of electrical wire in this informative article. Discover what materials are used in the manufacturing process, including copper and aluminum.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Electrical wire is an essential component of any electrical system, carrying electric current from one point to another. It is commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings to power various electrical devices and appliances.
But have you ever wondered what electrical wire is made of? The composition of electrical wire plays a crucial role in its performance and durability. In this article, we will delve into the different materials used to manufacture electrical wire and their unique properties.
Understanding the materials used in electrical wire is especially important for electricians, contractors, and homeowners who may need to choose the right type of wire for a specific application. Whether you are installing new electrical wiring or replacing old wiring, knowing the different options available can help you make an informed decision.
So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of electrical wire composition and explore the various materials used in its production.
Key Takeaways:
- Copper wire is widely used due to its excellent conductivity, flexibility, and corrosion resistance, but its higher cost and theft susceptibility should be considered when choosing the right wire for a specific project.
- Insulation materials, such as PVC, thermoplastic, XLPE, and specialized options like silicone rubber and Teflon, play a crucial role in protecting electrical wires and preventing electrical hazards. Understanding their unique properties is essential for ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical installations.
Read more: What Is Electrical Wire Insulation Made Of
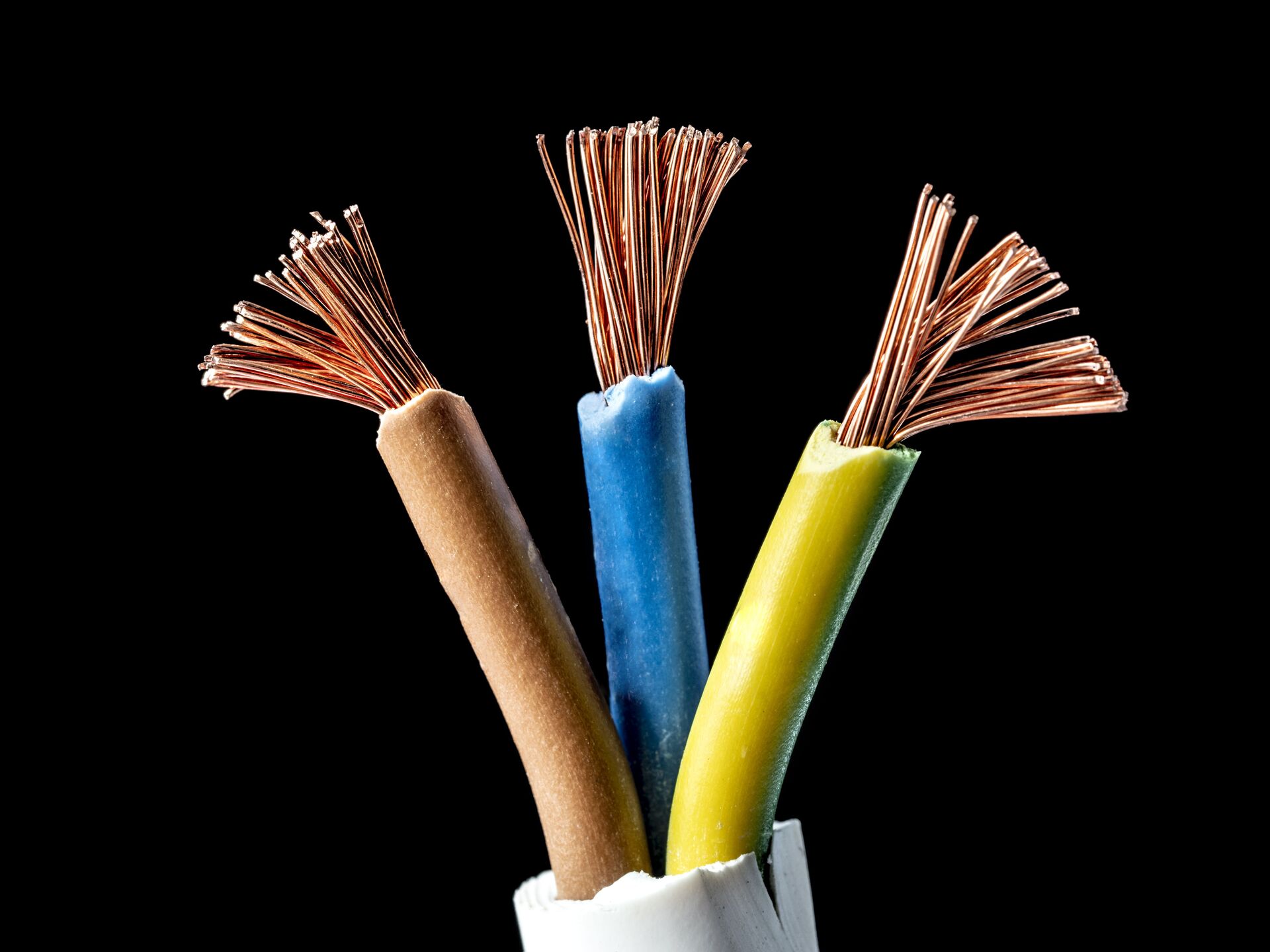
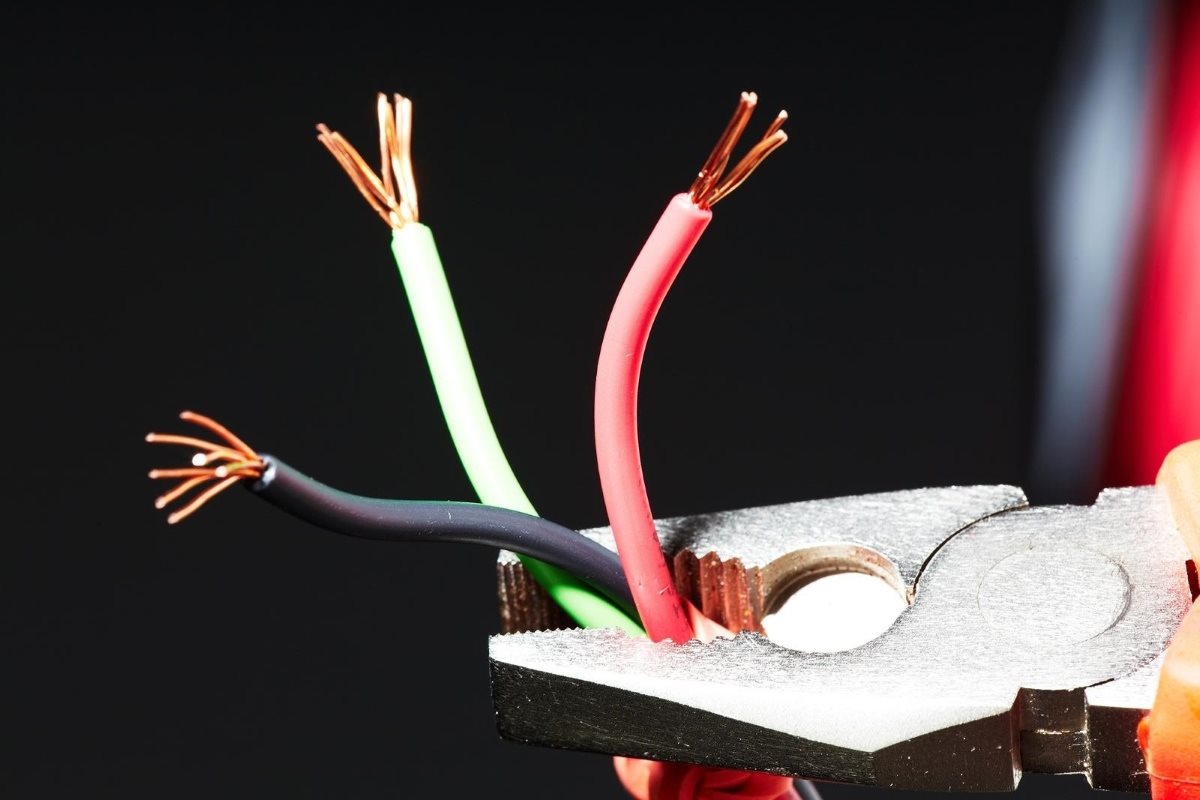
Copper Wire
One of the most common materials used in electrical wire is copper. Copper wire has been widely used in the electrical industry for its excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance.
Copper has a high electrical conductivity, meaning it allows electric current to flow easily. This makes it an ideal choice for transmitting electricity efficiently. In addition, copper has a low electrical resistance, which helps to minimize the electrical losses during transmission.
Copper wire is also known for its flexibility, allowing it to be easily bent and molded into different shapes during installation. This flexibility makes it easier to route the wire through walls, conduit, and other tight spaces.
Besides its electrical properties, copper is resistant to corrosion, making it a durable choice for electrical wiring. Copper wires are less likely to rust or corrode over time, ensuring a reliable and long-lasting electrical connection.
In terms of safety, copper is also a favorable material. It has a high melting point, which makes it less prone to electrical fires or overheating under normal operating conditions.
Furthermore, copper wire is environmentally friendly and recyclable. It can be easily recycled and reused, reducing the need for mining additional raw materials.
Despite its advantages, copper wire does have some drawbacks. One major drawback is its cost. Copper is a relatively expensive material, which can make copper wire more expensive compared to other alternatives.
Additionally, copper wire is susceptible to theft due to its high market value. This can create a security concern, especially in construction sites or areas where copper theft is prevalent.
In summary, copper wire is widely used in electrical applications due to its excellent electrical conductivity, flexibility, corrosion resistance, and safety features. However, its higher cost and susceptibility to theft should be taken into consideration when choosing the right wire for a specific project.
Aluminum Wire
Aluminum wire is another commonly used material in electrical wiring, particularly in residential and commercial settings. While it may not be as popular as copper wire, aluminum wire has its own set of advantages and considerations.
One key advantage of aluminum wire is its affordability. Aluminum is a cheaper alternative to copper, making it a cost-effective option for electrical installations, especially in larger projects where a significant amount of wire is needed.
Similar to copper, aluminum also possesses good electrical conductivity. While it is not as conductive as copper, aluminum wire can still effectively transmit electrical current.
However, there are a few considerations to keep in mind when using aluminum wire. One important factor is its higher electrical resistance compared to copper. This means that aluminum wire may experience higher electrical losses and a potential increase in heat generation. Proper installation techniques and appropriate wire sizing are crucial to mitigate these issues.
Another concern with aluminum wire is its susceptibility to oxidation, which can lead to corrosion. Aluminum naturally forms an oxide layer that can increase its electrical resistance over time. To mitigate this, aluminum wire used in electrical wiring is typically coated or treated with anti-corrosive materials.
Due to its thermal expansion properties, aluminum wire requires special connectors and terminals that are designed specifically for aluminum connections. This helps to prevent loose connections, which can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards.
It’s worth noting that aluminum wire was more commonly used in the past, especially during the 1960s and 1970s. However, it fell out of favor for residential applications due to concerns about its performance and the industry’s transition back to copper wire.
Overall, aluminum wire is a cost-effective alternative to copper wire, and it still has its practical applications in certain circumstances. However, it requires proper installation techniques, suitable connectors, and regular maintenance to ensure safe and reliable electrical connections.
Insulation Materials
Insulation materials are an integral part of electrical wire, as they provide protection and insulation from electrical shock, environmental factors, and potential damage. Different types of insulation materials are used depending on the specific requirements of the wire and its intended application.
The primary function of insulation is to prevent the flow of electricity from the wire to any surrounding objects or individuals. It acts as a barrier, ensuring that the electrical current stays within the wire and does not pose a risk to safety or cause unwanted interference.
There are several insulation materials commonly used in electrical wire manufacturing. Let’s explore a few of them:
PVC Insulation: Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a widely used insulation material in electrical wire. It is known for its excellent resistance to moisture, chemicals, and sunlight. PVC insulation provides good mechanical protection and electrical insulation properties, making it suitable for various applications.
Thermoplastic Insulation: Thermoplastic insulation materials, such as polyethylene and polypropylene, are commonly used in electrical wire. They offer good flexibility and resistance to heat, chemicals, and sunlight. These insulation materials can withstand a wide range of temperatures and are often used in outdoor and high-temperature applications.
Cross-Linked Polyethylene (XLPE) Insulation: XLPE insulation is a type of thermosetting insulation material that provides excellent thermal and mechanical properties. It has high heat resistance and is suitable for applications that require long-term durability and resistance to electrical stress. XLPE insulation is commonly used in high-voltage and underground electrical cables.
Other Types of Insulation: In addition to PVC, thermoplastic, and XLPE insulation, there are other insulation materials used in specialized applications. These include but are not limited to silicone rubber, Teflon (PTFE), and fiberglass. These materials offer unique properties such as high temperature resistance, chemical resistance, and flame retardancy.
The choice of insulation material depends on factors such as the intended use of the wire, environmental conditions, voltage requirements, and specific industry regulations and standards. It is crucial to select the appropriate insulation material to ensure the safety, performance, and longevity of the electrical wire.
Overall, insulation materials play a vital role in protecting electrical wire and preventing electrical hazards. The selection of the right insulation material is essential in ensuring the overall performance and safety of electrical installations.
PVC Insulation
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) insulation is one of the most commonly used insulation materials in electrical wire manufacturing. PVC is a versatile and cost-effective material that offers numerous benefits for electrical applications.
PVC insulation provides excellent electrical insulation properties, making it an ideal choice for preventing electrical current leakage and ensuring safe and reliable operation. It has a high dielectric strength, which means it can withstand high voltages without breaking down.
An important characteristic of PVC insulation is its resistance to moisture. It acts as a protective barrier, preventing water or other liquids from coming into direct contact with the conductor. This moisture resistance makes PVC-insulated wire suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
PVC insulation also exhibits good resistance to various chemicals, oils, and solvents. This property makes it highly suitable for use in industrial settings, where wires are exposed to potentially corrosive substances.
Additionally, PVC insulation offers excellent resistance to sunlight and ultraviolet (UV) radiation. This UV resistance makes PVC-insulated wire suitable for outdoor installations, where exposure to sunlight can deteriorate other types of insulation over time.
One of the key advantages of PVC insulation is its flexibility. PVC-insulated wire is known for its ease of handling, bending, and installation. The flexibility allows electricians to route the wire through narrow spaces and around corners without compromising its performance.
PVC insulation is also fire-resistant to a certain extent. It has a high ignition temperature and self-extinguishing properties, which means it is less likely to catch fire or contribute to the spread of flames in the event of an electrical fault or fire.
Furthermore, PVC insulation is a durable material that can withstand mechanical stress and abrasion. It provides a protective layer around the conductor, reducing the risk of damage during installation, maintenance, or normal use.
In terms of environmental considerations, PVC insulation is recyclable, reducing its impact on the environment. It can be processed and reused to minimize the need for new raw materials.
In summary, PVC insulation is a widely used and versatile insulation material in electrical wire manufacturing. Its excellent electrical insulation properties, moisture resistance, chemical resistance, UV resistance, flexibility, and fire resistance make it suitable for a wide range of applications. It remains a popular choice for electrical installations due to its cost-effectiveness, durability, and ease of handling.
Electrical wire is typically made of copper or aluminum, which are both excellent conductors of electricity. Copper is more commonly used due to its superior conductivity and resistance to corrosion.
Read more: What Is 4 Wire Electrical Wire
Thermoplastic Insulation
Thermoplastic insulation is a commonly used type of insulation material in electrical wire manufacturing. It refers to a range of materials that become soft and pliable when heated and solidify upon cooling, allowing them to be molded into various shapes.
There are several types of thermoplastic insulation materials used in electrical wiring, including polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP). These materials offer numerous advantages for electrical applications.
One of the key benefits of thermoplastic insulation is its excellent flexibility. Polyethylene and polypropylene wires are known for their ease of bending, making them suitable for installations that require routing the wire through tight spaces or around obstacles.
In addition to flexibility, thermoplastic insulation materials have good resistance to heat and high temperatures. They can withstand a wide range of operating temperatures without degrading or compromising their electrical properties.
Thermoplastic insulation also exhibits good resistance to chemicals and oils, making it suitable for various industrial applications. It can withstand exposure to solvents, fuels, and other corrosive substances commonly found in industrial environments.
Another advantage of thermoplastic insulation is its resistance to sunlight and UV radiation. This UV resistance allows wires with thermoplastic insulation to be used in outdoor applications without being degraded or affected by prolonged exposure to sunlight.
Thermoplastic insulation materials are known for their good electrical insulation properties, which help prevent electrical leakage and ensure safe operation. They have high dielectric strengths, allowing them to handle high voltages without breaking down.
These insulation materials are also known for their durability and resistance to abrasion. They provide a protective barrier around the wire, reducing the risk of damage from friction, mechanical stress, or accidental impact.
Furthermore, thermoplastic insulation materials are lightweight compared to other insulation types, making them easier to handle and install. This can be particularly advantageous in large-scale projects where a significant amount of wire needs to be installed.
Lastly, like other types of insulation, thermoplastic materials contribute to the fire safety of electrical systems. They have self-extinguishing properties and high ignition temperatures, reducing the risk of electrical fires spreading or being initiated by the wire insulation.
In summary, thermoplastic insulation materials, such as polyethylene and polypropylene, offer flexibility, heat resistance, chemical resistance, UV resistance, electrical insulation properties, and durability. These qualities make them suitable for a wide range of electrical applications, both indoors and outdoors.
Cross-Linked Polyethylene (XLPE) Insulation
Cross-Linked Polyethylene (XLPE) insulation is a specialized type of insulation material used in electrical wire manufacturing. It is commonly used in high-voltage and underground electrical cables, as well as in various industrial applications.
XLPE insulation offers several advantages that make it a preferred choice for certain electrical installations. One of its primary benefits is its excellent thermal and mechanical properties. XLPE insulation can withstand high temperatures without losing its structural integrity or electrical performance.
XLPE insulation is known for its exceptional resistance to electrical stress. It can handle high electrical voltages and minimize the risk of electrical breakdown or leakage. This property makes it suitable for use in high-voltage transmission lines and other specialized applications where electrical stress is a concern.
Another advantage of XLPE insulation is its resistance to moisture. It provides a reliable barrier against the ingress of water, preventing potential damage to the wire and preserving its electrical performance even in damp environments. This moisture resistance makes XLPE-insulated wire a popular choice for both outdoor and underground installations.
XLPE insulation also exhibits good resistance to chemicals and solvents, making it suitable for use in harsh environments where exposure to corrosive substances is a concern. It can withstand contact with oils, fuels, and other chemicals commonly found in industrial settings.
Additionally, XLPE insulation offers excellent mechanical strength and durability. It is resistant to abrasion, cuts, and impact, providing long-lasting protection to the wire. This durability ensures the integrity of the electrical connection even in demanding applications or environments.
Furthermore, XLPE insulation has a low dielectric constant, which allows for more efficient power transmission and reduced electrical losses. This property makes it an energy-efficient choice for electrical systems.
It’s important to note that XLPE insulation requires a special manufacturing process called cross-linking. This process involves treating the polyethylene material with heat or chemicals to form strong bonds between the polymer chains, enhancing the insulation’s properties and performance.
Overall, XLPE insulation offers exceptional thermal and electrical properties, moisture resistance, chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and durability. These qualities make it a preferred choice for high-voltage transmission lines, underground cables, and other specialized electrical applications that require reliable and robust insulation.
Other Types of Insulation
While PVC, thermoplastic, and XLPE insulation are commonly used in electrical wire manufacturing, there are other types of insulation materials available for specialized applications. These materials offer unique properties and cater to specific needs in the electrical industry.
Silicone Rubber: Silicone rubber insulation is known for its excellent high-temperature resistance. It can withstand extreme heat without degrading or losing its electrical properties. This makes it suitable for applications where wires are exposed to high temperatures, such as in industrial ovens or automotive wiring harnesses.
Teflon (PTFE): Teflon, also known as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), is a non-stick, high-temperature insulation material. It has excellent resistance to chemicals, oils, and solvents, making it suitable for extreme environments. Teflon insulation is commonly used in aerospace and military applications, as well as in industries that require high chemical resistance.
Fiberglass: Fiberglass is a type of insulation material made from fine strands of glass fibers. It offers excellent heat resistance, electrical insulation, and mechanical strength. Fiberglass insulation is commonly used in high-temperature applications, such as in heating elements and industrial furnaces.
Mineral Insulation: Mineral insulation, also known as mineral wool or rock wool, is made from natural minerals such as basalt or diabase. It offers excellent fire resistance and thermal insulation properties. Mineral insulation is commonly used in fire-rated electrical cables and applications where fire safety is a top priority.
Mica Insulation: Mica insulation is made from natural mica minerals and is known for its excellent electrical insulation properties and high-temperature resistance. It is often used in high-voltage applications such as transformers and power generators.
Composite Insulation: Composite insulation materials combine different types of insulators to leverage their unique properties. For example, a composite insulation may combine the heat resistance of silicone rubber with the chemical resistance of Teflon. These materials offer a customized insulation solution for specific applications that require multiple properties.
It’s important to consult industry standards and regulations to determine the appropriate insulation material for a specific electrical application. Understanding the unique properties and advantages of each insulation material can help ensure the safety, reliability, and performance of electrical wiring systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the composition of electrical wire plays a vital role in its performance, durability, and safety. Copper wire remains one of the most commonly used materials due to its excellent conductivity, flexibility, and resistance to corrosion. However, aluminum wire offers a cost-effective alternative with its affordability and suitability for certain applications.
Insulation materials are crucial in protecting electrical wires and preventing electrical hazards. PVC insulation provides a reliable and cost-effective solution, offering resistance to moisture, chemicals, and sunlight. Thermoplastic insulation materials, such as polyethylene and polypropylene, offer flexibility, heat resistance, chemical resistance, and UV resistance.
For specialized applications, XLPE insulation is preferred for its exceptional thermal and mechanical properties, moisture resistance, and high resistance to electrical stress. Other types of insulation materials, including silicone rubber, Teflon, fiberglass, mineral insulation, mica insulation, and composite insulation, cater to specific needs in terms of high-temperature resistance, chemical resistance, fire resistance, or unique combinations of properties.
When selecting the appropriate wire and insulation material, it is important to consider factors such as conductivity, flexibility, resistance to environmental conditions, mechanical strength, and compliance with industry regulations. Consulting with professionals and adhering to electrical codes and standards is crucial in ensuring the safety and effectiveness of electrical installations.
In summary, the knowledge of electrical wire composition and insulation materials empowers electricians, contractors, and homeowners to make informed decisions when it comes to selecting the right wire for a specific application. By understanding the properties and advantages of different materials, one can ensure the reliability, performance, and longevity of electrical wiring systems.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is Electrical Wire Made Of
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.








0 thoughts on “What Is Electrical Wire Made Of”