Home>Technology>Smart Home Devices>What Is Printer Ink Made Of


Smart Home Devices
What Is Printer Ink Made Of
Modified: February 18, 2024
Discover what printer ink is made of and how it impacts your smart home devices. Learn about the composition and importance of printer ink.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Storables.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Introduction
Let's take a closer look at the unsung hero of the printing world – printer ink. While we often marvel at the seamless operation of our printers, the intricate chemistry behind the ink often goes unnoticed. Printer ink is a complex mixture of various components carefully formulated to produce vibrant, long-lasting prints. Understanding the composition of printer ink not only sheds light on its remarkable properties but also unveils its environmental implications. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of printer ink, exploring its basic components, types, and environmental impact. So, buckle up as we embark on an illuminating journey through the realm of printer ink!
Key Takeaways:
- Printer ink is a complex mixture of pigments, dyes, solvents, and additives, carefully formulated to produce vibrant, long-lasting prints. Understanding its composition helps us make informed choices for our printing needs.
- The environmental impact of printer ink production, usage, and disposal raises important considerations. Embracing sustainable ink options and responsible printing practices contributes to a greener printing landscape.
Read more: What Is In Printer Ink
Basic Components of Printer Ink
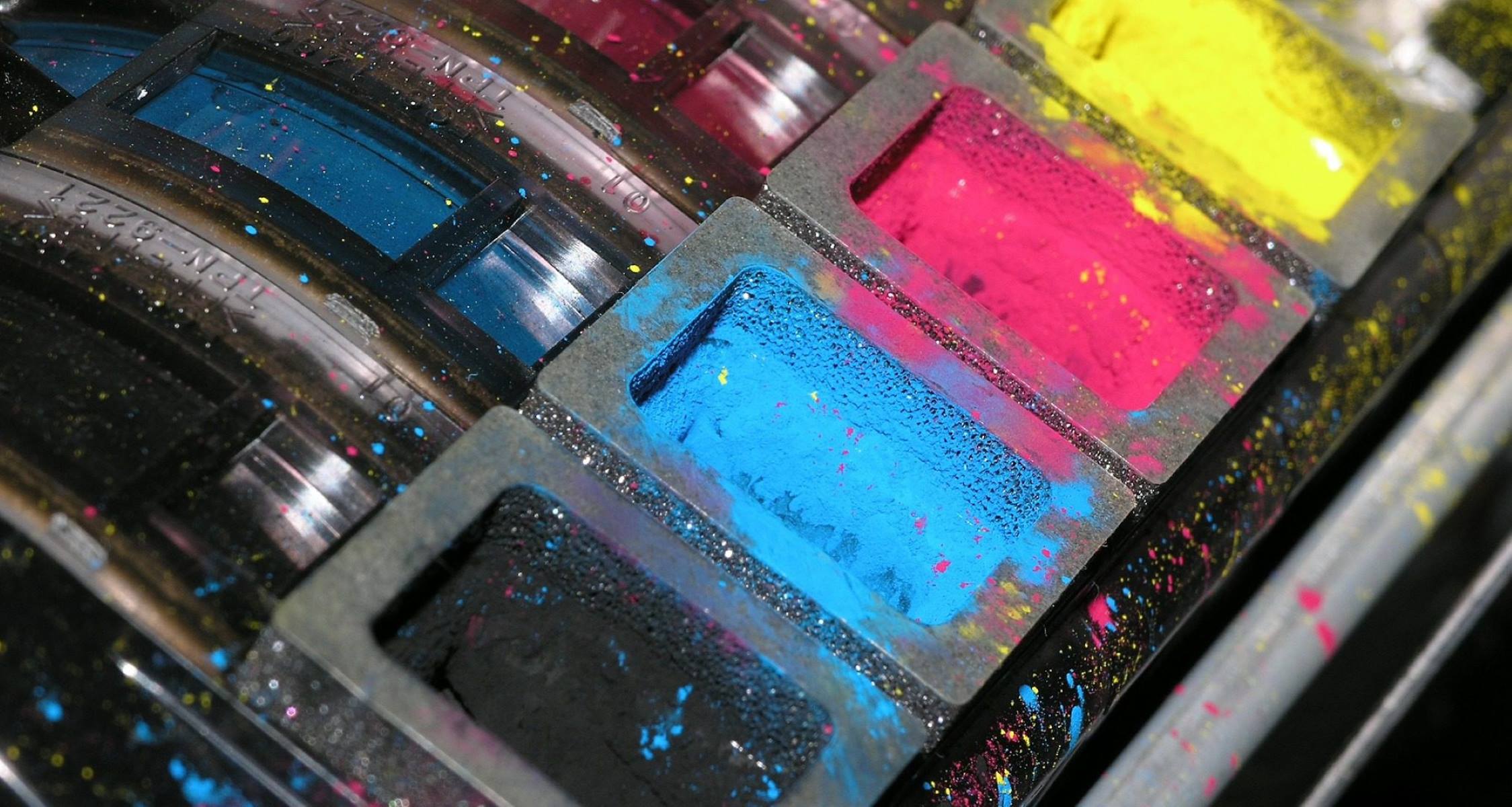
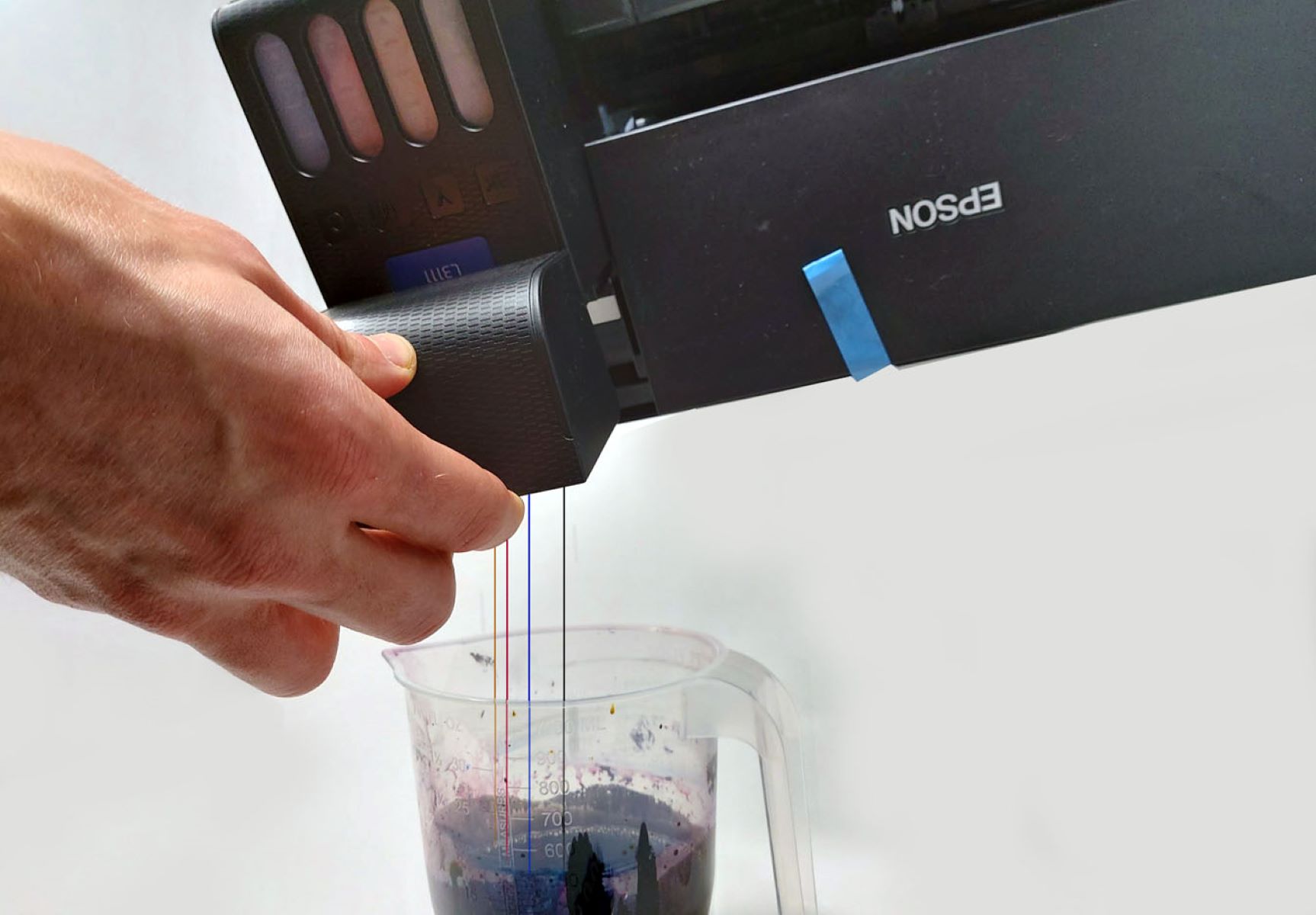
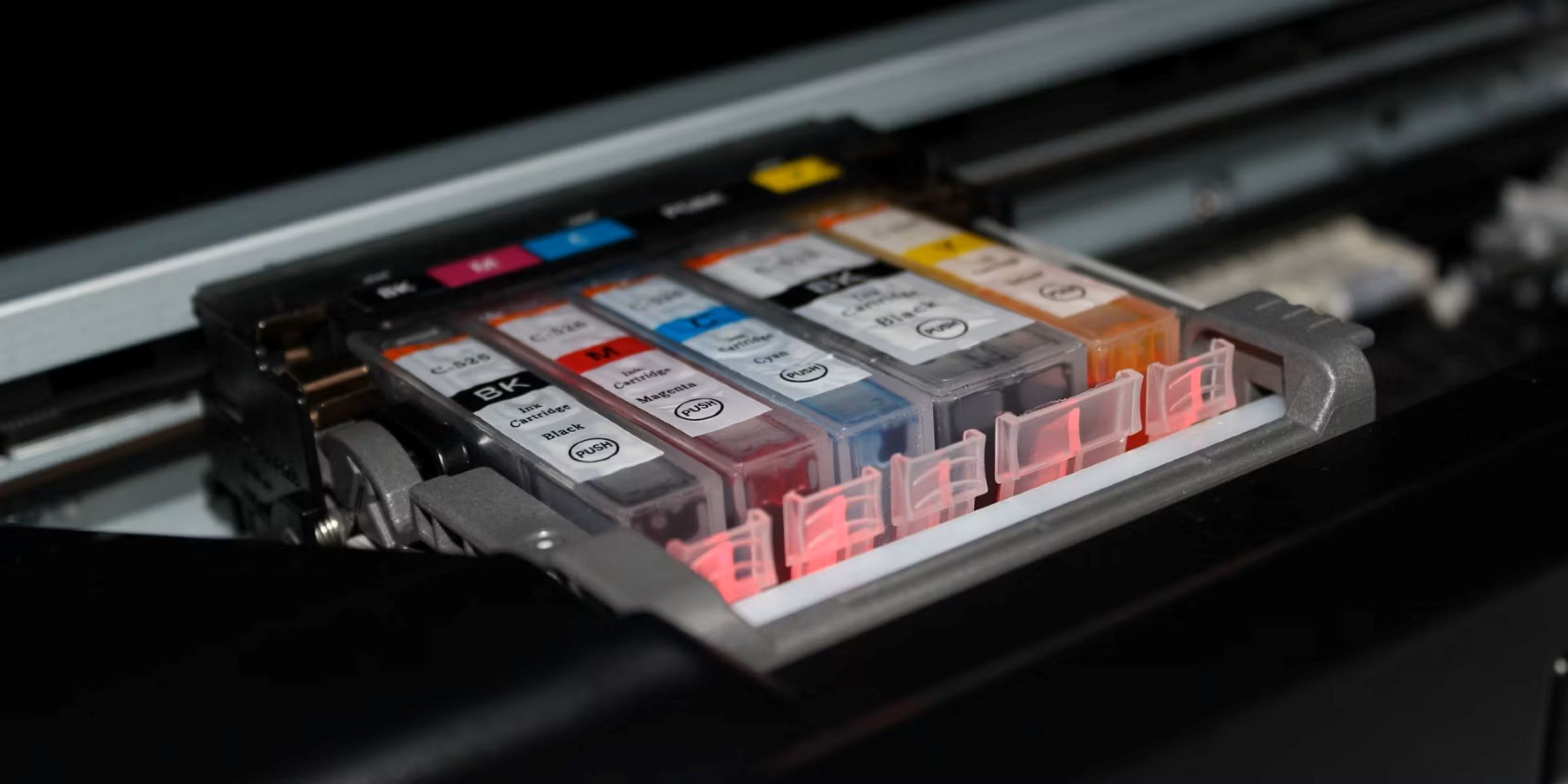
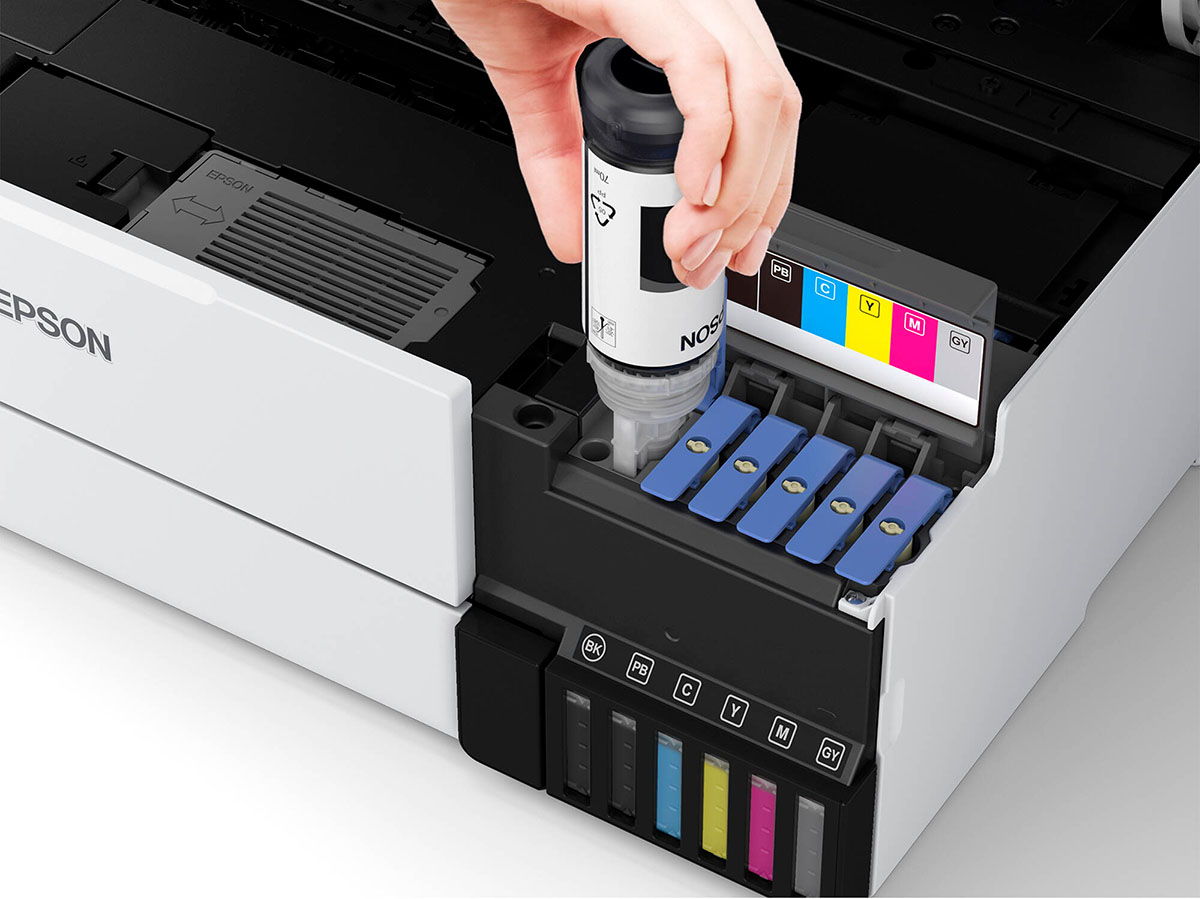
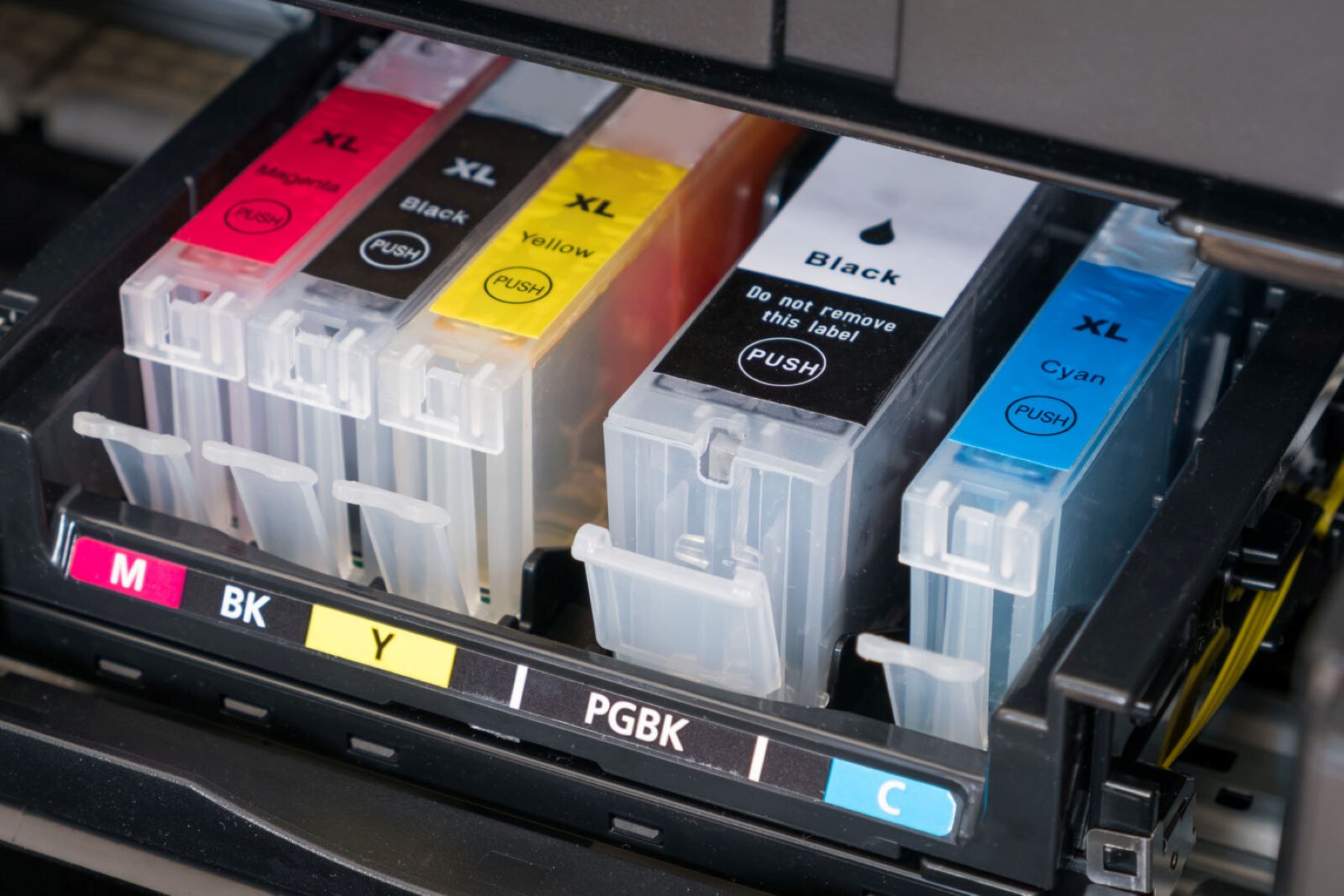
Printer ink, the lifeblood of every printed document and photograph, is composed of a few key elements that work in harmony to produce high-quality prints. These fundamental components include pigments or dyes, solvents, and various additives. Each of these components plays a crucial role in determining the ink’s color vibrancy, durability, and performance.
First and foremost, pigments and dyes are the primary coloring agents in printer ink. Pigments are finely ground solid particles that impart color to the ink, while dyes are soluble substances that dissolve in the ink vehicle to create vibrant hues. The selection of pigments or dyes depends on the desired color intensity, lightfastness, and compatibility with the printing substrate.
In addition to pigments and dyes, solvents serve as the carrier fluid that delivers the colorants onto the printing surface. These solvents ensure that the ink flows smoothly through the printer nozzles, adheres to the paper, and dries quickly to produce smudge-resistant prints. Furthermore, solvents contribute to controlling the viscosity and drying rate of the ink, thereby influencing its overall performance.
Furthermore, printer ink contains various additives that enhance its properties and performance. These additives may include surfactants to improve ink wetting and spreading, humectants to prevent the ink from drying out in the print head, and binders to promote adhesion to the paper. Additionally, anti-curl agents may be incorporated to minimize paper curling, especially in high-coverage prints.
The careful balance and interaction of these basic components result in printer ink formulations tailored to meet specific printing requirements, whether for crisp text documents or vivid color photographs. Understanding the role of each component in printer ink sets the stage for exploring the diverse types of inks available in the market and their unique characteristics.
Pigments and Dyes
When it comes to printer ink, the choice between pigments and dyes significantly influences the color quality, longevity, and versatility of the printed output. Pigments, composed of finely ground solid particles, offer exceptional color permanence and lightfastness, making them ideal for producing long-lasting prints. These solid particles are insoluble in the ink vehicle, providing excellent color stability and resistance to fading over time.
On the other hand, dyes, soluble substances that dissolve in the ink vehicle, exhibit remarkable color vibrancy and saturation. Dyes are known for their ability to produce vivid and intense colors, especially on glossy and coated papers. However, they are more susceptible to fading when exposed to light and environmental factors, making them better suited for applications where short-term color brilliance is prioritized over long-term durability.
Both pigments and dyes offer unique advantages, and the selection between the two depends on the intended use of the printed materials. For instance, pigment-based inks are favored for archival-quality photo prints and documents requiring exceptional color permanence. Their resistance to fading makes them an ideal choice for preserving cherished memories and important records for generations.
Conversely, dye-based inks are often preferred for producing vibrant graphics, high-resolution images, and promotional materials where color impact and visual appeal are paramount. Their ability to deliver rich, saturated colors on various media types makes them a popular choice for marketing collateral, artistic prints, and presentations.
Moreover, advancements in inkjet printing technology have led to the development of hybrid inks that combine the advantages of both pigments and dyes. These hybrid inks leverage the color vibrancy of dyes and the longevity of pigments, offering a versatile solution for a wide range of printing applications. By blending the unique characteristics of pigments and dyes, hybrid inks strike a balance between color brilliance and durability, catering to the diverse needs of modern printing.
Understanding the distinctions between pigments and dyes empowers users to make informed decisions when selecting printer inks that align with their specific printing requirements. Whether it’s preserving cherished memories with fade-resistant pigment inks or creating captivating visuals with vibrant dye-based inks, the choice between pigments and dyes plays a pivotal role in achieving the desired print quality and longevity.
Solvents and Additives
While pigments and dyes impart color to printer ink, the solvents and additives within the ink formulation play essential roles in ensuring optimal performance, print quality, and longevity. Solvents, serving as the carrier fluid for the colorants, facilitate the smooth flow of ink through the printer nozzles and its adhesion to the printing substrate. These solvents are carefully selected to balance evaporation rates, viscosity, and drying times, thereby influencing the ink’s behavior during printing and its final appearance on the paper.
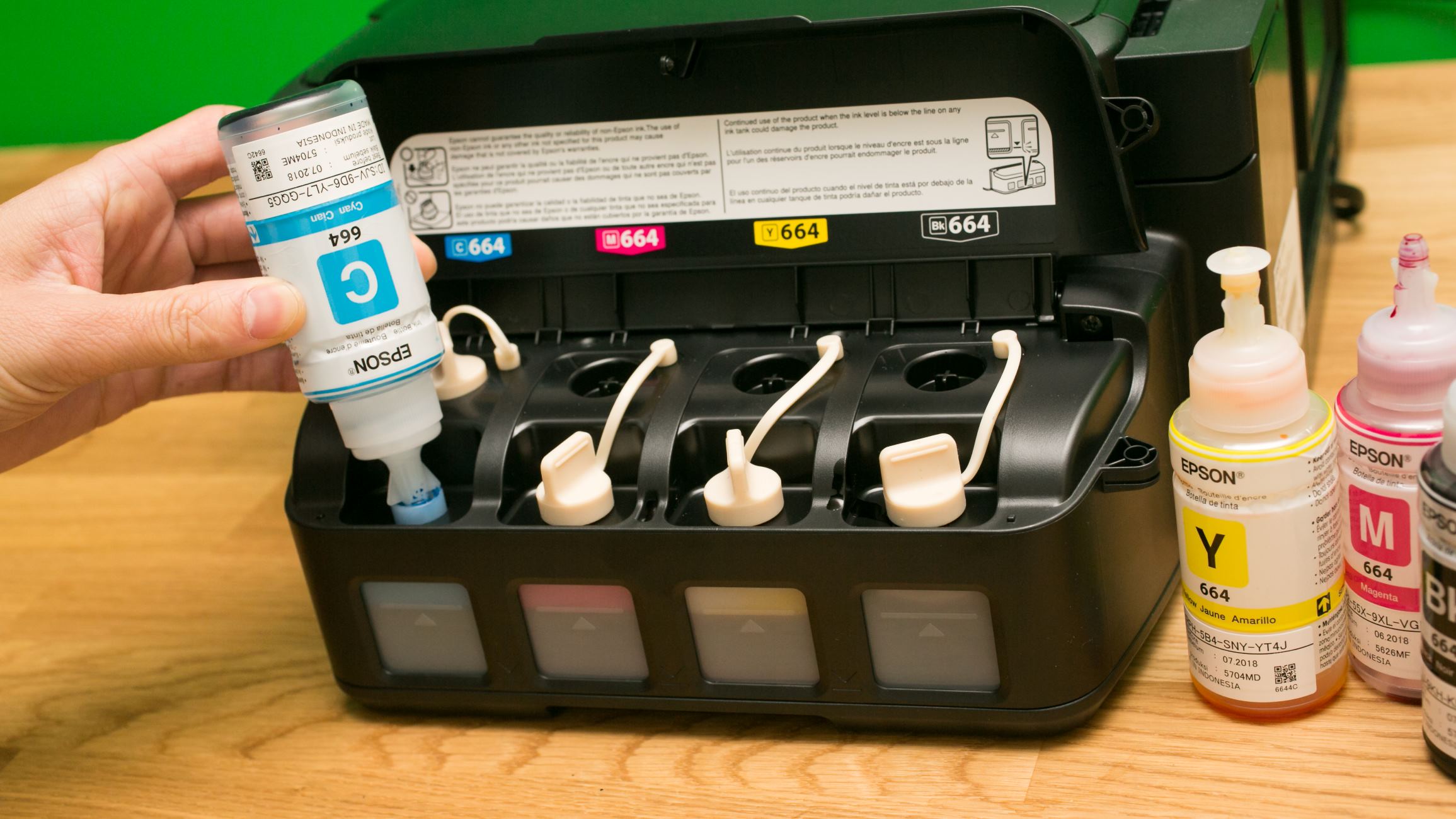
Common solvents used in printer inks include water, glycol ethers, and alcohols, each offering distinct advantages in terms of drying speed, compatibility with printing substrates, and environmental impact. Water-based inks, for instance, are renowned for their eco-friendliness and minimal odor, making them a preferred choice for home and office printing. On the other hand, solvent-based inks, containing glycol ethers or alcohols, are valued for their fast-drying properties and suitability for a wide range of media, including glossy and coated papers.
In addition to solvents, printer ink formulations incorporate a diverse array of additives to enhance specific properties and address printing challenges. Surfactants, for example, are included to improve ink wetting and spreading, ensuring uniform coverage and sharp image reproduction. These surfactants reduce surface tension, allowing the ink to adhere evenly to the printing substrate, resulting in crisp and precise prints.
Furthermore, humectants are employed to prevent the ink from drying out in the print head, maintaining consistent ink flow and preventing clogging issues that can compromise print quality. By regulating the ink’s viscosity and moisture content, humectants contribute to the reliable performance of the printer and the longevity of the ink cartridges.
Moreover, binders are added to printer inks to promote adhesion to the paper, enhancing the durability and resistance of the printed output to physical abrasion and environmental factors. These binders create a strong bond between the ink and the paper fibers, ensuring that the prints remain vibrant and intact over time, even in demanding usage scenarios.
As technology advances, the development of innovative additives continues to enhance printer ink performance, addressing evolving printing needs and environmental considerations. Anti-curl agents, for instance, are incorporated to minimize paper curling, especially in high-coverage prints, ensuring flat output that is ready for immediate use or further processing.
By understanding the role of solvents and additives in printer ink formulations, users can appreciate the meticulous engineering behind every printed page and the diverse considerations that contribute to achieving exceptional print quality, reliability, and environmental responsibility.
Printer ink is typically made of pigments or dyes mixed with solvents and other chemicals. Pigments provide color, while solvents help the ink flow and dry on the paper. Understanding the components of printer ink can help you make informed decisions when purchasing ink for your printer.
Types of Printer Inks
Printer inks are as diverse as the printing needs they cater to, offering a range of specialized formulations tailored to specific applications and printing technologies. Understanding the different types of printer inks provides valuable insight into their unique characteristics, advantages, and optimal uses, empowering users to make informed decisions when selecting the most suitable ink for their printing endeavors.
1. Water-Based Inks: Renowned for their eco-friendliness and minimal environmental impact, water-based inks have gained popularity in home and office printing. These inks, composed of water as the primary solvent, offer vibrant color reproduction and are well-suited for producing high-quality text and images on various paper types. Additionally, water-based inks are favored for their low odor and reduced emissions, contributing to a healthier printing environment.
2. Solvent-Based Inks: Leveraging glycol ethers or alcohols as the primary solvents, solvent-based inks are valued for their fast-drying properties and compatibility with a wide range of media, including glossy and coated papers. These inks are commonly used in large-format printing applications, outdoor signage, and industrial printing where durability and weather resistance are paramount.
3. Pigment-Based Inks: Recognized for their exceptional color permanence and resistance to fading, pigment-based inks are the go-to choice for archival-quality photo prints and documents requiring long-term durability. These inks, comprising finely ground solid particles, deliver outstanding color stability and are ideal for preserving cherished memories and important records.
4. Dye-Based Inks: Offering vibrant and intense color reproduction, dye-based inks are preferred for producing captivating graphics, high-resolution images, and promotional materials. These inks excel in delivering rich, saturated colors on various media types, making them a popular choice for marketing collateral, artistic prints, and presentations where visual impact is paramount.
5. UV-Curable Inks: Engineered to rapidly cure and solidify when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light, UV-curable inks are widely used in industrial and commercial printing applications. These inks offer exceptional adhesion to a variety of substrates and produce prints that are instantly dry and ready for immediate finishing, making them ideal for high-speed production environments.
6. Sublimation Inks: Specifically designed for dye-sublimation printing, sublimation inks undergo a unique process where they transition from a solid to a gas state under heat and pressure, bonding with polyester fibers and polymer-coated substrates. These inks are commonly used for producing vibrant, durable prints on items such as apparel, soft signage, and personalized gifts.
By familiarizing themselves with the diverse types of printer inks available, users can make informed choices based on their specific printing requirements, whether it involves producing archival-quality photo prints, vibrant promotional materials, or durable outdoor signage. Each type of ink offers distinct advantages, catering to a wide spectrum of printing needs and contributing to the seamless realization of creative and professional projects.
Read more: What Is The Ink Absorber On A Canon Printer
Environmental Impact of Printer Ink
While printer ink plays a pivotal role in bringing digital content to life on physical media, its production, usage, and disposal raise important considerations regarding environmental impact and sustainability. Understanding the environmental implications of printer ink sheds light on the industry’s efforts to minimize its ecological footprint and empowers users to make environmentally conscious choices in their printing practices.
1. Resource Consumption: The production of printer ink involves the utilization of various resources, including raw materials, energy, and water. From the extraction of colorants and solvents to the manufacturing of ink cartridges, the ink production process consumes significant resources, contributing to its environmental footprint. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting sustainable practices and resource-efficient technologies to minimize the environmental impact of ink production.
2. Carbon Emissions: The energy-intensive processes involved in ink manufacturing and cartridge production result in carbon emissions, contributing to the industry’s carbon footprint. Additionally, the transportation of ink products to distribution centers and end-users further adds to the carbon emissions associated with the ink supply chain. Efforts to optimize transportation logistics and invest in renewable energy sources aim to mitigate these emissions.
3. Waste Generation: The disposal of empty ink cartridges and residual ink raises concerns about waste generation and landfill impact. To address this, many manufacturers have implemented ink cartridge recycling programs, encouraging users to return used cartridges for remanufacturing or recycling. This approach reduces the volume of ink-related waste and promotes a circular economy model within the printing industry.
4. Chemical Management: The chemicals and additives used in printer ink formulations require careful management to minimize their environmental impact. Manufacturers are committed to adhering to stringent environmental regulations and employing eco-friendly alternatives whenever feasible. This includes the development of bio-based solvents, eco-friendly surfactants, and sustainable packaging materials to reduce the ecological footprint of ink products.
5. Eco-Friendly Formulations: The emergence of eco-friendly ink formulations, such as vegetable-based inks and soy inks, reflects the industry’s commitment to sustainable practices. These bio-based inks, derived from renewable resources, offer reduced environmental impact and are increasingly favored for their eco-friendly attributes. Furthermore, water-based inks, known for their minimal emissions and biodegradability, contribute to a greener printing ecosystem.
6. User Practices: In addition to industry initiatives, users can contribute to minimizing the environmental impact of printer ink through responsible ink usage and cartridge disposal. Opting for high-capacity ink cartridges, duplex printing, and selecting eco-friendly ink options aligns with sustainable printing practices. Furthermore, participating in ink cartridge recycling programs and exploring refillable ink systems promotes a circular and environmentally conscious approach to ink consumption.
By considering the environmental impact of printer ink and embracing sustainable printing practices, users play an active role in advancing the industry’s environmental stewardship. From the adoption of eco-friendly ink formulations to the responsible management of ink-related waste, the collective efforts of manufacturers and users contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally conscious printing landscape.
Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of printer ink, it becomes evident that this seemingly humble substance is a marvel of modern chemistry, engineering, and environmental stewardship. The intricate composition of printer ink, comprising pigments, dyes, solvents, and additives, underscores the meticulous craftsmanship dedicated to achieving vibrant, durable, and high-quality prints. From the enduring color permanence of pigment-based inks to the vivid brilliance of dye-based inks, each ink type offers unique attributes tailored to diverse printing needs.
Furthermore, the environmental impact of printer ink has prompted industry-wide initiatives to embrace sustainable practices, resource efficiency, and eco-friendly formulations. Manufacturers are committed to reducing their ecological footprint through the adoption of renewable resources, waste reduction strategies, and the development of environmentally responsible ink products. Users, too, play a crucial role in promoting sustainable printing practices by embracing eco-friendly ink options, responsible ink cartridge disposal, and the adoption of energy-efficient printing habits.
As technology continues to advance, the evolution of printer ink reflects a harmonious blend of innovation, performance, and environmental consciousness. The emergence of eco-friendly ink formulations, such as water-based inks and bio-based alternatives, exemplifies the industry’s dedication to minimizing its environmental impact while delivering exceptional print quality.
Ultimately, the world of printer ink transcends its role as a mere consumable, embodying a convergence of artistry, science, and sustainability. Whether it’s capturing cherished memories in archival-quality prints, producing captivating visuals for marketing endeavors, or realizing creative projects with minimal environmental impact, printer ink stands as a testament to the seamless fusion of technology and environmental responsibility.
As we continue to embrace the transformative power of printing, let us do so with a conscientious eye toward sustainable ink usage, responsible disposal practices, and the appreciation of the remarkable chemistry that brings our digital creations to life on paper. Through a collective commitment to environmentally conscious printing, we can ensure that the legacy of printer ink is one of enduring quality, environmental mindfulness, and boundless creativity.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Is Printer Ink Made Of
Was this page helpful?
At Storables.com, we guarantee accurate and reliable information. Our content, validated by Expert Board Contributors, is crafted following stringent Editorial Policies. We're committed to providing you with well-researched, expert-backed insights for all your informational needs.














0 thoughts on “What Is Printer Ink Made Of”