Home>diy>Architecture & Design>What Strategies In House Design For Cold Climate Entry Floor Plan

Architecture & Design
What Strategies In House Design For Cold Climate Entry Floor Plan
Modified: October 20, 2024
Discover effective strategies for designing entry floor plans in cold climates. Explore the best architecture design practices to ensure warmth and comfort in your home.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Designing a house for a cold climate requires careful consideration and planning. One important aspect of cold climate house design is the entry floor plan. The entryway serves as the gateway between the outdoors and the interior of the house, and it plays a crucial role in maintaining comfort, energy efficiency, and protection against the elements.
In this article, we will explore the challenges of designing a house for a cold climate and the significance of the entry floor plan in addressing these challenges. We will also discuss various strategies and design considerations that can be employed to create an efficient and functional entryway in cold climates.
Understanding the unique characteristics and demands of a cold climate is essential in order to design a house that will withstand the harsh conditions and provide a comfortable living environment. Cold climates are characterized by long, frigid winters, with temperatures often dropping below freezing. These climates also frequently experience snowfall, strong winds, and low humidity levels.
In such climates, it is crucial to minimize heat loss and ensure proper insulation to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature and reduce energy consumption. The entryway, being the primary point of contact between the house and the cold outdoor environment, requires specific design strategies to prevent heat loss, drafts, and the infiltration of cold air.
Furthermore, cold climates often require additional considerations for factors such as snow removal, storage for cold-weather gear, and the prevention of moisture accumulation. These challenges make the design of the entry floor plan particularly important in cold climate house design.
The entry floor plan is not only functional but also sets the tone for the rest of the house. It serves as the first impression of the home, welcoming guests and providing a glimpse into the overall design aesthetic. Furthermore, it serves practical purposes such as storage, seating, and transitioning from outdoor to indoor spaces.
By employing strategic design principles and incorporating features specific to cold climates, a well-designed entry floor plan can enhance the overall functionality, energy-efficiency, and comfort of a house in cold climates. In the subsequent sections, we will delve into specific strategies for designing the entry floor plan in cold climates.
Key Takeaways:
- Designing an efficient entry floor plan in a cold climate requires strategic planning, insulation, and weatherproofing to minimize heat loss and create a welcoming, functional space for residents and guests.
- Incorporating features such as mudrooms, vestibules, and passive solar design principles can enhance energy efficiency, reduce drafts, and provide additional insulation in the entry floor plan of a house in a cold climate.
Read more: What Is A Floor Plan
Understanding the Challenges of Cold Climate House Design
Designing a house for a cold climate presents a unique set of challenges that must be taken into account during the planning and construction phases. The primary challenge lies in maintaining a comfortable and energy-efficient indoor environment while combating the harsh weather conditions experienced in cold climates.
The first challenge is maintaining thermal comfort. In cold climates, keeping the interior of the house warm during the winter months is of utmost importance. The design must minimize heat loss and ensure effective insulation to prevent the cold air from penetrating the building envelope. This involves using insulation materials with high R-values and properly sealing any gaps or cracks where cold air could infiltrate.
Another challenge faced in cold climate house design is dealing with snow and ice. Heavy snowfall can accumulate on the roof, leading to potential structural issues and increased heat loss if not properly managed. Pitched roofs with sufficient slope and appropriate ventilation can help prevent snow buildup and ice dams. Additionally, incorporating features such as snow guards and using materials that are resistant to ice dam formation can help mitigate this challenge.
Energy efficiency is a major consideration in cold climates, as heating costs can be substantial. In order to reduce energy consumption, the design must focus on maximizing passive heating strategies. This includes properly orienting and placing windows to capture the sun’s warmth, as well as utilizing thermal mass, such as a well-insulated concrete floor, to absorb and release heat over time. The use of energy-efficient heating systems, such as radiant floor heating or geothermal heating, can also significantly contribute to energy savings.
Moisture control is another critical challenge in cold climate house design. Cold air holds less moisture, and when it enters a warmer interior space, it can result in condensation and potential mold and mildew issues. Proper ventilation systems, vapor barriers, and the use of moisture-resistant materials are essential in preventing moisture-related problems.
Furthermore, the design must also take into consideration the impact of cold climates on the overall lifespan of the building materials. Extreme temperature fluctuations, freeze-thaw cycles, and exposure to moisture can cause materials to degrade more quickly. Using durable and weather-resistant materials, as well as selecting construction methods that can withstand the demands of a cold climate, are crucial in ensuring the longevity of the house.
Understanding these challenges is essential in order to design a house that can withstand the unique demands of a cold climate. The entry floor plan, in particular, plays an integral role in addressing these challenges and creating a functional and efficient space that can withstand the harsh weather conditions. In the next section, we will explore the importance of the entry floor plan in cold climate design.
Importance of Entry Floor Plan in Cold Climate Design
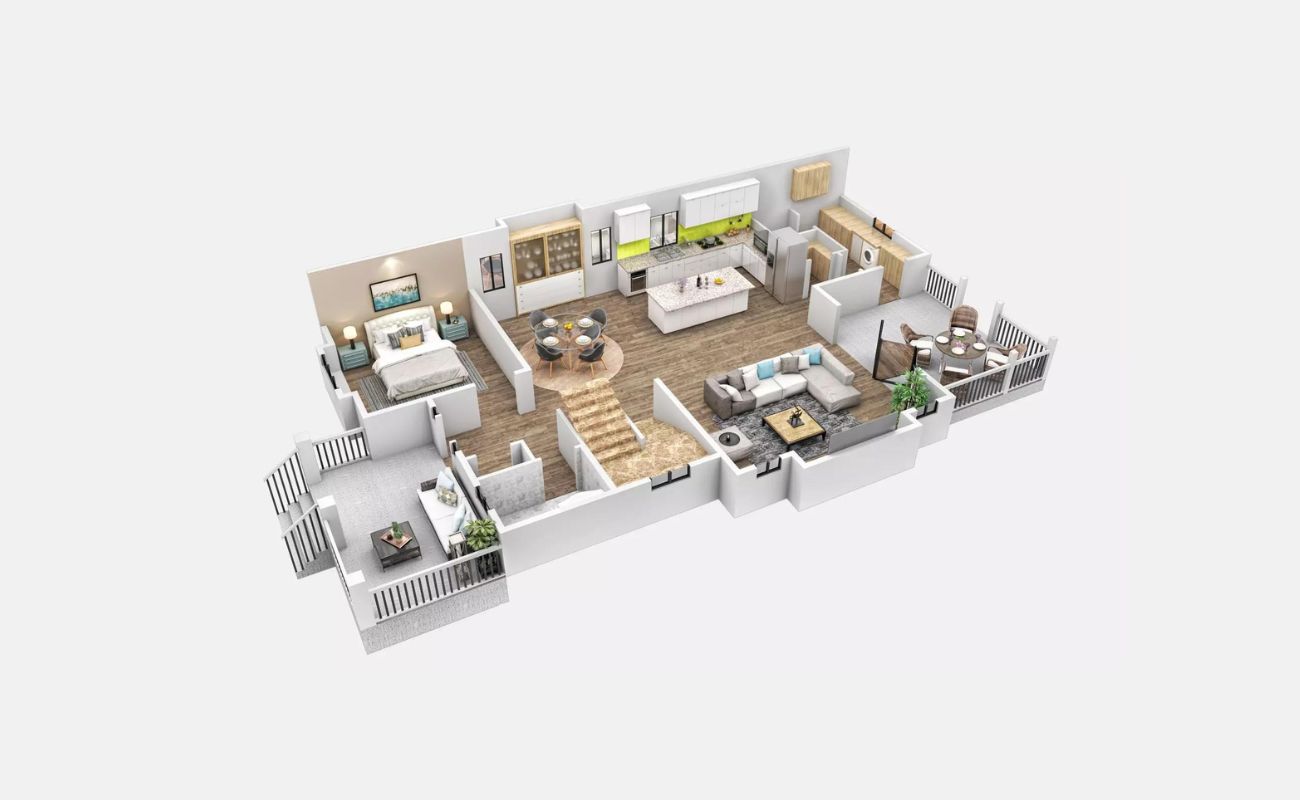
The entry floor plan is a crucial aspect of house design, especially in cold climates. It serves as a transitional space between the exterior and the interior, playing a significant role in maintaining comfort, energy efficiency, and protection against the elements.
One of the primary functions of the entry floor plan in cold climate design is to prevent heat loss and drafts. Since the entryway is the first point of contact between the house and the cold outdoor environment, it must be designed to minimize the transfer of cold air into the interior and retain the heat generated inside. This can be achieved through proper insulation, weatherstripping, and the use of energy-efficient materials and construction techniques.
The entry floor plan also serves as a buffer zone, allowing occupants to remove their outer layers of clothing and gear before entering the main living space. This is particularly important in cold climates, where individuals often wear bulky winter clothing and carry items such as boots, gloves, and hats. Incorporating storage options, such as coat closets or hooks, benches, and shoe racks, helps keep the entryway organized and prevents clutter from spreading into the rest of the house.
Another significant aspect of the entry floor plan in cold climate design is the prevention of moisture and dirt from being tracked indoors. In snowy or rainy climates, it is important to have a designated space in the entryway, such as a mudroom or an exteriors mat area, where individuals can remove wet or dirty footwear and clothing. This helps keep the rest of the house clean and dry, reducing the risk of slips, falls, and damage to flooring surfaces.
The placement and orientation of entryways in cold climate design are also important considerations. South-facing entryways allow for passive solar heating, as they capture the sunlight and help warm the space naturally during the winter months. Additionally, properly positioned entryways can minimize exposure to prevailing winds, reducing the risk of drafts and heat loss.
Furthermore, the design of the entry floor plan sets the tone for the rest of the house. It provides the first impression and welcomes guests into the home. By incorporating elements of the overall design aesthetic, such as materials, colors, and architectural details, the entryway creates a cohesive and inviting atmosphere.
Considering the importance of the entry floor plan in cold climate design, it is essential to implement strategies that prioritize energy efficiency, thermal comfort, and functionality. In the following sections, we will explore specific strategies and design considerations that can be utilized to create a well-designed entry floor plan in cold climates.
Strategies for Entry Floor Plan Design in Cold Climate
Designing an effective entry floor plan is crucial for ensuring thermal comfort, energy efficiency, and functionality in cold climate house design. Here are some strategies and considerations to keep in mind when designing the entry floor plan for a cold climate:
- Providing Adequate Entryway Space: It is important to ensure that the entryway has enough space to accommodate the removal of winter clothing and gear. Including features such as benches, coat closets, and shoe racks can help keep the space organized and prevent clutter from spreading into the rest of the house.
- Incorporating Mudrooms: Designating a separate area for mudrooms can be extremely beneficial in cold climates. This space allows occupants to remove wet or dirty footwear and clothing, preventing moisture and dirt from being tracked into the main living areas. Include features such as durable flooring, built-in storage, and easy-to-clean surfaces to make the mudroom functional and efficient.
- Using Proper Insulation and Weatherstripping: The entryway needs to be well-insulated and properly sealed to prevent heat loss and drafts. High-quality insulation materials and weatherstripping should be used on exterior doors, windows, and walls to minimize energy loss and maintain a comfortable indoor temperature.
- Considering Airlock Entry Designs: An airlock entry design, also known as a vestibule or an enclosed porch, can further enhance energy efficiency in cold climates. This design creates an additional barrier between the exterior and interior, reducing drafts and providing extra insulation. Airlock entryways can be heated or unheated, depending on the specific climate and heating requirements.
- Orientation and Placement of Entryways: Consider the orientation and placement of entryways to maximize passive solar heating and minimize exposure to prevailing winds. South-facing entryways can capture the sun’s warmth, contributing to the heating of the space naturally. Additionally, positioning entryways away from strong winds can help reduce heat loss and drafts.
- Utilizing Passive Solar Design Principles: Incorporating passive solar design principles in the entry floor plan can significantly contribute to energy efficiency. This includes using materials with high thermal mass, such as concrete or stone, to absorb and store heat. Large south-facing windows can also allow for the entryway to receive ample sunlight during the winter months.
- Incorporating Vestibules: Consider adding a vestibule or an enclosed area between the exterior and interior doors. This small transitional space can help insulate the house by acting as an additional barrier against cold air infiltration. Vestibules can be heated or unheated, depending on the specific climate and heating requirements.
By implementing these strategies and design considerations, the entry floor plan can contribute to creating a well-designed and efficient space in cold climates. It will help maintain thermal comfort, minimize energy loss, and provide functionality and convenience for occupants. The entry floor plan sets the tone for the rest of the house and serves as a welcoming space for both residents and guests.
Providing Adequate Entryway Space
One of the key strategies in designing the entry floor plan for a house in a cold climate is to provide adequate space in the entryway. The entryway serves as the first point of contact between the exterior and the interior and plays a crucial role in maintaining thermal comfort, managing winter gear and clothing, and preventing clutter from spreading into the rest of the house.
When designing the entryway, it is important to consider the functional requirements of the space. The entryway should have enough room for occupants to comfortably remove and store their winter clothing and gear, such as coats, hats, gloves, boots, and scarves. This can be achieved by incorporating features such as benches, coat closets, shoe racks, and hooks.
A bench provides a convenient seating option for individuals to sit down while removing or putting on their winter footwear. It also serves as a place to set down bags or other items while getting ready to leave or enter the house. The bench can be complemented with additional storage underneath, such as drawers or cubbies, to keep items organized and easily accessible.
Coat closets or closets with hooks are essential for storing winter coats, jackets, and other outerwear. Hanging hooks at different heights can accommodate items of various sizes, such as long coats, scarves, and hats. Including shelves or cubbies in the closet can provide storage for smaller items like gloves and mittens.
A dedicated shoe rack or a shoe storage cabinet is beneficial to keep winter footwear separate from the rest of the house. This prevents dirt, snow, and moisture from being tracked inside. Make sure to choose a shoe storage solution that can hold multiple pairs of shoes and boots and has proper ventilation to allow them to dry.
By providing adequate entryway space with benches, coat closets, shoe racks, and hooks, you create a functional and organized area for occupants to transition between the outdoors and the interior of the house. This helps keep winter gear and clothing in one designated area, preventing clutter and maintaining a clean living environment.
In addition to the practical functionality, an entryway with sufficient space can also contribute to the aesthetic appeal of the house. You can choose materials, colors, and finishes that align with the overall design style of the home. Integrating elements like mirrors, artwork, or decorative hooks can add a personal touch and make the entryway more inviting.
Overall, providing adequate entryway space is a critical strategy in designing the entry floor plan for a house in a cold climate. It enables efficient management of winter gear and clothing, reduces clutter, and enhances the overall functionality and aesthetic appeal of the space. A well-designed entryway sets the tone for the rest of the house and creates a welcoming atmosphere for both residents and guests.
Read more: What Is An In-Law Floor Plan
Incorporating Mudrooms
In cold climate areas, incorporating mudrooms into the entry floor plan is a highly beneficial and practical design strategy. Mudrooms provide a designated space for occupants to remove wet or dirty footwear and clothing before entering the main living areas of the house. They play a crucial role in maintaining cleanliness, preventing indoor moisture, and organizing winter gear.
Mudrooms serve as a transitional area between the outdoors and the interior of the house, acting as a buffer zone to prevent dirt, snow, and moisture from being tracked inside. By incorporating a mudroom, you create a space where these elements can be contained and easily managed.
When designing a mudroom, it is important to consider the specific needs and requirements of the household. Here are some key elements to incorporate:
- Durable Flooring: Choose flooring materials that can withstand heavy foot traffic, moisture, and dirt. Options such as ceramic tile, vinyl, or concrete are excellent choices for mudrooms, as they are tough and easy to clean.
- Built-in Storage: Include built-in storage solutions to accommodate winter gear, such as coats, hats, scarves, gloves, and boots. Hooks, cubbies, shelves, and dedicated shoe storage can keep everything organized and easily accessible. Consider incorporating individual sections for each family member to personalize and organize their belongings.
- Utility Sink: Installing a utility sink in the mudroom is a practical addition that allows for easy cleanup. It provides a designated area for handwashing, cleaning off dirty items, and filling watering cans or pet dishes.
- Bench or Seating Area: Including a bench or seating area in the mudroom provides a convenient spot for individuals to sit down while removing or putting on their footwear. This helps to prevent back strain and makes the process more comfortable. A bench with storage underneath can also serve as a handy place to store winter boots or other items.
- Mudroom Entryway: Ensure that the entryway to the mudroom is well-designed to handle wet and dirty conditions. Incorporate hooks or racks to hang wet umbrellas or outdoor clothing, and consider adding a durable mat or boot tray where occupants can wipe or shake off excess snow, dirt, or mud from their footwear.
Incorporating a mudroom into the entry floor plan not only helps maintain cleanliness and organization but also contributes to the overall functionality and efficiency of the house. By containing winter gear and preventing the spread of dirt and moisture, the living areas of the house stay cleaner for longer periods of time. This reduces the time and effort required for regular cleaning and upkeep.
Additionally, mudrooms offer a dedicated space for storing and organizing seasonal items. During the warmer months, the mudroom can serve as storage for outdoor gear such as gardening tools, sports equipment, or beach accessories. This versatility makes the mudroom a valuable and practical space throughout the year.
In summary, incorporating mudrooms into the entry floor plan of a house in a cold climate is an effective strategy for maintaining cleanliness, preventing indoor moisture, and organizing winter gear. By carefully considering the specific needs of the household and incorporating elements such as durable flooring, built-in storage, a utility sink, a seating area, and a well-designed entryway, you create a functional and efficient space that enhances the overall functionality and organization of the house.
When designing a house for a cold climate, consider creating an entry floor plan that includes a mudroom or vestibule to provide a buffer from the cold and minimize heat loss when entering the home. This can also serve as a space to store outerwear and boots.
Using Proper Insulation and Weatherstripping
Proper insulation and weatherstripping are essential strategies in designing the entry floor plan of a house in a cold climate. These measures help to minimize heat loss, improve energy efficiency, and ensure thermal comfort in the entryway area.
The entryway is a critical area where the exterior and interior environments meet. Without proper insulation and sealing, cold air can infiltrate, resulting in drafts and significant heat loss. To address this, it is important to focus on insulation and weatherstripping in the entry floor plan.
Insulation: Insulating the walls, ceiling, and floor of the entryway is crucial in preventing heat loss. High-quality insulation materials with a high R-value should be used to effectively trap heat inside the house. Insulating materials commonly used in cold climates include fiberglass, cellulose, and spray foam insulation.
When insulating the entry floor plan, pay particular attention to areas vulnerable to heat loss, such as exterior walls and the ceiling. The insulation should be installed properly, without any gaps or voids that could allow cold air to penetrate. Additionally, insulation should extend to the exterior door frames and the flooring to create a continuous thermal barrier.
Weatherstripping: Weatherstripping refers to the process of sealing gaps and cracks around doors and windows to prevent drafts and air infiltration. In the entry floor plan, weatherstripping should be applied to the exterior doors leading to the entryway.
Various types of weatherstripping materials are available, including adhesive strip weatherstripping, door sweeps, and door shoe sweeps. These materials are applied to the bottom of the door or the door jamb to form a tight seal when the door is closed. Weatherstripping materials should be selected to accommodate the specific climate and provide a sufficient barrier against cold air infiltration.
In addition to insulation and weatherstripping, it is important to assess the overall integrity of the entryway in terms of air leaks. Inspect the entry floor plan for any gaps or cracks in the walls, windows, or doors that may need to be sealed. Caulking and sealing these openings ensures that cold air cannot enter the space and compromise the thermal efficiency of the entryway.
By using proper insulation and weatherstripping, you can significantly enhance the energy efficiency of the entry floor plan in a cold climate. Adequately insulating the walls, ceiling, and floor, and applying effective weatherstripping to exterior doors, minimizes heat loss and prevents drafts. This not only improves comfort levels in the entryway but also reduces energy consumption and lowers utility costs.
In summary, proper insulation and weatherstripping are essential strategies for designing the entry floor plan in a house located in a cold climate. By focusing on these measures, you can create a well-insulated and sealed entryway that minimizes heat loss, energy consumption, and drafts. This ensures thermal comfort and contributes to the overall energy efficiency of the house.
Considering Airlock Entry Designs
In cold climate house design, one effective strategy for the entry floor plan is to consider incorporating an airlock entry design. Also known as vestibules or enclosed porches, airlock entry designs create an additional barrier between the exterior and interior spaces, which helps to improve energy efficiency, reduce drafts, and enhance thermal comfort.
An airlock entry functions as a buffer zone between the outdoors and the main living areas of the house. It consists of two doors with a small enclosed space in between. This design prevents direct exposure of the interior to the outdoor elements, such as cold air, wind, and drafts.
The airlock entry design offers several advantages in cold climate house design:
Improved Energy Efficiency: By incorporating an airlock entry, heat loss from the main living areas of the house is minimized. The enclosed space acts as an insulating layer, preventing the direct infiltration of cold air into the house when the outer door is opened. This reduces the workload on the heating system and helps to maintain a more stable indoor temperature.
Draft Reduction: Airlock entry designs effectively reduce drafts, as there is an extra layer of protection against the outdoor elements. When the outer door is closed, the enclosed space helps to trap cold air, preventing it from directly reaching the interior of the house. This creates a more comfortable and draft-free entryway for occupants and reduces the likelihood of cold air entering the living areas of the house.
Additional Insulation: The enclosed space in an airlock entry design provides an opportunity for additional insulation. By insulating the walls, floor, and ceiling of the airlock space, thermal transfer between the outdoors and the interior can be further minimized. This extra layer of insulation contributes to improved energy efficiency and thermal comfort.
Enhanced Convenience: Airlock entries provide a convenient place for occupants to transition between the outdoors and the interior. It allows for the removal of outdoor clothing and gear before entering the main living areas, preventing dirt, snow, and moisture from being tracked inside. The extra space also provides storage options for coats, boots, and other winter accessories, keeping them organized and easily accessible.
When designing an airlock entry, consider the specific climate and space limitations. If space is limited, a small vestibule or enclosed porch can still provide benefits by creating a buffer zone. Insulate the walls, floor, and ceiling of the airlock space with high-quality insulation materials to maximize thermal comfort and energy efficiency.
Additionally, the design of the airlock entry should ensure proper sealing and weatherstripping around the doors to prevent drafts. This includes using door sweeps or weatherstripping materials to seal the bottom of the doors and ensuring a tight fit when closed. Proper insulation and sealing materials will improve the overall effectiveness of the airlock entry design.
Incorporating an airlock entry design into the entry floor plan of a house in a cold climate offers multiple benefits, including improved energy efficiency, reduced drafts, and enhanced convenience. By creating a buffer zone and providing an additional layer of insulation, the airlock entry helps to maintain a comfortable and energy-efficient transition space between the outdoors and the interior of the house.
Orientation and Placement of Entryways
In cold climate house design, careful consideration of the orientation and placement of entryways is crucial. The strategic positioning and alignment of entryways can maximize passive solar heating, minimize exposure to prevailing winds, and ultimately enhance the energy efficiency and thermal comfort of the entry floor plan.
South-Facing Entryways: Orienting entryways towards the south can harness the sun’s heat during the winter months in cold climates. South-facing entryways receive the most sunlight throughout the day, allowing for natural warming of the entry floor plan. This passive solar heating can help reduce the reliance on artificial heating systems, lowering energy consumption and costs. To optimize the benefits, consider using large windows or glazed doors that allow for maximum sunlight penetration.
Sheltered Entryways: When positioning entryways, it is important to consider the prevailing winds in the area. If possible, place entryways on the leeward side of the house, sheltered from the strongest winds. This orientation helps minimize the impact of cold drafts entering the house when doors are opened. Creating natural windbreaks with landscaping or architectural features, such as walls or overhangs, can further enhance the protection against wind infiltration.
Separate Service Entryways: In some cases, it may be beneficial to have separate service entryways in addition to the main entryway. Service entryways are typically used for utility access, deliveries, or bringing in supplies, and can be designed for functionality rather than aesthetics. Separating these entries helps to minimize air exchange and heat loss during routine household activities, such as unloading groceries or taking out the trash.
Avoiding Direct Paths to Living Spaces: When designing the entry floor plan, it is advisable to avoid direct paths from entryways to main living areas. This helps to prevent cold air from spreading throughout the house. Instead, consider designing a separate transitional space, such as a foyer or hallway, that acts as a buffer zone between the entryway and the main living spaces. This can help maintain comfort levels and prevent drafts from affecting the rest of the house.
Proper Air Sealing: Regardless of the orientation and placement of entryways, proper air sealing is essential. Ensure that the doors, windows, and frames are properly sealed to prevent air leaks and drafts. Weatherstripping should be applied to create a tight seal around the edges of doors and windows. Insulation should be correctly installed to prevent heat loss and infiltration of cold air. Regular maintenance and inspection of seals and weatherstripping is required to ensure their effectiveness over time.
By carefully considering the orientation and placement of entryways, you can optimize passive solar heating, minimize exposure to cold winds, and create a more energy-efficient and comfortable entry floor plan in a cold climate. These strategic design choices enhance the overall performance of the house, reduce energy consumption, and contribute to a more sustainable living environment.
Read more: What Is An Open Floor Plan
Utilizing Passive Solar Design Principles
In cold climate house design, utilizing passive solar design principles in the entry floor plan can significantly contribute to energy efficiency and thermal comfort. Passive solar design harnesses the power of the sun’s natural heat and light to warm the space and reduce the reliance on artificial heating systems. Incorporating these principles into the entry floor plan can enhance the overall sustainability and comfort of the house.
Orientation and Window Placement: Proper orientation and placement of windows in the entry floor plan play a critical role in passive solar design. South-facing windows allow for maximum sunlight penetration and heat gain during the winter months, when the sun is lower in the sky. This can help warm the entryway naturally, reducing the need for additional heating. Additionally, consider using high-performance glazing or double-glazed windows that have low emissivity coatings to minimize heat loss.
Thermal Mass: Incorporating thermal mass elements in the entry floor plan helps to absorb, store, and release heat over time. Materials such as concrete, stone, or tile have high thermal mass properties and can retain and slowly release heat. By incorporating these materials in the walls, floor, or even as interior finishes in the entryway, the space can act as a heat sink, absorbing the sun’s warmth during the day and radiating it back into the space at night.
Overhangs and Shading: Properly designed overhangs or shading devices can help control the amount of direct sunlight entering the entry floor plan, especially during the warmer months. These features prevent overheating while still allowing sunlight penetration during the colder months when the sun is lower in the sky. Adjustable shading systems, such as awnings or blinds, can provide flexibility in managing solar heat gain throughout the year.
Natural Ventilation: Passive solar design also considers natural ventilation and the movement of air within the entry floor plan. Windows or vents strategically placed in the entryway can facilitate airflow, allowing for the release of warm air during hot periods and the introduction of fresh air when needed. This helps maintain comfort levels and supports indoor air quality.
Insulation and Air Sealing: Effective insulation and air sealing are critical components of passive solar design. A well-insulated entry floor plan reduces heat loss and prevents the infiltration of cold air. Insulate walls, floors, and ceilings with high-quality insulation materials to create a thermal barrier that minimizes heat transfer. Properly seal any gaps or cracks to eliminate drafts and air leaks, ensuring optimal energy efficiency.
By incorporating passive solar design principles into the entry floor plan, you can harness the natural energy of the sun, reduce energy consumption, and enhance thermal comfort in a cold climate. Utilizing proper window placement, maximizing thermal mass, controlling shading, promoting natural ventilation, and ensuring insulation and air sealing contribute to a more sustainable and energy-efficient entryway.
It is important to note that passive solar design should be tailored to the specific climate and site conditions. Consulting with an architect or design professional experienced in cold climate design can ensure that the passive solar principles are applied effectively and appropriately to maximize their benefits within the entry floor plan.
Incorporating Vestibules
Incorporating vestibules into the entry floor plan of a house in a cold climate is a practical design strategy that can enhance energy efficiency, reduce drafts, and provide additional insulation. Vestibules, also known as entryway extensions or enclosed porches, serve as an extra transitional space between the outdoors and the interior of the house. They offer several benefits in terms of thermal comfort, energy conservation, and protection against the elements.
Insulation and Air Sealing: Vestibules provide an additional layer of insulation and air sealing for the entry floor plan. The enclosed space acts as a buffer, preventing direct contact between the exterior and interior temperatures. When properly insulated and sealed, vestibules minimize heat loss, reduce drafts, and contribute to maintaining a comfortable indoor environment.
Minimize Heat Infiltration: Vestibules help in reducing heat infiltration into the main living areas of the house. When an exterior door is opened, the enclosed space acts as a barrier, preventing cold air from directly entering the house. This reduces the amount of warm air escaping and the potential for drafts, resulting in energy savings and increased thermal efficiency.
Extra Storage Space: Incorporating a vestibule provides an additional area for storage. Coats, boots, umbrellas, and other outdoor gear can be stored in the vestibule, preventing them from cluttering the main living areas. This not only improves organization but also minimizes the tracking of dirt and moisture into the rest of the house.
Mudroom Combination: A vestibule can be combined with a mudroom design, offering a functional space for removing and storing winter gear. This combination provides an efficient and well-organized zone for transitioning from the outdoors, removing wet or dirty items, and keeping the main living areas clean.
Enhanced Security: Vestibules can provide an added layer of security for the house. When the exterior door is closed, the vestibule acts as a second barrier against potential intruders. This added security can contribute to peace of mind and a sense of safety for residents.
Aesthetic Appeal: Vestibules can enhance the overall aesthetic appeal of the entry floor plan. They can be designed to match the architectural style of the house, adding character and visual interest to the facade. Materials, colors, and finishes can be selected to create a welcoming and aesthetically pleasing entryway for residents and visitors.
When incorporating vestibules into the entry floor plan, it is important to consider the appropriate size and configuration based on the available space and specific needs of the household. The vestibule should be designed to accommodate the desired functionalities, such as storage, seating, or a dedicated mudroom area.
Proper insulation, weatherstripping, and ventilation should be considered when designing vestibules to maintain energy efficiency and indoor air quality. Insulating the walls, floor, and ceiling of the vestibule, and ensuring adequate weatherstripping around doors and windows, will help minimize heat loss and drafts. Proper ventilation through operable windows or vents is important for air circulation and maintaining a healthy indoor environment.
Incorporating vestibules into the entry floor plan of a house in a cold climate offers numerous benefits, including energy efficiency, draft reduction, extra storage space, enhanced security, and aesthetic appeal. By creating an additional insulated space, vestibules contribute to the overall comfort, functionality, and energy efficiency of the house.
Conclusion
Designing the entry floor plan for a house in a cold climate requires careful consideration, strategic planning, and an understanding of the unique challenges posed by the harsh weather conditions. The entryway serves as the gateway between the outdoors and the interior, playing a vital role in maintaining comfort, energy efficiency, and protection against the elements.
Throughout this article, we have explored various strategies for designing an efficient and functional entry floor plan in a cold climate. Providing adequate entryway space, incorporating mudrooms, using proper insulation and weatherstripping, considering airlock entry designs, and optimizing the orientation and placement of entryways are all important strategies to enhance the entryway’s performance in a cold climate.
The entry floor plan is not only functional but also sets the tone for the rest of the house. It serves as the first impression of the home, welcoming guests and providing a glimpse into the overall design aesthetic. By incorporating design elements that align with the overall style and incorporating features such as storage, seating, and transitional zones, the entryway becomes a practical and attractive space.
In a cold climate, where winters can be long and frigid, attention to insulation, weatherstripping, and energy efficiency measures is vital. The entryway must be properly insulated, the doors and windows sealed effectively, and drafts minimized to prevent heat loss and maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. Incorporating features like passive solar design principles, vestibules, and mudrooms further enhance energy efficiency and thermal comfort.
By implementing these strategies and design considerations, a well-designed entry floor plan can create a welcoming, functional, and energy-efficient space in a cold climate. An efficient entryway helps to maintain thermal comfort, prevent drafts and heat loss, and organize winter gear and clothing, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable and enjoyable living environment.
In conclusion, designing the entry floor plan for a cold climate requires a comprehensive approach that integrates architectural design principles, energy efficiency strategies, and a focus on functionality. With careful planning, proper insulation, weatherstripping, and attention to detail, the entry floor plan can become a standout feature in a house that not only withstands the challenges of a cold climate but provides a warm and inviting welcome to all who enter.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Strategies In House Design For Cold Climate Entry Floor Plan
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.







0 thoughts on “What Strategies In House Design For Cold Climate Entry Floor Plan”