Home>diy>Planning & Engineering>What Does R2 Zoning Mean

Planning & Engineering
What Does R2 Zoning Mean
Modified: December 7, 2023
Learn the meaning of R2 zoning and its implications for planning and engineering. Discover how this zoning classification influences property use and development.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Welcome to the world of zoning regulations, where planning and engineering come together to shape the built environment. If you’re a homeowner or a potential buyer, understanding zoning codes can be essential in making informed decisions about your property. One common type of zoning is R2 zoning – but what exactly does R2 zoning mean?
R2 zoning is a designation that is used by local governments to regulate land use within specific areas or districts. It determines the type of buildings and activities that are allowed on a property. In this article, we will explore the definition of R2 zoning, its purpose, the restrictions and regulations it imposes, the permitted uses, and we’ll even touch on how it can impact property values.
So, let’s dive in and unravel the mystery of R2 zoning.
Key Takeaways:
- R2 zoning regulates residential land use, promoting neighborhood stability and preserving property values. It balances density, aesthetics, and community well-being to shape harmonious residential environments.
- Understanding R2 zoning’s purpose, regulations, and impact on property values is crucial for homeowners, buyers, and developers. It shapes neighborhoods, maintains character, and influences desirability and marketability.
Read more: What Does Zoning R Mean
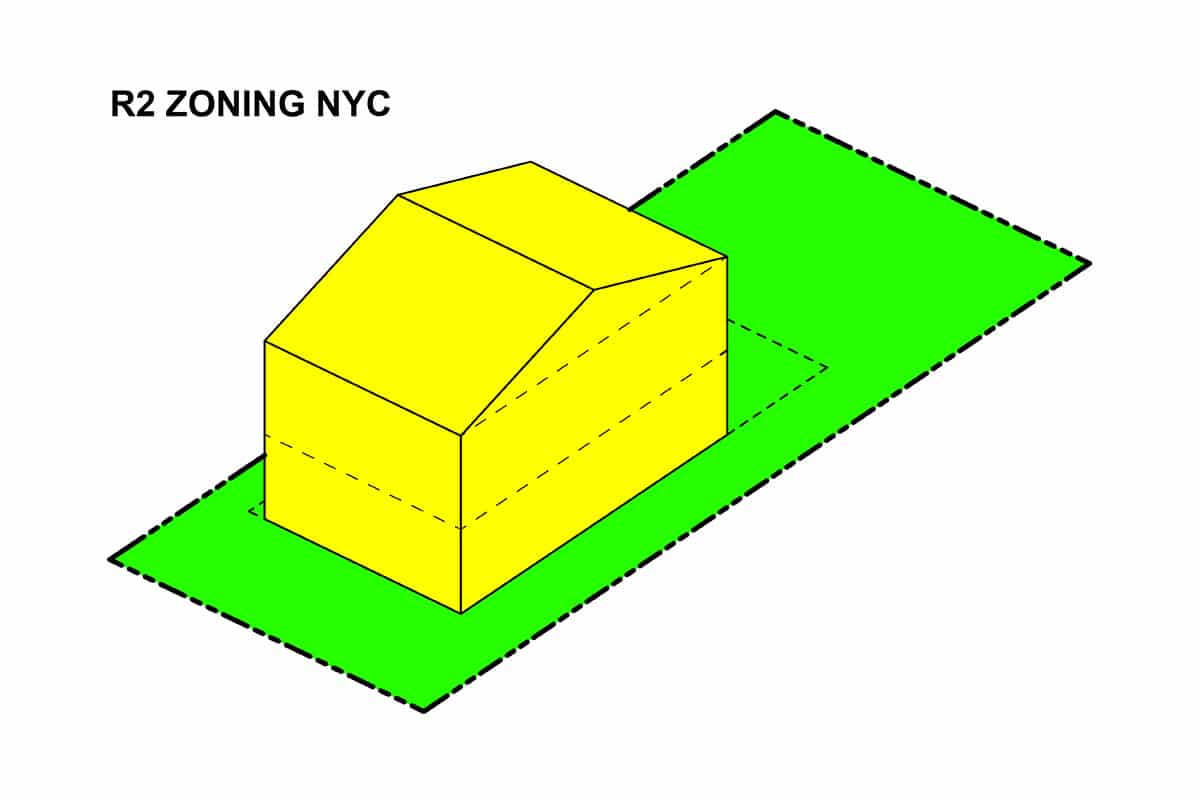
Definition of R2 Zoning
R2 zoning is a specific zoning classification that is commonly used in urban and suburban areas. It is intended to regulate residential land use and determine the density of housing units in a particular district. R2 zoning typically allows for the construction of single-family homes, duplexes, and sometimes multi-family dwellings such as townhouses or apartment buildings.
The “R” in R2 zoning stands for “residential,” indicating that the primary purpose of the zone is to provide areas for housing and limit commercial or industrial activities. This zoning designation helps maintain the character of neighborhoods, ensure compatibility with surrounding properties, and manage urban growth.
R2 zoning often comes with specific requirements regarding setbacks, lot size, building height, and other parameters. These regulations are put in place to maintain the desired aesthetic, preserve green spaces, and ensure the safety and functionality of the neighborhood.
It’s important to note that R2 zoning varies from city to city and can even vary within different districts of the same city. Therefore, it’s crucial to consult the specific zoning ordinances and regulations of your local jurisdiction to understand the precise requirements and restrictions imposed by R2 zoning.
Now that we have a clear understanding of what R2 zoning is, let’s explore its purpose and objectives.
Purpose of R2 Zoning
The purpose of R2 zoning is to carefully plan and manage residential development within a community. By designating certain areas as R2 zones, local governments can establish guidelines that encourage compatible and cohesive neighborhoods, while also ensuring appropriate land use and density.
One of the primary goals of R2 zoning is to promote a healthy balance between residential housing and other land uses. This helps to preserve the quality of life for residents by minimizing the negative impacts that may arise from incompatible land uses. It also helps to create a sense of community and identity within neighborhoods.
R2 zoning also plays a role in managing urban growth and controlling population density. By setting specific requirements for setbacks, lot sizes, and building heights, R2 zoning limits the number of housing units that can be built on a given piece of land. This ensures that the infrastructure and services in the area can adequately support the population without strain.
Another key purpose of R2 zoning is to protect property values. By establishing guidelines for property use and appearance, R2 zoning helps to maintain the character and aesthetic appeal of residential neighborhoods. It also limits the potential for disruptive or incompatible activities that could negatively impact property values.
R2 zoning may also include provisions for the protection of natural resources, such as green spaces and trees. By requiring setbacks and open space requirements, R2 zoning encourages the preservation of natural elements within the community, promoting sustainability and environmental awareness.
Overall, the purpose of R2 zoning is to create harmonious and sustainable residential neighborhoods that contribute to the well-being and satisfaction of residents. By carefully regulating land use, R2 zoning helps to shape communities that are aesthetically pleasing, functional, and conducive to a high quality of life.
Now that we understand the purpose of R2 zoning, let’s delve into the restrictions and regulations associated with this zoning designation.
Restrictions and Regulations of R2 Zoning
R2 zoning comes with a set of restrictions and regulations that govern the use and development of properties within the designated areas. These regulations are put in place to maintain the integrity of the neighborhood, ensure compatibility among properties, and protect the interests of both residents and the community as a whole.
One of the key restrictions of R2 zoning is the limitation on the types of buildings allowed. Generally, R2 zoning permits the construction of single-family homes, duplexes, and sometimes multi-family dwellings such as townhouses or apartment buildings. These regulations aim to maintain the primarily residential character of the area and prevent the intrusion of commercial or industrial uses.
R2 zoning often imposes requirements regarding setbacks, which are the distances between a property’s boundaries and the location where buildings can be constructed. Setbacks help to create space between buildings, maintain privacy, and preserve green areas. The specific setback requirements can vary depending on the local zoning ordinances, but they typically ensure adequate spacing between structures and prevent buildings from encroaching on neighboring properties.
Other regulations may include restrictions on building heights to maintain a consistent skyline appearance, minimum lot sizes to prevent overcrowding, and provisions for parking spaces to ensure sufficient parking for residents and visitors. In some cases, R2 zoning may also regulate the use of land for amenities such as parks, playgrounds, or community facilities.
In addition to these general regulations, R2 zoning may also include specific guidelines for architectural design and materials to maintain a cohesive aesthetic within the neighborhood. These guidelines help create a visually appealing and harmonious environment.
It’s crucial for property owners and developers to familiarize themselves with the specific restrictions and regulations outlined in their local jurisdiction’s zoning ordinances. Violations of these regulations can result in penalties or the need for costly modifications to bring a property into compliance.
Now that we’ve covered the restrictions and regulations of R2 zoning, let’s discuss the permissible uses within R2 zoning.
Permitted Uses in R2 Zoning
R2 zoning allows for a variety of residential uses, each with its own specific requirements and limitations. While the exact permitted uses can vary depending on local zoning regulations, there are common types of housing that are typically allowed within R2 zoning areas.
One of the primary uses allowed in R2 zoning is the construction of single-family homes. These are standalone houses designed to accommodate one family. Single-family homes provide a sense of privacy and independence for residents and are often the most prevalent housing type within R2 zones.
Another common use within R2 zoning is the construction of duplexes. A duplex is a building that contains two separate housing units, each with its own entrance. These units can be side-by-side or stacked on top of each other. Duplexes allow for increased housing density while still maintaining the feel of a residential neighborhood.
Depending on the specific zoning regulations, R2 zoning may also permit the construction of multi-family dwellings such as townhouses or apartment buildings. Townhouses are typically multi-level structures attached to one another, while apartment buildings contain multiple units in a single building. These types of housing provide a higher density of housing units within the R2 zone.
R2 zoning may also allow for certain accessory uses or structures, such as home offices, accessory dwelling units (ADUs), or garages. These accessory structures must typically meet specific guidelines and be secondary to the primary residential use of the property.
It’s important to note that while R2 zoning primarily focuses on residential uses, there may be certain limited non-residential uses allowed within the zoning designation. This can include home-based businesses, certain community services, or other uses that are compatible with the residential character of the area.
It’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the exact permitted uses outlined in your local zoning ordinances. These regulations will provide you with detailed information on what types of residential structures are allowed within the R2 zone and any additional requirements or restrictions that may apply.
Now that we’ve covered the permitted uses within R2 zoning, let’s explore some examples of R2 zoning requirements.
Read more: What Does R20 Zoning Mean
Examples of R2 Zoning Requirements
R2 zoning comes with specific requirements that property owners must adhere to when developing or renovating their properties. While the exact requirements can vary depending on local zoning ordinances, here are some common examples of R2 zoning requirements:
- Lot Size: R2 zoning often specifies a minimum lot size requirement for properties within the zone. This requirement helps to ensure that there is sufficient space for residential structures and amenities within the designated area.
- Setbacks: Setbacks determine the distance between a property’s boundaries and the location where buildings can be constructed. R2 zoning typically imposes setbacks to maintain privacy, create spacing between structures, and preserve green areas. For example, the zoning regulations may require a minimum setback of 20 feet from the front property line and 10 feet from the side and rear property lines.
- Building Height: R2 zoning may restrict the maximum height of buildings within the zone to maintain a consistent skyline and ensure compatibility with neighboring structures. For instance, the regulations may limit building heights to two or three stories.
- Parking Requirements: R2 zoning often includes parking requirements to ensure that there is sufficient parking space for residents and visitors. The regulations may specify the number of off-street parking spaces required per unit or per square footage of residential floor area.
- Architectural Design: R2 zoning may have guidelines for architectural design and materials to ensure a cohesive and aesthetically pleasing neighborhood. These guidelines can include restrictions on exterior colors, façade materials, roof type, and other design elements.
- Additional Amenities: Some R2 zoning requirements may call for the inclusion of specific amenities within the development. This can include provisions for parks, playgrounds, green spaces, or community facilities. These amenities contribute to the quality of life within the neighborhood.
It’s important to note that these examples are general in nature, and the specific requirements for R2 zoning can vary depending on the jurisdiction. It’s essential to consult the local zoning ordinances for precise details on the requirements that apply to your property.
Now that we’ve explored examples of R2 zoning requirements, let’s consider the pros and cons of R2 zoning.
Pros and Cons of R2 Zoning
R2 zoning, like any zoning classification, comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding the pros and cons can help property owners and potential buyers make informed decisions. Let’s explore them:
Pros of R2 Zoning:
- Preservation of Residential Character: R2 zoning helps to maintain the primarily residential character of the neighborhood, ensuring that it remains a peaceful and desirable place to live.
- Compatibility and Aesthetics: R2 zoning guidelines and regulations ensure that new developments or renovations are in harmony with the existing structures, preserving the overall aesthetic appeal of the neighborhood.
- Controlled Density and Urban Growth: R2 zoning allows for a controlled density of housing units, preventing overcrowding and ensuring that the infrastructure and services in the area can adequately support the population.
- Protection of Property Values: By maintaining strict regulations on property use and appearance, R2 zoning helps to protect property values within the neighborhood and prevent incompatible uses that could lower property values.
- Promotion of Green Spaces: R2 zoning often includes requirements for setbacks and open spaces, preserving green areas and promoting sustainable development practices.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: R2 zoning aims to create a cohesive and well-designed community, fostering a sense of pride and satisfaction among residents.
Cons of R2 Zoning:
- Restricted Property Use: R2 zoning limits the types of buildings and activities allowed within the designated areas, which can restrict flexibility for property owners and potential developers.
- Potential for Increased Housing Costs: The controlled density and strict regulations of R2 zoning can result in higher housing costs due to limited supply and increased demand.
- Neighborhood Uniformity: While R2 zoning ensures a consistent aesthetic, it can also lead to a lack of architectural diversity and individuality within the neighborhood.
- Challenges for Small-scale Developers: The specific requirements and regulations of R2 zoning can pose challenges for small-scale developers who may face financial and logistical hurdles in meeting the zoning requirements.
- Potential for Inefficient Land Use: R2 zoning often emphasizes single-family homes or low-density housing, which can result in inefficient land use, especially in areas with high housing demand.
It’s important to consider these pros and cons in the context of your specific situation and goals. Consulting with local zoning officials and professionals can provide further clarity and guidance.
Now that we’ve examined the pros and cons, let’s explore how R2 zoning can affect property values.
Read more: What Does R30 Zoning Mean
How R2 Zoning Affects Property Value
R2 zoning can have a significant impact on property values within a neighborhood. The zoning regulations and restrictions imposed in R2 zones can influence the desirability and marketability of properties, which ultimately affects their value. Let’s explore how R2 zoning affects property value:
1. Stability and Neighborhood Character:
The existence of R2 zoning in a neighborhood can promote stability and maintain the residential character of the area. This can contribute to a sense of community, enhanced quality of life, and a perception of a safe and comfortable environment. These factors often lead to increased property values as buyers are willing to pay a premium for homes in well-regulated and attractive neighborhoods.
2. Compatibility and Aesthetics:
R2 zoning ensures that new developments and renovations within the neighborhood are compatible with the existing structures, creating a cohesive and visually appealing environment. This consistency in architectural styles and design elements enhances the overall aesthetics of the area, making it more desirable for potential buyers. As a result, properties in R2 zones may experience increased demand and higher property values.
3. Limited Commercial and Industrial Intrusion:
R2 zoning aims to protect the primarily residential character of a neighborhood by limiting commercial and industrial activities. This helps to maintain the peaceful ambiance and preserve property values. Residents are often willing to pay a premium for homes in areas free from noise, traffic, and potential disruptions associated with non-residential land uses.
Read more: What Does R4 Zoning Mean
4. Controlled Density and Infrastructure Demand:
R2 zoning regulates the density of housing units and ensures that the infrastructure and services in the area can adequately support the population. Controlled density can prevent overcrowding and strain on resources, leading to a better quality of life for residents. This, in turn, can positively impact property values as buyers are willing to invest in areas where infrastructure needs are well-maintained.
5. Potential Challenges for Developers and Investors:
R2 zoning can pose challenges for developers and investors due to the specific requirements and regulations. Meeting these requirements may entail additional costs and restraints on property development, which can affect marketability and potential returns on investment. These challenges can indirectly impact property values by limiting the number of available housing options and potential development opportunities.
Overall, R2 zoning can have a positive impact on property values by promoting neighborhood stability, maintaining aesthetic appeal, and preserving the residential character of an area. However, it’s important to note that property values are influenced by various factors, such as location, market conditions, and other external factors, in addition to the zoning regulations.
Now that we understand how R2 zoning can affect property values, let’s conclude our exploration of this zoning classification.
R2 zoning typically allows for single-family and two-family residential properties. Check with your local zoning office for specific regulations and restrictions in your area.
Conclusion
In conclusion, R2 zoning plays a crucial role in shaping residential neighborhoods and managing land use within urban and suburban areas. By designating specific areas as R2 zones, local governments can regulate the type of buildings, density, and overall character of the neighborhood.
Throughout this article, we have explored the definition of R2 zoning, its purpose, the restrictions and regulations it imposes, the permitted uses, and how it can impact property values. R2 zoning is primarily focused on residential land use, allowing for single-family homes, duplexes, and sometimes multi-family dwellings within the designated areas.
The purpose of R2 zoning is to create harmonious and sustainable residential neighborhoods that contribute to the well-being and satisfaction of residents. Through regulations on setbacks, building heights, parking requirements, and architectural design, R2 zoning aims to preserve the character, compatibility, and quality of life within the community.
R2 zoning has both pros and cons. It helps maintain neighborhood stability, enhances aesthetics, and limits commercial and industrial intrusion. However, it can also restrict property use and pose challenges for developers and investors. Additionally, R2 zoning can have a positive impact on property values by promoting neighborhood desirability and maintaining a residential environment.
It’s important for property owners, buyers, and developers to familiarize themselves with the specific requirements and regulations of R2 zoning in their local jurisdiction. Understanding the zoning ordinances and consulting with local zoning officials can provide valuable guidance when developing, renovating, or purchasing property within an R2 zone.
In the end, R2 zoning serves as a mechanism to create and maintain well-planned residential communities. By striking the right balance between regulation and flexibility, R2 zoning helps to shape neighborhoods that provide a high quality of life, preserve property values, and create a sense of belonging for residents.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of R2 zoning and its impact. As always, it’s essential to consult with professionals and local authorities for specific advice and guidance tailored to your unique situation.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Does R2 Zoning Mean
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.









0 thoughts on “What Does R2 Zoning Mean”