Home>Furniture>How Long Does It Take For A Lava Lamp To Heat Up?


Furniture
How Long Does It Take For A Lava Lamp To Heat Up?
Modified: May 6, 2024
Discover the average time it takes for a lava lamp to heat up and add a stylish touch to your furniture with this quirky and mesmerizing home decor piece.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
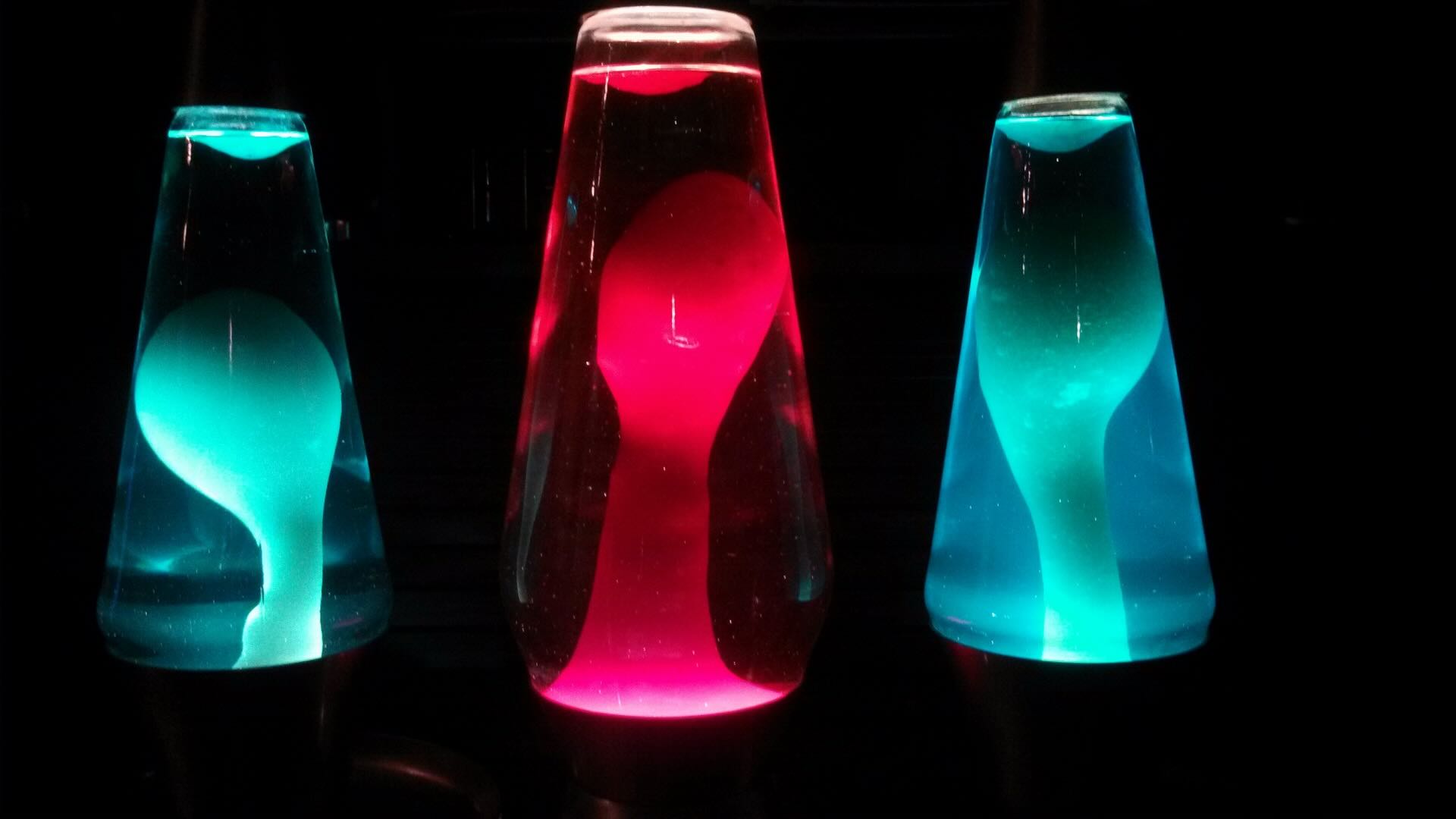
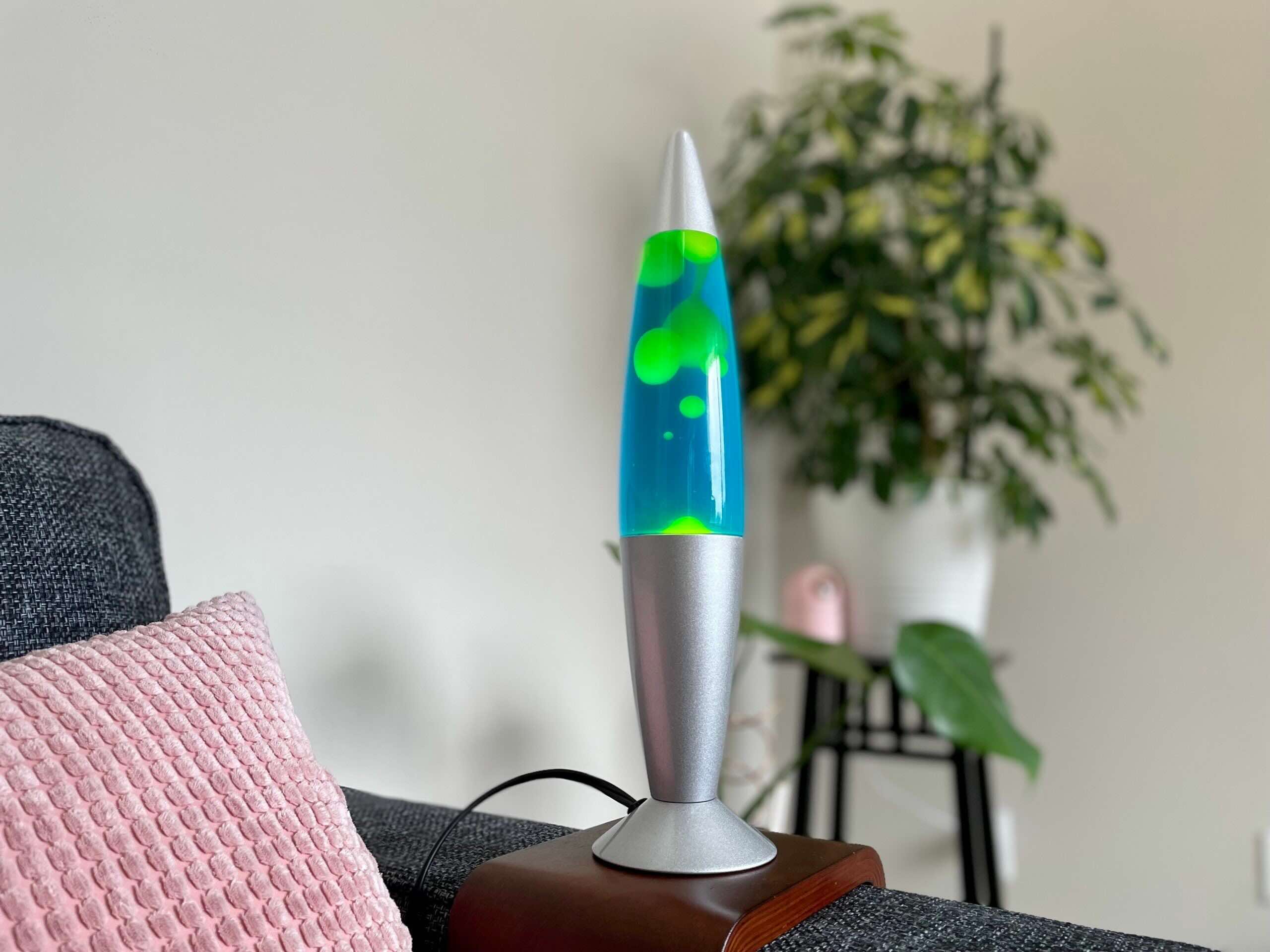
Lava lamps are not just decorative pieces; they are mesmerizing works of art that can transform the ambiance of any room. The swirling blobs of colored wax gracefully moving up and down create a soothing and hypnotic effect. It’s no wonder that lava lamps have become a popular accessory for homes, offices, and even restaurants.
Have you ever wondered how long it takes for a lava lamp to heat up? The heating time of a lava lamp can vary depending on various factors, such as the size of the lamp, the type of bulb used, and the surrounding temperature. Understanding these factors can help you determine the optimal time to turn on your lava lamp and enjoy its mesmerizing display.
In this article, we will explore the science behind lava lamps, the factors that affect their heating time, typical heating times for different sizes of lava lamps, and provide some tips to reduce the heating time. So, let’s dive in and uncover the secrets of lava lamp heating!
Key Takeaways:
- Embrace the mesmerizing flow of a lava lamp by understanding its heating time factors, such as lamp size, initial temperature, bulb wattage, and surrounding temperature. Patience is key for larger lamps, but pre-warming and higher wattage bulbs can expedite the process.
- Keep the anticipation alive as you await the captivating display of a lava lamp. Reduce heating time by pre-warming the lamp, choosing a higher wattage bulb, maintaining a suitable room temperature, and ensuring regular maintenance. Enjoy the soothing flow of lava with these tips in mind.
The Science Behind Lava Lamps
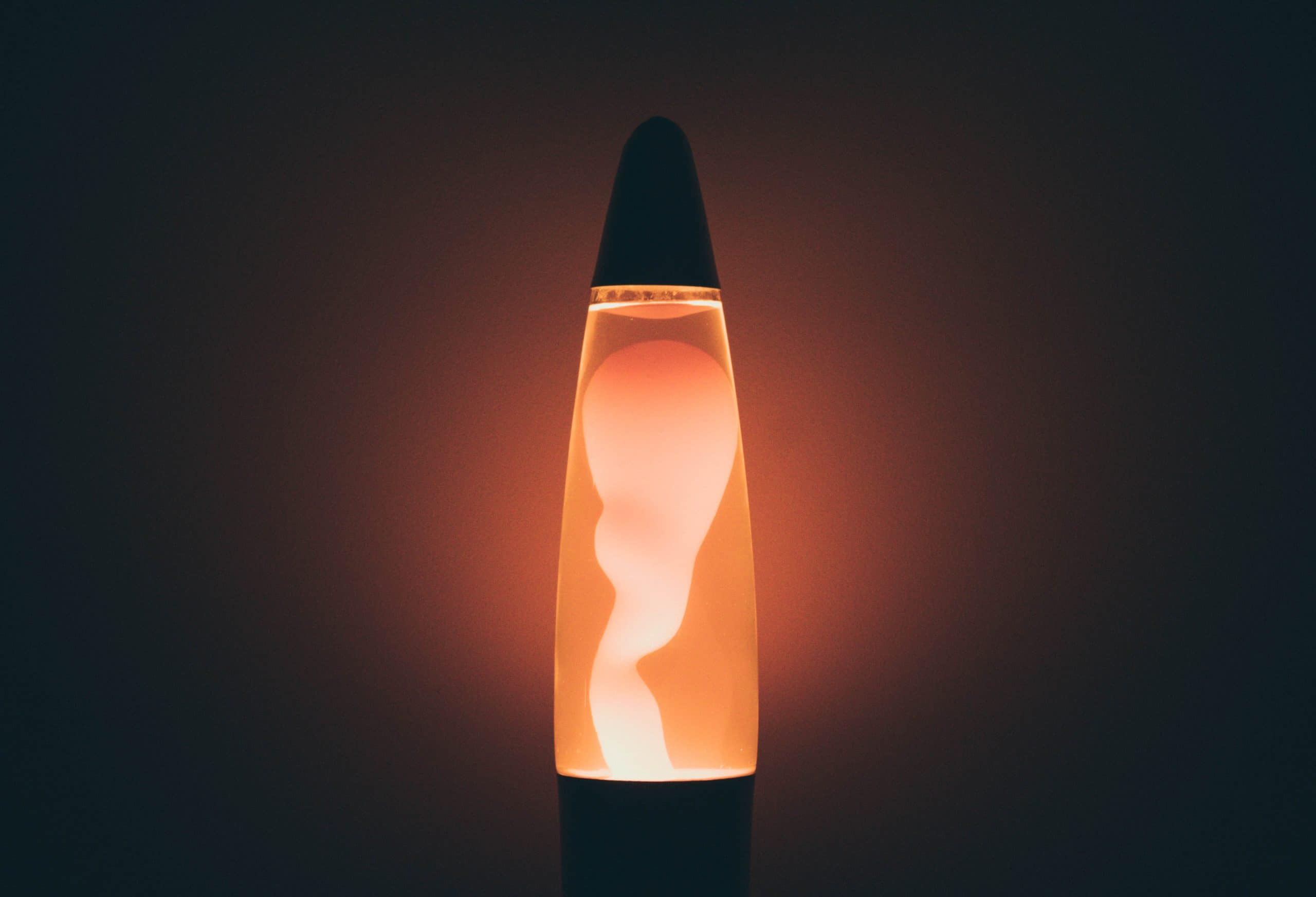
Lava lamps operate on a simple yet fascinating principle. The lamp consists of a glass container filled with a special type of wax and a clear liquid, often water or a mineral oil. Inside the container, there is also a heat source, usually a light bulb placed at the base. When you turn on the lamp, the heat from the bulb causes the wax to melt and rise to the top of the container.
The wax, once heated, becomes less dense than the liquid and starts floating to the top. As it reaches the top, it cools down and becomes denser, causing it to sink back down. This continuous cycle of melting, rising, cooling, and sinking creates the mesmerizing movement and patterns we associate with lava lamps.
The key components of a lava lamp are the wax and the liquid. The wax is typically a combination of paraffin or mineral oil, along with colored dyes to give it the vibrant hues. The liquid, usually water or mineral oil, acts as a medium for the wax to move through. The specific densities of the wax and liquid, along with their interaction with heat, determine the flow characteristics and patterns of the lava lamp.
The heat source, typically a light bulb, plays a crucial role in the heating process. The bulb provides the necessary heat to melt the wax and initiate the rising and sinking motion. The wattage of the bulb affects the heating time, with higher wattage bulbs generating more heat and thus heating up the lamp faster.
Now that we have a basic understanding of the science behind lava lamps, let’s explore the factors that can influence their heating time.
Key Takeaways:
- Embrace the mesmerizing flow of a lava lamp by understanding its heating time factors, such as lamp size, initial temperature, bulb wattage, and surrounding temperature. Patience is key for larger lamps, but pre-warming and higher wattage bulbs can expedite the process.
- Keep the anticipation alive as you await the captivating display of a lava lamp. Reduce heating time by pre-warming the lamp, choosing a higher wattage bulb, maintaining a suitable room temperature, and ensuring regular maintenance. Enjoy the soothing flow of lava with these tips in mind.
The Science Behind Lava Lamps
– Principles of Operation
Lava lamps operate on a fascinating principle that combines heat, density, and fluid dynamics to create their mesmerizing motion. The key to understanding their operation lies in the relationship between the wax, liquid, and heat source.
When you turn on a lava lamp, the heat from the bulb begins to warm up the wax. As the wax heats up, it begins to melt and form blobs. These melted blobs of wax have a lower density than the surrounding liquid, causing them to rise to the top of the lamp.
Once at the top, the wax blobs cool down due to the air temperature, causing them to become denser. The denser wax then sinks back down to the bottom of the lamp. This continuous cycle of melting, rising, cooling, and sinking creates the flowing and swirling motion that is characteristic of lava lamps.
The principle of the lava lamp relies on the fact that the wax and liquid have different densities. The wax is carefully formulated to have a density slightly lower than that of the liquid. This density difference allows the wax to rise and fall within the lamp, creating the beautiful cascading effect.
The movement of the wax is also influenced by fluid dynamics. As the wax rises, it creates a current within the liquid. This current disrupts the surrounding liquid, causing it to move and create the swirling patterns that we observe in lava lamps.
It’s important to note that the viscosity of the liquid also plays a role in the operation of lava lamps. The viscosity affects the speed at which the wax rises and falls. A higher viscosity liquid will result in slower movement, while a lower viscosity liquid will allow for faster and more active motion.
The principles of operation behind lava lamps are a combination of heat, density, and fluid dynamics. Understanding these principles allows us to appreciate the captivating and hypnotic motion that lava lamps create.
Key Takeaways:
- Embrace the mesmerizing flow of a lava lamp by understanding its heating time factors, such as lamp size, initial temperature, bulb wattage, and surrounding temperature. Patience is key for larger lamps, but pre-warming and higher wattage bulbs can expedite the process.
- Keep the anticipation alive as you await the captivating display of a lava lamp. Reduce heating time by pre-warming the lamp, choosing a higher wattage bulb, maintaining a suitable room temperature, and ensuring regular maintenance. Enjoy the soothing flow of lava with these tips in mind.
The Science Behind Lava Lamps
– Components and Materials
A lava lamp consists of several key components, each playing a crucial role in its functionality and visual appeal. Let’s take a closer look at the components and materials used in the construction of lava lamps.
1. Glass Container: The outer casing of a lava lamp is typically made of glass. This transparent material allows for the full display of the mesmerizing flow of the wax and liquid inside. The shape and size of the glass container can vary, ranging from cylindrical to spherical designs.
2. Wax: The wax used in lava lamps is specially formulated to have a lower density than the liquid. This allows it to rise and fall within the lamp. The wax is usually a combination of paraffin or mineral oil, along with other additives to give it various colors and visual effects.
3. Liquid: The liquid in a lava lamp serves as the medium through which the wax moves. Common liquids used include water and mineral oil. The choice of liquid depends on factors such as viscosity and compatibility with the wax.
4. Heat Source: The heat source in a lava lamp is typically a light bulb, which is placed at the base of the lamp. The bulb provides the necessary heat to warm up the wax and initiate its movement. The wattage of the bulb can vary, with higher wattage bulbs generating more heat and speeding up the heating process.
5. Cap: The cap or top of the lava lamp holds the light bulb and protects it from external elements. It also helps to direct the heat towards the wax, maximizing the efficiency of the heating process.
6. Base: The base of the lava lamp houses the electrical components and provides stability to the lamp. It often features an on/off switch and may incorporate additional features such as color-changing LEDs or dimming options.
The materials used in lava lamps are carefully selected to ensure safety and functionality. The glass container provides durability and transparency, allowing for an unobstructed view of the lava lamp’s mesmerizing display. The wax and liquid are specially formulated to create the desired flow characteristics, while the heat source and base components ensure proper heating and stability.
Now that we understand the components and materials used in lava lamps, let’s explore the factors that can affect the heating time of these captivating decorative pieces.
Key Takeaways:
- Embrace the mesmerizing flow of a lava lamp by understanding its heating time factors, such as lamp size, initial temperature, bulb wattage, and surrounding temperature. Patience is key for larger lamps, but pre-warming and higher wattage bulbs can expedite the process.
- Keep the anticipation alive as you await the captivating display of a lava lamp. Reduce heating time by pre-warming the lamp, choosing a higher wattage bulb, maintaining a suitable room temperature, and ensuring regular maintenance. Enjoy the soothing flow of lava with these tips in mind.
The Science Behind Lava Lamps
– Heat Sources and Heating Time Factors
The heat source in a lava lamp is a critical component that directly impacts the heating time and overall performance of the lamp. Let’s examine the various factors related to heat sources that can affect the heating time of a lava lamp.
1. Type of Bulb: The type of bulb used as the heat source determines the amount of heat generated. Incandescent bulbs, such as the ones commonly used in lava lamps, emit a significant amount of heat. LED bulbs, on the other hand, generate minimal heat. Therefore, lava lamps equipped with LED bulbs may have longer heating times compared to those with traditional incandescent bulbs.
2. Wattage: The wattage of the bulb is another crucial factor influencing the heating time. Higher wattage bulbs produce more heat, leading to faster heating of the wax. Lower wattage bulbs, on the other hand, generate less heat and may result in longer heating times.
3. Lamp Size: The size of the lava lamp impacts the heating time as well. Larger lamps generally contain more wax and liquid, which requires more time to reach the desired temperature. As a result, larger lava lamps tend to have longer heating times compared to smaller ones.
4. Material of Lamp Base: The material used for the base of the lamp can affect the heating time indirectly. Some materials, such as metal, are better at conducting heat and may help in distributing the heat evenly throughout the lamp. This can result in faster heating times compared to lamps with bases made of materials with poor heat conductivity.
5. Initial Temperature: The starting temperature of the wax and liquid can influence the heating time as well. If the lamp has been stored in a cold environment, it may take longer for the wax to melt and begin its movement. Pre-warming the lamp by placing it in a slightly warmer location can help reduce the heating time.
6. Surrounding Temperature: The ambient temperature of the room also plays a role in the heating time of a lava lamp. If the room is colder, the lamp may take longer to heat up as it has to compensate for the lower temperature. Conversely, in a warmer room, the heating time may be shorter.
It’s important to note that the heating time of a lava lamp can vary based on the combination of these factors. It’s always a good idea to refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for specific guidelines on heating times for your particular lava lamp model.
Now that we have explored the factors affecting the heating time of a lava lamp, let’s dive into typical heating times for different sizes of lamps.
Factors Affecting the Heating Time of a Lava Lamp
Several factors can influence the heating time of a lava lamp. Understanding these factors can help you estimate how long it will take for your lava lamp to reach its optimal temperature. Let’s explore the key factors that affect the heating time:
1. Lamp Size and Design: The size and design of the lava lamp play a significant role in its heating time. Generally, larger lamps contain more wax and liquid, requiring more time to heat up fully. Additionally, lava lamps with intricate designs or shapes that may impede the flow of heat might take longer to heat up compared to more straightforward designs.
2. Initial Temperature of the Lamp: If your lava lamp has been sitting in a colder environment, it will take longer to heat up. Cold wax and liquid will need more time to reach the desired temperature and start flowing properly. To reduce heating time, you can store your lava lamp in a warmer location before turning it on.
3. Type of Bulb and Wattage: The type and wattage of the bulb used in the lava lamp’s heat source directly impact the heating time. Incandescent bulbs emit more heat, allowing the wax to melt faster. On the other hand, LED bulbs produce less heat, resulting in longer heating times. Higher wattage bulbs generally generate more heat, heating up the lamp faster than lower wattage bulbs.
4. Surrounding Temperature: The ambient temperature of the room can affect the heating time of a lava lamp. If the room is colder, it will take longer for the lamp to heat up as it needs to compensate for the lower temperature. Conversely, a warmer room will help the lamp heat up more quickly.
5. Quality of the Lamp: The quality of the lava lamp can influence its heating time. Higher-quality lamps are often designed and constructed to maximize heat distribution and optimize the heating process, resulting in shorter heating times. Cheaper or inferior quality lamps may take longer to warm up due to inefficient heat transfer.
6. Maintenance and Cleaning: Regular maintenance and cleaning can also affect the heating time of a lava lamp. Dust and debris can accumulate on the bulb, inhibiting heat emission and increasing the heating time. Keeping the lamp clean and free from obstructions will ensure efficient heating.
It’s important to note that the actual heating time can vary depending on the combination of these factors. As each lava lamp is unique, it’s recommended to refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for specific guidelines on heating times.
Now that we understand the factors influencing the heating time of a lava lamp, let’s explore the typical heating times for different sizes of lava lamps.
Factors Affecting the Heating Time of a Lava Lamp
– Lamp Size and Design
The size and design of a lava lamp can significantly impact its heating time and overall performance. Let’s delve into how these factors influence the heating process:
1. Size: The size of a lava lamp directly affects its heating time. Larger lamps, with more volume of wax and liquid, generally take longer to heat up compared to smaller lamps. This is because it requires more heat to raise the temperature of a larger quantity of wax and liquid. If you have a small lava lamp, it will typically reach its optimal temperature faster than a larger one.
2. Design: The design of a lava lamp can also play a role in its heating time. Lava lamps come in various shapes and formations, from traditional cylindrical or conical designs to more intricate and unique shapes. Lamps with complex designs that have narrow or twisted sections might impede the flow of heat, resulting in longer heating times. Simple and straightforward designs tend to heat up faster as heat can circulate more freely within the lamp.
3. Surface Area: The surface area of the glass container can affect the heating time of a lava lamp. Lamps with larger and wider surface areas allow for more heat dissipation, accelerating the heating process. Conversely, lamps with smaller surface areas might take longer to reach the optimal temperature as there is less contact with the surrounding air to facilitate heat transfer.
4. Material: The material of the glass container can influence the heating time as well. Different materials have different thermal conductivity properties. For example, glass with higher thermal conductivity will distribute heat more efficiently, resulting in shorter heating times. Conversely, glass with lower thermal conductivity might slightly slow down the heating process.
When considering a lava lamp, it’s essential to be mindful of its size and design to ensure the desired heating time aligns with your preferences. Smaller lamps may heat up quicker, offering a faster display of the mesmerizing lava movement. On the other hand, larger lamps often provide a more prolonged and captivating visual experience once they reach their optimal temperature.
Now that we’ve examined the impact of lamp size and design on heating time, let’s explore the effect of the initial temperature of the lamp.
Factors Affecting the Heating Time of a Lava Lamp
– Initial Temperature of the Lamp
The initial temperature of a lava lamp can play a significant role in determining its heating time. The starting temperature of the wax and liquid inside the lamp can affect how quickly the lamp reaches its optimal temperature. Let’s dive into how the initial temperature impacts the heating process:
1. Cold Environment: If your lava lamp has been stored in a colder environment, it will typically take longer to heat up. Cold wax and liquid require more time and energy to reach their melting points. In these situations, the lamp needs to compensate for the lower initial temperature, which can result in an extended heating time.
2. Pre-Warming: To reduce the heating time, you can pre-warm your lava lamp before turning it on. Placing the lamp in a slightly warmer room or near a gentle heat source (such as a radiator) can help raise the initial temperature of the wax and liquid. This pre-warming process provides a head start to the heating process, resulting in a faster overall heating time.
3. Ambient Room Temperature: The ambient temperature of the room where the lava lamp is located also affects its heating time. A room with a lower temperature will require more time for the lamp to reach its desired temperature, as it needs to compensate for the colder surroundings. Conversely, a room with a warmer temperature can expedite the heating process, reducing the overall heating time.
It’s essential to consider the initial temperature when estimating the heating time of your lava lamp. Storing the lamp in a room with moderate temperature or pre-warming it can help ensure a quicker and more efficient heating process.
Now that we have explored the impact of the initial temperature of a lava lamp, let’s investigate the effect of the type of bulb and wattage on the heating time.
Factors Affecting the Heating Time of a Lava Lamp
– Type of Bulb and Wattage
The type of bulb and its wattage are crucial factors that affect the heating time of a lava lamp. Let’s delve into how these factors influence the heating process:
1. Type of Bulb: Different types of bulbs can be used as the heat source in a lava lamp. Traditional incandescent bulbs, which produce light by heating a filament, emit a significant amount of heat during operation. This heat is essential for warming up the wax and initiating the lava flow. LED bulbs, on the other hand, are energy-efficient and produce little heat. As a result, lava lamps equipped with LED bulbs may experience longer heating times compared to those with traditional incandescent bulbs.
2. Wattage: The wattage of the bulb directly influences the amount of heat it generates. Higher wattage bulbs produce more heat, accelerating the heating process. If your lava lamp uses a higher wattage bulb, it will heat up faster compared to lamps using lower wattage bulbs. However, it’s crucial to note that using bulbs with wattages higher than the manufacturer’s recommendation can potentially damage the lamp or compromise its safety.
3. Compatibility: When replacing the bulb of your lava lamp, ensure it is compatible with the lamp’s specifications. Using the right type of bulb recommended by the manufacturer guarantees optimal performance and the intended heating time. Consult the lava lamp’s manual or contact the manufacturer if you’re unsure about the appropriate bulb type and wattage.
Whether you are using an incandescent bulb or an LED bulb, it’s important to find the right balance between heat generation and energy efficiency to achieve the desired heating time for your lava lamp.
Now that we’ve explored the impact of the type of bulb and wattage on the heating time, let’s move on to discussing the effect of surrounding temperature.
Factors Affecting the Heating Time of a Lava Lamp
– Surrounding Temperature
The surrounding temperature of the room where a lava lamp is located can have a significant impact on its heating time. Let’s explore how the surrounding temperature affects the heating process:
1. Cold Surroundings: If the room where the lava lamp is placed is colder, it will take longer for the lamp to heat up. The lamp needs to compensate for the lower temperature by generating more heat to warm up the wax and liquid inside. As a result, the heating time of the lamp will be extended. To minimize the impact of a cold environment, you can move the lamp to a warmer area or provide additional heat sources nearby to help accelerate the heating process.
2. Warm Surroundings: Conversely, if the room has a warmer ambient temperature, the heating time of the lava lamp will be shorter. The lamp will need less time to reach the desired temperature as it does not have to overcome a significant temperature difference. Excessive warmth, however, should be avoided as it can lead to the lamp overheating and potentially impacting its performance or safety.
3. Consistent Temperature: Maintaining a consistent room temperature can help regulate the heating time of the lava lamp. Fluctuations in temperature can cause the wax and liquid to cool and solidify, interrupting the flow and extending the heating time. Keeping the room temperature relatively stable will ensure a more consistent and predictable heating process for the lamp.
Please note that the surrounding temperature is just one of the factors that influence the heating time of a lava lamp. Other factors like lamp size, design, type of bulb, and wattage also play a significant role. Therefore, it’s important to consider all these factors in combination to estimate the overall heating time accurately.
Now that we have explored the impact of the surrounding temperature, let’s discuss the typical heating times for different sizes of lava lamps.
Typical Heating Times for Lava Lamps
The heating time of a lava lamp can vary depending on factors such as lamp size, initial temperature, bulb wattage, and surrounding temperature. While individual lava lamp models may have specific guidelines provided by the manufacturer, let’s explore the general heating times for different sizes of lava lamps:
1. Small Lava Lamps: Small lava lamps typically have a height of around 11 inches (28 cm) and contain less wax and liquid. On average, it can take about 1 to 2 hours for a small lava lamp to heat up and start displaying its mesmerizing flow. However, factors such as the initial temperature and surrounding temperature can influence the actual heating time.
2. Medium Lava Lamps: Medium-sized lava lamps stand around 16 to 17 inches (40 to 43 cm) tall and have a larger volume of wax and liquid compared to small lamps. It generally takes around 2 to 3 hours for medium lava lamps to heat up and reach the optimal flow state. Again, variations in the initial and surrounding temperatures can affect the specific heating time.
3. Large Lava Lamps: Large lava lamps, which can be around 20 to 27 inches (51 to 69 cm) in height, require more time to heat up due to their greater volume of wax and liquid. The heating time for larger lava lamps can range from 3 to 4 hours or even longer. Patience is key when waiting for a large lava lamp to heat up, but the extended heating time is often rewarded with a captivating and expansive display of flowing lava.
It is important to note that these are general estimates and actual heating times can vary depending on various factors. Additionally, different lava lamp models may have specific recommendations provided by the manufacturer, so it is always advisable to refer to the instructions accompanying your specific lava lamp.
Now that we have discussed typical heating times for different sizes of lava lamps, let’s explore some tips to help reduce the heating time of your lava lamp.
Typical Heating Times for Lava Lamps
– Small Lava Lamps
Small lava lamps are charming decorative pieces that create an enchanting ambiance in any space. Due to their compact size, small lava lamps typically have shorter heating times compared to larger counterparts. Let’s explore the typical heating times for small lava lamps:
Small lava lamps usually stand around 11 inches (28 cm) in height and have a smaller volume of wax and liquid. The reduced volume allows for faster heating and initiation of the lava flow. On average, it takes around 1 to 2 hours for a small lava lamp to heat up and begin displaying its captivating swirling motion.
Several factors can influence the specific heating time of a small lava lamp. The initial temperature of the lamp plays a role, as a colder lamp will require additional time for the wax and liquid to reach their melting points. Pre-warming the lamp by placing it in a slightly warmer location can help reduce the heating time.
The type of bulb and its wattage also affect the heating time. Higher wattage bulbs generate more heat, accelerating the heating process. Incandescent bulbs, commonly used in lava lamps, emit a substantial amount of heat, ensuring quicker warm-up times for small lamps compared to LED bulbs, which produce less heat.
The surrounding temperature also plays a role in the heating time of a lava lamp. If the room is colder, the lamp may take longer to reach its optimal temperature. Conversely, a warmer room will help expedite the heating process, resulting in a shorter overall heating time for the small lava lamp.
In addition to these factors, it’s important to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and instructions for your specific small lava lamp model. These recommendations can provide more accurate estimates for the heating time and ensure optimal performance.
Now that we’ve discussed the heating times for small lava lamps, let’s move on to explore medium-sized lava lamps.
Typical Heating Times for Lava Lamps
– Medium Lava Lamps
Medium-sized lava lamps offer a perfect balance between a captivating display and a manageable size. With their larger volume of wax and liquid, medium lava lamps require a bit more time to heat up compared to small lava lamps. Let’s explore the typical heating times for medium lava lamps:
Medium lava lamps typically stand around 16 to 17 inches (40 to 43 cm) in height. The increased volume of wax and liquid means that it takes a bit longer for the lamp to reach its optimal temperature and begin its mesmerizing flow. On average, medium lava lamps take around 2 to 3 hours to heat up fully.
Just like with small lava lamps, several factors can influence the heating time of medium-sized lava lamps. The initial temperature of the lamp is an important consideration, as a colder lamp will require additional time for the wax and liquid to melt. Pre-warming the lamp by placing it in a slightly warmer location can help reduce the overall heating time.
The type of bulb used and its wattage also play a role in the heating time. Higher wattage bulbs generate more heat, speeding up the heating process. Traditional incandescent bulbs, commonly used in lava lamps, emit a significant amount of heat, resulting in faster warm-up times for medium lava lamps compared to LED bulbs, which produce less heat.
The surrounding temperature of the room also affects the heating time. A colder room will necessitate a longer heating time, as the lamp has to compensate for the lower ambient temperature. Conversely, a warmer room will help expedite the heating process, leading to a shorter overall heating time for the medium lava lamp.
It’s important to refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and instructions specific to your medium lava lamp model to ensure accurate estimates for the heating time and to maximize its performance.
Now that we’ve explored the heating times for medium lava lamps, let’s move on to discuss the heating times for large lava lamps.
Typical Heating Times for Lava Lamps
– Large Lava Lamps
Large lava lamps make a bold statement in any space with their impressive size and captivating lava flow. Due to their larger volume of wax and liquid, large lava lamps require more time to heat up compared to smaller sizes. Let’s explore the typical heating times for large lava lamps:
Large lava lamps typically stand around 20 to 27 inches (51 to 69 cm) in height, making them the largest available size. With their significant volume of wax and liquid, large lava lamps require more time to reach their optimal temperature and initiate the mesmerizing flow. On average, it can take around 3 to 4 hours, or even longer, for a large lava lamp to heat up fully.
Several factors can influence the specific heating time of a large lava lamp. The initial temperature of the lamp plays a role, as a colder lamp will require additional time for the wax and liquid to reach their melting points. Pre-warming the lamp by placing it in a slightly warmer location can help reduce the heating time.
The type of bulb used and its wattage also affect the heating time. Higher wattage bulbs generate more heat, resulting in a faster heating process. It’s important to check the wattage recommended by the manufacturer for your specific lava lamp model to ensure safe and optimal performance.
The surrounding temperature of the room is another factor that impacts the heating time. A colder room will necessitate a longer heating time, as the lamp has to compensate for the lower ambient temperature. Conversely, a warmer room will help expedite the heating process, reducing the overall heating time for the large lava lamp.
Given the extended heating time, patience is key when waiting for a large lava lamp to heat up. However, the wait is often rewarded with a captivating and expansive display of flowing lava, creating an impressive visual centerpiece.
Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and instructions specific to your large lava lamp model for accurate estimates of the heating time and to ensure optimal performance.
Now that we have explored the heating times for large lava lamps, let’s move on to discuss some tips for reducing the heating time of any lava lamp.
Tips for Reducing Heating Time of a Lava Lamp
Waiting for a lava lamp to heat up can be an exciting and anticipatory process. However, if you’re looking to reduce the heating time and enjoy the captivating lava flow sooner, here are some tips to consider:
1. Pre-Warm the Lamp: Before turning on your lava lamp, consider pre-warming it. Place the lamp in a slightly warmer location, such as near a gentle heat source or in a slightly warmer room. This will raise the initial temperature of the wax and liquid, helping kickstart the heating process and reducing the overall time it takes for the lamp to heat up.
2. Choose a Higher Wattage Bulb: Opt for a bulb with a higher wattage to generate more heat. Higher wattage bulbs emit more heat, accelerating the heating process and decreasing the overall heating time of the lava lamp. However, make sure to stay within the recommended wattage range provided by the manufacturer to ensure safe and optimal performance.
3. Consider Room Temperature: The ambient temperature of the room can affect the heating time of the lava lamp. If the room is colder, it will take longer for the lamp to reach its desired temperature. Therefore, keeping the room at a slightly warmer temperature can help expedite the heating process. However, avoid placing the lamp in an excessively warm environment to prevent overheating or compromising the lamp’s performance.
4. Regular Maintenance: Ensure that your lava lamp is clean and free from dust or debris. Dust particles or obstructions on the bulb can hinder heat transfer and increase the heating time. Clean the lamp’s glass container and bulb periodically to maintain optimal heat distribution and efficiency.
5. Use a Suitable Bulb: Use the appropriate type of bulb recommended by the manufacturer for your lava lamp model. Different bulbs have different heat output and energy efficiency levels. Consult the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure you are using the right bulb for optimal performance and heating efficiency.
These tips can help reduce the heating time of your lava lamp, allowing you to enjoy the captivating lava flow sooner. Always refer to the specific instructions provided by the manufacturer for your lava lamp model to ensure safe and proper operation.
Now that we have explored tips for reducing the heating time of a lava lamp, let’s conclude our discussion.
Read more: How Does A Lava Lamp Work?
Conclusion
Lava lamps provide a mesmerizing and enchanting display of flowing wax that can transform the ambiance of any room. Understanding the factors that affect the heating time of a lava lamp allows you to make the most of this captivating decorative piece.
We explored the science behind lava lamps, delving into their principles of operation, components, and materials. The combination of heat, density, and fluid dynamics creates the mesmerizing flow of wax within the lamp, resulting in the captivating swirling motion.
Factors such as lamp size, initial temperature, type of bulb, wattage, and surrounding temperature all impact the heating time of a lava lamp. Larger lamps require more time to heat up due to their greater volume of wax and liquid, while colder environments prolong the heating process.
We also discussed typical heating times for small, medium, and large lava lamps. Smaller lamps tend to heat up in 1 to 2 hours, while larger lamps can take 3 to 4 hours or more. However, it’s important to note that these are general estimates, and specific heating times can vary depending on various factors and the individual model of the lava lamp.
To reduce the heating time of a lava lamp, consider pre-warming the lamp, using a higher wattage bulb (within the recommended range), maintaining a suitable room temperature, and regularly cleaning the lamp to ensure efficient heat transfer.
Remember to refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and instructions for your specific lava lamp model to ensure safe and optimal performance.
Now, armed with the knowledge of how lava lamps work and the factors influencing their heating time, you can sit back, relax, and enjoy the captivating and soothing display of flowing lava in your lava lamp.
Curious about stepping up your decor game with some seriously cool lava lamps? Make sure to check out our feature on the latest and greatest in lava lamp designs for the upcoming year. Whether you're looking to brighten your space or just want a groovy light source, this guide has it all covered.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Long Does It Take For A Lava Lamp To Heat Up?
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.








0 thoughts on “How Long Does It Take For A Lava Lamp To Heat Up?”