Home>diy>Architecture & Design>How To Design A Solar-Powered House


Architecture & Design
How To Design A Solar-Powered House
Modified: January 9, 2024
Learn how to design a solar-powered house with our expert tips and techniques in architecture design. Create an eco-friendly and sustainable home for a greener future.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in sustainable living and reducing our carbon footprint. One of the most effective ways to achieve this is by designing and building a solar-powered house. With advancements in technology and decreased costs, solar energy has become a viable and environmentally-friendly option for homeowners.
A solar-powered house utilizes photovoltaic (PV) panels to convert sunlight into electricity. This renewable energy source not only reduces dependency on fossil fuels but also provides numerous benefits, including lower energy bills and increased energy independence. To design a solar-powered house, several key steps need to be followed, from assessing energy needs to integrating sustainable design features.
This article will guide you through the process of designing a solar-powered house. By following these steps, you can create an energy-efficient home that harnesses the power of the sun while minimizing your environmental impact.
Key Takeaways:
- Designing a solar-powered house involves assessing energy needs, optimizing site selection, integrating battery storage, and implementing sustainable design features. It’s a holistic approach to creating an energy-efficient and environmentally responsible home.
- Financing and incentives play a crucial role in making the investment in a solar-powered house more affordable. Exploring solar loans, incentives, and rebates can offset costs and contribute to long-term financial and environmental benefits.
Read more: Who Can Design A Passive Solar House
Step 1: Assessing Your Energy Needs
The first step in designing a solar-powered house is to assess your energy needs. This involves determining the amount of electricity your household uses on a daily basis. By understanding your energy consumption, you can properly size your solar panel system and ensure it meets your requirements.
To assess your energy needs, start by examining your past utility bills. Look for the average monthly kilowatt-hour (kWh) usage to get an idea of your household’s electricity consumption. Take note of any seasonal variations or fluctuations in usage.
Next, consider any changes you plan to make in your daily routines or appliances used in the future. For example, if you are planning to add energy-intensive equipment or increase your living space, you will need to account for the additional electricity demand.
It’s also important to consider your location and the availability of sunlight. Different regions receive varying amounts of sunshine throughout the year, which impacts the potential energy generation from solar panels. Research the solar irradiance in your area to gauge the system’s performance and estimate the number of panels needed.
Lastly, consider any energy-saving measures you can implement to reduce your overall energy consumption. This may include upgrading to energy-efficient appliances, using LED lighting, improving insulation, and minimizing energy waste through smart home automation systems. By reducing your energy needs, you can optimize your solar panel system and potentially save even more on your energy bills.
By assessing your energy needs accurately, you can determine the size and capacity of your solar panel system. This information will be essential in the subsequent steps of designing and installing your solar-powered house.
Step 2: Site Selection and Orientation
Once you have assessed your energy needs, the next step is to choose the optimal site for your solar-powered house and ensure proper orientation of the panels. Site selection and orientation play a crucial role in maximizing solar energy generation.
When selecting a site, look for unobstructed areas with ample sunlight exposure throughout the day. Avoid locations that are shaded by trees, buildings, or other structures that may hinder the efficiency of your solar panels. Additionally, consider the size of the roof or available space for ground-mounted installations.
Furthermore, the orientation of your solar panels is key to capturing the maximum amount of sunlight. Ideally, panels should face south in the northern hemisphere or north in the southern hemisphere to receive the most sunlight throughout the day. The tilt angle should also correspond to your latitude for optimal performance.
If your site does not have ideal orientation or shading is unavoidable, consider using solar tracking systems that automatically adjust the position of the panels to track the sun’s movement. While these systems can increase energy production, they may also add complexity and costs to the installation.
Additionally, it’s essential to consider any legal regulations or homeowner association guidelines that may impact the placement and orientation of solar panels. Check with local authorities or HOA regulations to ensure compliance and avoid any potential issues.
By carefully selecting the site for your solar-powered house and optimizing the orientation of the panels, you can maximize the efficiency and energy output of your system. This will enable you to harness the power of the sun to its full potential and achieve optimal energy savings.
Step 3: Solar Panel Installation
After assessing your energy needs and selecting the site, it’s time to proceed with the installation of your solar panels. Solar panel installation involves several key steps to ensure a safe and efficient setup.
The first step is to hire a professional solar installer or contractor with experience in solar panel installations. They will assess your site, provide recommendations, and handle the technical aspects of the installation process. Working with an expert ensures that the panels are installed correctly and in compliance with local building codes.
Once you have chosen an installer, they will begin by mounting the solar panels on your roof or a ground-mounted system. The panels are securely attached using mounting brackets, and proper sealing is done to ensure waterproofing and protection against the elements.
Next, the wiring and electrical connections are made. This involves connecting the panels to an inverter, which converts the direct current (DC) generated by the panels into alternating current (AC) used to power your home. The inverter is typically installed in a convenient location, such as the garage or utility room.
In addition, a meter is installed to monitor the amount of electricity generated and exported back to the grid, if applicable. This will help track your energy production and any potential credits or savings.
It’s important to note that the installation process may vary depending on the type of solar panel system (grid-tied, off-grid, or hybrid) and any additional components, such as batteries for energy storage. Your installer will guide you through the specific requirements based on your energy needs and goals.
Throughout the installation process, safety measures should be followed to ensure the well-being of the installers and the longevity of the system. This includes using proper protective equipment, following electrical safety protocols, and adhering to industry best practices.
Once the solar panels are installed, the system will undergo a series of tests and inspections to ensure it is functioning correctly. This may include checks for proper wiring, grounding, and system performance.
By following the necessary installation steps and working with a professional installer, you can have peace of mind knowing that your solar panel system is installed safely and efficiently, ready to power your solar-powered house.
Step 4: Battery Storage System
Incorporating a battery storage system into your solar-powered house allows you to store excess energy generated during the day for later use when the sun is not shining. This ensures a reliable and uninterrupted power supply, increasing your energy independence.
The first step in installing a battery storage system is to assess your energy storage needs. Determine how much energy you want to store and for what duration. This will depend on various factors, such as your energy consumption patterns, the size of your solar panel system, and the desired level of backup power during grid outages.
When selecting a battery storage system, consider factors like capacity, lifespan, efficiency, and compatibility with your solar panel system. Lithium-ion batteries are the most commonly used due to their high energy density, longer lifespan, and better efficiency compared to other battery types.
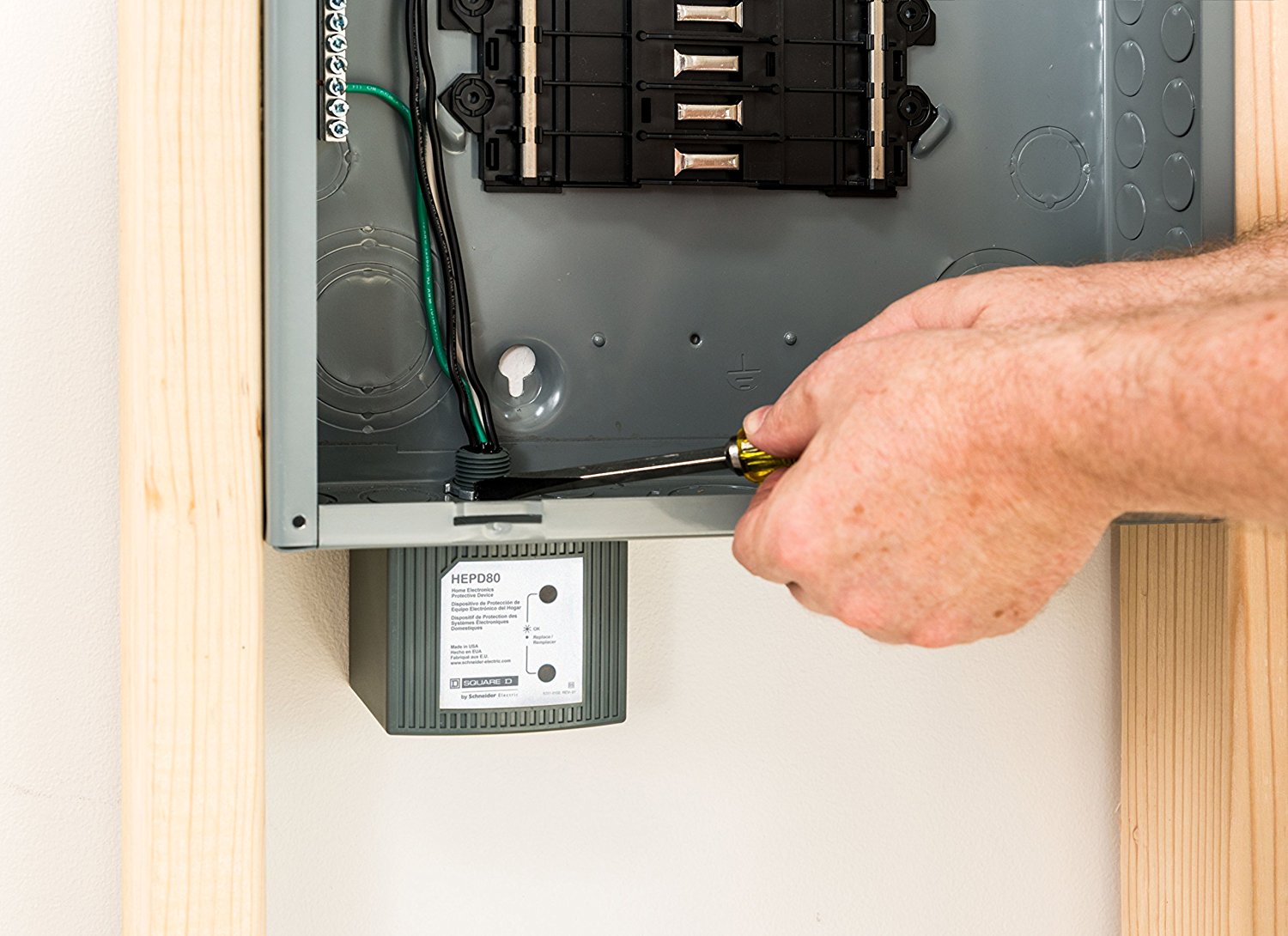
Once you have chosen the battery storage system, it needs to be connected to your solar panel system and electrical grid. This usually involves installing a hybrid inverter or a separate battery inverter to manage the flow of electricity between the solar panels, batteries, and the grid.
During installation, proper wiring and circuit protection measures should be followed to ensure the safe operation of the system. Additionally, the batteries should be installed in a well-ventilated area with appropriate temperature regulation to optimize their performance and lifespan.
A battery management system is also installed to monitor the charging and discharging of the batteries to maximize their efficiency and protect against overcharging or deep discharging. This helps prolong the lifespan of the batteries and ensures optimal performance over time.
It’s important to note that integrating a battery storage system adds complexity to the overall solar panel system setup. Consulting with a professional solar installer or contractor experienced in battery storage systems is recommended to ensure proper installation and seamless integration with your solar-powered house.
By incorporating a battery storage system, you can store excess solar energy and use it during peak demand times or during grid outages. This enhances the reliability and independence of your solar-powered house, reducing your reliance on the electrical grid and providing peace of mind.
When designing a solar-powered house, consider the orientation and tilt of the roof to maximize sun exposure for solar panels. This will ensure maximum energy production from the system.
Read more: How To Connect A Porch Roof To House
Step 5: Energy Management and Monitoring
To maximize the efficiency and performance of your solar-powered house, incorporating energy management and monitoring systems is essential. These systems allow you to track your energy usage, monitor the performance of your solar panels, and optimize your energy consumption.
The first step in energy management is to install a smart energy meter. This device measures your energy usage in real-time, providing you with valuable insights into your electricity consumption patterns. With this information, you can identify areas where energy is being wasted and make necessary adjustments to reduce your overall energy usage.
In addition to the smart meter, you can install a home energy management system (HEMS). A HEMS integrates with your solar panel system, battery storage system, and other smart devices in your home, allowing you to monitor and control your energy consumption remotely. It provides real-time data on your energy generation, usage, and storage, empowering you to make informed decisions about your energy consumption.
With the help of a HEMS, you can schedule energy-intensive tasks, such as running appliances or charging electric vehicles, during periods of high solar energy production. This maximizes your energy self-consumption and minimizes reliance on the grid.
Furthermore, energy management systems can provide alerts and notifications when your energy consumption or production exceeds predefined thresholds. This helps you identify any issues or anomalies and take prompt action.
Energy monitoring systems also play a crucial role in maintaining the performance of your solar panel system. These systems capture data on the output of each solar panel, allowing you to identify if any panels are underperforming or need maintenance. Early detection of issues can help ensure optimal energy generation and prolong the lifespan of your solar panels.
By actively managing and monitoring your energy usage, you can optimize your solar-powered house’s performance, increase energy efficiency, and maximize your savings. These systems empower you to have better control over your energy consumption and make informed decisions to reduce your environmental impact.
Step 6: Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating your solar-powered house with existing systems is an important step to ensure seamless functionality and optimal energy efficiency. This step involves connecting your solar panel system, battery storage, and other renewable energy components to your home’s electrical and HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems.
The first consideration is integrating your solar panel system with your electrical system. This typically involves installing a solar inverter, which converts the DC electricity generated by the solar panels into AC electricity that can be used to power your home. The inverter is connected to your main electrical panel, allowing the solar energy to be distributed throughout the house.
Next, if you have a battery storage system, you will need to integrate it with your home’s electrical system as well. This involves connecting the battery inverter to the main electrical panel, enabling the battery to store excess energy and provide power during periods when solar energy is not available.
Integrating your solar-powered house with your HVAC system is another important consideration. By connecting your solar energy system to your heating and cooling systems, you can optimize your energy usage and reduce reliance on traditional energy sources.
If you have an electric heating or cooling system, such as an electric heat pump or electric furnace, you can directly power these systems with the electricity generated by your solar panels. This helps reduce your reliance on fossil fuels for heating and cooling, further lowering your carbon footprint.
In addition, integrating smart thermostats or other smart home automation systems allows you to control and optimize your HVAC system based on energy production and usage patterns. These systems can adjust temperature settings and schedules to maximize energy efficiency and comfort.
Furthermore, consider integrating your solar-powered house with other energy-efficient appliances and systems, such as energy-efficient lighting, water heating systems, and smart appliances. This holistic approach ensures that your solar energy system works seamlessly with other components of your home, maximizing overall energy efficiency and sustainability.
By carefully integrating your solar-powered house with existing systems, you can create a fully functional and energy-efficient home. This integration allows for the optimal utilization of solar energy and helps reduce reliance on non-renewable sources, contributing to a greener and more sustainable future.
Step 7: Sustainable Design Features
Designing a solar-powered house goes beyond just installing solar panels. It involves incorporating sustainable design features that further enhance energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact. This step focuses on integrating sustainable practices and technologies into the overall design and construction of your home.
One important aspect is optimizing insulation and air sealing. Proper insulation helps maintain comfortable indoor temperatures, reduces heat loss or gain, and minimizes the need for excessive heating or cooling. Additionally, air sealing prevents drafts and energy leakage, further improving energy efficiency.
Another sustainable design feature is incorporating energy-efficient windows and doors. These should have good thermal performance, low emissivity (low-e) glass, and proper seals to prevent heat transfer and improve energy efficiency.
Natural lighting is another aspect to consider. By maximizing natural light through the strategic placement of windows, skylights, and light tubes, you can reduce the need for artificial lighting during the day, saving energy. Additionally, installing energy-efficient LED lighting fixtures helps minimize energy consumption even further.
Utilizing energy-efficient appliances and fixtures throughout your home is also crucial. Look for Energy Star-rated appliances, low-flow plumbing fixtures, and smart thermostats to reduce energy and water usage, enhancing sustainability and reducing utility bills.
When it comes to materials and construction practices, opt for sustainable and eco-friendly options. This includes using recycled or reclaimed materials, locally sourced materials, and implementing efficient waste management during construction. Choosing sustainable materials and construction methods not only reduces the environmental impact but also promotes healthier indoor air quality.
Consider incorporating passive design strategies that take advantage of the natural climate and surroundings. This may include proper orientation to maximize natural ventilation and shading, using thermal mass materials for heat absorption and retention, and designing outdoor spaces to promote natural cooling and heating.
Landscaping and outdoor design can also play a role in sustainability. Incorporate native plants that require less water and maintenance, install irrigation systems with moisture sensors, and consider rainwater harvesting for irrigation purposes.
Lastly, integrating a renewable technology beyond solar panels, such as small wind turbines or micro-hydropower systems if feasible in your location, can further enhance your energy production and sustainability efforts.
By incorporating these sustainable design features into your solar-powered house, you can create an environmentally-friendly and energy-efficient home. These features work synergistically with your solar energy system, allowing you to live more sustainably while enjoying the benefits of renewable energy.
Step 8: Financing and Incentives
Financing your solar-powered house project is an important step in making it a reality. Fortunately, there are various financing options and incentives available to help make the investment more affordable and financially beneficial.
One common financing option is through solar loans. These are specialized loans that allow homeowners to finance the upfront costs of installing a solar panel system. Solar loans typically have low-interest rates and flexible repayment terms, making it easier to budget for the project.
Another financing option is through home equity loans or lines of credit, where you can leverage the equity in your home to fund the solar-powered house project. These loans often offer competitive interest rates and may provide tax benefits, but it’s important to carefully consider the terms and potential risks.
Additionally, some solar manufacturers and installers offer leasing or power purchase agreement (PPA) options. With a solar lease or PPA, you essentially “rent” the solar panel system and pay a fixed monthly fee or purchase the electricity generated by the panels at a predetermined rate. This option eliminates the upfront costs but may have long-term financial implications, so carefully review the terms and conditions.
It’s crucial to explore available incentives and rebates when financing your solar-powered house. Many governments, utility companies, and organizations offer financial incentives to encourage the adoption of renewable energy. These incentives can include tax credits, grants, rebates, and net metering programs, which allow you to sell excess electricity back to the grid.
Research and understand the eligibility requirements and the specific incentives available in your region. You may need to work with your installer to ensure the system meets the necessary criteria to qualify for these incentives.
When evaluating financing and incentives, consider the long-term financial benefits of a solar-powered house. The savings on energy bills, potential increase in property value, and the positive environmental impact can far outweigh the initial investment.
Consult with solar financing professionals and reach out to local authorities or organizations that specialize in renewable energy financing to get personalized advice and explore all available options.
By carefully considering financing options and taking advantage of available incentives, you can make the investment in a solar-powered house more affordable and reap the long-term benefits both financially and environmentally.
Read more: How To Add A Porch To Your House
Conclusion
Designing a solar-powered house is a rewarding endeavor that combines sustainability, energy efficiency, and environmental responsibility. With the advancements in technology and decreasing costs, solar energy has become a viable and practical solution for homeowners looking to reduce their carbon footprint and save on energy bills.
By following the step-by-step process outlined in this guide, you can successfully design and implement a solar-powered house. Assessing your energy needs, selecting the ideal site and orientation, installing solar panels and battery storage, integrating with existing systems, incorporating sustainable design features, and exploring financing and incentives are all important considerations on your journey towards a greener home.
It’s crucial to work with experienced professionals throughout the process, from solar installers to energy management system providers, ensuring the highest quality installation and performance. They can guide you through the technical aspects and help you optimize your solar-powered house for maximum efficiency and savings.
Remember, designing a solar-powered house is not just about harnessing the sun’s energy but also making sustainable choices in terms of insulation, lighting, appliances, and construction materials. Incorporating these features enhances the overall efficiency and reduces your environmental impact.
Furthermore, consider the various financing options available, such as solar loans and leasing agreements, to make the investment more financially feasible. Take advantage of government incentives, tax credits, and rebate programs to further offset the costs and accelerate your return on investment.
By creating a solar-powered house, you are taking a proactive step towards a cleaner, more sustainable future. Not only will you enjoy the financial benefits of reduced energy bills and potential incentives, but you will also contribute to a healthier environment and a greener planet for generations to come.
So, embrace the power of the sun, design your solar-powered house, and be a part of the renewable energy revolution.
Frequently Asked Questions about How To Design A Solar-Powered House
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.













0 thoughts on “How To Design A Solar-Powered House”